|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
The following procedure was used to investigate the temperature changes that occur when sodium hydroxide solution is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(i) Place the acid in a glass beaker and record its temperature. (ii) Add a known volume of sodium hydroxide solution. (iii) Stir the mixture and record the highest temperature reached. (iv) Repeat steps (ii) and (iii) with different volumes of sodium hydroxide solution. (a) State two factors that must be kept constant in this experiment (b) Explain how the use of a polystyrene cup will affect the results.
ANSWERS
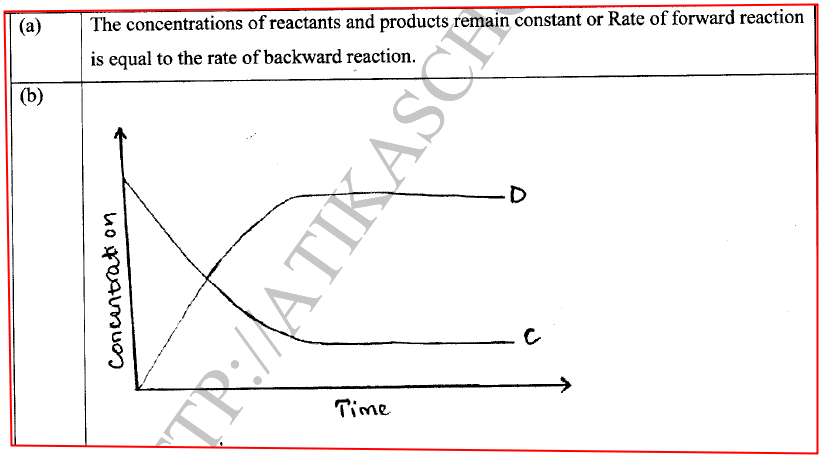
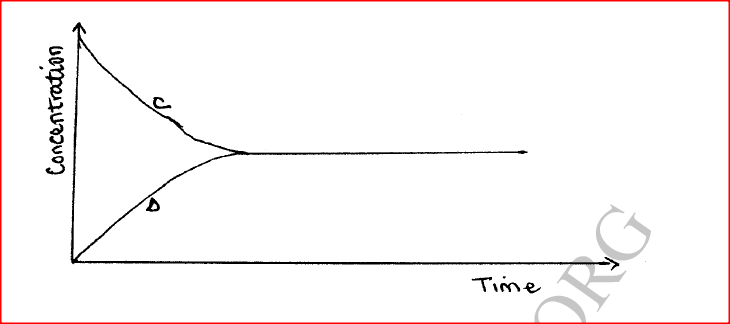
(a) State one characteristic of a reaction where equilibrium has been attained.
(a) Methanol is manufactured from carbon (IV) oxide and hydrogen gas according to the equation:
The reaction is carried out in the presence of a chromium catalyst at 700K and 30kPa. Under these conditions, equilibrium is reached when 2% of the carbon (IV) oxide is converted to methanol
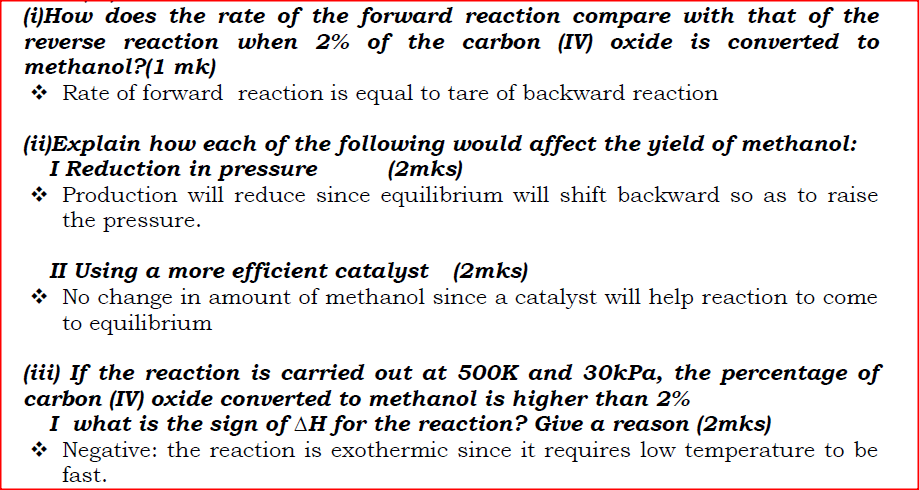
(i)How does the rate of the forward reaction compare with that of the reverse reaction when 2% of the carbon (IV) oxide is converted to methanol? (ii)Explain how each of the following would affect the yield of methanol: I Reduction in pressure II Using a more efficient catalyst (iii) If the reaction is carried out at 500K and 30kPa, the percentage of carbon (IV) oxide converted to methanol is higher than 2% I what is the sign of ΔH for the reaction? Give a reason II Explain why in practice the reaction is carried out at 700K but NOT at 500K (b)Hydrogen peroxide decomposes according to the following equation:
2H2O2(aq) →2H2O(l) + O2 (g)
In an experiment, the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide was found to be 6.0 x 10-8 mol dm-3 S-1. (i)Calculate the number of moles per dm3 of hydrogen peroxide that had decomposed within the first 2 minutes (ii) In another experiment, the rate of decomposition was found to be 1.8 x 10 - 7 mol dm -3S-1. The difference in the two rates could have been caused by addition of a catalyst. State, giving reasons, one other factor that may have caused the difference in two rates of decomposition
