Comprehensive KCSE Form 3 Chemistry Notes: Gas Laws and PrinciplesReview:
The "KCSE FORM 3 CHEMISTRY NOTES.pdf" is a comprehensive resource for Form 3 students studying Chemistry. The document covers the topic of gas laws and principles, providing a thorough understanding of the properties of gases and how they are affected by temperature and pressure. The notes explain the concepts in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to grasp the fundamental principles. The document starts by introducing the three states of matter and then focuses on gases, highlighting their unique characteristics. It explains the SI units of temperature and pressure, along with their interconversion. Practice examples are provided to help students practice converting temperature units and understanding pressure calculations. The document then delves into Boyle's law, which states the inverse relationship between the volume and pressure of a gas at constant temperature. The mathematical equation is presented and explained, and practice examples are given to strengthen understanding. Similarly, Charles' law, which relates the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure, is thoroughly discussed. Graphical representations and real-life examples are used to enhance comprehension. The document also addresses the concept of absolute zero, the lowest temperature at which a gas can exist, and its relationship to volume. Overall, the "KCSE FORM 3 CHEMISTRY NOTES.pdf" provides a comprehensive overview of gas laws and principles. The content is well-structured, and the explanations are easy to follow. It is an invaluable resource for Form 3 students preparing for their Chemistry exams.
0 Comments
The Versatile Applications of Sulphur: From Fertilizers to PharmaceuticalsSulphur has a wide range of industrial uses due to its unique properties. Some common industrial uses of sulphur include:
The Chemistry of Sulphur: Properties, Extraction, and UsesReview: The Chemistry of Sulphur: Properties, Extraction, and Uses is a comprehensive guide that delves into the fascinating world of sulphur. This essential element, found in Group VI of the Periodic table, has numerous applications in various industries. The content begins by discussing the occurrence of sulphur, highlighting its presence as a free element in certain regions such as Texas, Louisiana, and Sicily. Next, the extraction process of sulphur from Frasch's method is explained in detail. This method involves drilling concentric pipes and using superheated water and compressed air to melt and collect the sulphur. The diagram provided helps visualize the process, making it easier to understand. The content then explores the different allotropes of sulphur, namely rhombic sulphur and monoclinic sulphur. Their unique properties, such as melting points, densities, and structures, are discussed. The transition temperature between the two allotropes is also explained. Heating sulphur is another important aspect covered in the content. The changes in sulphur's physical state as it is heated are described, including the formation of long chains and the eventual vaporization and solidification process. The observations and explanations provided enhance the reader's understanding of sulphur's behavior under different conditions. The content concludes by addressing the physical and chemical properties of sulphur, including its solubility, conductivity, and melting and boiling points. It also highlights the reactions of sulphur with other substances, as well as its various uses in industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. Overall, The Chemistry of Sulphur: Properties, Extraction, and Uses provides a comprehensive overview of this versatile element. With its detailed explanations, diagrams, and practical applications, this content serves as an excellent resource for students, researchers, and anyone interested in the fascinating world of chemistry. Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen: Properties, Preparations, and UsesReview
The Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen provides a comprehensive overview of the properties, laboratory preparations, and uses of various oxides of nitrogen. Nitrogen, belonging to the second period of Group V in the periodic table, forms five different oxides when combined with oxygen in different ratios. The document presents the oxides of nitrogen in a tabular form, including their names, formulas, oxidation states of nitrogen, and the ratio of nitrogen to oxygen. It explains that NO and N2O are neutral gases, while the other oxides are acidic. The guide also highlights that the oxides of NO and N2O are brownish gases, while NO and N2O are gases. The laboratory preparation methods for each oxide are described in detail. For example, nitric oxide (NO) is prepared by treating metallic copper with moderately concentrated nitric acid. The document provides the chemical equation for the reaction and explains the use of Wolfe's apparatus for collecting the gas. It also outlines the purification process using freshly prepared ferrous sulfate solution. The physical and chemical properties of each oxide are thoroughly explained. For instance, NO is not combustible but decomposes into N2 and O2 at high temperatures. The document also discusses the oxidizing and reducing properties of NO, as well as its reactions with other substances such as potassium permanganate and halogens. The Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen also covers nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) in detail. It provides information on their structures, laboratory preparations, physical properties, and chemical reactions. The uses of each oxide are highlighted, including the preparation of nitric acid and the use of nitrous oxide as a mild anaesthetic. Overall, this document serves as a comprehensive guide for students studying oxides of nitrogen in chemistry. It provides a clear understanding of the properties, laboratory preparations, and uses of these important compounds. With detailed explanations and examples, students can enhance their knowledge and excel in their chemistry studies. Chemistry Practical Guide: Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis TechniquesReview
The Chemistry Practical Guide is a comprehensive resource that provides students with specific objectives and techniques for conducting chemistry experiments. The guide aims to test students' abilities to select and handle apparatus, make accurate observations, and draw conclusions based on those observations. It focuses on three main areas: qualitative analysis, quantitative analysis, and graphical work. Qualitative analysis involves performing chemical tests to identify substances. To obtain accurate results, students need to accurately identify the test reagents, understand what these reagents test, and predict the expected results. One of the key aspects of qualitative analysis is testing for cations, which involves adding certain reagents to a solution and noting the resulting observations and inferences. The guide provides a detailed list of cations and their corresponding observations and inferences. Another important aspect of qualitative analysis is testing for anions. This involves adding specific reagents and observing the resulting precipitates or color changes. The guide outlines the steps and observations for testing six common anions. Quantitative analysis focuses on making accurate measurements. It involves techniques such as titration and gravimetric analysis to determine the concentration or amount of a substance in a given sample. The guide provides an overview of these techniques and their applications. Graphical work involves the interpretation and analysis of data using graphs and charts. It includes techniques such as plotting graphs, determining gradients, and analyzing trends. Overall, the Chemistry Practical Guide serves as a valuable resource for students to enhance their understanding and skills in experimental chemistry. It provides clear instructions, observations, and inferences for qualitative and quantitative analysis techniques. By following the guide, students can develop the necessary proficiency in handling apparatus, making accurate observations, and drawing conclusions. With a strong foundation in practical chemistry, students will be well-prepared for their examinations and future scientific endeavors. Comprehensive Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes for Effective LearningReview:
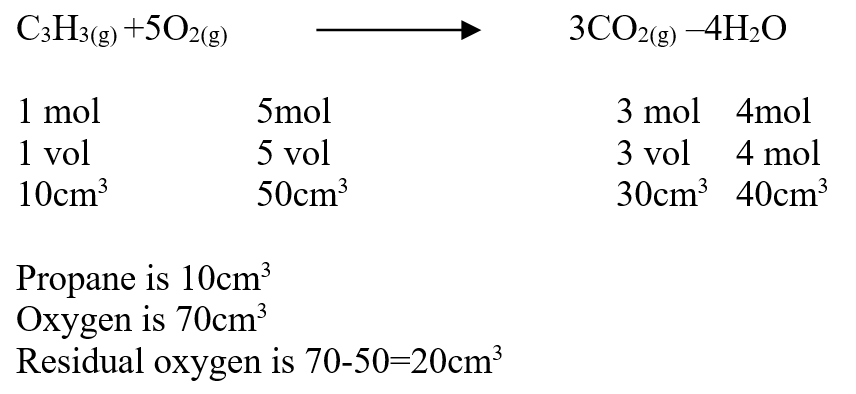
