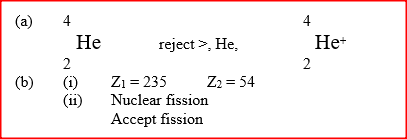
|
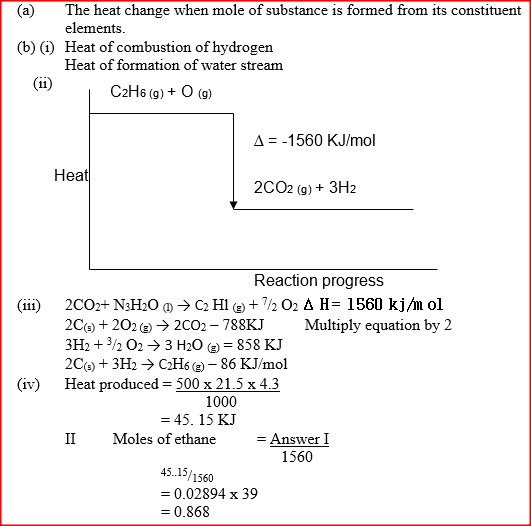
(a) Define the standard enthalpy of formation of a substance
(b) Use the thermochemical equations below to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name two types of heat changes represented by ΔH3
(ii) Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction represented by equation 1 (iii) Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of ethane (iv) When a sample of ethane was burnt, the heat produced raised the temperature of 500g of water by 21. 5 K, (specific heat capacity of water = 4.2Jg-1K). Calculate the: I. Heat change for the reaction II. Mass of ethane was burnt. ( relative formula mass of ethane= 30)
0 Comments
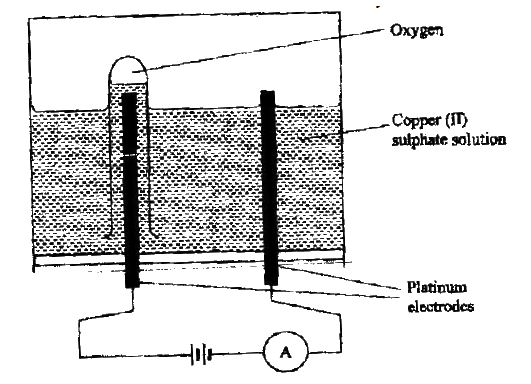
The diagram below represents a set up that can be used to electrolyze aqueous copper (II) sulphate.
(a) (i) Describe how oxygen gas is produced during the electrolysis
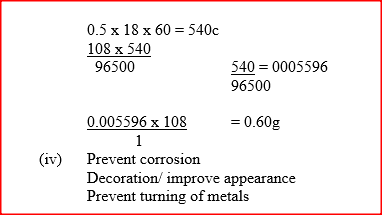
(ii) Explain why copper electrodes are not suitable for this electrolysis (b) Impure copper is purified by an electrolytic process (i) Name one ore from which copper is obtained (ii) Write the equation for the reaction that occur at the cathode during the purification of copper (iii) In an experiment to electroplate a copper spoon with silver, a current of 0.5 A was passed for 18 minutes. Calculate the amount of silver deposited on the spoon (π = 96500 coulombs, Ag = 108) (iv) Give two reasons why some metals are electroplated
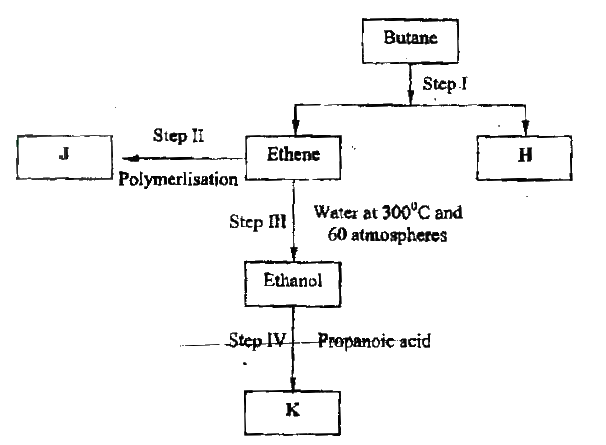
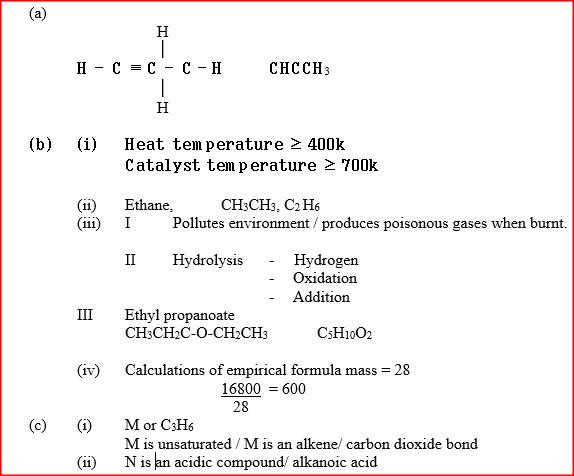
(a) Alkanes, alkenes and alkynes can be obtained from crude oil. Draw the structure of the second member of the alkyne homologous series.
