|
(a) Give the systematic names for the following compounds
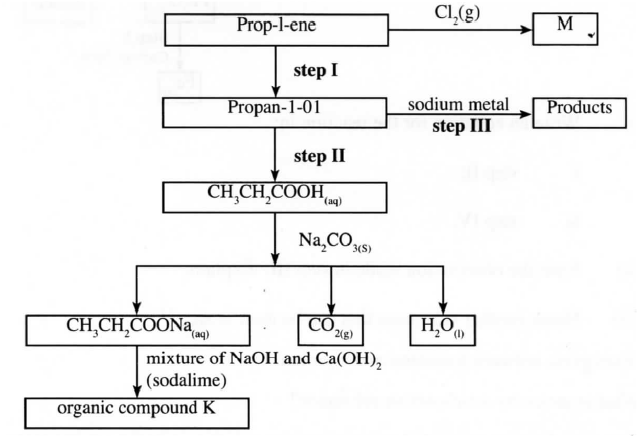
(b) Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow
(i) Identify the organic compound K
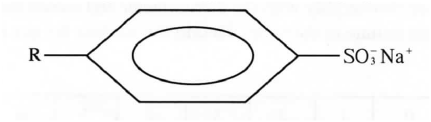
(ii) Write the formula of M (iii) Give one reagent that can be used in (a) Step I (b) Step II (iv) Write the equation of the reaction in step III (c) The structure below represents a type of a cleaning agent
Describe how the cleansing agent removes grease from a piece of cloth
0 Comments
(a) distinguish between a neutron and proton
(b) What is meant by a radioactive substance? (c) State two dangers associated with radioactive substance in the environment
(i) What is the atomic
a. Mass of Y b. Number of Y (ii) What name is given to the type of reaction undergone by the isotopes of hydrogen? (e)(i) What is meant by half-life of a radioactive substance (ii) 288 g of a radioactive substance decayed to 9 g in 40 days. Determine the half-life of the radioactive substance
(a) describes one method that can be used to distinguish between sodium sulphate and sodium hydrogen sulphate.
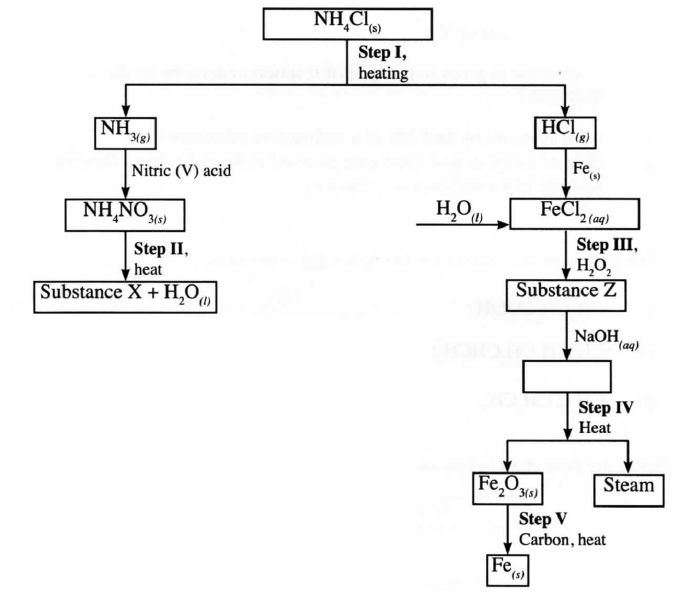
b) Describe how a pure sample of lead (II) sulphate can be prepared in the laboratory starting with lead metal c) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
i) Write an equation for the reaction in:
I step II; II step IV ii) State the observation made in step III. Explain. iii) Name another substance that can be used in step V.
ANSWERS
(a)Test the acidity using a litmus pager. There will be no change on litmus when dipped into a solution of sodium sulphate . The litmus paper turns to red when dipped into a solution of sodium hydrogen sulphate .