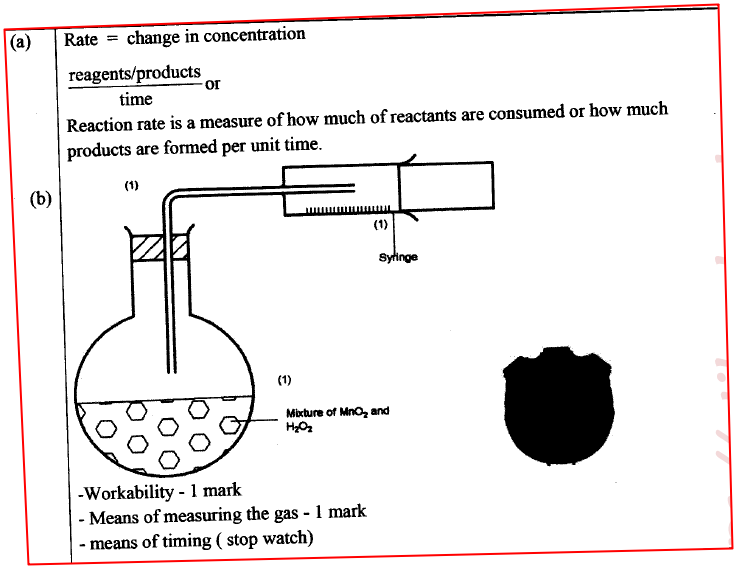
(a) What is meant by rate of reaction. (1 mark)
(b) In the space provided, sketch the diagram of a set-up that can be used to determine the rate of reaction between manganese(IV) oxide and hydrogen peroxide. (3 marks)
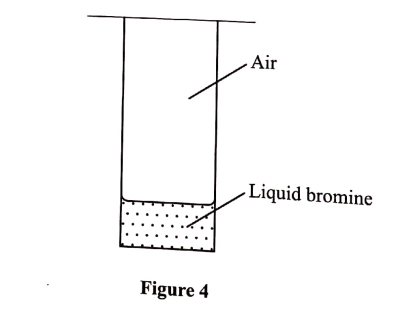
(e) A student placed a small amount of liquid bromine at the bottom of a sealed gas jar of air as shown in Figure 4.
(i) Describe what will be observed: (1 mark)
I. after two minutes . II. after 30 minutes
(ii) Use the Kinetic theory to explain the observations: (2 marks)
I. after 2 minutes . II. after 30 minutes
(d) Some plants have seeds that contain vegetable oil.
In an experiment on rates of reaction, potassium carbonate was reacted with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid.
(a) What would be the effect of an increase in the concentration of the acid on the rate of the reaction? (b) Explain why the rate of reaction is found to increase with temperature.
ANSWERS
(a)The rate of reaction increases. This is because when the concentration is high: the number of collisions between particles is also high hence reacts faster,
(b)Increase in temperature results in increase in the kinetic energy of the particles. This makes particles move faster and collide frequently leading to faster rate of reaction.
(a) Other than concentration, state two factors that determine the rate of a reaction.
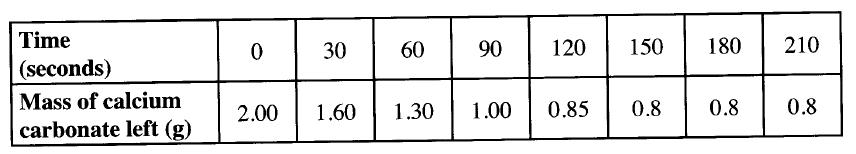
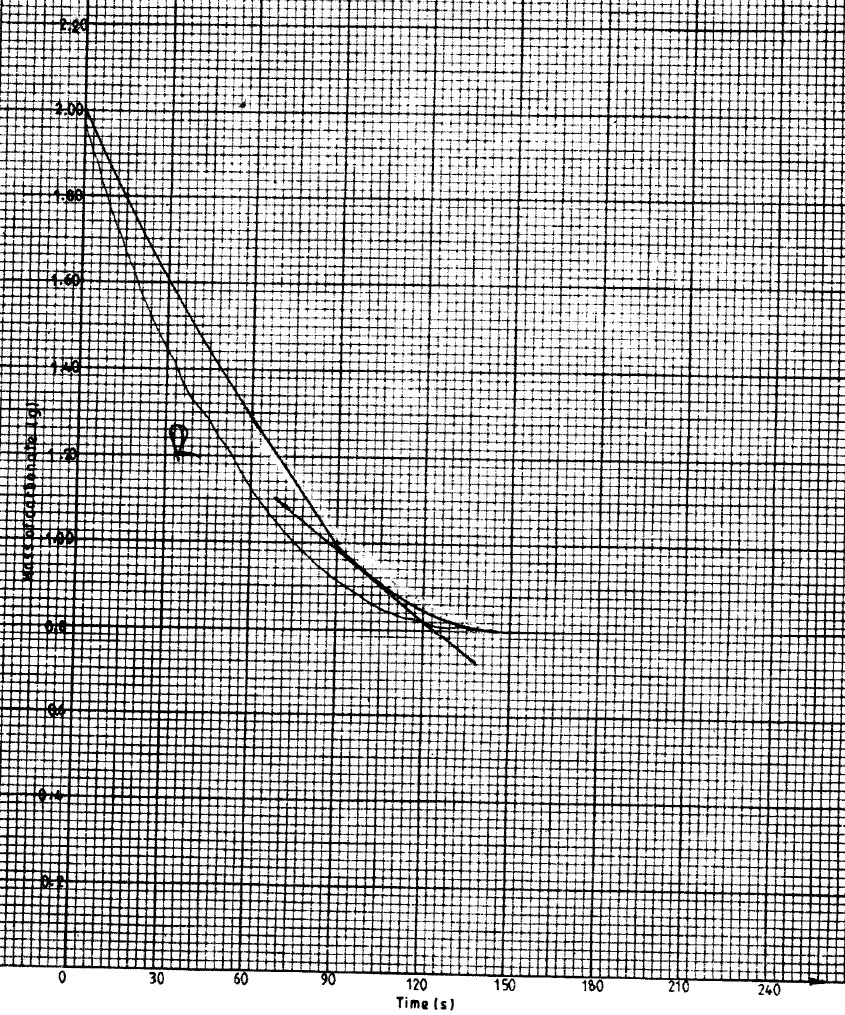
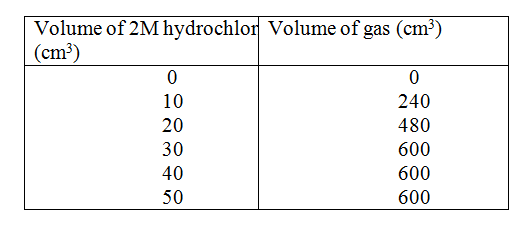
b) In an experiment to determine the rate of reaction, excess lambs of calcium carbonate were added to 2 M hydrochloric acid. The mass of calcium carbonate left was recorded after every 30 seconds. The results are shown in the table below
i) Write the equation for the reaction that took place