Our Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes are an invaluable resource for students seeking a thorough understanding of the subject. The notes cover a wide range of topics, from the states of matter to the role of chemistry in society. Each concept is explained in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to grasp even the most complex ideas. One of the strengths of these notes is the inclusion of practical examples, which help students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. For example, the section on separation of mixtures provides simple methods that can be used to separate different substances, allowing students to see the practical applications of their learning. Furthermore, the notes emphasize the importance of safety in the chemistry laboratory. Clear guidelines are provided to ensure that students understand how to handle chemicals safely and minimize the risk of accidents. This focus on safety is crucial in fostering responsible and conscientious scientific practices. The layout and organization of the notes are also commendable. Each topic is presented in a logical sequence, building upon previous knowledge and paving the way for a smooth progression of learning. The use of headings, subheadings, and bullet points makes it easy for students to navigate through the content and locate specific information. Overall, our Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes provide a comprehensive and well-structured resource for students studying chemistry. With its clear explanations, practical examples, and emphasis on safety, this resource is sure to enhance students' understanding and appreciation of the subject. Comprehensive Chemistry Summary Notes for Form 1 to Form 4Review: The "FORM 1 TO FORM 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES.pdf" is an invaluable resource for students studying chemistry at the Form 1 to Form 4 level. The notes provide a comprehensive overview of the entire chemistry syllabus, covering all the key topics and concepts. The document is well-organized, with each topic clearly outlined and explained in a concise manner. The content is presented in a way that is easy to understand, making it suitable for students of all levels of ability. The notes include detailed explanations, diagrams, and examples to help students grasp the fundamental principles of chemistry. One of the standout features of these notes is the inclusion of practical applications and real-life examples. This helps students to see the relevance of chemistry in everyday life and enhances their understanding of the subject. The document also includes a section on exam tips and strategies, which is particularly helpful for students preparing for their chemistry exams. It provides guidance on how to approach different types of questions, how to structure answers, and how to effectively revise for exams. Overall, the "FORM 1 TO FORM 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES.pdf" is a comprehensive and well-structured resource that covers all the essential topics in chemistry. Whether you are a student looking for additional study material or a teacher seeking a reference guide, these notes are a valuable asset. A volume of 80cm3 of a mixture of propane (C3H8) and oxygen were ignited in an experiment. The products were cooled and passed through an aqueous sodium hydroxide. The final volume was reduced by 30cm3a) Write the equation for the combustion of propane (1mk)b) Determine the volume of;i) The component of the original mixture (2mks)ii) Residual oxygen (1mk)
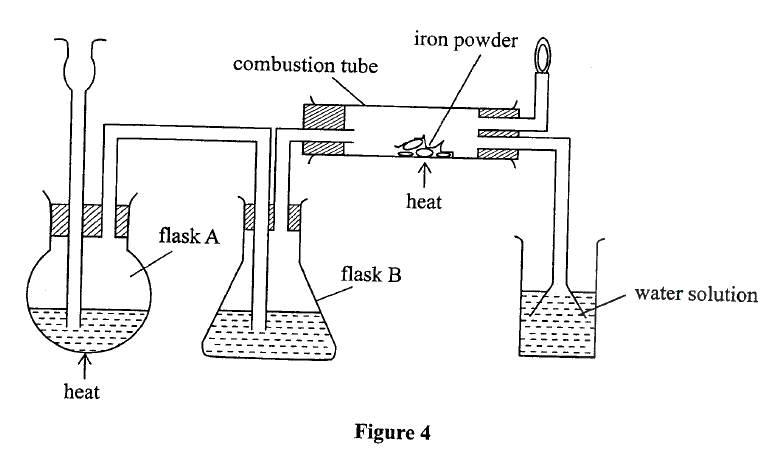
(a) The diagram in Figure 4 was used to prepare hydrogen chloride gas which was passed over heated iron powder.
(i) Give a pair of reagents that will produce hydrogen chloride gas in flask A.
(ii) Name the substance in flask B. (iii) State the observation made in the combustion tube. (iv) Write an equation for the reaction in the combustion tube. (v) Describe a chemical test for hydrogen chloride gas. (b) (1) Identify the gas that burns at the jet. (ii) Explain why the gas in (b) (I) is burned. (c) Give reasons why excess hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved using the funnel arrangement. (d) State what will be observed when the reaction in the combustion tube is complete. (e) Another experiment was carried out where hydrogen chloride gas was bubbled through methylbenzene and water in separate beakers. The resulting solutions were tested with blue litmus papers and marble chips. (i) Write the observations made in the following table.
(ii) Explain the observations in (e) (i).