OR Add a solid carbonate to each solution. No effervescence observed when the carbonate is added to a solution of sodium sulphate. Effervescence is observed when the carbonate is added to a solution of sodium hydrogen sulphate. (b)Add dilute nitric acid to lead to form a soluble salt, Pb(NO3)2, add a soluble salt, Na2SO4. Then dry the salt between filter papers . (c)(i) NH4 NO3 → N2O + 2H2O II 2Fe(OH)3(S) → Fe2O3(s) + 3H2O(l) (ii) The colour changes from pale green to brown . The iron (II) is oxidised to iron (III) chloride by hydrogen peroxide (iii) Carbon monoxide
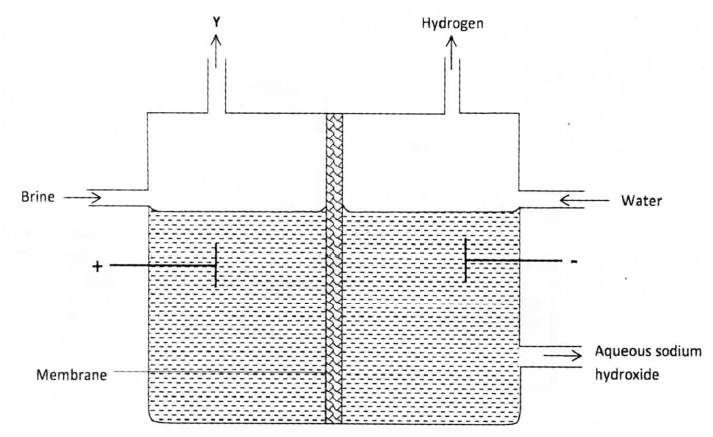
(a) the set below can be used to produce sodium hydroxide by electrolyzing brine
(i) Identify gas Y
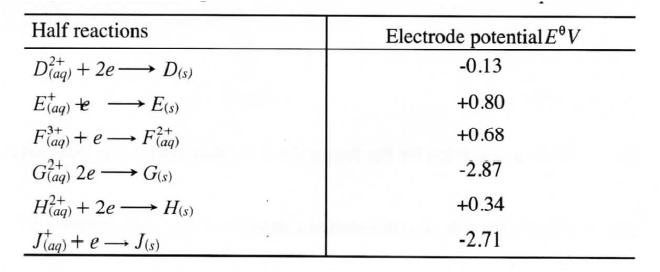
(ii) Describe how aqueous sodium hydroxide is formed in the above set-up (iii)One of the uses of sodium hydroxide is in the manufacturing of soaps state one other use of sodium hydroxide (b).study the information given in the table below and answer the question that follows
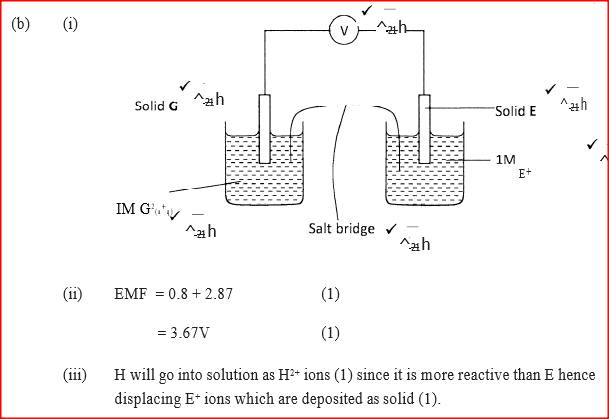
(i) Construct an electrochemical cell that will produce the largest emf
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in(i) above (iii) Why is it not advisable to store a solution containing E+ ions in a container made of H?
ANSWERS
(a)(i)Gas Y is chlorine
(ii) sodium and hydrogen ions migrate to the cathode . The hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged, liberating hydrogen gas. chlorine and hydroxide ions migrate to the anode . The chloride ions are preferentially discharged liberating chlorine gas. the sodium ions migrate to the cathode through the membrane . the sodium ions combine with the hydroxide ions to form sodium hydroxide . (iii) Glass making/paper manufacture (1), unclogging of drains, etching NaClo3, Purification of bauxite.
