|
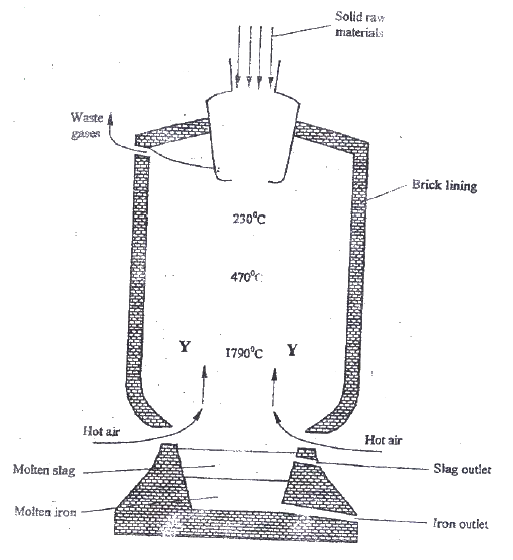
Iron is obtained from haematite using a blast furnace shown if figure 5 below.
a) Four raw materials are required for the production of iron. Three of these are iron oxide, hot air and limestone
Give the name of the fourth raw material b) Write an equation for the reaction in which carbon (IV) oxide is converted into carbon (II) oxide. c) Explain why the temperature in the region marked Y is higher than that of the incoming hot air. d) State one physical property of molten slag other than density that allows it to be separated from molten iron as shown in figure 5. e) One of the components of the waste gases is Nitrogen (IV) oxide describe the adverse effects it has on the environment. f) Iron from the blast furnace contains about 5% carbon i) Describe how the carbon content is reduced. ii) Why is it necessary to reduce the carbon content?
ANSWERS
(a) Coke/ coal/ Charcoal/ Carbon
(b) C(s) + CO2 (g) → 2 CO(g) (c) The reaction between coke/ coal and the hot air is highly exothermic (d) Slog is immiscible with molten iron (e) Nitrogen (iv) oxide gas forms acid rain. Which corrodes metallic materials and destroys vegetation the environment. (f) (i) By passing/ blowing oxygen into molten iron which converts carbon into carbon (iv) Oxide (ii) To increase the tensile strength/ making the iron less brittle/ making it more malleable / making it more ductile.
0 Comments
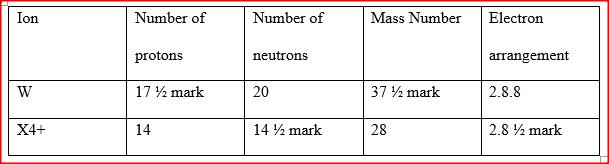
a) Study the table below and complete it. (W-1 and X4+ are not the actual symbols of the ions).
b) State the observation that would be made in the following tests to distinguish between:
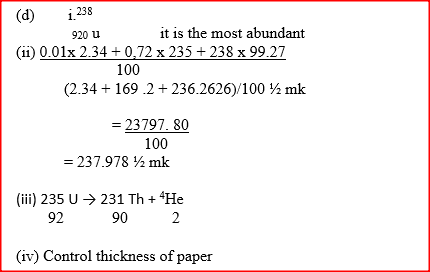
i) Sodium and copper burning pieces of each in air. ii) Sodium and Magnesium by placing small pieces of each in cold water which contains two drops of phenolphalein. c) The atomic numbers of Na and Mg are 11 and 12 respectively. Which of the elements has a higher ionization energy? Explain. d) Naturally occurring uranium consists of three isotopes which are radioactive.
i) Which of these isotopes has the longest half-life? Give a reason
ii) Calculate the relative atomic mass of uranium
(iv)State one use of radioactive isotopes in the paper industry
ANSWERS
(b) (i) Sodium burns with a yellow flame & yellow white/ solid powder is formed while copper burn with a blue green flame & black powder/ silic is formed.