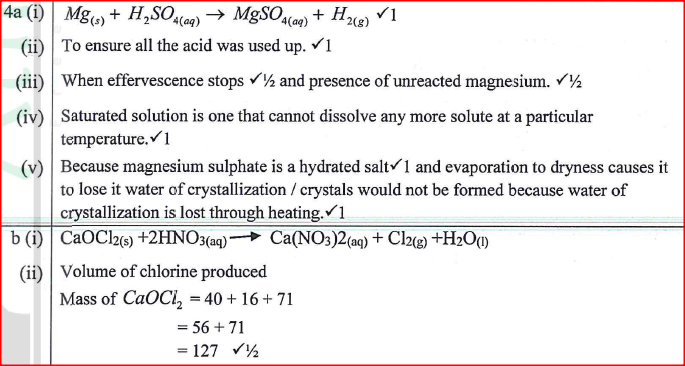
An experiment was carried out to prepare crystals of magnesium sulphate. Excess magnesium powder was added to 100 cm3 of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid in a beaker and warmed until no further reaction took place. The mixture was filtered and the filtrate evaporated to saturation, then left to cool for crystals to form.
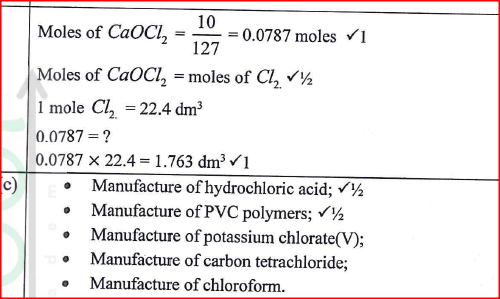
(a) (i) Write an equation for the reaction. (ii) Explain why excess magnesium powder was used. (iii) State how completion of the reaction was determined. (iv) What is meant by a saturated solution? (v) Explain why the filtrate was not evaporated to dryness. (b) When bleaching powder, CaOCl2, is treated with dilute nitric(V) acid, chlorine gas is released. This reaction can be used to determine the chlorine content of various samples of bleaching powders and liquids. (i) Write an equation for the reaction of nitric(V) acid with bleaching powder. (ii) Calculate the volume of chlorine produced when 10g of CaOCl2 is treated with excess nitric (v) acid. (Ca = 40.0; 0 = 16.0; Cl = 35.5; 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4dm3 at s.t.p) (c) Apart from use of chlorine gas in bleaches and water treatment, state two other uses of chlorine gas.
Distinguish between empirical and molecular formula of a compound.
ANSWERS
(NH4)2HPO4 is a fertilizer used by farmers to boost their crop production.
(a) Calculate the mass of phosphorus in a 20 kg packet 14.0; H = 1.0; P = 31.0; 0 16.0) (b) State one advantage of this fertilizer, (NH4)2HPO4 over urea CO(NH2)2
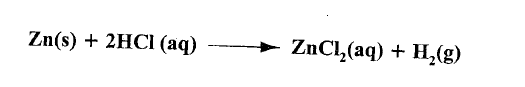
(a) Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following equation.
Identify the reducing agent. Give a reason for the answer.
(b) Iron sheets are dipped in molten zinc to prevent rusting. Name this process.
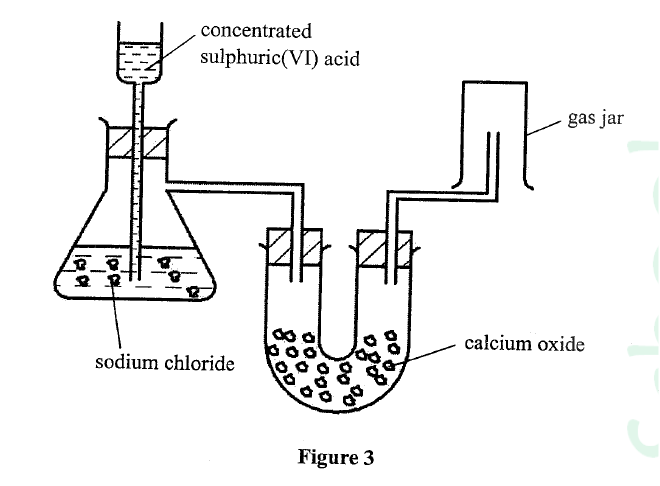
Figure 3 shows a set-up used by a student to prepare dry chlorine gas in the laboratory.
