|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts: A Comprehensive GuideReview:
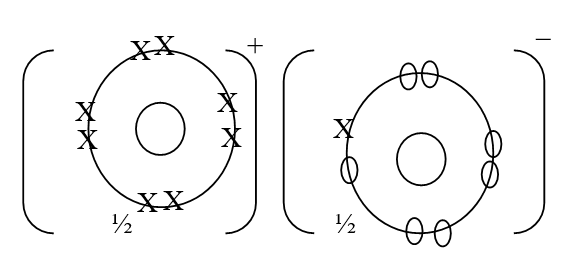
Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts: A Comprehensive Guide Acids, bases, and salts play crucial roles in various chemical reactions and are fundamental concepts in chemistry. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of these substances, shedding light on their definitions, properties, and reactions. The guide begins by introducing the different definitions of acids and bases. According to the Arrhenius definition, an acid is a substance that dissolves in water to form H+ or H3O+ ions, while a base dissolves in water to form OH- ions. The Bronsted-Lowry definition expands upon this, defining an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. To illustrate these definitions, the guide presents examples of acid-base reactions, highlighting the exchange of protons between the reactants. Through these examples, readers gain a deeper understanding of how acids and bases interact with each other. The guide also emphasizes the importance of water as a solvent for acids and bases. It explains that acids and bases exhibit their acidic or alkaline properties only in water, making it a crucial medium for their reactions. In other solvents, acids and bases may not display their characteristic properties. Furthermore, the guide explores the various properties and characteristics of acids and bases. It explains how acids can turn litmus paper red and have low pH values, while bases can turn litmus paper blue and have higher pH values. Additionally, acids and bases are good electrolytes and can undergo electrolysis. The guide also touches upon the reactions of acids and bases with metals and metal carbonates. It explains how acids can react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and salts, while reacting with metal carbonates can produce carbon dioxide gas, water, and salts. It also highlights how acids can neutralize metal oxides and hydroxides to form salts and water. In summary, "Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts: A Comprehensive Guide" provides a detailed exploration of these essential chemical substances. It offers a clear understanding of their definitions, properties, and reactions, making it an invaluable resource for students and enthusiasts of chemistry. Comprehensive KCSE Form 3 Chemistry Notes: Gas Laws and PrinciplesReview:
The "KCSE FORM 3 CHEMISTRY NOTES.pdf" is a comprehensive resource for Form 3 students studying Chemistry. The document covers the topic of gas laws and principles, providing a thorough understanding of the properties of gases and how they are affected by temperature and pressure. The notes explain the concepts in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to grasp the fundamental principles. The document starts by introducing the three states of matter and then focuses on gases, highlighting their unique characteristics. It explains the SI units of temperature and pressure, along with their interconversion. Practice examples are provided to help students practice converting temperature units and understanding pressure calculations. The document then delves into Boyle's law, which states the inverse relationship between the volume and pressure of a gas at constant temperature. The mathematical equation is presented and explained, and practice examples are given to strengthen understanding. Similarly, Charles' law, which relates the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure, is thoroughly discussed. Graphical representations and real-life examples are used to enhance comprehension. The document also addresses the concept of absolute zero, the lowest temperature at which a gas can exist, and its relationship to volume. Overall, the "KCSE FORM 3 CHEMISTRY NOTES.pdf" provides a comprehensive overview of gas laws and principles. The content is well-structured, and the explanations are easy to follow. It is an invaluable resource for Form 3 students preparing for their Chemistry exams. Comprehensive KCSE Form 2 Chemistry Notes for Effective LearningReview:
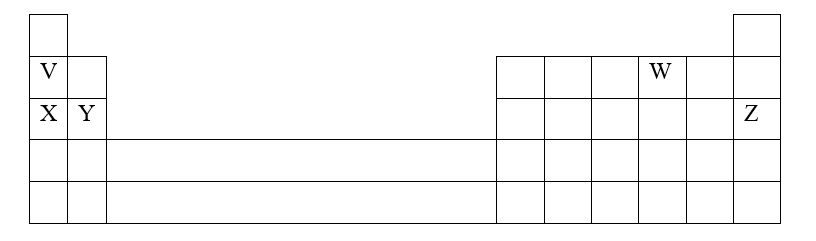
These KCSE Form 2 Chemistry Notes are a valuable resource for students studying chemistry at the secondary level. The document covers essential topics such as atomic structure, periodic table trends, isotopes, and relative atomic mass. The content is presented in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to understand and apply the concepts. The notes provide detailed explanations of the three subatomic particles (protons, electrons, and neutrons) and their relative positions within an atom. The periodic table is also thoroughly discussed, emphasizing the trends across and down the table. This knowledge is essential for understanding chemical bonding and structure. One of the strengths of these notes is the inclusion of examples and calculations. This allows students to apply the concepts they have learned and practice their problem-solving skills. The document also provides a table showing the atomic structure of the first twenty elements, which serves as a useful reference. Furthermore, the notes explain the concept of isotopes and how to calculate the relative atomic mass using the relative abundance of isotopes. The examples provided help students grasp this concept effectively. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of the mass spectrometer in determining accurate relative atomic masses. Overall, these KCSE Form 2 Chemistry Notes are a comprehensive and well-structured resource for students. They cover all the necessary topics and provide ample examples for practice. By using these notes, students can build a strong foundation in chemistry and excel in their studies. Introduction to Chemistry: States of Matter, Mixtures, Conductors, and DrugsThis detailed article on the introduction to chemistry covers a wide range of topics, making it a valuable resource for students and enthusiasts alike. The content is well-structured, starting with an overview of the states of matter and their properties. The explanations are clear and concise, making it easy to understand the differences between solids, liquids, and gases. The section on the separation of mixtures provides simple methods that can be easily understood by beginners. The discussion on conductors and non-conductors of electricity is informative, with a list of examples for better comprehension. The article also highlights the role of chemistry in society, emphasizing its importance in various fields such as medicine, manufacturing, and diagnostics. The section on drugs provides a clear distinction between drugs and medicines, highlighting the significance of correct prescription and dosage. Overall, this article is a comprehensive guide to the basics of chemistry and its practical applications, making it a valuable resource for anyone interested in the subject. The Versatile Applications of Sulphur: From Fertilizers to PharmaceuticalsSulphur has a wide range of industrial uses due to its unique properties. Some common industrial uses of sulphur include:
The Chemistry of Sulphur: Properties, Extraction, and UsesReview: The Chemistry of Sulphur: Properties, Extraction, and Uses is a comprehensive guide that delves into the fascinating world of sulphur. This essential element, found in Group VI of the Periodic table, has numerous applications in various industries. The content begins by discussing the occurrence of sulphur, highlighting its presence as a free element in certain regions such as Texas, Louisiana, and Sicily. Next, the extraction process of sulphur from Frasch's method is explained in detail. This method involves drilling concentric pipes and using superheated water and compressed air to melt and collect the sulphur. The diagram provided helps visualize the process, making it easier to understand. The content then explores the different allotropes of sulphur, namely rhombic sulphur and monoclinic sulphur. Their unique properties, such as melting points, densities, and