(ii) Sodium darts on the surface of water / rapid fast effervescence (fast production of bubbles; solution becomes pink immediately. Magnesium sinks in water/ slow (production of bubbles) effervescence/ solution becomes pink gradually. (c) Magnesium it has a higher nuclear charge which pulls outer electrons more strongly
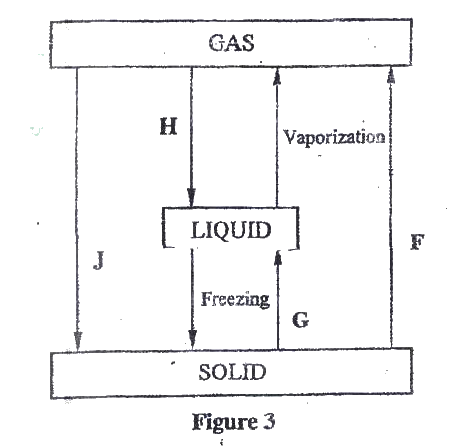
(a)Figure 3 show the changes that take place between states of matter. Some of them have been identified and others labelled.
i) Give the names of the processes
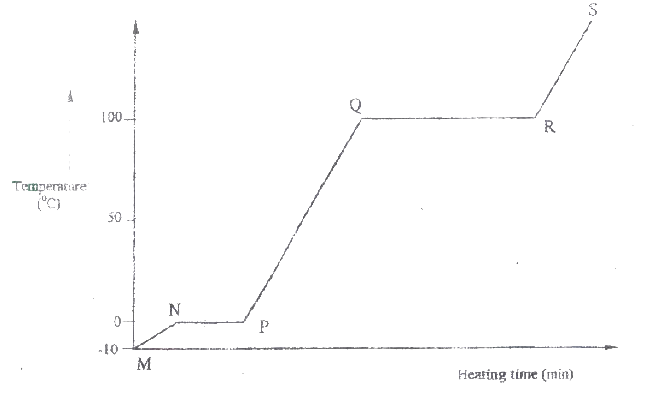
I H II G ii) Name one substance that can undergo process F when left in an open container in the laboratory. iii) The process J is called deposition. Using water as an example, write an equation that represents the process of deposition. b) Figure 4 shows the beating curve for water.
i) Give the names of the intermolecular forces of attraction in the segments;
I MN II RS ii) The heats of fusion and vaporization of water are 334.4 Jg-1 and 1159.4 Jg-1 respectively. I Explain why there is a big difference between the two. II How is the difference reflected in the curve? c) Coal, oil and natural gas are major sources of energy. They are known as fossil fuels. Hydrogen is also a source of energy. i) State and explain two reasons why hydrogen is a very attractive fuel compared to fossils. ii) State one disadvantage of using hydrogen fuel instead of fossil fuels.
ANSWERS
(a)
(i) I. Condensation II. Melting (ii) Iodine, Benzoic acid, Camphos, Dry Ice. Solid CO2 Naphthalene (iii) H2O(g) →H2O(g) (b) (i) Van des waals and hydrogen bonding II Van des waals forces (ii)I. The separation distance is smaller during fusion than during vaporization hence requires much lower energy than in vaporization and vice versa. II. Heating time NP is far much less than heating time in QR/ Heating time (c) (i) Hydrogen burns to produce steam which is a non pollutant/ does not cause pollution to the environment Hydrogen has a high energy content hence very small amount produce a lot of heat energy Hydrogen is renewable hence cannot be exhausted/ used completed. (ii) It can easily explore when burning/ highly flammable unlike fossils fuels expensive.