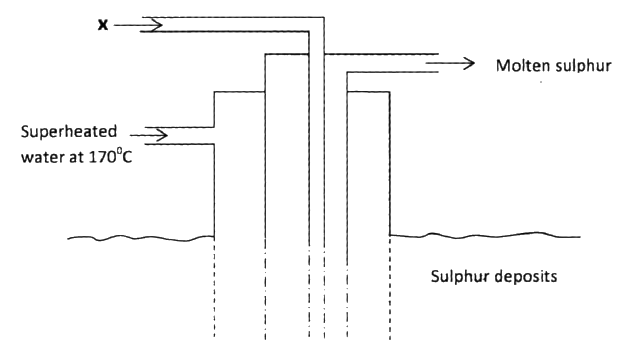
(a) The diagram below shows the frasch process used for extraction of sulphur
Use it to answer the question that follows
(i) Identify X
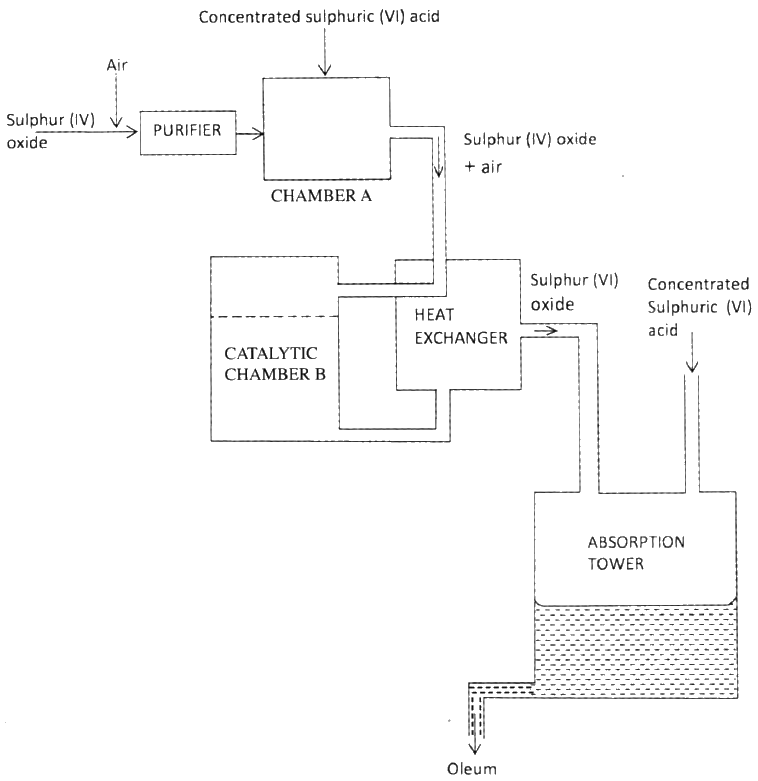
(ii) Why is it necessary to use superheated water in this process (iii) State two physical properties of sulphur that makes it possible for it to be extracted by this method (b) The diagram below shows part of the process in the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow
(I) Write an equation for the formation of sulphur (IV) oxide from sulphur
(II) What is the role of concentrated sulphur (VI) acid in chamber A? (III) Name two catalysts that can be used in the catalytic chamber B. (IV) State two roles of the heat exchanger (c) Explain one way in which sulphur (IV) oxide is a pollutant (d).what observation will be made when a few drops of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid are added to crystals of sugar? Explain your answer
ANSWERS
(a)(i)Hot compressed air
(ii)To melt the sulphur and maintain it in molten state (iii)low melting point of sulphur - insolubility of sulphur in water - less dense than water (b)(i)S + O2 → SO2 (ii)To dry the SO2 and air (iii)Vanadium (v) oxide and platinum or titanium (iv)it provides the reactants (SO2 and O2) with enough energy to react - it removes heat from the product hence preventing decomposition or conserves heat, or recycles heat or reduces cost of production. (c)- contributes to acid rain which corrodes buildings OR - causes aquatic solutions to be acidic hence affecting aquatic life etc. - poisonous/toxic (d)Turns black conc H2SO4 removes hydrogen and oxygen from the sugar molecule leaving only carbon which is black . Dehydration of sugar forms carbon which is black.
