|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
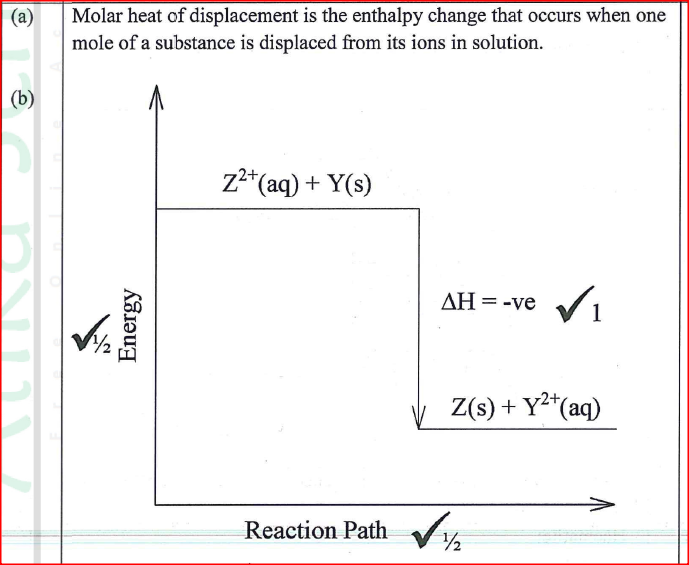
(a) Define molar heat of displacement.
(b)The following ionic equation represents the reaction between metal Y and an aqueous solution of Z2+.
Draw an energy level diagram to represent the reaction
In the Haber process, nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the following equation.
(a)What would be the effect of adding a catalyst on the position of the equilibrium?
(b) Explain why it is not advisable to use temperatures higher than 773 K in the Haber process.
ANSWERS
(a)No effect/does not affect the position of the equilibrium.
(b)Forward reaction is exothermic, excessive temperatures would favour the backward reaction therefore lowering the yield of ammonia.
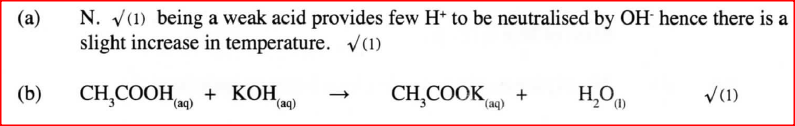
The following procedure was used to investigate the temperature changes that occur when sodium hydroxide solution is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(i) Place the acid in a glass beaker and record its temperature. (ii) Add a known volume of sodium hydroxide solution. (iii) Stir the mixture and record the highest temperature reached. (iv) Repeat steps (ii) and (iii) with different volumes of sodium hydroxide solution. (a) State two factors that must be kept constant in this experiment (b) Explain how the use of a polystyrene cup will affect the results.
ANSWERS
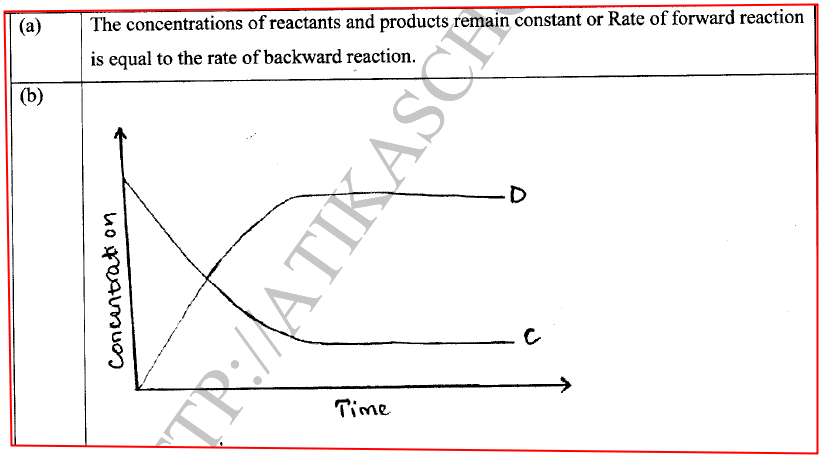
(a) State one characteristic of a reaction where equilibrium has been attained.