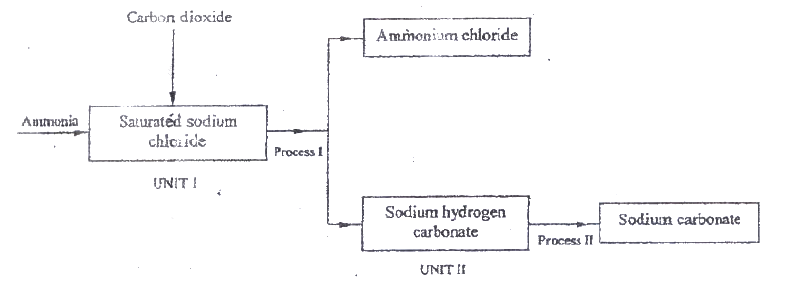
a) the schematic diagram shows part of the Solvay process used for the manufacture of sodium carbonate.
i) Explain how the sodium chloride required for this process is obtained from sea water.
ii) Two main reactions take place in UNIT I . The first one is the formation of ammonium hydrogen carbonate. I. Write an equation for this reaction II. Write an equation for the second reaction iii) State how the following are carried out: I Process I II) Process II iv)In an experiment to determine the percentage purity of the sample of sodium carbonate produced in the Solvay process, 2.15 g of the sample reacted completely with 40.0cm3 of 0.5 M sulphuric acid. I calculate the number of moles of sodium carbonate that reacted. II Determine the percentage of sodium carbonate in the sample. (Na= 23.0, C= 12.0, O = 16.0) b) Name two industrial uses of sodium carbonate
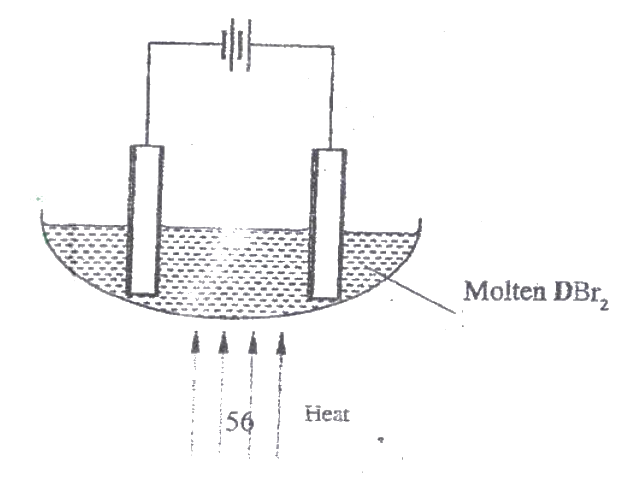
The set-up below (figure 2) was used to electrolyse a bromide of metal D DBr2
i) Write equation for the reactions at the
I cathode II anode ii) The electrodes used in the experiment were made of carbon and metal D. which of the two electrodes was used as the anode? Give a reason. iii) Give a reason why this experiment is carried out in a fume cupboard. iv) When a current of 0.4A was passed for 90 minutes, 2.31 g of metal D were deposited. I Describe how the amount of metal D deposited was determines. II Calculate the relative atomic mass of metal D. (I Faraday = 96500 coulombs)