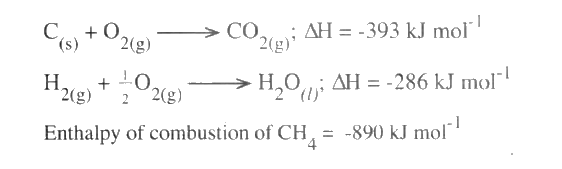
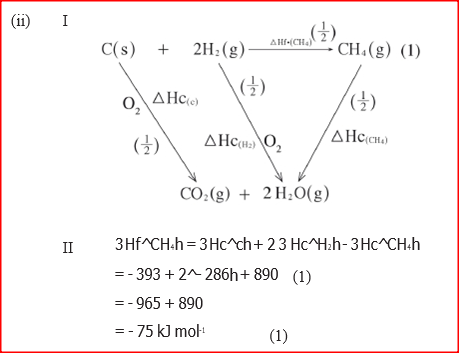
(a) (i) what is meant by the term Enthalpy of formation?
(ii) The enthalpies of combustion of carbon, methane and hydrogen are indicated below:
(i) Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the enthalpy of formation of methane to enthalpies of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and methane
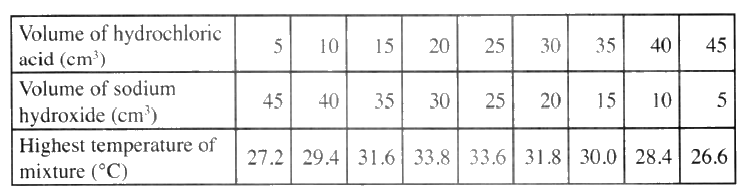
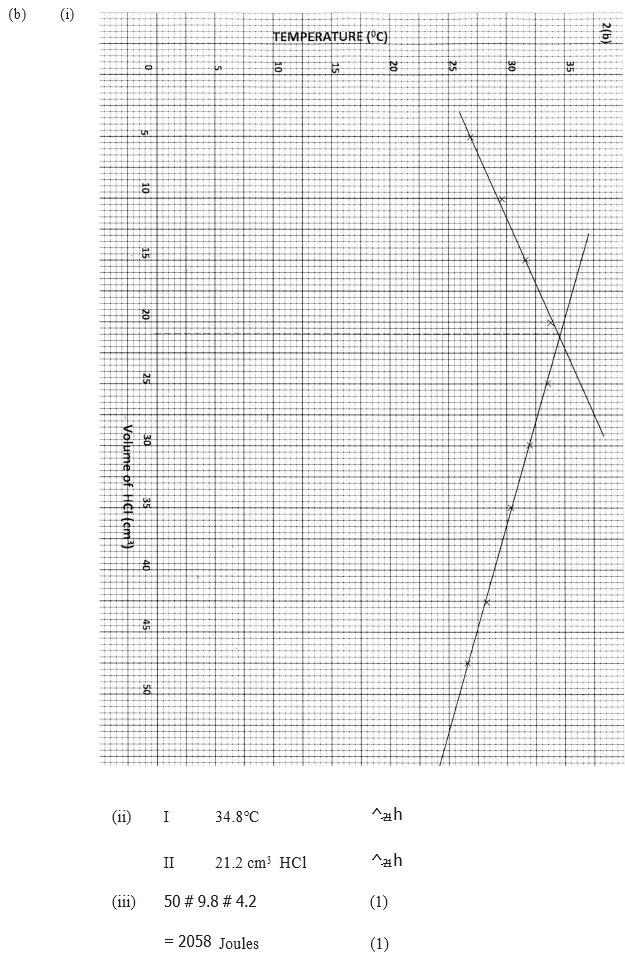
(ii) Determine the enthalpy of formation of methane (b) An experiment was carried out where different volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide both at 25°C were mixed and stirred with a thermometer. The highest temperature reached by each mixture was recorded in the table below
(i) On the grid provided. plot a graph of highest temperature (vertical axis) against volume of hydrochloric acid ( horizontal axis)
(ii) Using your graph , determine the (a) Highest temperature reached (b) Volume of acid and base reacting when highest temperature is reached
(iii) Calculate the amount of heat liberated during the neutralization process .(specify heat capacity is 4.2 j g -1 k-1 and the density of solution is 1.0 g cm-3)
(c) The molar enthalpy of neutralization between hydrochloric acid and ammonia solution was found to be -52.2 kJ mol-1, while that of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide was – 57.1 Kj mol-1. Explain the difference in these values.
