|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN13
State two characteristics of the image formed on the retina
ANSWERS
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN13
Name the part of retina where image is formed
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2007PP2QN07
Describe the structure and functions of the various parts of the human ear
answers
The ear is an organ involved in perceiving sound and maintaining body balance and posture. It is made of the following sections
Pinna – That is funnel shaped structure made of skin and cartilage. It receives sound waves and directs them to the ear tube. External/auditory meatus – That is a canal lined with air and wax. It allows passage of sound waves to the middle ear. The hairs and wax trap dust particles that enter the ear. Tympanic membrane – That is a thin flexible sheet-like structure receives sound waves and pass the vibration to the ossicles. Middle ear that is composed of Tiny bones known as ossicles – They are anvil and incus. They amplify vibration from the tympanic membrane. Eustachian tube – That connects the ear to the nasal cavity. It balances pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane. Oral window – That is a thin flexible membrane that opens into the inner ear. it receives vibrations from the ossicles and passes them to the inner ear. Inner ear that is compost of; Vestibular apparatus- That are the semicircular canals, utricles and saccules. They help in maintenance of body balance and posture. Cochlea – That is a coiled structure that has sensory cells for hearing. It connected to the auditory nerve that is involved in transmission of sounds to the brain K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2007PP1QN22
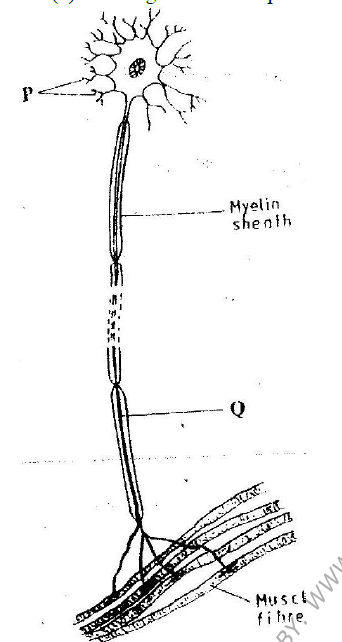
The diagram below represents a neurone
(i) Name the neurone
(ii) Name the parts labeled P and Q P……………………………………………………………………….. Q………………………………………………………………………. (c) State a function of myelin sheath
ANSWERS
(b) Motor neutron
(ii) P- Dendrites Q- Axoplasm (Axon) (d) Insulates the axon
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2007PP1QN22
Where in the human body are relay neurons found
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN23
State the function of each of the following parts of human ear.
a) Ear ossicles b) Cochlea c) Semi circular canals d) Eustachian tube.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN22
State two functional differences between the rods and cones in the human eye.
answers
Rodes Cones
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN22
State the function of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN21
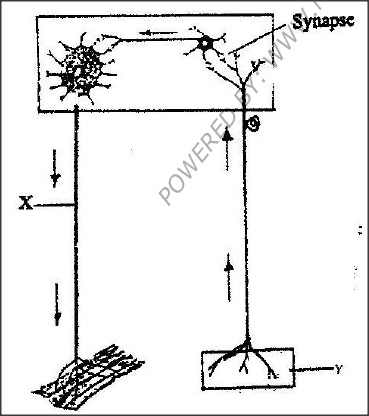
The diagram below represents a reflex are in human.
a) Name the parts labeled X and Y
b) Name the substance that is responsible for the transmission of an impulse across the synapse.
answers
(a) X- motor neurone- accept of motor neurone rej. Axon alone
Y- Sense organ/ receptor (b) Acetyl; chlorine/ noradrenaline ( Nerepinephrine)
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN20
State three biological importance of tropisms plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN20
What name is given to response to contact with surface exhibited by tendrils and climbing stems in plants?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN10
State the important of tactic response among some members of kingdom protista.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN19
How is the human eye adapted to its function?
answers
Adaptations of the eye.