(a) What ¡s meant by molar heat of neutralisation? (1 mark)
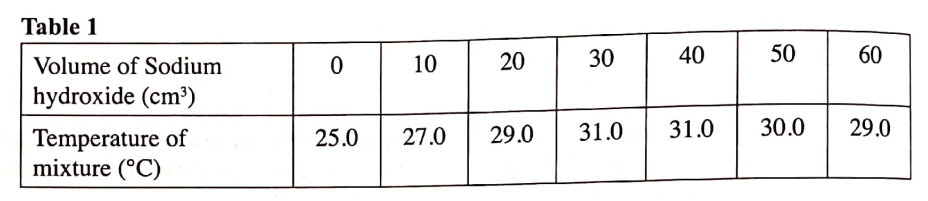
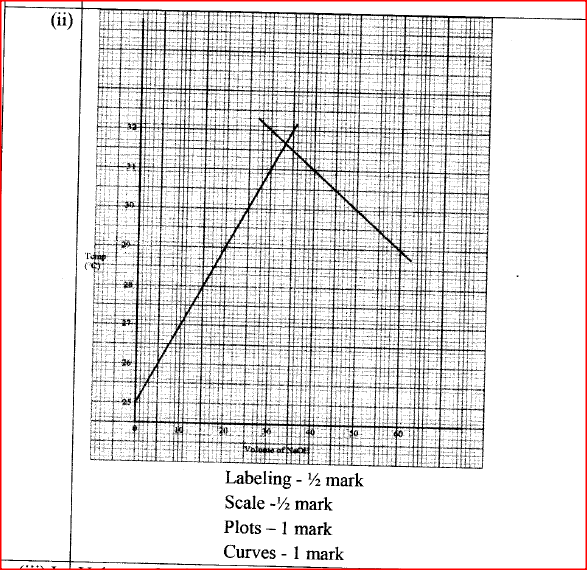
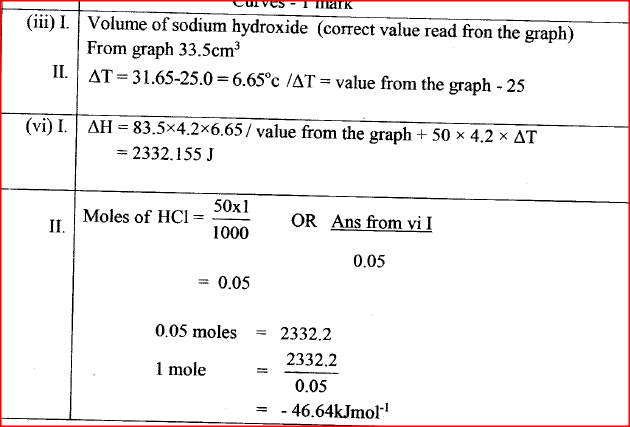
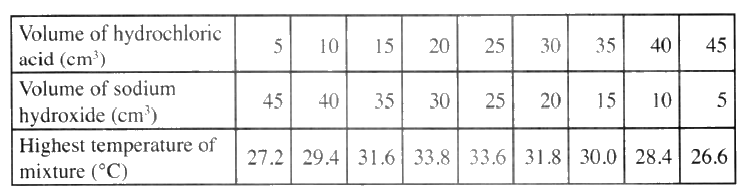
(b) In an experiment to determine the molar heat of neutralisation, 50 cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid was neutralised by adding 10 cm3 portions of dilute sodium hydroxide. During the experiment, the data in Table 1 was obtained.
(iii) Determine from the graph the: I. volume of sodium hydroxide which completely neutralises 50 cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid. (1 mark) II. change in temperature,△T, when complete neutralisation occurred. (1 mark) (iv) Calculate: I. the heat change, △H when complete neutralisation occurred. (Specific heat capacity = 4.2 Jg-1K-1, density of solution 1.0 gcm-3) (2 marks) II. molar heat of neutralisation of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide. (1 mark) (v) How would the value of molar heat differ if 50 cm3 of 1M ethanoic acid was used instead of 1M hydrochloric acid? Give a reason. (2 marks)
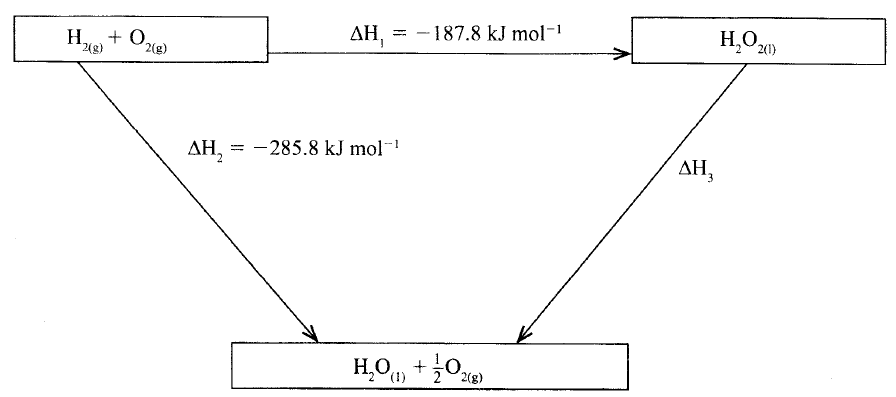
The figure below shows an energy cycle.