(b) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
(i) State the conditions for the reaction in step 1 to occur
(ii) Identify substance II (iii) Give: I. One advantage of the continued use of substance such as J II The name of the process that takes place in step III III The name and the formula of substance K Name: Formula: (iv) The relative molecular mass of J is 16,800. Calculate the number of monomers that make up J. (c) The table below give the formula of four compounds L,M,N and P
Giving a reason in each case, select the letter which represents a compound that:
(i) Decolorizes bromine in the absence of UV light (ii) Gives effervescence when reacted with aqueous sodium carbonate
a) (i) State the Le chatelier‟s principle.
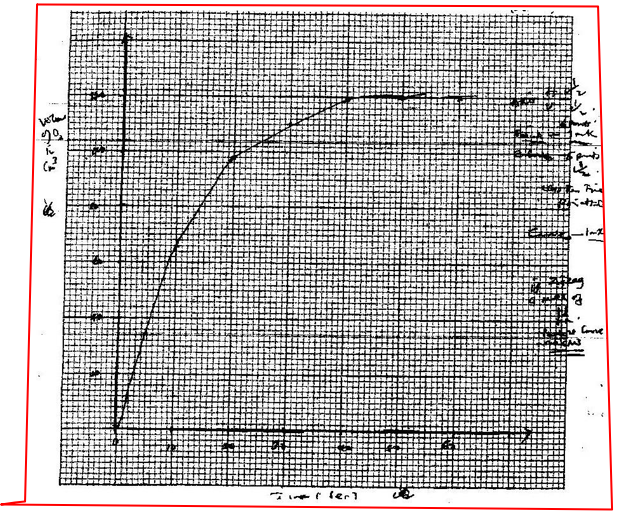
(ii) Carbon (II) oxide gas reacts with steam according to the equation; CO(g) + H2O(g)→ H2(g)+ CO2(g) What would be the effect of increasing the pressure of the system at equilibrium? Explain. b) The table below gives the volumes of oxygen gas produced at different times when hydrogen peroxide decomposed in the presence of a catalyst.
(i) Name the catalyst used for this reaction
(ii) On the grid provided, draw the graph of volume of oxygen gas produced (vertical axis) against time. (iii) Using the graph, determine the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide after 24 seconds. (iv) Give a reason why the total volume of oxygen gas produced after 50 seconds remains constant.
ANSWERS
(a)(i) When change is made to a system in equilibrium the System moves so as to oppose the change.
(ii)Pressure has no effect to equilibrium The moles/Volume/ molecules of gases is reactants and product are equal (iii) DH –ve ( negative) Since lowering of temperature moves to equilibrium to direction which heat is produced. Decrease in temperature favours exothermic reaction (b) (i) Manganese IV oxide
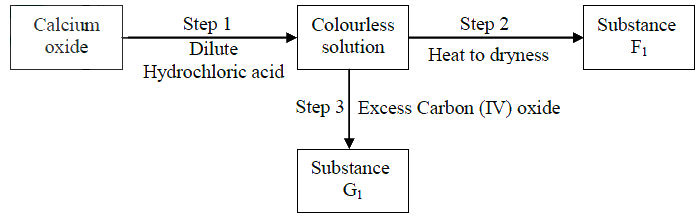
(a) Describe the process by which Nitrogen is obtained from air on a large scale.
(b) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Identify gas J.
(ii) Using oxidation numbers, show that ammonia is the reducing agent in step (VI) (iii) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs in step (V). (iv) Give one use of ammonium nitrate. c) The table below shows the observations made when aqueous ammonia was added to cations of elements F2F and G until in excess.