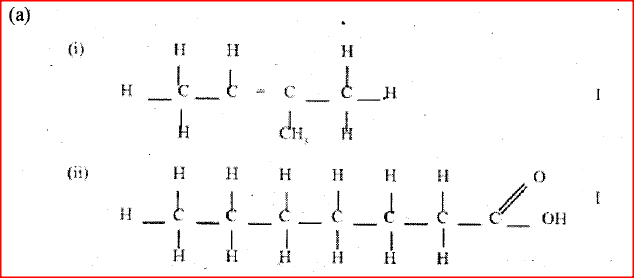
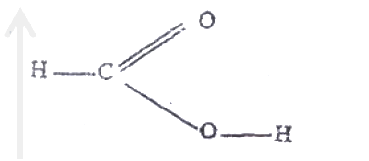
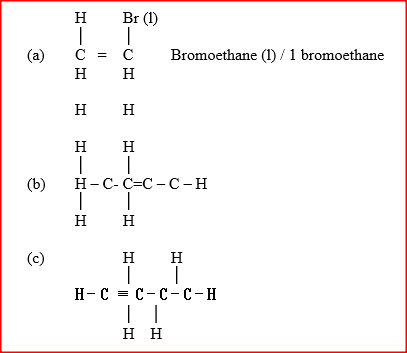
a) Draw the structures of the following compounds:
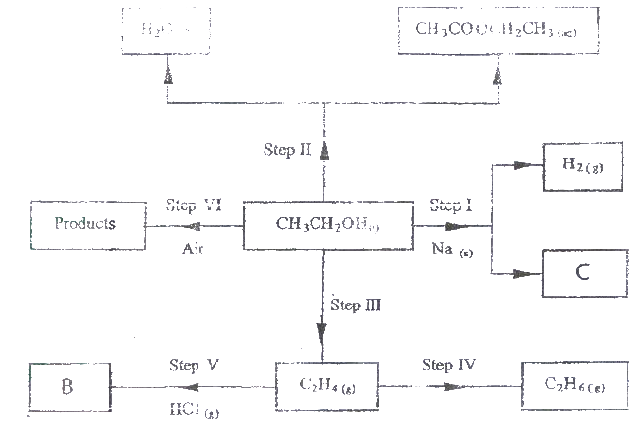
i) 2- methylbut -2 ene; ii) heptanoic acid b) Describe a physical test that can be used to distinguish between methanol and hexanol. c) Use the flow chart below to answer the questions that follow.
i) Name: (I) the type of reaction that occurs in step II; (II) Substance B. ii) Give the formula of substance C. iii) Give the reagent and the conditions necessary for the reaction in step (IV)
ANSWERS
(b)
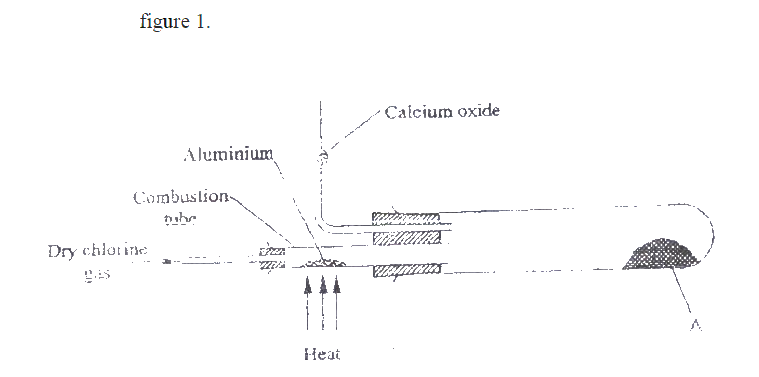
a) Two reagents that can be used to prepare chlorine gas are manganese (IV) oxide and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
i) Write an equation for the reaction. ii) Give the formula of another reagent that can be reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid to produce chlorine gas. iii) Describe how the chlorine gas could be dried in the laboratory b) In an experiment, dry chlorine gas was reacted with aluminium as shown in figure 1.
i) Name substance A.
ii) Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube. iii) 0.84 g of aluminium reacted completely with chlorine gas. Calculate the volume of chlorine gas used (Molar gas volume is 24dm3, Al = 27). iv) Give two reasons why calcium oxide is used in the set up.
Starting with red roses, describe how;
(i) a solution containing the red pigment may be prepared (ii) the solution can be shown tobe an indicator.