structures, are discussed. The transition temperature between the two allotropes is also explained. Heating sulphur is another important aspect covered in the content. The changes in sulphur's physical state as it is heated are described, including the formation of long chains and the eventual vaporization and solidification process. The observations and explanations provided enhance the reader's understanding of sulphur's behavior under different conditions. The content concludes by addressing the physical and chemical properties of sulphur, including its solubility, conductivity, and melting and boiling points. It also highlights the reactions of sulphur with other substances, as well as its various uses in industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. Overall, The Chemistry of Sulphur: Properties, Extraction, and Uses provides a comprehensive overview of this versatile element. With its detailed explanations, diagrams, and practical applications, this content serves as an excellent resource for students, researchers, and anyone interested in the fascinating world of chemistry. Understanding the Rates of Chemical Reactions: Factors, Theories, and MeasurementsReview:
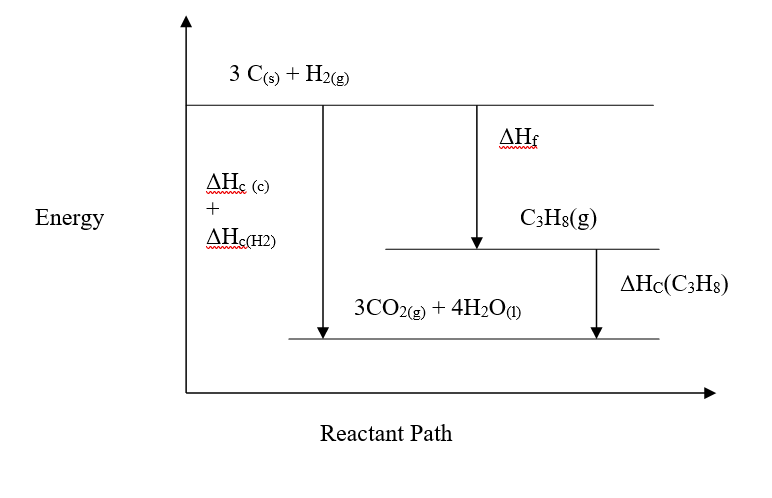
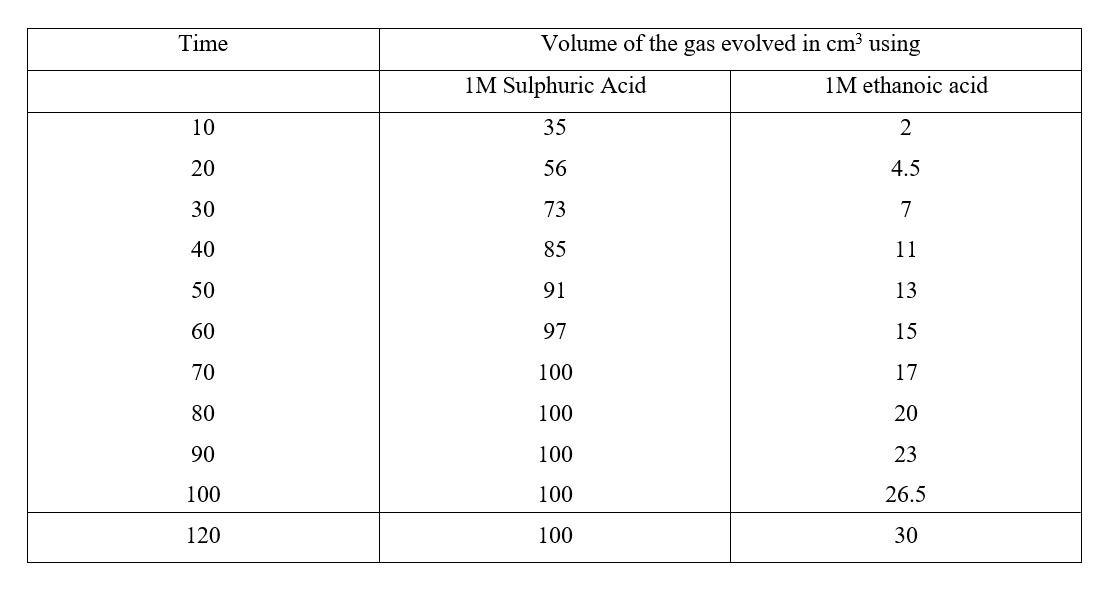
Chemistry is a fascinating subject that delves into the intricacies of matter and its transformations. One important aspect of chemistry is understanding the rates of chemical reactions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the factors that influence reaction rates, delve into the collision theory, discuss activation energy, and highlight various methods of measuring reaction rates. The concept of reaction rates is crucial as it helps us understand how quickly a chemical reaction proceeds. Factors such as concentration, pressure, temperature, surface area, and the presence of catalysts can significantly alter the rate of a chemical reaction. By manipulating these factors, scientists can optimize reaction conditions to maximize efficiency and profitability in industries. The collision theory is an essential concept in understanding reaction rates. According to this theory, for a reaction to occur, the reacting particles must collide. However, not all collisions are successful in initiating a chemical reaction. Successful collisions require the particles to have the required energy and the correct orientation, increasing the chances of forming products. Activation energy, also known as the Enthalpy of Activation, is another critical theory related to reaction rates. It represents the minimum amount of energy that the reactants must overcome before they can react. Activation energy is necessary for bond breaking, which is an endothermic process. The energy level diagrams help visualize the activation energy required for both exothermic and endothermic reactions. Measuring the rate of a chemical reaction is essential for studying its kinetics. Various methods can be employed, such as measuring the volume of gas produced or consumed, monitoring changes in mass, observing the formation of precipitates, or tracking the complete conversion of reactants to products. These measurement methods provide valuable insights into the reaction kinetics and help validate theoretical predictions. In conclusion, understanding the rates of chemical reactions is crucial for various applications in industries and scientific research. By exploring the factors influencing reaction rates, the collision theory, activation energy, and measurement methods, we gain a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of chemical kinetics. Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen: Properties, Preparations, and UsesReview
The Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen provides a comprehensive overview of the properties, laboratory preparations, and uses of various oxides of nitrogen. Nitrogen, belonging to the second period of Group V in the periodic table, forms five different oxides when combined with oxygen in different ratios. The document presents the oxides of nitrogen in a tabular form, including their names, formulas, oxidation states of nitrogen, and the ratio of nitrogen to oxygen. It explains that NO and N2O are neutral gases, while the other oxides are acidic. The guide also highlights that the oxides of NO and N2O are brownish gases, while NO and N2O are gases. The laboratory preparation methods for each oxide are described in detail. For example, nitric oxide (NO) is prepared by treating metallic copper with moderately concentrated nitric acid. The document provides the chemical equation for the reaction and explains the use of Wolfe's apparatus for collecting the gas. It also outlines the purification process using freshly prepared ferrous sulfate solution. The physical and chemical properties of each oxide are thoroughly explained. For instance, NO is not combustible but decomposes into N2 and O2 at high temperatures. The document also discusses the oxidizing and reducing properties of NO, as well as its reactions with other substances such as potassium permanganate and halogens. The Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen also covers nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) in detail. It provides information on their structures, laboratory preparations, physical properties, and chemical reactions. The uses of each oxide are highlighted, including the preparation of nitric acid and the use of nitrous oxide as a mild anaesthetic. Overall, this document serves as a comprehensive guide for students studying oxides of nitrogen in chemistry. It provides a clear understanding of the properties, laboratory preparations, and uses of these important compounds. With detailed explanations and examples, students can enhance their knowledge and excel in their chemistry studies. Chemistry Practical Guide: Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis TechniquesReview
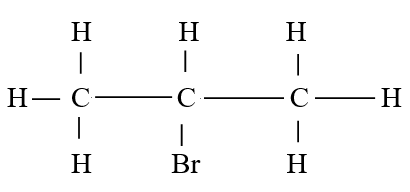
The Chemistry Practical Guide is a comprehensive resource that provides students with specific objectives and techniques for conducting chemistry experiments. The guide aims to test students' abilities to select and handle apparatus, make accurate observations, and draw conclusions based on those observations. It focuses on three main areas: qualitative analysis, quantitative analysis, and graphical work. Qualitative analysis involves performing chemical tests to identify substances. To obtain accurate results, students need to accurately identify the test reagents, understand what these reagents test, and predict the expected results. One of the key aspects of qualitative analysis is testing for cations, which involves adding certain reagents to a solution and noting the resulting observations and inferences. The guide provides a detailed list of cations and their corresponding observations and inferences. Another important aspect of qualitative analysis is testing for anions. This involves adding specific reagents and observing the resulting precipitates or color changes. The guide outlines the steps and observations for testing six common anions. Quantitative analysis focuses on making accurate measurements. It involves techniques such as titration and gravimetric analysis to determine the concentration or amount of a substance in a given sample. The guide provides an overview of these techniques and their applications. Graphical work involves the interpretation and analysis of data using graphs and charts. It includes techniques such as plotting graphs, determining gradients, and analyzing trends. Overall, the Chemistry Practical Guide serves as a valuable resource for students to enhance their understanding and skills in experimental chemistry. It provides clear instructions, observations, and inferences for qualitative and quantitative analysis techniques. By following the guide, students can develop the necessary proficiency in handling apparatus, making accurate observations, and drawing conclusions. With a strong foundation in practical chemistry, students will be well-prepared for their examinations and future scientific endeavors. Exploring Flames, Apparatus, and Chemical Reactions in ChemistryReview