(i) Select the cation that is likely to be Zn2+
(ii) Given that the formula of the cation of element E is E 2+, write the ionic equation for the reaction between E2+ (aq) and aqueous ammonia.
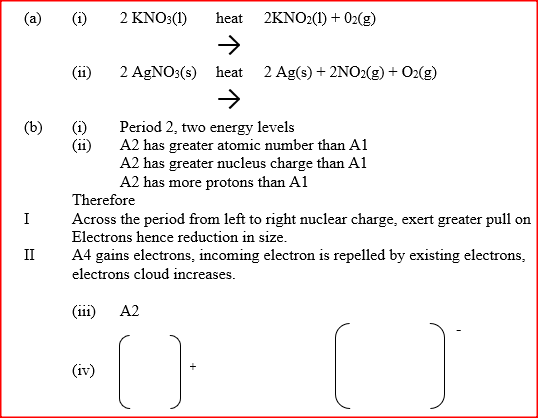
a) Write an equation to show the effect of heat on the nitrate of:
(i) Potassium b) The table below gives information about elements A1,A2,A3, and A4
(i) In which period of the periodic table is element A2? Give a reason
(ii) Explain why the atomic radius of: I A1 is greater than that of A2; II A4 is smaller than its ionic radius (iii) Select the element which s in the same group as A3 (iv) Using dots (.) and crosses(x) to represent outermost electrons. Draw a diagram to show the bonding in the compound formed when A1 reacts with A4
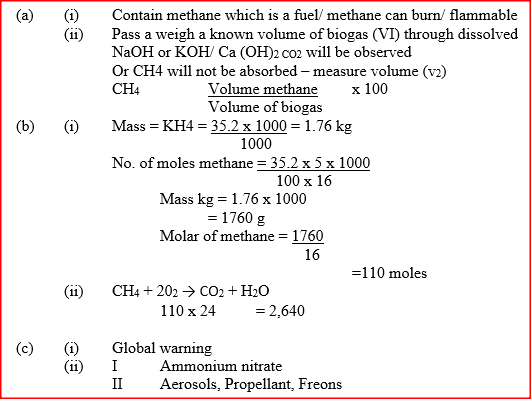
a) Biogas is a mixture of mainly carbon (IV) oxide and methane.
(i) Give a reason why biogas can be used as a fuel. (ii) Other than fractional distillation, describe a method that can be used to determine the percentage of methane in biogas. b) A sample of biogas contains 35.2% by mass of methane. A biogas cylinder contains 5.0 kg of the gas. Calculate the; (i) Number of moles of methane in the cylinder. (Molar mass of methane=16) (ii) Total volume of carbon (IV) oxide produced by the combustion of methane in the cylinder (Molar gas Volume=24.0 dm-3+ at room temperature and pressure). c) Carbon (Iv) oxide, methane, nitrogen (I) oxide and trichlorofluoromethane are green-house gases. (i) State one effect of an increased level of these gases to the environment. (ii) Give one source from which each of the following gases is released to the environment; I Nitrogen (i) oxide II Trichlorofluoromethane.
ANSWERS
(a) Neutralization
(b)(i)Calcium hydrogen carbonate (ii)Drying agent Extraction of sodium metal
Crude oil contains sulphur. What would be the effect to the environment of using fuel containing sulphur?
ANSWERS
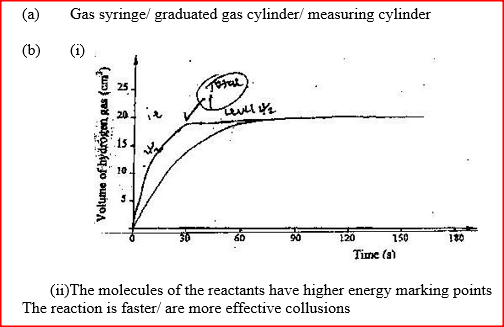
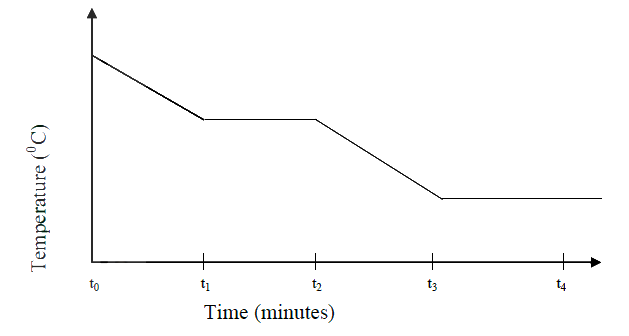
A certain mass of a metal E1 reacted with excess dilute hydrochloric acid at 25°C. The volume of hydrogen gas liberated was measured after every 30 seconds. The results were presented as shown in the graph below.