(a)Give the name of the enthalpy change ΔH1.
(b)Determine the value of ΔH3.
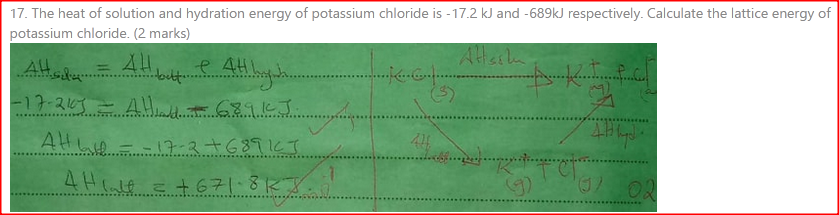
The heat of solution and hydration energy of potassium chloride is —17.2kJ and —689kJ respectively. Calculate the lattice energy of potassium chloride. (2 marks)
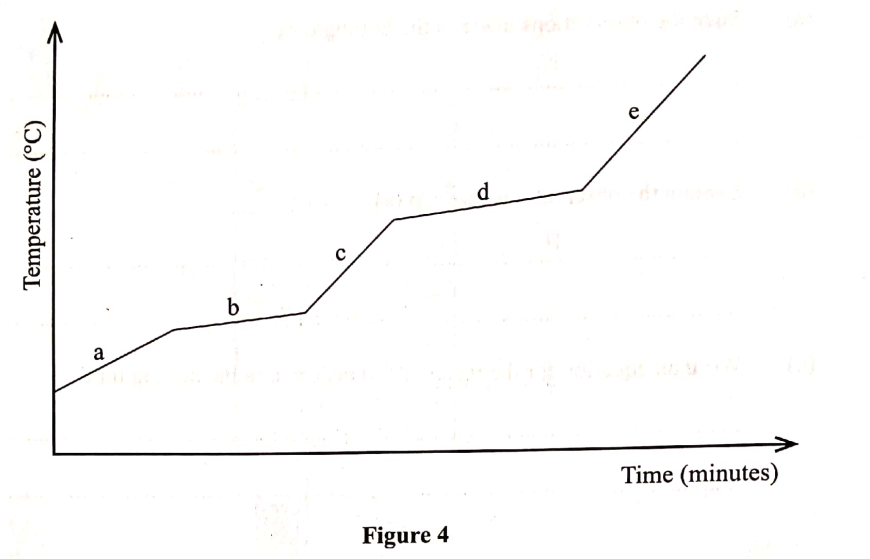
The graph in Figure 4 was obtained when a certain substance was heated and its temperature recorded at regular intervals.
(a) State the purity of the substance. (I mark)
(b) Explain the answer in (a). (2 marks)
(a) What is meant by lattice energy?
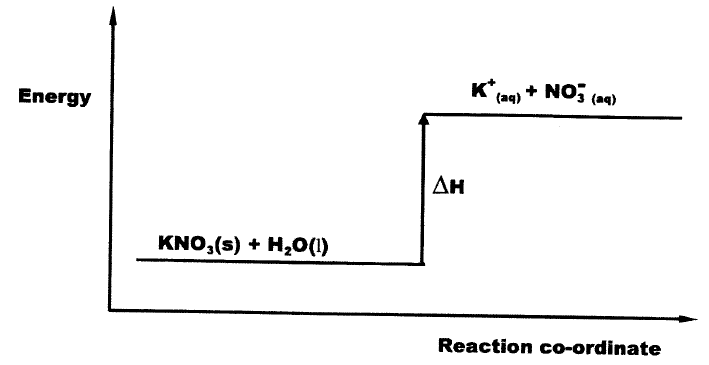
b) Study the energy level diagram below and answer the question that follows
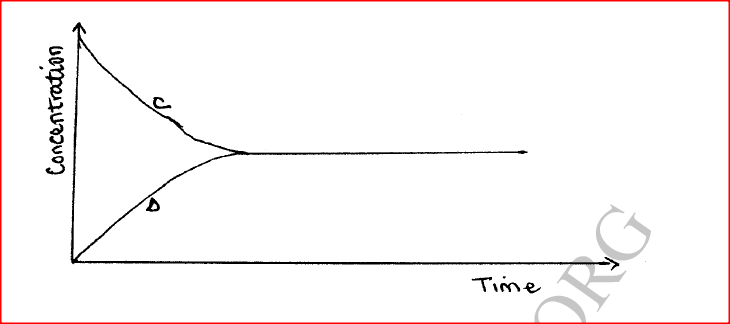
What type of reaction is represented by the diagram?