The presence of:-
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN01
Apart from hearing, state another function of the human ear.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN06
The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in a defective eye.
a) Name the defect:
b) Explain how the defect named in (a) above can be corrected
answers
a) Myopia/ shortsightedness / short sight
b) Concave lens / divergent lends; to diverge the rays so that the image is focused on the retina Acc. Concave.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN18
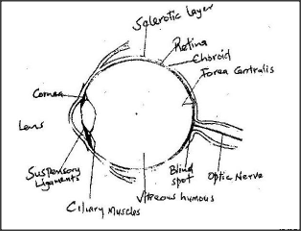
Describe the functions of the various parts of the human eye.
answers
Sclerotic layer – (made up of collagen fibres thus) protects the eye maintains shape of eyeball.
Cornea
Eyelids
Lens – Refracts light rays / focuses light on retina Vitrerous aqueous humour once. Aqueous Humour – Nourishes cornea / lens Refracts light Irus – ( pigmented thus) – gives the eye its colour / absorbs light controls amount of light entering the eye / adjusts size of pupil impulses. Pupil – light enters the eyes through pupil. Retina – has photoreceptor cells / rods / cones / image formation ;l generates impulses. Fever / yellow spot – visual acuity / most sensitive part of retina with only cones. Blind spot – point where nerve fibre emerges from the optic nerve / where the optic nerve leaves the eye / point where blood vessels & nerve fibres enter the eye. Optic nerve – transmit impulses to brain.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2001PP1QN17b
Describe how semicircular canals perform their functions
answers
There are three semi – circular canals; arranged in planes at right angle to each other; at the end of each canal is swelling called ampulla’s which contains receptors.
The movement of the cause movement of the fluid in at least one canal, the fluid movement deflects / displaces the coperta and thus stimulating the receptors / sensory hairs, the impulse / nerve sensory impulse is transmitted / conducted to the brain; by auditory nerve, about the movement of the body / head. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2001PP1QN17a
State the functions of the following parts of the mammalian ear;
(i) Tympanic membrane (ii) Eustachian tube (iii) Ear ossicles
answers
a) i) Tympanic membrane.
Receives sound waves (from the air); and vibrates / transforms sound wave into vibrations to transmit them to the ear osssicles / malleus; acc. Hammer for malleus. ii) Eustachain tube. Equalizes the air pressure in the middle ear to that in the outer ear. iii) Ear ossicles Amplify / transmits vibrations from the tymphanic membrane in the inner ear / venestra ovalis / oval window.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2000PP1QN01
What is the function of the following cells in the retina of human eye ? Cones
answers
(a) Cones Discrimination of colours/ details/ accurate/ vision colour perception/ sensitivity to high intensity/ bright
(b) Rods Dim light vision/ low light intensity K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 1999PP1QN09
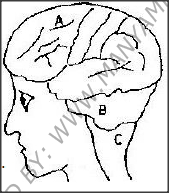
The diagram below shows surface view of a human brain.
a)Name the parts labeled B and C.
b) State three functions of the part labelled A c) State what would happen if the part labeled B was damaged.
answers
a) B- Cerebellum
C- Medulla Oblongata ; Acc Oblongata alone b) Control locomotion motor area/sends impulse to affectors/controls
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 1998PP1QN17
The diagram below represents a nerve cell.
(a) (i) Identify the nerve cell.
(ii) Give a reason your answer in (a) (i) above (b) Name the structure labeled T (c) Using an arrow indicate on the diagram the direction of movement of an impulse in the cell.
answers
(a) (i) Sensory neurone/sensory nerve cell; reject sensory nerve
(ii) Cell body on a branch/ at the side of axon/off the axon/cell body unipolar both axon and dendron are long. (b) T- myelin sheath; Acc Neurilema (c) Direction of impulse from receptor towards cell body. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 1998PP1QN06
In an experiment it was found that when maggots are exposed to light they move to dark areas.
(a) Name the type of response exhibited by the maggots (b) Name the advantages of the response to the maggots
ANSWERS
(a) Phototais
(b) To avoid desiccation/ drying/ dehydration Escape from predators;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 1997PP1QN07
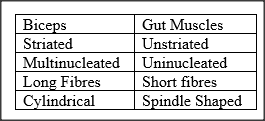
State three structural differences between biceps muscles of the gut.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 1997PP1QN05
In an accident a victim suffered brain injury. Consequently he had loss of memory. Which part of the brain was damaged?
ANSWERS
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

