|
a) Dissolving of potassium nitrate in water is an endothermic process. Explain the effect of increase in temperature on the solubility of potassium nitrate
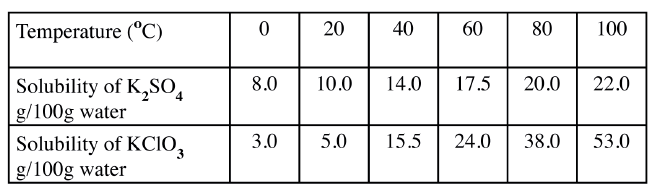
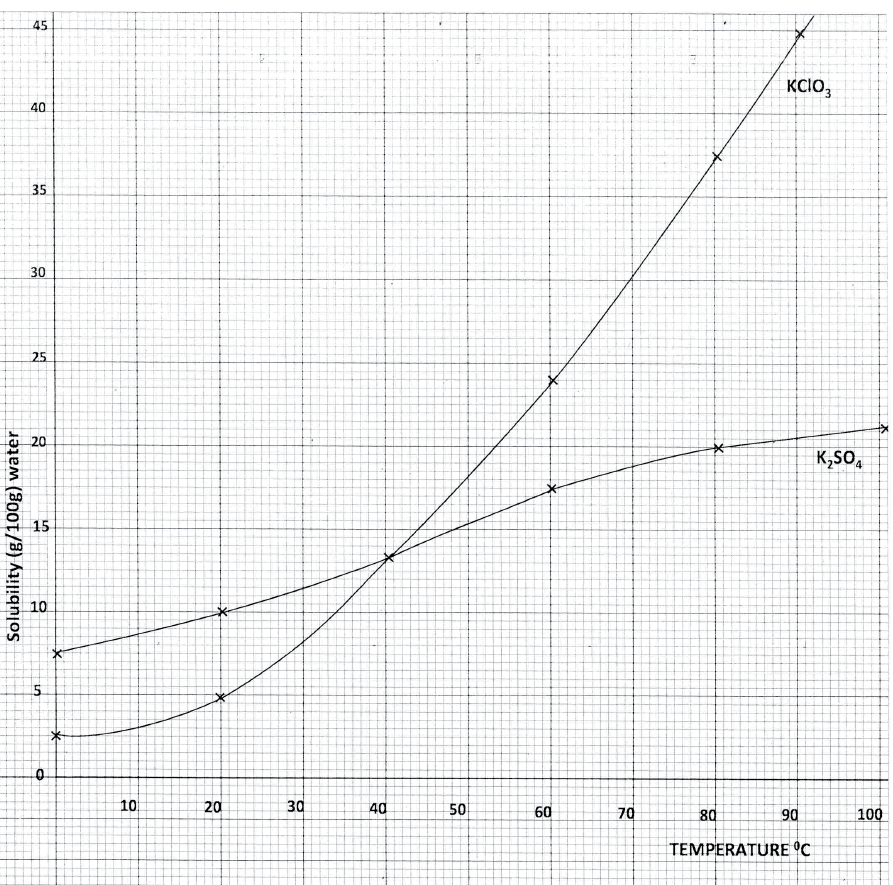
b) The table below shows the solubilities of potassium sulphate and potassium chlorate (V) at different temperatures.
i) Draw the solubility curves for both salts on the same axis. (Temperature on the X-axis
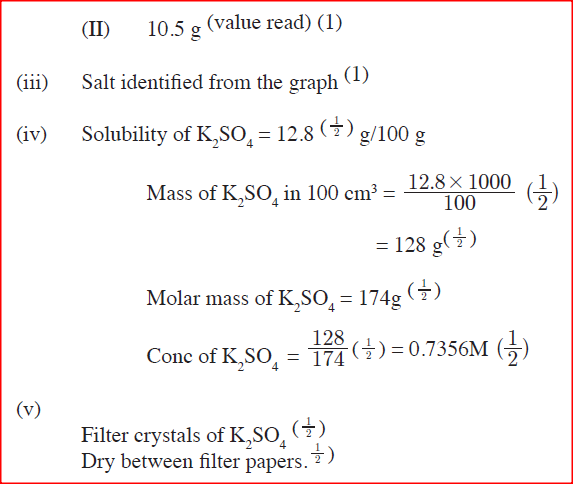
ii)A solution of potassium sulphate contains 20g of the salt dissolved in 100 g of water at 100°C. This solution is allowed to cool to 25°C I) at what temperature will crystals first appears? II) What mass of crystals will be present at 25°C? iii) Which of the two salts is more soluble at 30°C? iv) Determine the concentration of potassium sulphate in moles per litre when the solubility of the two salts are the same (K= 39.0, O=16.0 ; S=32.0) v) 100 g of water at 100°C contains 19g of potassium sulphate and 19 g of potassium chlorate (V). Describe how a solid sample of potassium sulphate at 60°C can be obtained
0 Comments
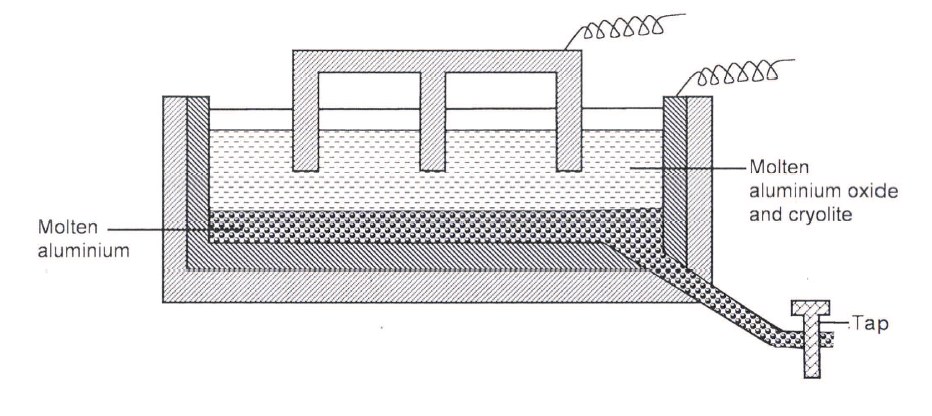
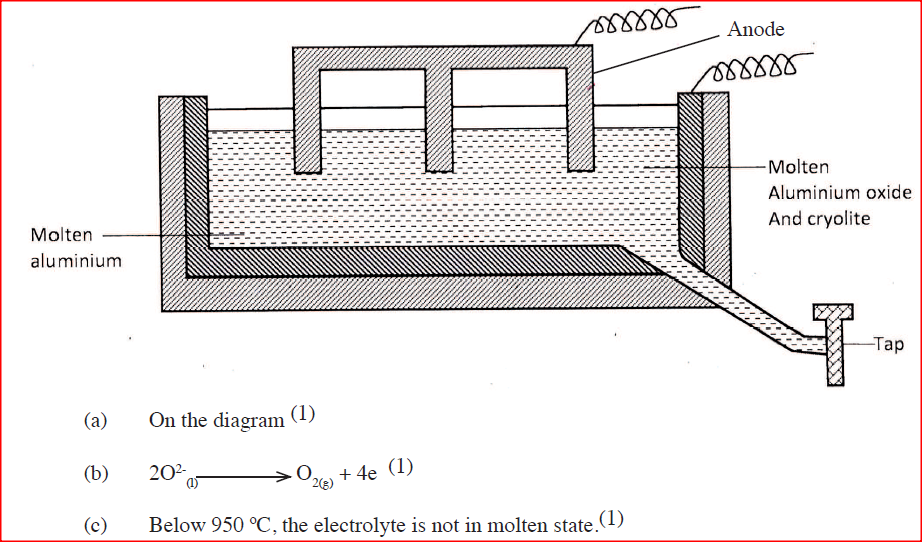
The diagram below represents a set up of an electrolytic cell that can be used in the production of aluminium
(a) One the diagram, label the anode