ii) On the grid provided, plot a graph of mass of calcium carbonate vertical axis Against time (iii) Determine the rate of reaction at the 105th second. (c) Why does the curve level off after some time? (d) On the same grid, sketch a curve for the same reaction using 4 M hydrochloric acid and label the curve R.
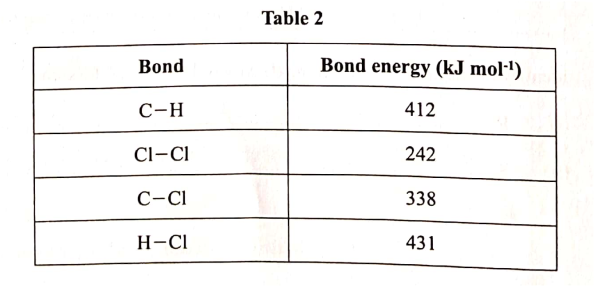
Use the information in Table 2 to answer the questions that follow.
(a) State what is meant by heat of reaction. (1 mark)
(b) Calculate the heat change when one mole of methane reacts completely with excess chlorine in the presence of UV light. (2 marks)
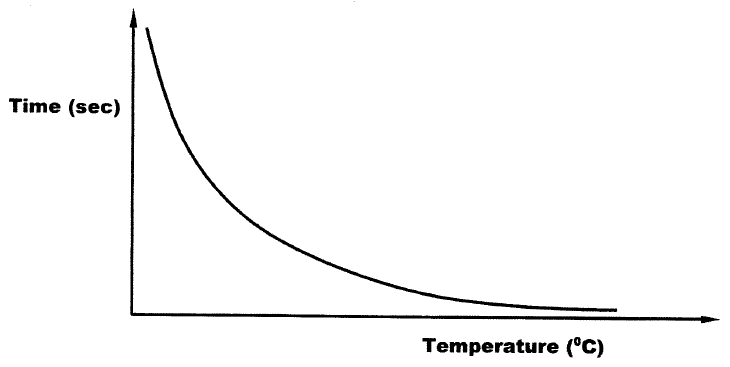
The curve shown below shows the variation of time against temperature for the reaction between sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid.
a) Write the equation for the reaction between sodium thiosulphate and dilute hydrochloric acid
b) Explain the shape of the curve
ANSWERS
When solid A was heated strongly, it gave off water and a solid residue. When water was added to the solid residue, the original solid A, was formed
(a) What name is given to the process described? (b) Give one example of solid A
ANSWERS
(a)Type of reaction: Reversible reaction/temporary reaction.
(b)Copper (II) Sulphate salt (Crystals) Copper (II) Chloride hydrated. Any other hydrated salts e.g. Cobalt (II) Chloride
(a) Other than temperature, state two factors that determine the rate of a chemical reaction.
(b) A solution of hydrogen peroxide was allowed to decompose and the oxygen gas given off collected. After 5 minute, substance G was added to the solution of hydrogen peroxide. The total volume of oxygen evolved was plotted against time as shown in the graph below
(i)Describe the procedure of determining the rate of the reaction at minute 12.
(ii)How does the production of oxygen in region AB compare with that in region BC? Explain (iii)Write an equation to show the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. (c) Sulphur (IV) oxide react with oxygen to form Suplhur (VI) oxide as shown in the equation below
(ii)Name one catalyst used for the reaction.