Identify three mistakes in the set-up, and give a reason for each.
ANSWERS
When ethene gas is compressed at a high temperature, a solid is formed.
(a) Give the name of the solid. (b) Explain why it is not advisable to allow the solid to accumulate in the environment.
ANSWERS
(a)Polythene / Polyethene
(b)It is non-biodegradable, hence pollutes the environment.
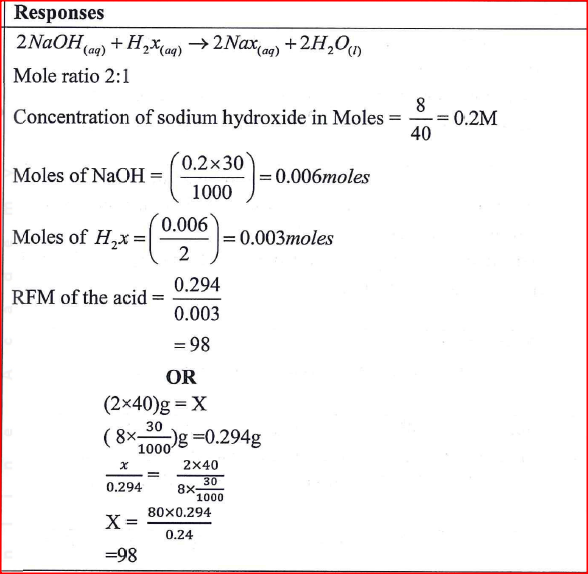
30.0 cm3 of aqueous sodium hydroxide containing 8.0 g per litre of sodium hydroxide were completely neutralized by 0.294 g of a dibasic acid. Determine the relative formula mass of the dibasic acid. (Na = 23.0 ; 0 = 16.0; H 1.0)
(a) State Graham’s law of diffusion
(b) Explain why a balloon filled with helium gas deflates faster than a balloon of the same size filled with argon gas.
ANSWERS
(a) Graham’s Law of diffusion
The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density at constant temperature and pressure. (b)Helium is less dense than argon hence it diffuses out of the balloon faster than argon.
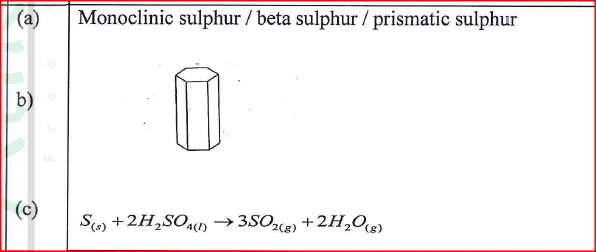
One of the allotrope s of sulphur is rhombic sulphur.
(a) Name the other allotrope of sulphur. (b) Draw a diagram to show the shape of the allotrope named in (a) above. (c) Write an equation for the reaction between concentrated sulphur(VI) acid and sulphur
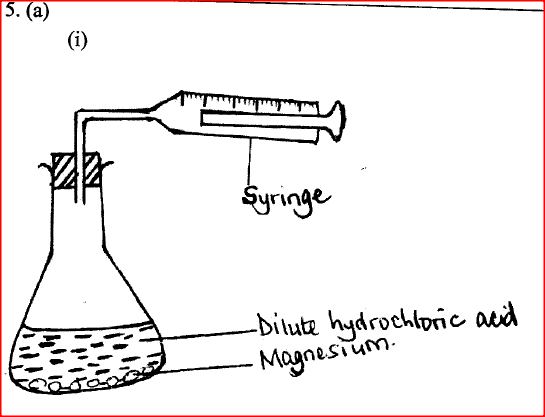
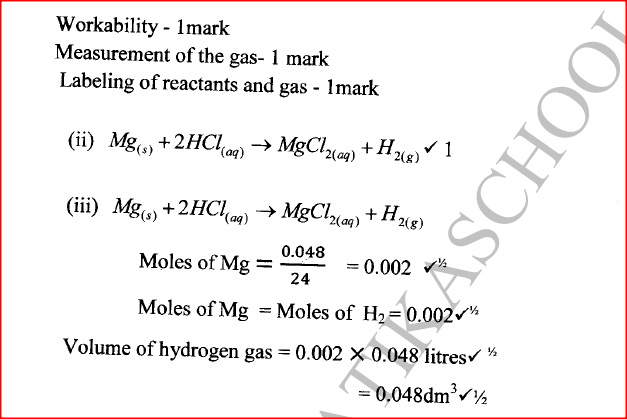
(a) When 0.048 g of magnesium was reacted with excess dilute hydrochloric acid at room temperature and pressure, 50 cm3 of hydrogen gas was collected. (Mg = 24.0; Molar gas volume = 24.0 dm3)
(i) Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to carry out the experiment described above.