ANSWERS
(a) Enthalpy change, when one mole of crystal lattice is broken into its ions in gaseous state.
(b) Endothermic reaction (process)
When 20cm3 of 1 M sodium hydroxide was mixed with 20cm3 of 1 M hydrochloric acid, the temperature rose by 6.70C Assuming the density of the solution is 1 g/cm3 and the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.2Jg-1k-1.
(a) Calculate the molar heat of neutralization; (b) When the experiment was repeated with 1 M ethanoic acid, the temperature changes was found to be lower than that with 1 M hydrochloric acid. Explain.
Hydrogen peroxide decomposes according to the equation below:
8.5 gm of hydrogen peroxide contained in 100cm3 of solution with water were completely decomposed. Determine the rise in temperature due to the reaction. Specific density of water = 1g/cm3 O =16, H = 1,).
Expected Response
(a) (i) what is meant by the term Enthalpy of formation?
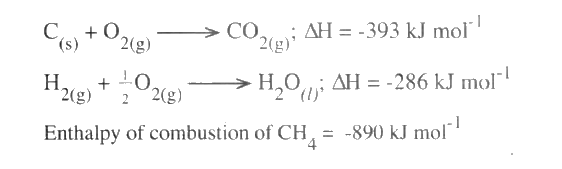
(ii) The enthalpies of combustion of carbon, methane and hydrogen are indicated below:
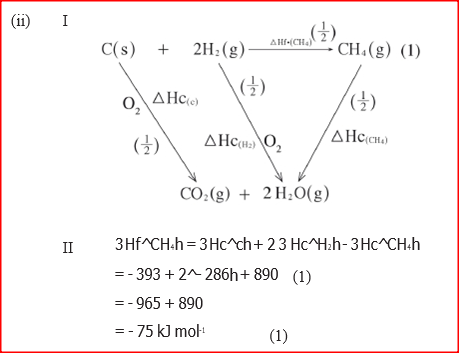
(i) Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the enthalpy of formation of methane to enthalpies of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and methane
(ii) Determine the enthalpy of formation of methane (b) An experiment was carried out where different volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide both at 25°C were mixed and stirred with a thermometer. The highest temperature reached by each mixture was recorded in the table below
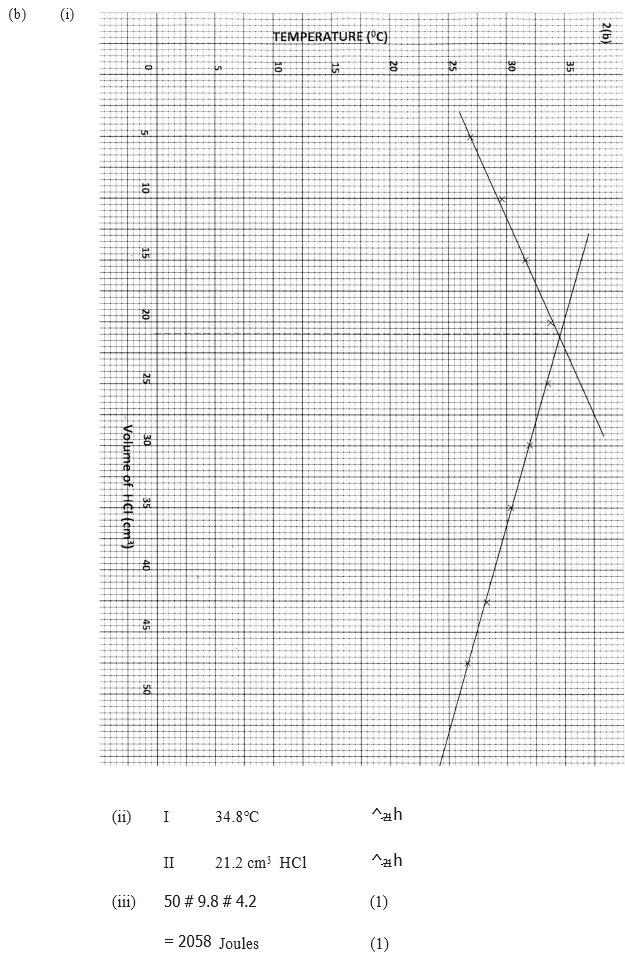
(i) On the grid provided. plot a graph of highest temperature (vertical axis) against volume of hydrochloric acid ( horizontal axis)
(ii) Using your graph , determine the (a) Highest temperature reached (b) Volume of acid and base reacting when highest temperature is reached
(iii) Calculate the amount of heat liberated during the neutralization process .(specify heat capacity is 4.2 j g -1 k-1 and the density of solution is 1.0 g cm-3)
(c) The molar enthalpy of neutralization between hydrochloric acid and ammonia solution was found to be -52.2 kJ mol-1, while that of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide was – 57.1 Kj mol-1. Explain the difference in these values.