ANSWERS
(a)(i)This is the heat absorbed or evolved when one mole of any substance is formed from its constituent elements in their normal states.
(c)The molar heat of neutralisation between a strong acid and a weak base is low because some of the heat is used to ionise (1) the weak base before neutralization.
For strong acid and strong base they are completely ionised.
The grid given below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the element
(i) Select a letter which represents an element that looses electrons most readily. Give a reason for your answer.
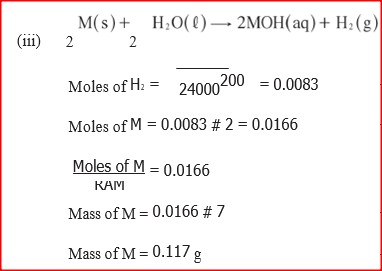
(ii) Explain why the atomic radius of P is found to be smaller than that of N (iii) Element M reacts with water at room temperature to produce 0.2 dm3 of gas. Determine the mass of M which was reacted with water. (molar gas volume at room temperature is 24 dm3 , relative atomic mass of M=7 (b) Use the information in the table below to answer the question that follows. (The letters are not the symbols of the elements)
Identify a letter which represents an element in the table that could be calcium, carbon or sculpture. Give reasons in each case.
(i) Calcium: Reason (ii) Carbon Reason (iii)Sulphur: Reason
ANSWERS
(a)(i)R - it has the largest atomic radius with the weakest nuclear attraction for outermost electron
(ii)Across the period the atomic radius decreases due to the increase in nuclear attraction Number of electrons in P is greater than in H
(b)(i) W - forms a basic oxide which forms an ionic bond
(ii)Y - the oxide is gaseous that forms a neutral solution (iii)U - the oxide is solid at room temperature, which is acidic with covalent bond
A student investigated the effect of an electric current by passing it through some substances.
The student used inert electrodes, and connected a bulb to the circuit. The table below shows the substances used and their states.
a) In which experiments did the bulb not light?
b) Explain your answer in (a) above.
A student investigated a property of acids M and N by reacting equal volumes of acid M and N of the same concentration with equal volumes of 2M potassium hydroxide.
The results were recorded in the table below.
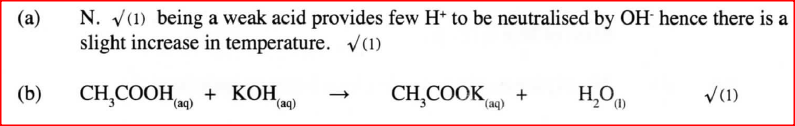
a) Which of the acids is likely to be a weak acid? Explain.
b) Write the equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and potassium hydroxide.
By using aqueous sodium chloride, describe how a student can distinguish calcium ions from lead ions.
State and explain what would happen if a dry red litmus paper was dropped in a gas jar of dry chlorine.
ANSWERS
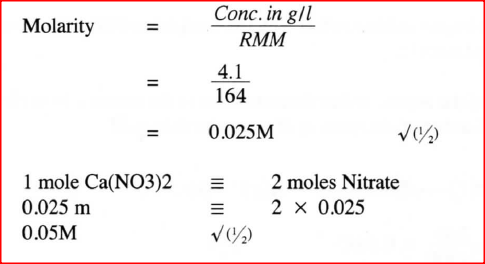
A solution was made by dissolving 8.2g of calcium nitrate to give 2 litres of solution. (Ca= 40.0; N=14.0; O= 16.0)
Determine the concentration of nitrate ions in moles per litre.