(b) Write the equation for the reaction at the anode (c) Give a reason why the electrolytic process is not carried out below 950°C (d) Give a reason why the production of aluminium is not carried out using reduction process (e) Give two reasons why only the aluminium ions are discharged (f) State two properties of duralumin that makes it suitable for use in aircraft industry (g)Name two environmental effects caused by extraction of aluminium
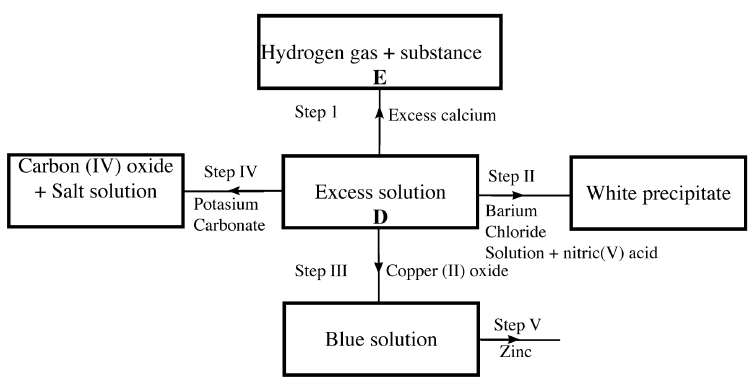
(a) The scheme below shows some of the reaction of solution D. Study it and answer the questions that follow
(i) Give a possible caution present in solution D
(ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in Step II (iii) What observations would be made in Step V? Give a reason (iv) Explain why the total volume of hydrogen gas produced in step 1 was found to be very low although calcium and solution D were in excess. (v) State one use of substance E. (b)Starting with solid sodium chloride, describe how a pure sample of lead (II) Chloride can be prepared in the laboratory (c) (i) State a property of anhydrous calcium chloride which makes it suitable for use as a drying agent for chlorine gas. (ii) Name another substance that can be used to dry chlorine gas
(a) Other than temperature, state two factors that determine the rate of a chemical reaction.