ANSWERS
(a)(i)This is the heat absorbed or evolved when one mole of any substance is formed from its constituent elements in their normal states.
(c)The molar heat of neutralisation between a strong acid and a weak base is low because some of the heat is used to ionise (1) the weak base before neutralization.
For strong acid and strong base they are completely ionised.
A student investigated a property of acids M and N by reacting equal volumes of acid M and N of the same concentration with equal volumes of 2M potassium hydroxide.
The results were recorded in the table below.
a) Which of the acids is likely to be a weak acid? Explain.
b) Write the equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and potassium hydroxide.
a) Write an equation for the reaction
b) Using the bond energies given below, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction in (a) above
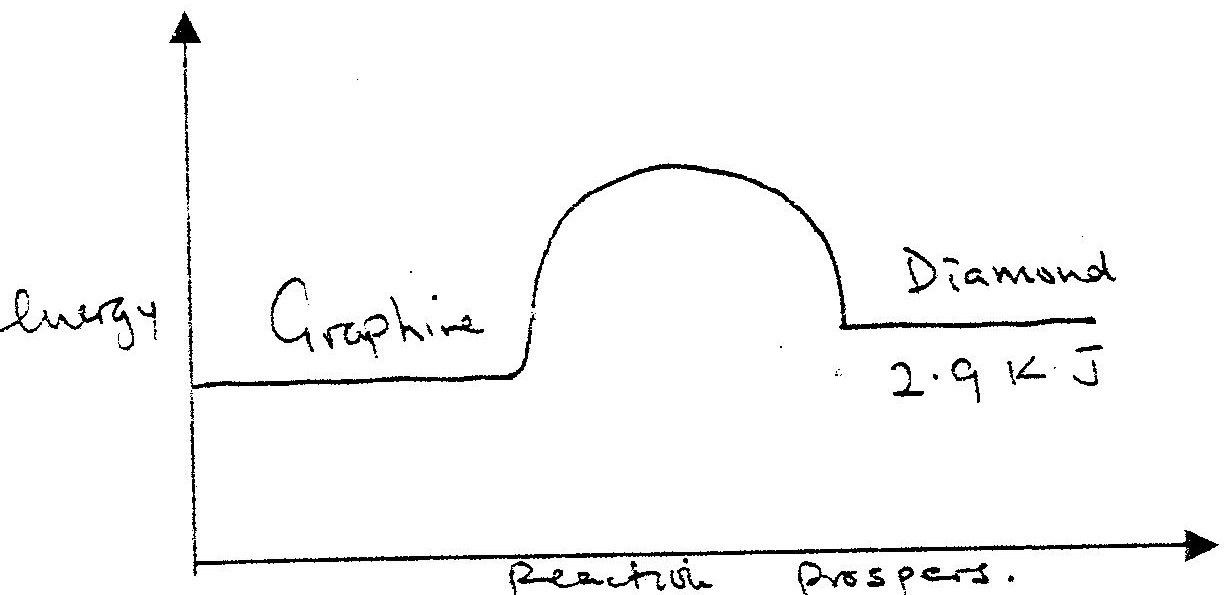
At 298K and 1 atmosphere, graphite changes into diamond according to the equation:
In the space provided, sketch a simple energy level diagram for the above change.