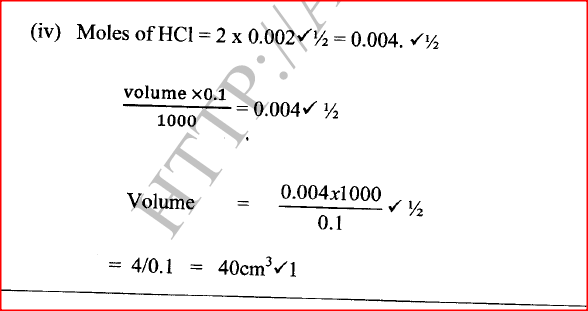
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction. (iii) Calculate the volume of hydrogen gas produced. (iv) Calculate the volume of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid required to react with 0.048 g of magnesium.
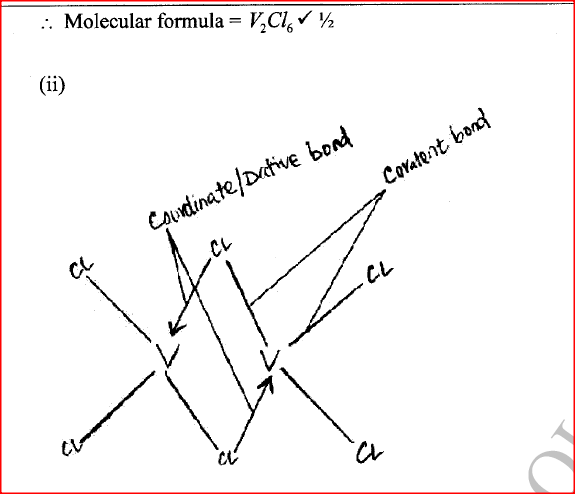
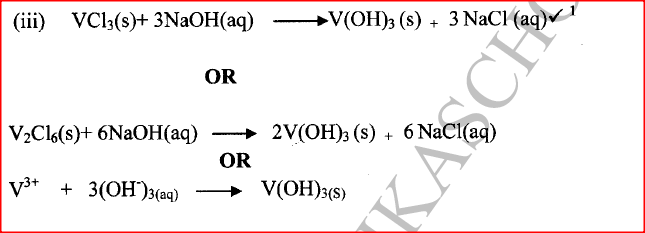
W is a colourless aqueous solution with the following properties:
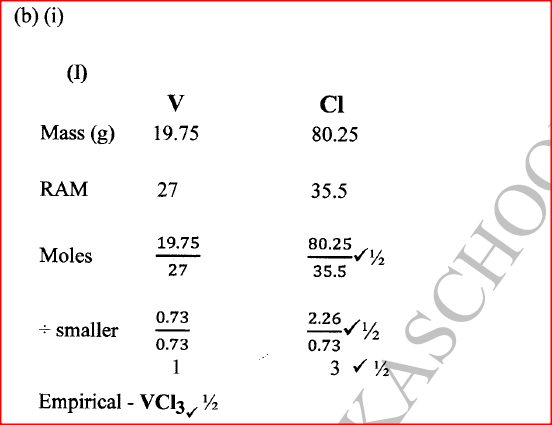
(ii) Give the identity of W. (iii) Name the colourless solution formed in (II) and (III). (iv) Write an ionic equation for the reaction indicated in (V). (b) Element V conducts electricity and melts at 933K. When chlorine gas is passed over heated V, it forms a vapour that solidifies on cooling. The solid chloride dissolves in water to form an acidic solution. The chloride vapour has a relative molecular mass of 267 and contains 19.75% of V. At a higher temperature, it dissociates to a compound of relative molecular mass 133.5. When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to the aqueous solution of the chloride, a white precipitate is formed which dissolves in excess alkali. (V = 27.0 ; CI = 35.5) (i) Determine the:
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction that form a white precipitate with sodium hydroxide.