a) Name one piece of apparatus that may have been used to measure the volume of gas liberated. b) (i) On the same axis, sketch the curve that would be obtained if the experiment was repeated at 35°C. (ii) Explain the shape of your curve in b(i) above.
ANSWERS
(a)(i)Cryolite
(ii)Electrolysis (b)Good conductor Does not rust Malleable Light High M.P Does not corrode easily
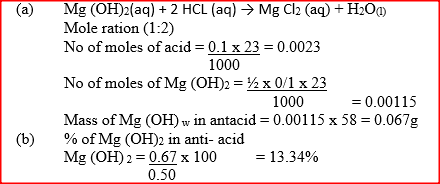
In an experiment to determine the percentage of magnesium hydroxide in an anti-acid, a solution containing 0.50 g of the anti-acid was neutralized by 23.0 cm3 of 0.010m hydrochloric acid (Relative formula mass of magnesium hydroxide =58)
a) Mass of magnesium hydroxide in the anti-acid; b) Percentage of magnesium hydroxide in the anti-acid
When solid B1 was heated, a gas which formed a white precipitate when passed through lime water was produced. The residue was dissolved in dilute nitric (V) acid to form a colourless solution B2. when dilute hydrochloric acid was added to solution B2 a white precipitate which dissolved on warning was formed.
a) Write the formula of the; I Cation in solid B1 II anion in solid B1 b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction between the resdue and dilute nitric (V) acid.
ANSWERS
(a)Cooling
(b)Latent heat of fusion
In a closed system, aqueous iron (III) chloride reacts with sulphide gas as shown in the equation below.
2FeCl3(aq) + H2S(g) → 2FeCl2(aq) 2HCl(aq) + S(s) State and explain the observation that would be made if dilute hydrochloric acid is added to the system at equilibrium.
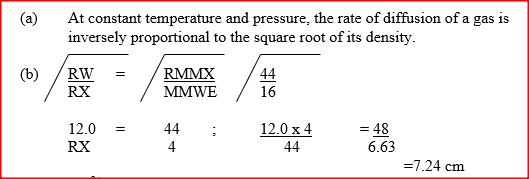
a) State the Graham's law diffusion.
b) The molar masses of gases W and X are 16.0 and 44.0 respectively. If the rate of diffusion of W through a porous material is 12cm3s-1 calculate the rate of diffusion of X through the same material. Related Chemistry Questions and Answers on Gas Laws Form 3 Level
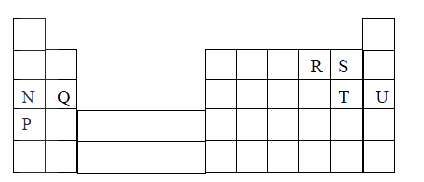
The grid below is part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow, (the letters are not the actual symbols of the elements).
a) Indicate on the grid the position of an element represented by letter V whose atomic number is 14.
b) Select a letter which reaction between Q and T.
ANSWERS
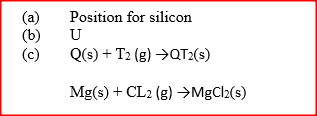
(a)Amphoteric
(b)Lead (II), Zinc and Aluminium
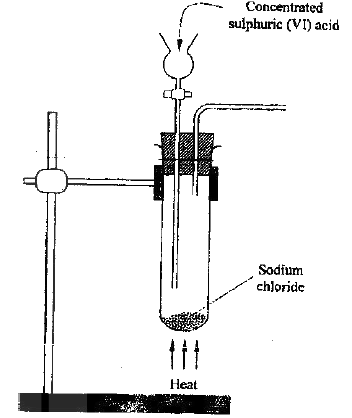
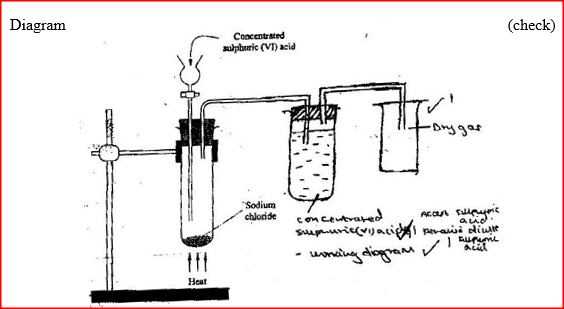
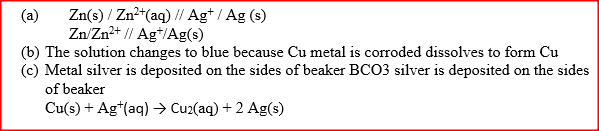
Starting with copper metal, describe how a sample of crystals of copper (II) chloride may be prepared in the laboratory.