Study the energy level diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Give the name of ΔHA
(b) How can ΔHB be reduced? Give a reason.
ANSWERS
(a) Heat of reaction
(b) Using a catalyst Catalyst reduce activation energy.
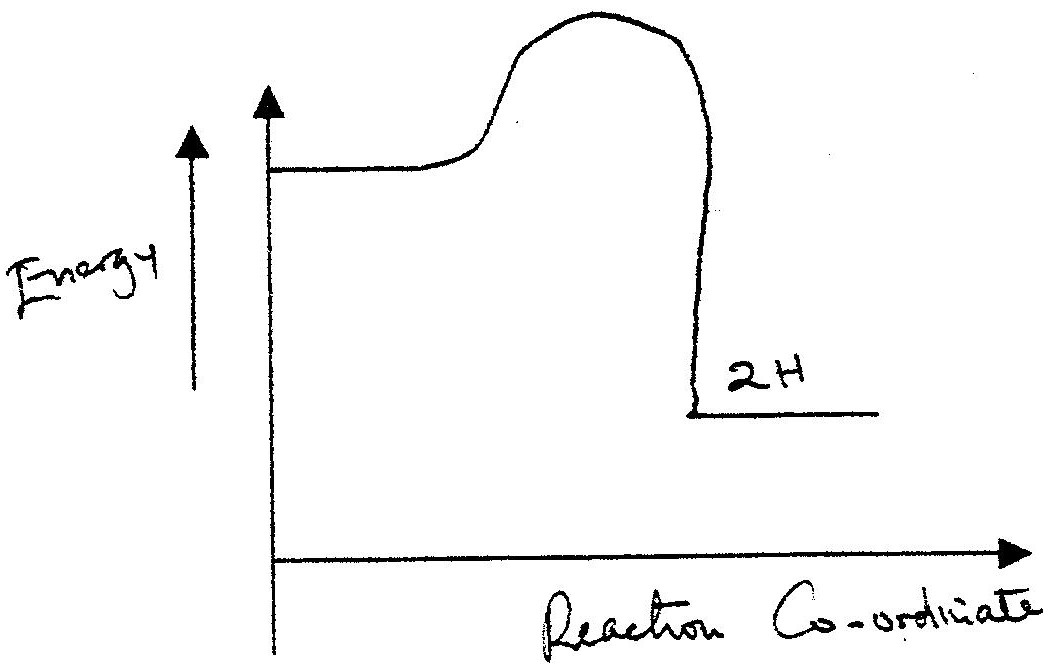
Hydrogen and fluorine react according to the equation below
(a) What is meant by molar heat of combustion?
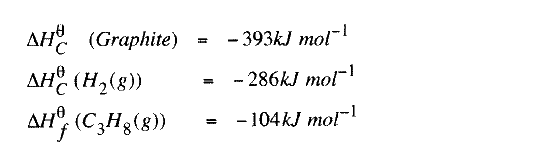
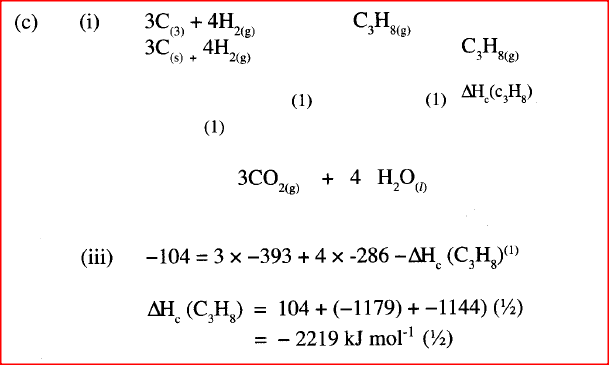
(b) State the Hess's Law. c) Use the following standard enthalpies of combustion of graphite, hydrogen and enthalpy of formation of propane.
(i) Write the equation for the formation of propane.
(ii) Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the heat of formation of propane with its heat of combustion and the heats of combustion of graphite and hydrogen. (iii) Calculate the standard heat of combustion of propane. Other than the enthalpy of combustion, state one factor which should be considered when choosing a fuel. (e) The molar enthalpies of neutralization for dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric (V) acid are -57.2kJ/mol while that of ethanoic acid is -55.2kJ/mol. Explain this. observation.
ANSWERS
(a) The amount of heat liberated when one mole of a substance is burnt in excess Oxygen.