When an aqueous solution of compound X was mixed with a few drops of bromine water, the colour of the mixture remained yellow.
When another portion of solution X was reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI), the colour of the mixture changed from orange to green. (a) What conclusion can be made from the use of: (i) bromine water? (ii) acidified potassium dichromate(VI)? (b) Solution X was reacted with a piece of a metal and a colourless gas was produced. Describe a simple experiment to identify the gas.
(a) What is meant by the term bleaching?
(b) Write the formula of the bleaching nent formed when chlorine gas reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide. (c) State the role of chlorine in water treatment.
Study the flow chart in Figure 5 and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Identify substances K and L. K:
(b) Name one reagent that can be used to carry out process J.
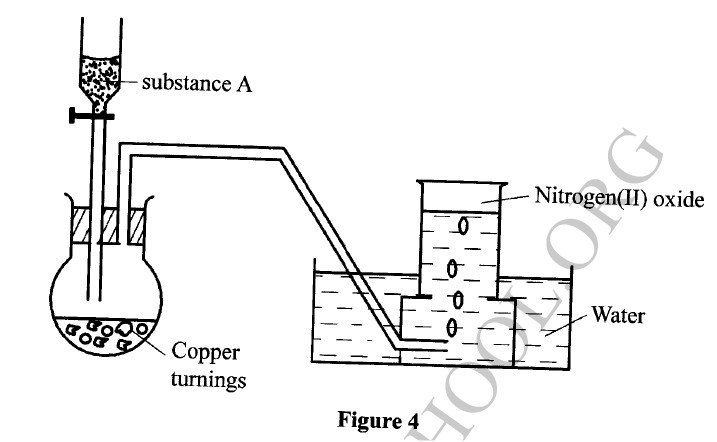
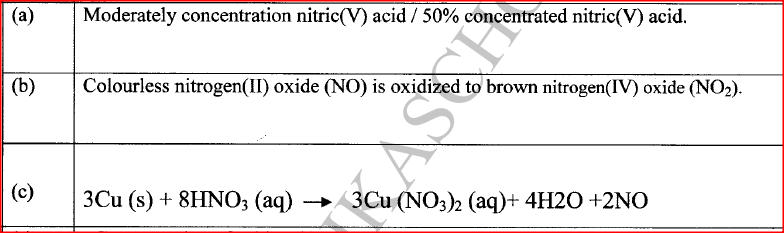
The set-up in Figure 4 can be used to prepare nitrogen (II) oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name substance A
(b) When the gas jar containing nitrogen (II) oxide is exposed to air, a brown color is observed. Explain. (c) Write an equation for the reaction which occurred in the flask.
In an experiment, concentrated nitric(V) acid was reacted with iron(II) sulphate. State and explain the observations made.
ANSWERS
The mixture changed from green to yellow / formation of a brown gas;
Iron(II) ions is oxidized by nitric(V) acid to Iron(III) ions / nitric(V) acid is reduced to nitrogen(1I) oxide which is oxidized by oxygen to nitrogen(IV ) oxide. |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











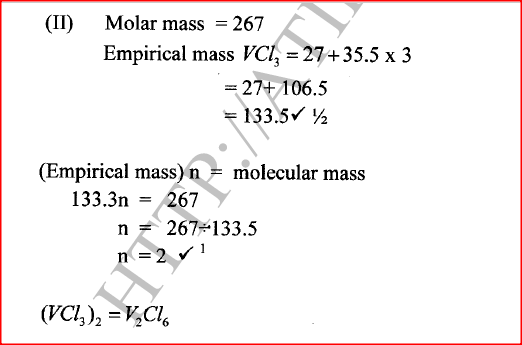





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