ANSWERS
(i)Crush the roses with a suitable solvent Filter to obtain pigment
(ii)Add pigment to an acid . It turns read
ANSWER
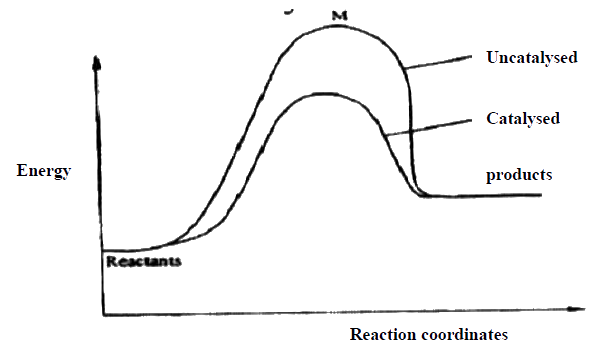
(a) Energy of the activated energy Therefore more molecules will take part in effective collision. Or Energy of the activated/intermediate complex of the unanalyzed reaction
(b) Catalyst lowers the activation energy therefore more molecules will take effective collision
ANSWERS
ANSWERS
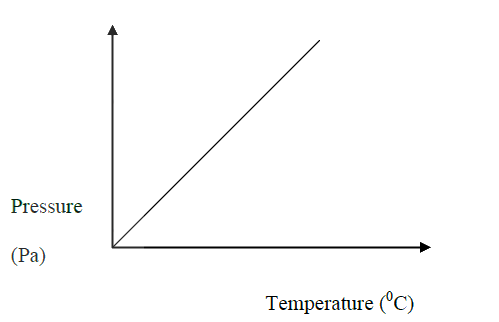
(a) Temperature and pressure are directly proportional (l) IR words towards that of real
(b) With increase in temperature, the gas particles gain more Kinetic energy They move faster and collide with the walls of the container more frequently hence increasing pressure.
For each of the following reactions, state the observation and write the formula of the
Compound responsible for the observation: a) Bromine water is added to aqueous potassium iodide; b) Excess aqueous ammonia is added to copper (II) hydroxide (precipitate).
ANSWERS
(a) SiH4 it has a higher boiling point
(b) No hydrogen bonding in CH4 and SiH4 while the hydrogen bond in H2O is stronger than that in H2S
ANSWERS
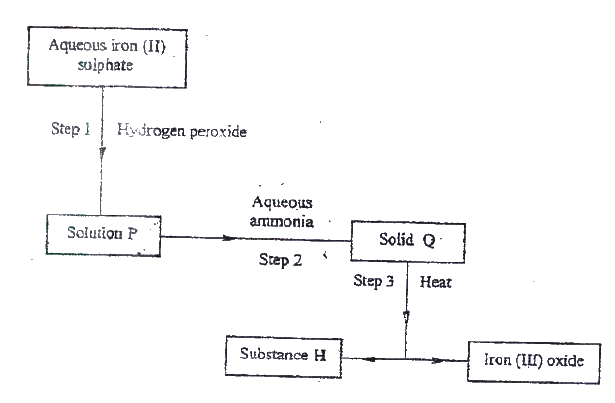
(a) Pale green solution turns yellow
(b) Sodium hydroxide Potassium hydroxide (c) Water
ANSWERS
Give the name of the product formed when magnesium reacts with phosphorus.
ANSWERS
ANSWERS
(a) Chemical change
(b) Physical change (c) Chemical change
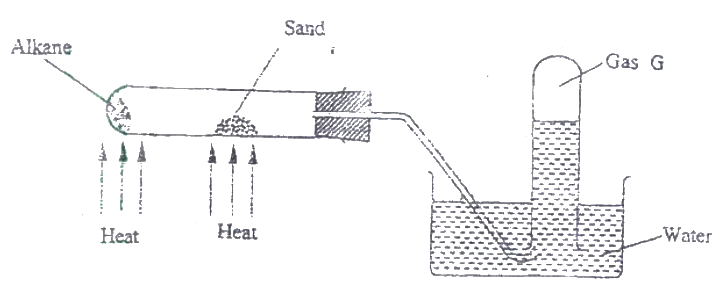
The figure below represents the set up that was used to crack an alkane.
a) What was the purpose of the sand?
b) After some time, a colourless gas G collected in the test-tube. Describe a chemical test and the observations that would be made in ordered to identify the class of compounds to which gas G belongs.