In an experiment on rates of reaction, potassium carbonate was reacted with dilute sulphuric (Vi) acid
(a)What would be the effect of an increase in the concentration of the acid on the rate of the reaction? (b) Explain why the rate of reaction is found to increase with temperature.
ANSWERS
(a) Rate increases.
(b) Temperature increases the kinetic energy of the particles increasing the number of collisions.
Describe how an increase in concentration increases the rate of a reaction. (2 marks)
Expected Response
As the concentration increases the number of reactivity of particles per unit volume increases thus affecting collisions. This leads to increase in the rate of reaction
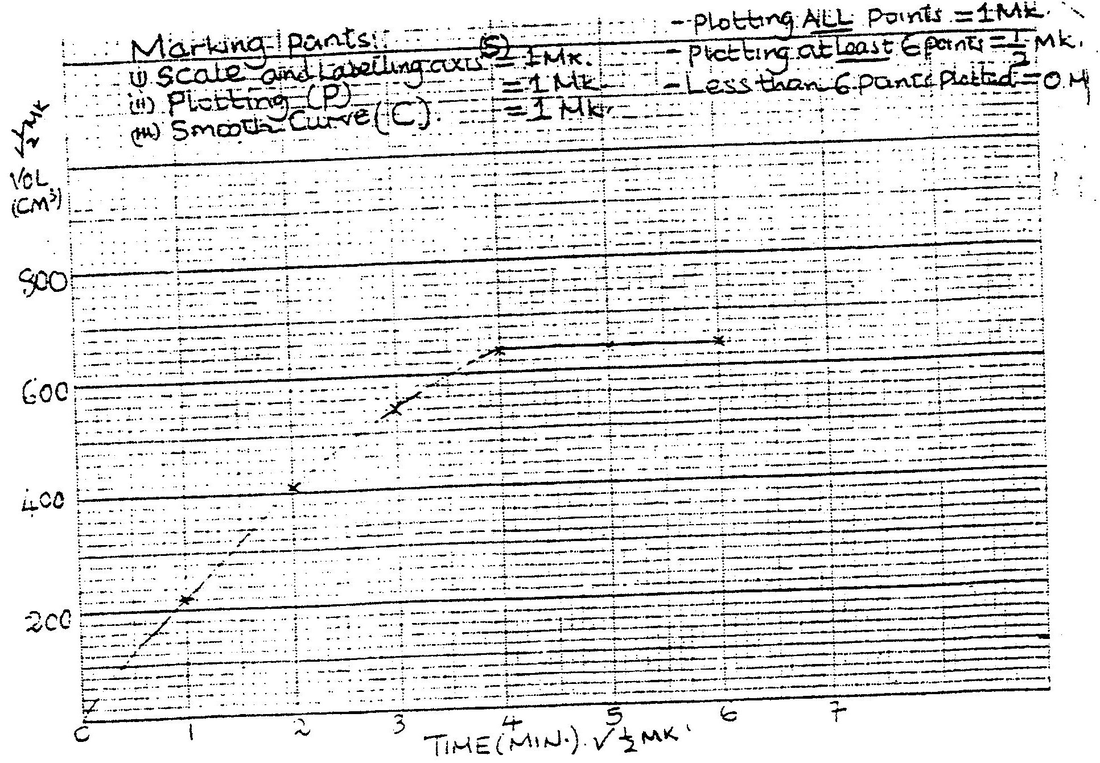
In an experiment to study the rate for reaction between duralumin (an alloy of aluminium, magnesium and copper) and hydrochloric acid, 0.5g of the alloy were reacted with excess 4M hydrochloric acid. The data in the table below was recoded.
Use it to answer the questions that follow. a) i) On the grid provided, plot a graph of total volume of gas produced (vertical axis) again time. ii) From the graph, determine the volume of gas produced at the end of 2 ½ minutes. b) Determine the rate of reaction between the 3rd and 4th minute. c) Give a reason why some solid remained at the end of the experiment d) Given that 2.5cm3 of the total volume of the gas was from the reaction between magnesium and aqueous hydrochloric acid, calculate the percentage mass of aluminium present in 0.5g of the alloy. (Al = 27.0 and Molar gas volume = 24,000cm3 at 298k) e) State two properties of duralumin that make it more suitable than aluminium in aeroplane construction.