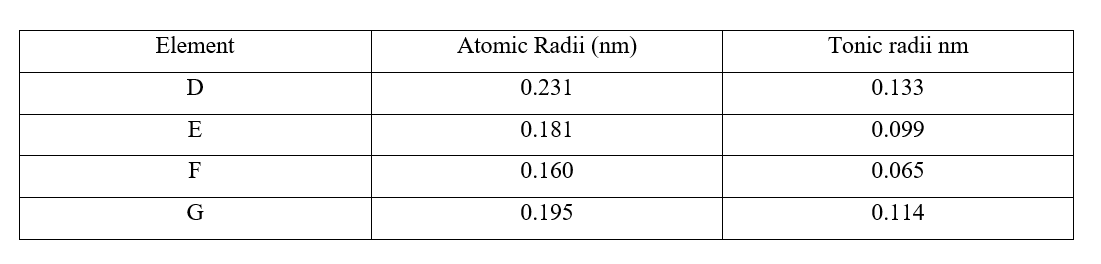
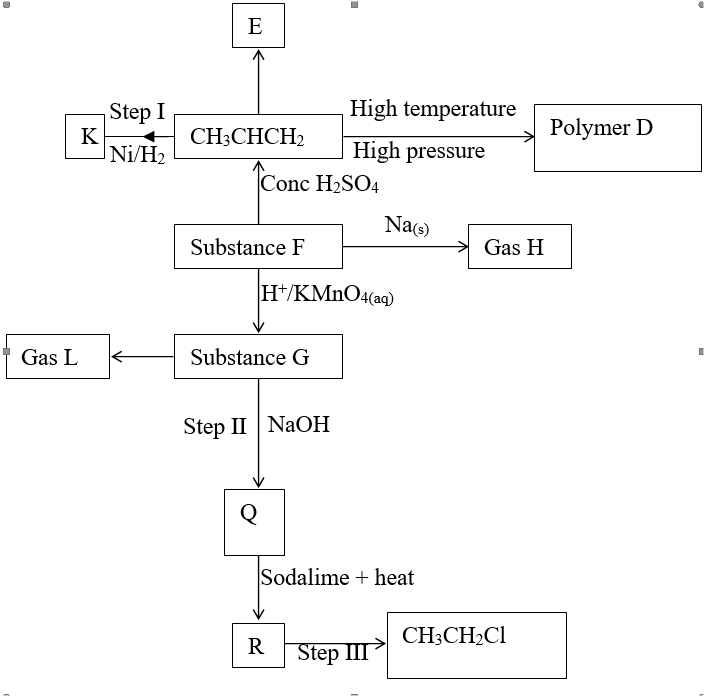
"Exploring Flames, Apparatus, and Chemical Reactions in Chemistry" is an insightful document that provides a comprehensive understanding of different aspects of chemistry. The document begins by explaining the differences between flames, specifically the non-luminous flames F and G, which were observed during an experiment. It also describes the order and arrangement of apparatus required to investigate the pH of an onion solution. The document further delves into the concept of drugs, defining them and highlighting their abuse by the youth. It identifies three common methods for collecting gases in the laboratory, which are often employed for various experiments. Moreover, the document discusses the separation of mixtures using the example of a mixture of hexane and water. It explains the states and functions of various apparatus commonly used in the laboratory, providing a deeper understanding of the equipment's roles in chemical experiments. The document also sheds light on the appearance of paper pieces in different parts of a non-luminous flame, revealing which region of the flame is better suited for heating. Additionally, the document includes an experiment involving copper (II) sulfate and water, which investigates the ionic radii of different substances. It explains the observations made during the experiment and provides a simple classification of substances based on heating curves. Overall, "Exploring Flames, Apparatus, and Chemical Reactions in Chemistry" is a comprehensive document that covers a wide range of topics in chemistry. It provides clear explanations, diagrams, and examples to enhance understanding. This document is a valuable resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in gaining a deeper knowledge of chemistry and its applications. Comprehensive Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes for Effective LearningReview:
Our Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes are an invaluable resource for students seeking a thorough understanding of the subject. The notes cover a wide range of topics, from the states of matter to the role of chemistry in society. Each concept is explained in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to grasp even the most complex ideas. One of the strengths of these notes is the inclusion of practical examples, which help students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. For example, the section on separation of mixtures provides simple methods that can be used to separate different substances, allowing students to see the practical applications of their learning. Furthermore, the notes emphasize the importance of safety in the chemistry laboratory. Clear guidelines are provided to ensure that students understand how to handle chemicals safely and minimize the risk of accidents. This focus on safety is crucial in fostering responsible and conscientious scientific practices. The layout and organization of the notes are also commendable. Each topic is presented in a logical sequence, building upon previous knowledge and paving the way for a smooth progression of learning. The use of headings, subheadings, and bullet points makes it easy for students to navigate through the content and locate specific information. Overall, our Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes provide a comprehensive and well-structured resource for students studying chemistry. With its clear explanations, practical examples, and emphasis on safety, this resource is sure to enhance students' understanding and appreciation of the subject. Comprehensive Chemistry Summary Notes for Form 1 to Form 4Review: The "FORM 1 TO FORM 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES.pdf" is an invaluable resource for students studying chemistry at the Form 1 to Form 4 level. The