ANSWERS
(a) Catalyst or words to that effect
(b) Add bromine water or acidified potassium magnate (VII) if they decolorize then gas is either an alkene or an alkynes
ANSWERS
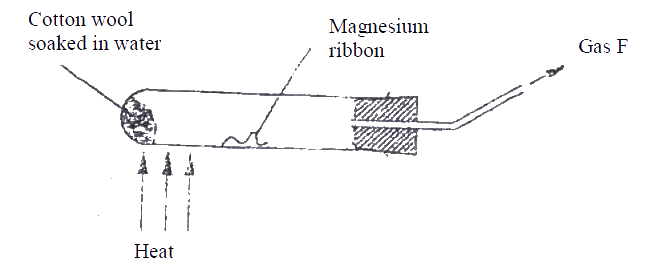
A student used the set up shown in the diagram below in order to study the reactions of some metals with steam. The experiment was carried out for ten minutes
a) What observation would be made if gas F is ignited?
b) When the experiment was repeated using iron powder instead of magnesium ribbon very little gas F was obtained. i) Give a reason for this observation ii) What change in the conditions of the experiment should the student have made in order to increase the volume of gas F Produced?
ANSWERS
(a) The gas burns with a blue flame
(b) (i) The iron isles reactive than magnesium (ii) Heat the iron powder
a) Draw and name the structure of the compound formed when one mole of ethyne reacts with one mole of hydrogen bromide.
b) Draw the structures of the alkynes whose molecular formula is C4H6
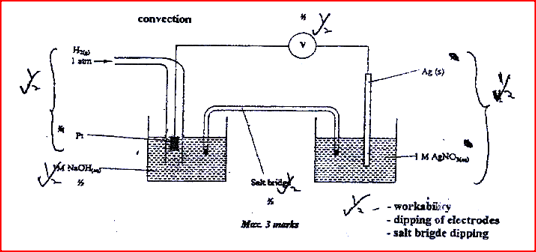
The standard reduction potentials of two half –cells are:
Ag+(aq) + e → AG(s) ; E = 0.80V 2H2O (l) + 2e → H2 (g) + 2OH (aq); E1 = 0.83V Draw a labelled diagram of an electro chemical cell that can be constructed using the two half –cells |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
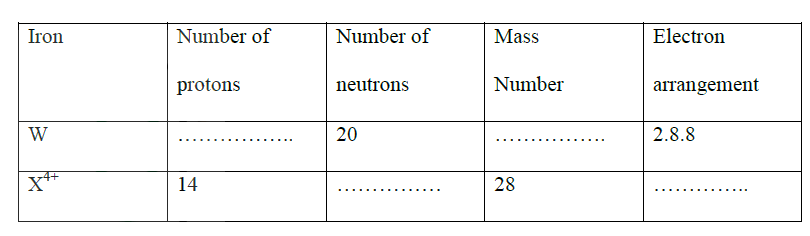
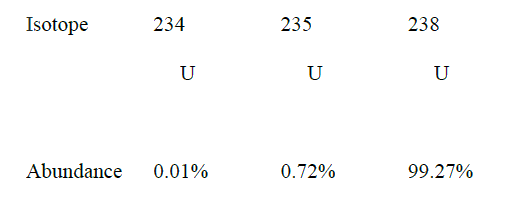
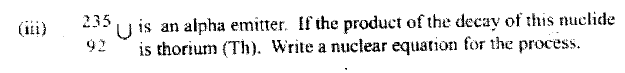




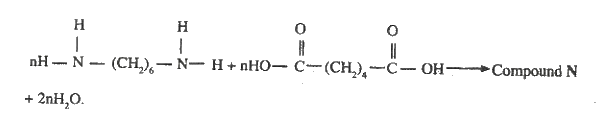


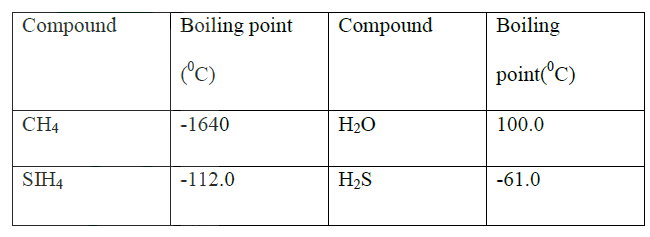





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