ANSWER
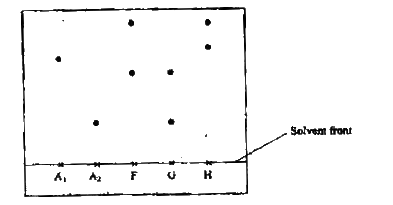
Samples of urine from three participants F, G and H at an international sports meeting were spotted onto a chromatography paper alongside two from illegal drugs A1 and A2.
A chromatogram was run using methanol. The figure below shows the chromatogram.
a) Identify the athlete who had used an illegal drug.
b) Which drug is more soluble in methanol?
ANSWERS
(a)A1
(b)A1 using baseline |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
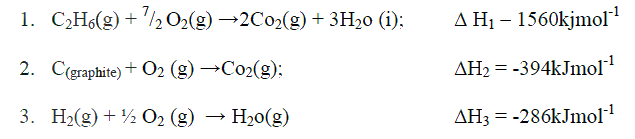

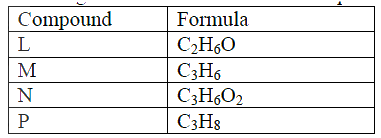
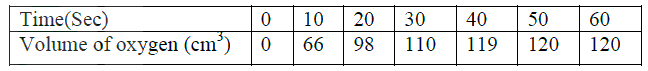
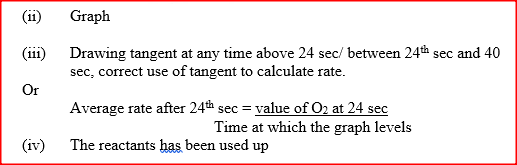


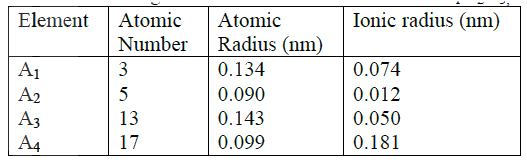
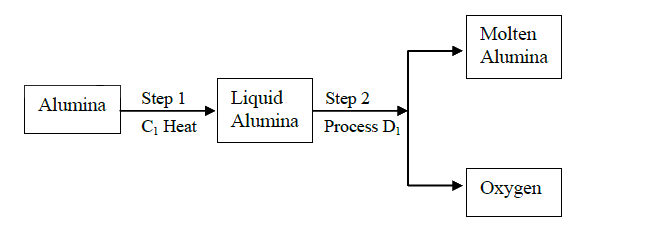
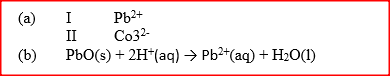
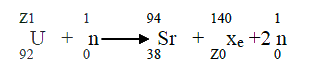


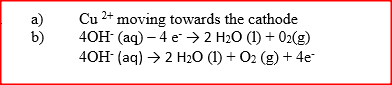
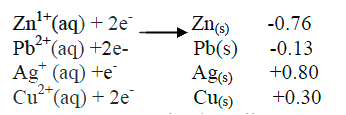
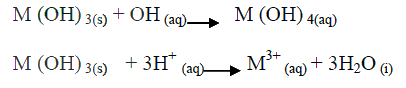

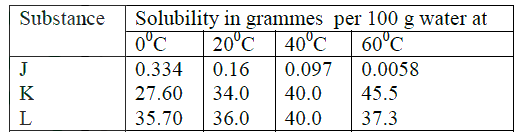

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