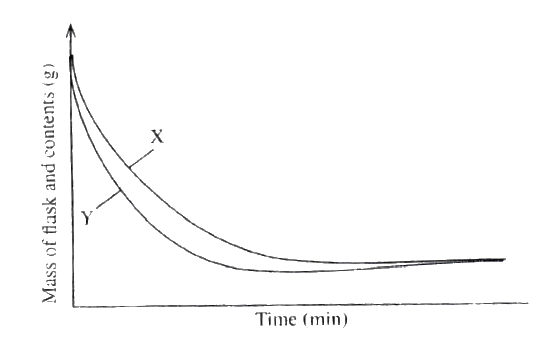
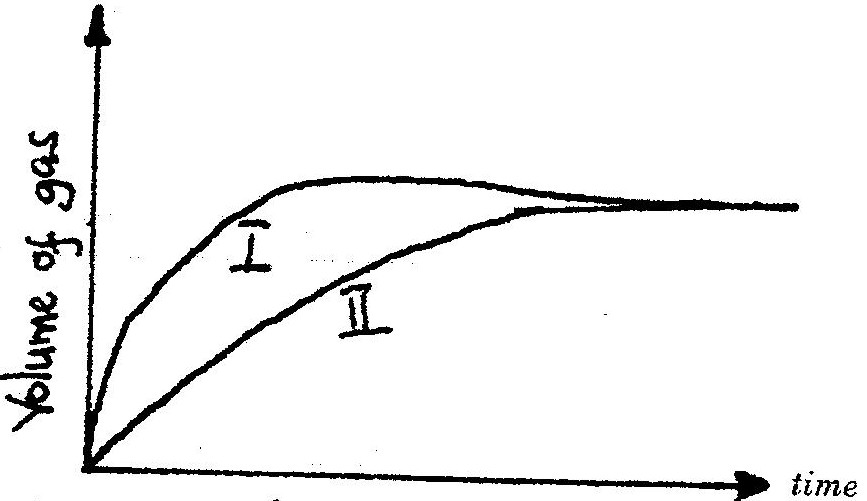
The curves below represent the change in mass when equal masses of powered zinc and zinc granules were reacted with excess 2M hydrochloric acid. Study them and answer the question below.
Which curve represents the reaction with zinc granules? Explain your answer.
ANSWERS
X - Zinc granules
The gradient of the graph is less steep because there is less surface area.
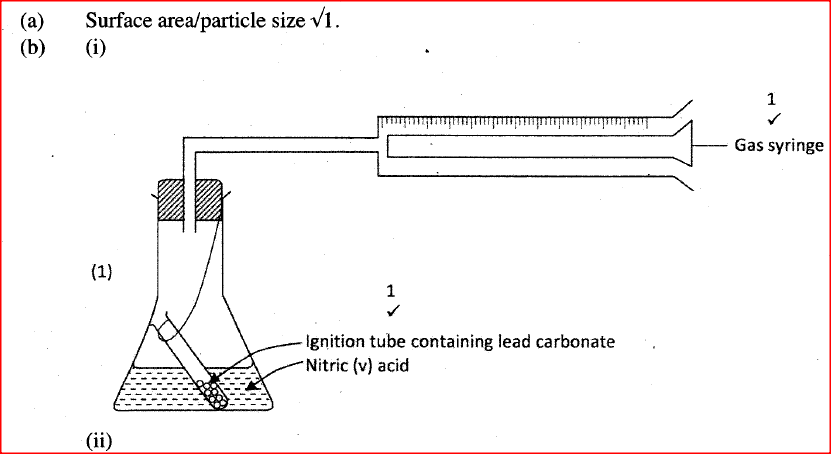
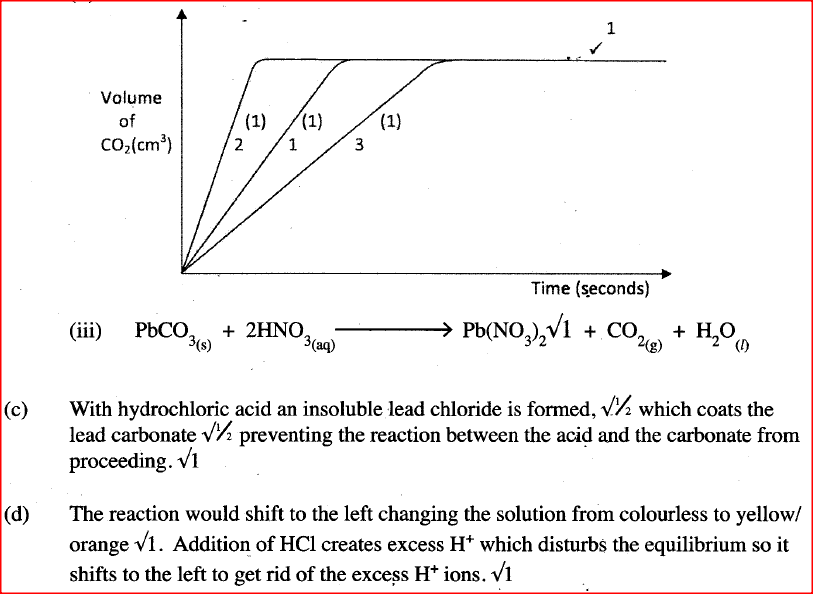
The factors which affect the rate of reaction between lead carbonate and dilute nitric (V) acid were investigated by carrying out three experiments;
a) Other than concentration , name the factor that was investigated in the experiments.
b) For each experiment, the same volume of acid (excess) and mass of lead carbonate were used and the volume of gas liberated measured with time. i) Draw a set up that can be used to investigate the rate of reaction for one of the experiments. ii) On the grid provided, sketch the curves obtained when the volume of gas produced was plotted against time for each of the three experiments and label each as 1, 2 or 3.
iii) Write an equation for the reaction that took place.
c) If the experiments were carried out using dilute hydrochloric acid in place of dilute nitric (V) acid, the reaction would start, slow down and eventually stop. Explain these observations. d) A solution of bromine gas in water is an example of a chemical reaction in a state of balance. The reaction involved is represented by the equation below.
State and explain the observation made when hydrochloric acid is added to the mixture at equilibrium.