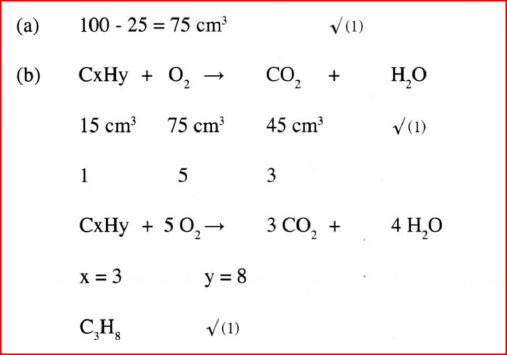
When 15 cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, P, was burnt in 100cm3 of oxygen, the resulting gaseous mixture occupied 70cm3 at room temperature and pressure.When the gaseous mixture was passed through potassium hydroxide solution, its volume decreased to 25cm3
a) What volume of oxygen was used during the reaction? b) Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon
a) Name two ores from which copper is extracted
b) During extraction of copper metal, the ore is subjected to froth flotation. Give a reason why this process is necessary. c) Name one alloy of copper and state its use.
ANSWERS
(a) Copper pyrites chalcocite, malachite
(b) To concentrate the ore (c) Brass Batteries
On heating a pale green solid K, carbon (IV) oxide gas and a black solid M were formed. On reacting K with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon (IV) oxide gas and
green solution S were formed. When excess aqueous ammonia was added to solution S, a deep blue solution was formed. a) Identify the cation in solid K b) Identify the two onions in solution S.
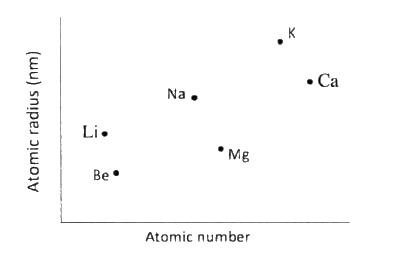
The plots below were obtained when the atomic radii of some elements in groups I and II were plotted against atomic numbers.
Explain:
a) The trend shown by Li, Na and K. b) Why the atomic radii of elements Be, Mg, and Ca are lower than those of Li, Na and K.
ANSWERS
(a)The atomic radii increase with increase in atomic number. This is due to increase in energy levels.
(b) The group II elements have more protons than group I elements hence this increases the nuclear attraction for the outer electrons.
(a) Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. What is meant by an allotrope?
(b) Explain why graphite can be used as a lubricant while diamond cannot.
ANSWERS
(a) These are different forms carbon in the same physical state.
(b) The hexagonal graphite rings have weak Van der Waals forces between the layers that allow the layers to slide over each other , while in diamond the atoms are held by strong Covalent bonds.
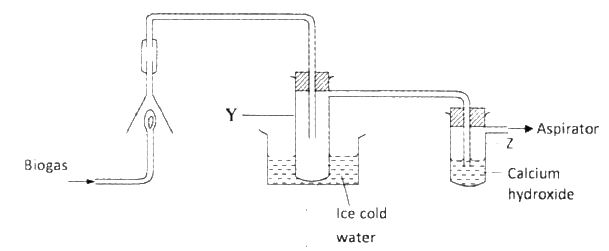
The set-up below was used to investigate the products of burning biogas (methane).
Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) What product will be formed in test- tube Y?
b) State and explain the observations which would be made in Z?
When fuels burn in the internal combustion engine at high temperature, one of the products formed is nitrogen (II) oxide.
a) Write the equation for the formation of nitrogen (II) oxide. b) Give a reason why nitrogen (II) oxide is not formed at room temperature. c) Describe how formation of nitrogen (II) oxide in the internal combustion engine leads to gaseous pollution.
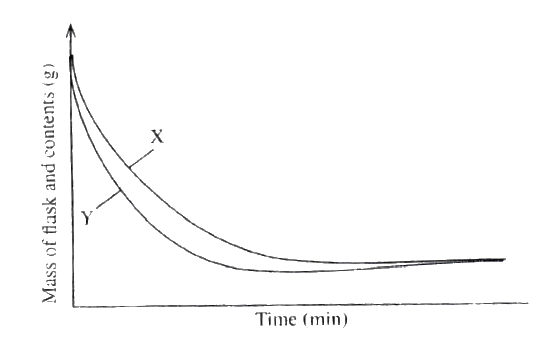
The curves below represent the change in mass when equal masses of powered zinc and zinc granules were reacted with excess 2M hydrochloric acid. Study them and answer the question below.