(b) The heat evolved are absorbed in a chemical change is the same whether the change occurs in one step or through many steps.
(d) cost
effect on environment availability storage (e) Ethanoic acid is a weak acid therefore heat is used to ionize it before neutralization occurs . It value is therefore lower than that of hydrochloric acid which is fully ionized
The thermal chemical reaction between carbon and sulphur is as shown by the equation below:
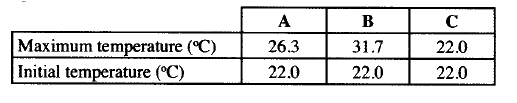
a. 50cm3 of 1M copper (II)sulphate solution was placed in a 100cm3 plastic beaker. The temperature of the solution was measured. Excess metal A powder was added to the solution, the mixture stirred and the maximum temperature was repeated using powder of metals B and C. The results obtained are given in the table below:
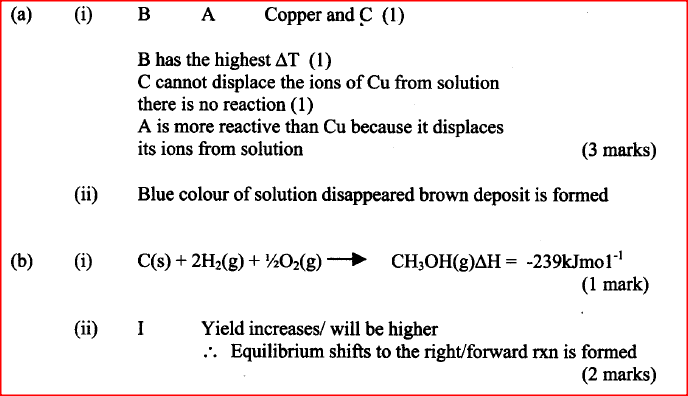
i. Arrange the metal A, B, C and copper in order of reactivity starting with the least reactive. Give reasons for the order.
ii. Other than temperature change, state one other observation that was made when the most reactive metal was added to the copper(II) sulphate solution.
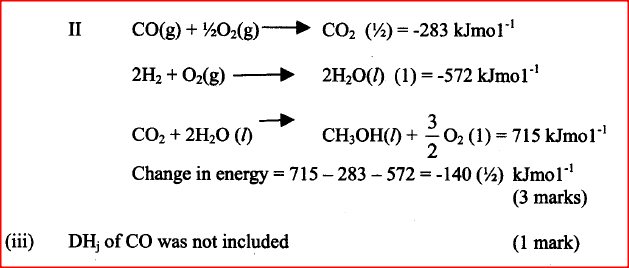
b. The standard enthalpy change of formation of methanol is -239 kJmol-1
i) Write the thermol chemical equation for the standard enthalpy change of formation of methanol.
iii) The calculate enthalpy change in part B(ii) (II) above differ from the standard enthalpy change of formation of methanol. Give a reason.
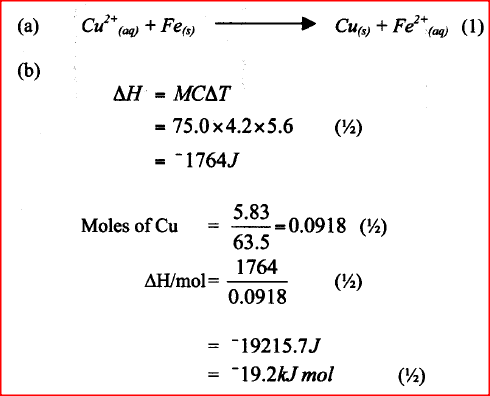
A beaker contained 75.0cm3 of aqueous copper (II) sulphate at 23.7°C. when scrap iron metal was added to the solution, the temperature rose to 29.3°C.
a) Write an ionic equation for the reaction that took place. b) Given that the mass of copper deposited was 5.83g, calculate the molar enthalpy change in kJmol-1. (specific heat capacity of solution = 4.2Jg-1 K-1, density of solution 1.0gcm-3, Cu = 63.5)
Use the information below to answer the question that follows
What is the name given to each of the following:
(a)Figure 3 show the changes that take place between states of matter. Some of them have been identified and others labelled.