In an experiment, 0.8gm of magnesium of powder were reacted with excess dilute sulphuric acid at 250C . The time for the reaction to come to completion was recorded. The experiment was repeated at 400C. In which experiment was the time taken shorter? Explain your answer.
Expected Response
Experiment II. At a high temperature the particles have more energy, hence rate of high energy collisions increase.
A dynamic equilibrium is established when hydrogen and carbon (IV) oxide react as shown below:
What is the effect of adding powdered iron catalyst on the position of the equilibrium?
Give a reason.
ANSWERS
The curves below were obtained when two equal volumes of hydrogen peroxide of the same concentration were allowed to decompose separately. In one case, manganese (IV) oxide was added to the hydrogen peroxide
Which curve represents the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide with manganese (IV) oxide? Explain
Expected Response
19. I – Manganese (iv) Oxide is a catalyst and increases the rate of decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide.
The table below gives the volume of the gas provided when different volumes of 2M hydrochloric were reacted with 0.6g of magnesium powder at room temperature
(a) Write an equation fro the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid
(b) On the grid provided plot a graph of the volume of gas produced (vertical axis), against the volume of acid added (Note the reaction comes to completion, the volume of the gas produced directly proportional to completion, the acid added). From the graph determine c)
e) Given that one mole of the gas occupied 24000cm3 at room temperature.
(a) Ethanol can be manufactured from ethene and steam as shown in the equation below:
Temperature and pressure will affect the position of equilibrium of the above reaction. Name the other factor that will affect the position of equilibrium of the above reaction.
(b) The data in the table below was recorded when one mole of ethene was reacted with excess steam. The amount of ethanol in the equilibrium mixture was recorded under different conditions of temperature and pressure. Use the data to answer the questions that follow.
(i)State whether the reaction between ethene and steam is exothermic or endothermic.
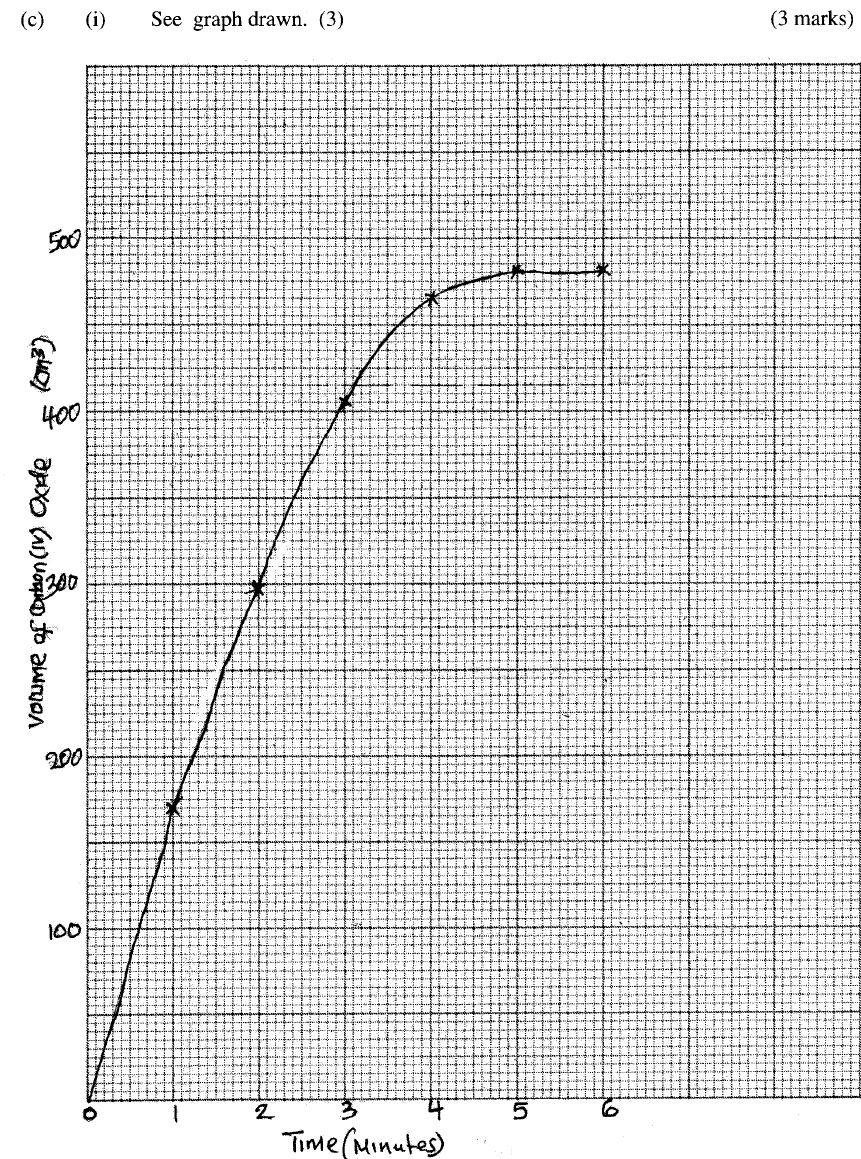
Explain your answer. (ii) State and explain one advantage and one disadvantage of using extremely high pressure in this reaction. I Advantage II disadvantage (c) In an experiment to determine the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid, 2g of calcium carbonate were reacted with excess 2 M hydrochloric acid, The volume of carbon (IV) oxide evolved was recorded at regular intervals of one minute for six minutes. The results are shown in the table below.