Which curve represents the reaction with zinc granules? Explain your answer.
ANSWERS
X - Zinc granules
The gradient of the graph is less steep because there is less surface area.
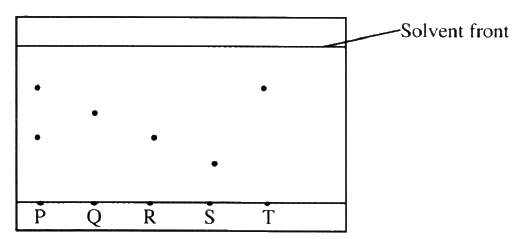
The chromatogram below was obtained from a contaminated food sample P.
Contaminants Q, R, S and T are suspected to be in P. Use it to answer the following questions.
a) Identify the contaminants in mixture P.
b) Which is the most soluble contaminant in P.?
(a) State the Charles’ law
(b) A certain mass of gas occupies 146 dm3 at 291 K and 98.31 kPa. What will be its temperature if its volume is reduced to 133 dm3 at 101.325 kPa?
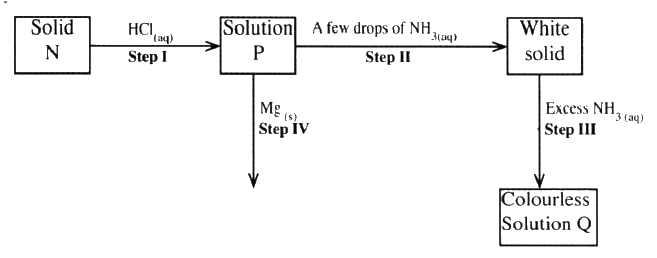
The scheme below shoes some reaction sequence starting with slid N. Study it and answer the questions that follows.
a) Write the formula of the complex ion in solution Q.
b) Write an equation for the reaction in step IV.
a) What would be observed if sulphur (IV) oxide is bubbled through acidified potassium manganate (VII)
(b) In an experiment, sulphur (IV) oxide was dissolved in water to form solution L. (i) What would be observed if a few drops of barium nitrate solution were immediately added to solution L? (ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction that occurred between solution L and aqueous barium nitrate in (b) (i) above. |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
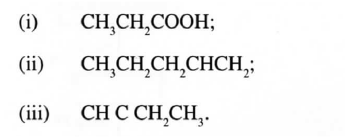















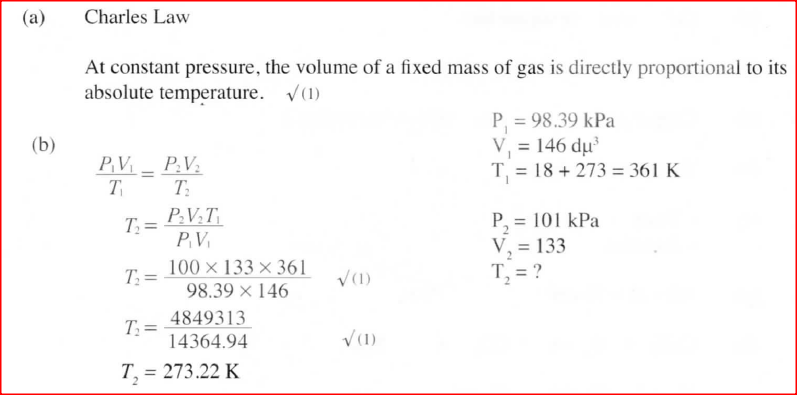
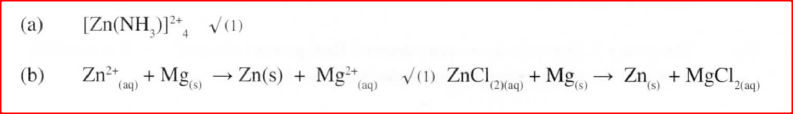


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