i) Give the names of the processes
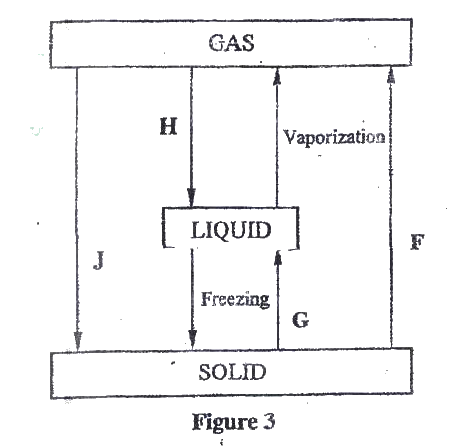
I H II G ii) Name one substance that can undergo process F when left in an open container in the laboratory. iii) The process J is called deposition. Using water as an example, write an equation that represents the process of deposition. b) Figure 4 shows the beating curve for water.
i) Give the names of the intermolecular forces of attraction in the segments;
I MN II RS ii) The heats of fusion and vaporization of water are 334.4 Jg-1 and 1159.4 Jg-1 respectively. I Explain why there is a big difference between the two. II How is the difference reflected in the curve? c) Coal, oil and natural gas are major sources of energy. They are known as fossil fuels. Hydrogen is also a source of energy. i) State and explain two reasons why hydrogen is a very attractive fuel compared to fossils. ii) State one disadvantage of using hydrogen fuel instead of fossil fuels.
ANSWERS
(a)
(i) I. Condensation II. Melting (ii) Iodine, Benzoic acid, Camphos, Dry Ice. Solid CO2 Naphthalene (iii) H2O(g) →H2O(g) (b) (i) Van des waals and hydrogen bonding II Van des waals forces (ii)I. The separation distance is smaller during fusion than during vaporization hence requires much lower energy than in vaporization and vice versa. II. Heating time NP is far much less than heating time in QR/ Heating time (c) (i) Hydrogen burns to produce steam which is a non pollutant/ does not cause pollution to the environment Hydrogen has a high energy content hence very small amount produce a lot of heat energy Hydrogen is renewable hence cannot be exhausted/ used completed. (ii) It can easily explore when burning/ highly flammable unlike fossils fuels expensive. |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
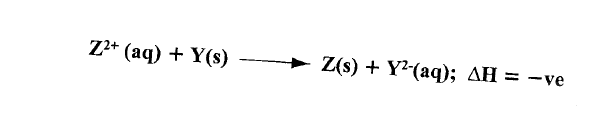
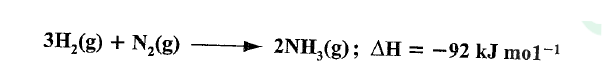

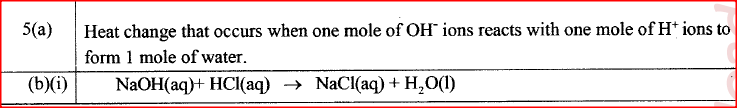

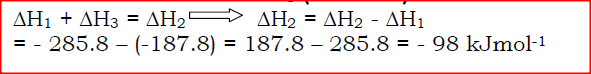





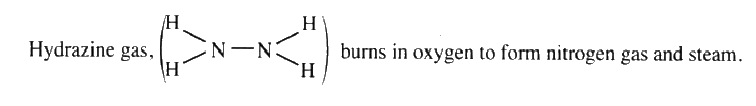

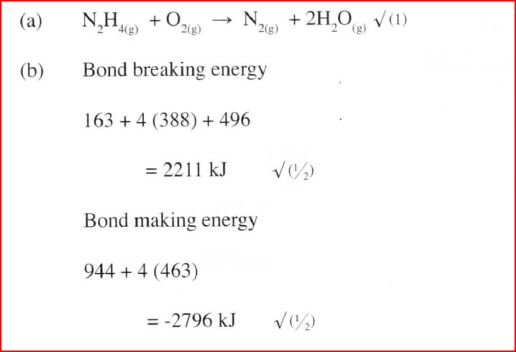



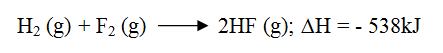



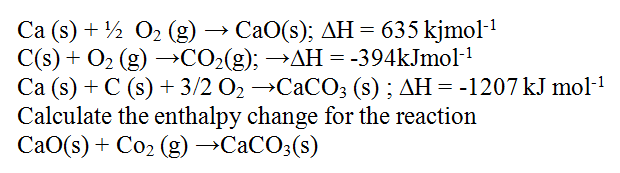



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