(i) plot a graph of time in minutes on the horizontal axis against volume of carbon (IV) oxide on the vertical axis.
(ii) determine the rate of reaction at 4 minutes
ANSWERS
(a) Increase or change in amount of reagent either reactants or products.
(Concentration). (b) (i) Exothermic increase in temperature from 250 - 350 at constant pressure the amount of ethanol formed at equilibrium decreases. (ii) I Advantage - it would increase the yield of ethanol ; since increase in pressure will favour side with less moles i.e. the products. II Disadvantage - it would mean investment in equipment to withstand the high pressure and would be expensive.
Ethanoic acid and ethanol react as shown in the equation below:
Other than warming, how would the state of equilibrium be established within a short time?
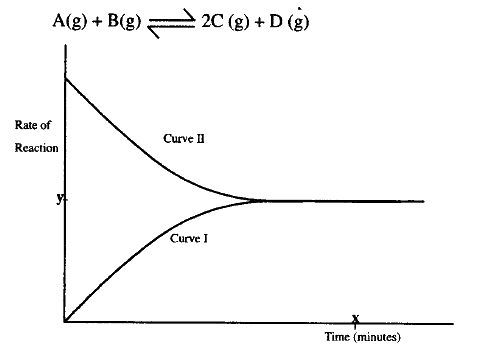
The figure below shows how the rate of the following reaction varies with the time.
i) Which of the two curves represent the rate of the reverse reaction? Give a reason
ii) What is the significance of point X and Y on the figure? b) State and explain the effect of an increase in pressure on the rates of the following reactions.
i) On a grid plot a graph of volume of gas produced (vertical axis) against time
ii) From the graph, determine the rate of the reaction at: (I) 15 seconds (II) 120 seconds (III) Give a reason for the difference between the two values.
ANSWERS
(a)Curve 1
The concentration of products are increasing The rate of reaction is increasing. At time x equilibrium has been established, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of reverse reaction and this has a value of Y. (b)(i) Increasing pressure increases rate of reaction. Molecules are brought closer, more collision of gases particles. Increasing pressure has no effect on liquids. Under certain conditions, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form methanol (CH3OH) and oxygen as shown below
What would be the effect on the yield of methanol if the temperature of the reaction mixture is increased? Explain
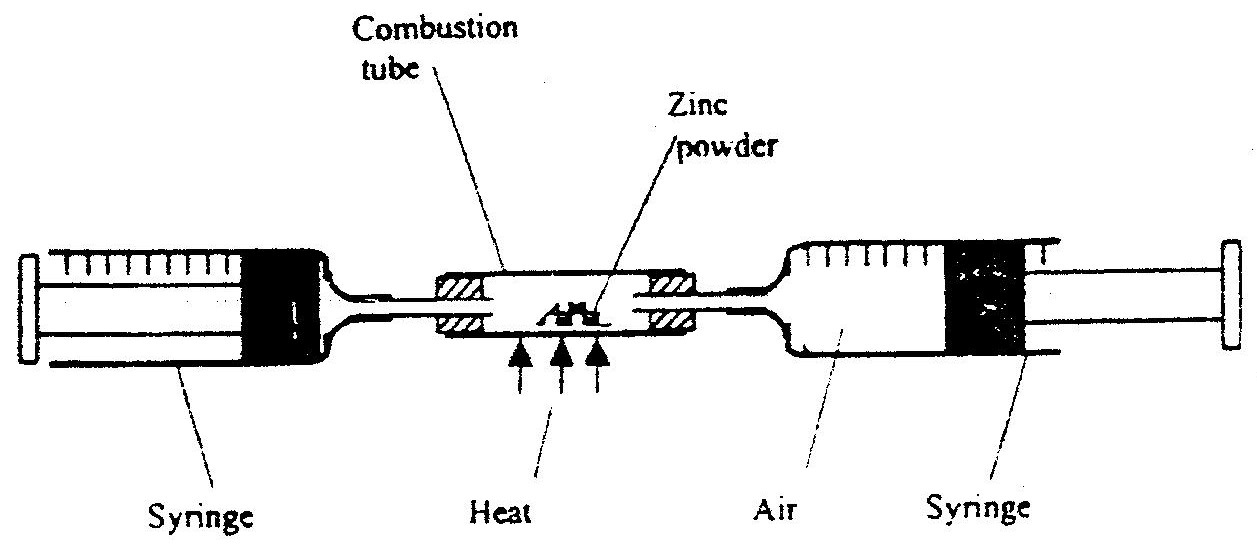
In an experiment a certain volume of air was passed from syringe to syringe over heated zinc powder as shown in the diagram below
The experiment was repeated using excess magnesium powder. In which of two experiments was the change in volume of the air greatest. (Give reasons)
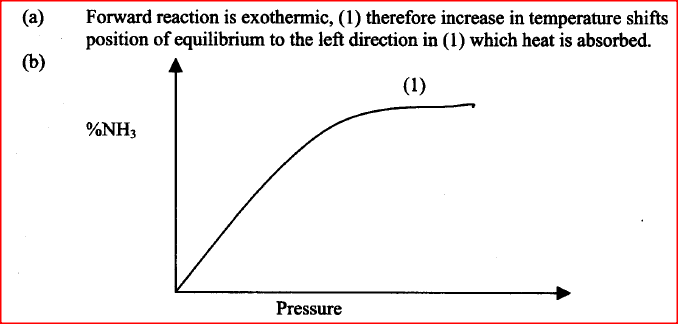
Nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia gas as shown in the following equation:
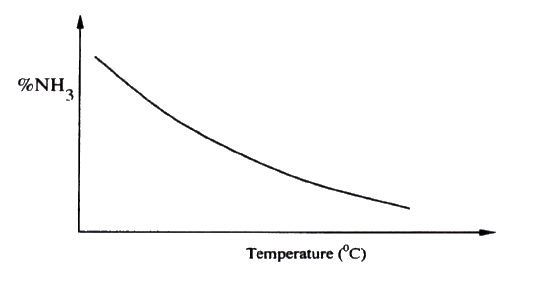
a) The figure below shows how the percentage of ammonia gas in the equilibrium mixture change with temperature.