notes provide a comprehensive overview of the entire chemistry syllabus, covering all the key topics and concepts. The document is well-organized, with each topic clearly outlined and explained in a concise manner. The content is presented in a way that is easy to understand, making it suitable for students of all levels of ability. The notes include detailed explanations, diagrams, and examples to help students grasp the fundamental principles of chemistry. One of the standout features of these notes is the inclusion of practical applications and real-life examples. This helps students to see the relevance of chemistry in everyday life and enhances their understanding of the subject. The document also includes a section on exam tips and strategies, which is particularly helpful for students preparing for their chemistry exams. It provides guidance on how to approach different types of questions, how to structure answers, and how to effectively revise for exams. Overall, the "FORM 1 TO FORM 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES.pdf" is a comprehensive and well-structured resource that covers all the essential topics in chemistry. Whether you are a student looking for additional study material or a teacher seeking a reference guide, these notes are a valuable asset. Preparation of Pure Barium Carbonate from Barium Nitrate SolutionTo obtain a pure sample of barium carbonate in the laboratory from a barium nitrate solution, several steps can be followed. Here is a detailed procedure:
The Fascinating World of Allotropes: Exploring the Different Forms of ElementsUnderstanding Allotropes
An allotrope refers to different forms or structural arrangements of an element that exist in the same physical state but have distinct properties. These variations arise due to differences in the bonding arrangement or the way atoms are arranged within the substance. Allotropes can exhibit different physical and chemical properties, such as color, density, hardness, and reactivity. One well-known example of allotropes is carbon. Carbon can exist in several allotropes, including diamond, graphite, and fullerenes. Diamond, with its rigid lattice structure, is the hardest naturally occurring substance and is transparent. Graphite, on the other hand, has a layered structure, making it soft and suitable for use as a lubricant or in pencil leads. Fullerenes, such as buckminsterfullerene (C60), have a unique spherical shape and are used in various applications, including in nanotechnology. Another example is oxygen, which can exist as dioxygen (O2) and ozone (O3). Dioxygen is a colorless, odorless gas that is essential for supporting life through respiration. Ozone, on the other hand, is a pale blue gas that has a distinct smell and plays a crucial role in the Earth's ozone layer, protecting us from harmful ultraviolet radiation. Allotropes can also exist for other elements, such as sulfur, phosphorus, and selenium, among others. Each allotrope of these elements has different properties and uses. For instance, sulfur can exist as rhombic sulfur, which is yellow and brittle, or as monoclinic sulfur, which is reddish-brown and more stable. The study of allotropes is important in various scientific fields, including materials science and chemistry. Understanding the different forms of elements and their properties can lead to the development of new materials, technologies, and applications. In conclusion, an allotrope refers to different forms or structural arrangements of an element that exist in the same physical state but have distinct properties. Allotropes can exhibit different physical and chemical characteristics and play a significant role in various scientific applications and industries. When 3.18g of cuo were heated carefully in a steam of dry hydrogen,2.54g of Cu and 0.72g of H2O were formed.
|
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










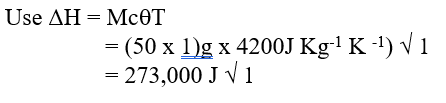

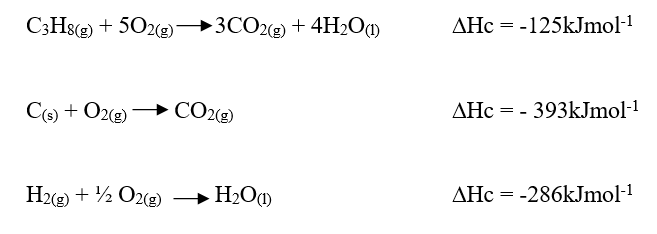


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