Explain why the percentage of ammonia gas change as shown in the figure.
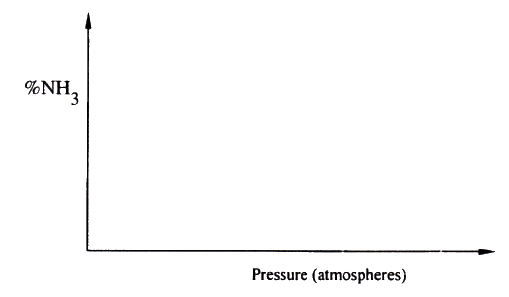
b) On the axes below, sketch a graph showing how the percentage of ammonia gas in equilibrium mixture changes with pressure. |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |

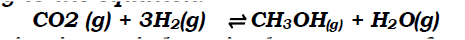




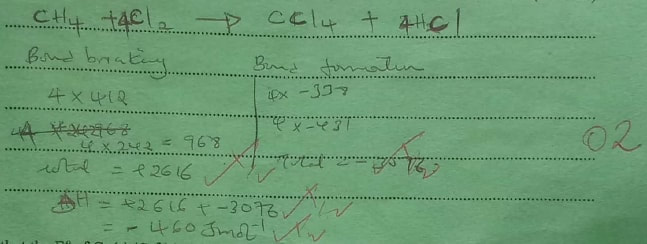
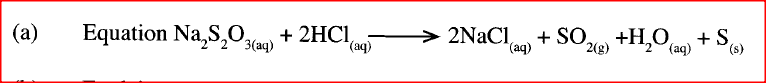

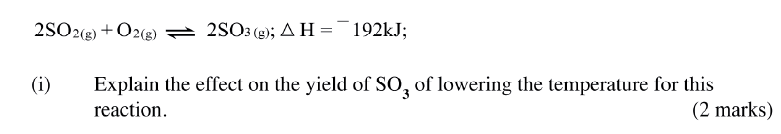
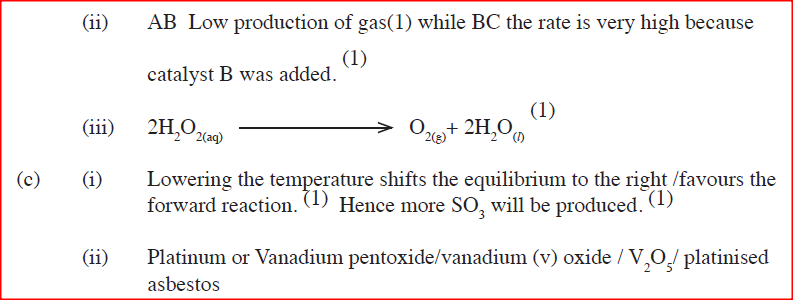
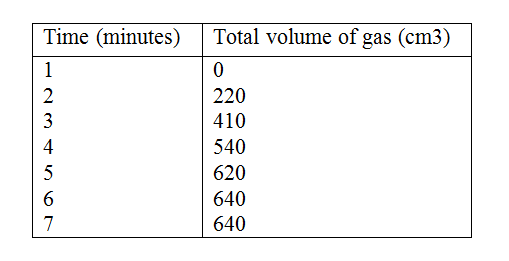

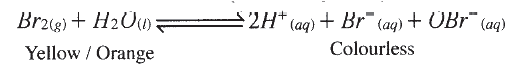
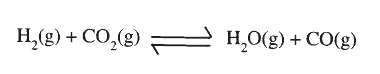

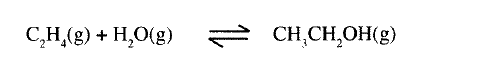


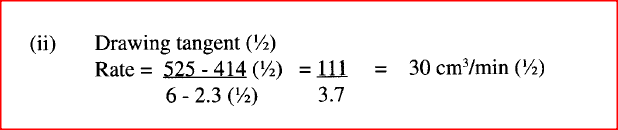
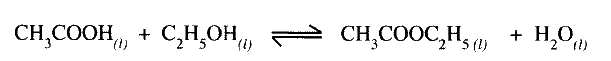




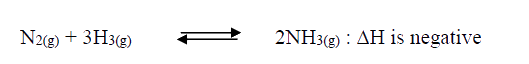

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