(b) A solution of hydrogen peroxide was allowed to decompose and the oxygen gas given off collected. After 5 minute, substance G was added to the solution of hydrogen peroxide. The total volume of oxygen evolved was plotted against time as shown in the graph below
(i)Describe the procedure of determining the rate of the reaction at minute 12.
(ii)How does the production of oxygen in region AB compare with that in region BC? Explain (iii)Write an equation to show the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. (c) Sulphur (IV) oxide react with oxygen to form Suplhur (VI) oxide as shown in the equation below
(ii)Name one catalyst used for the reaction.
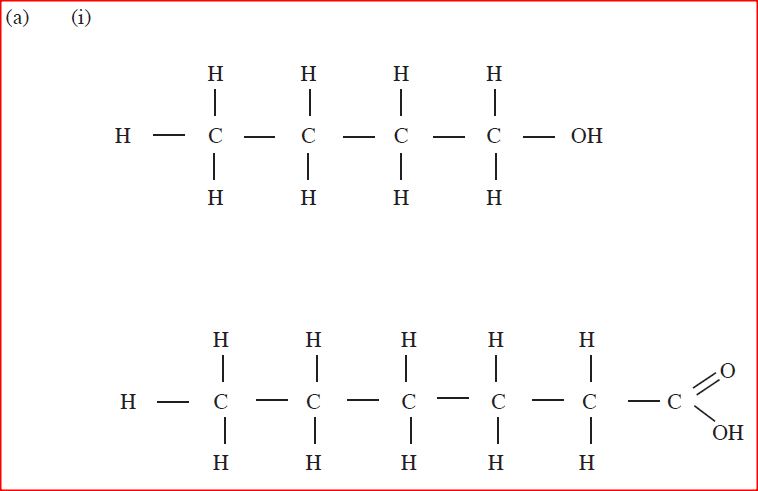
(a) Draw the structures of the following.
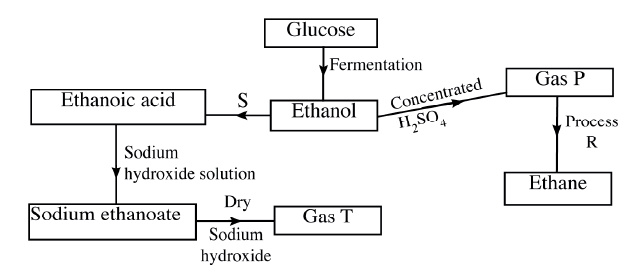
(i)Butan -1-ol (ii)Hexanoic acid. (b) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
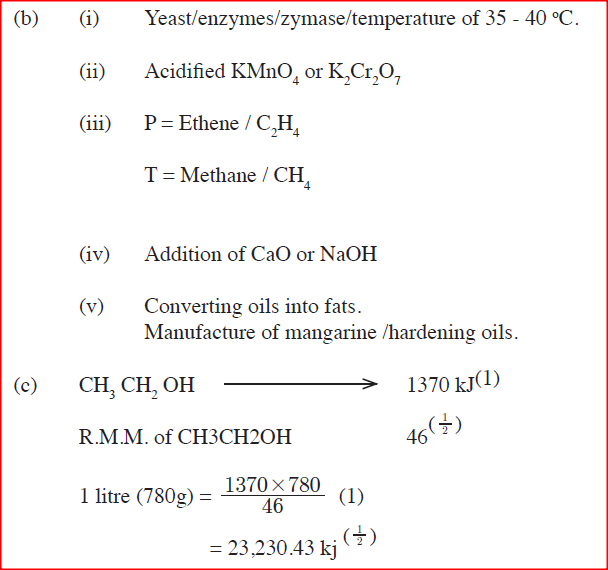
(i) State the conditions necessary for fermentation of glucose to take place
(ii) State one reagent that can be used to carry out process S. (iii) Identify gases P: T: (iv) How is sodium hydroxide kept dry during the reaction (v) Give one commercial use of process R. (c) When one mole of ethanol is completely burnt in air, 1370kJ of heat energy is released. Given that 1 lire of ethanol is 780 g , calculate the amount of heat energy released when 1 litre of ethanol is completely burnt (C = 12.0; H=1.0; 0=16.0) (d) State two uses of ethanol other than as an alcoholic drink.
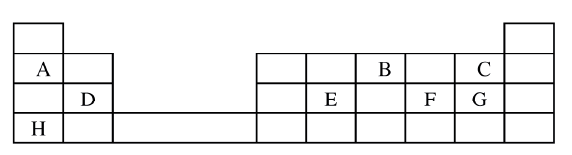
(a) The grid below represents part of the periodic table . Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements
i) Select the most reactive metal. Explain
ii) Select an element that can form an ion with a charge of 3- iii) Select an alkaline earth metal iv) Which group 1 element has the highest first ionization energy? Explain v) Element A combines with chlorine to form a chloride of A. State the most likely pH value of a solution of a chloride of A. Explain (b) (i) Explain why molten calcium chloride and magnesium chloride conduct electricity while carbon tetrachloride and silicon tetrachloride do not. (ii) Under the same conditions , gaseous neon was found to diffuse faster than gaseous fluorine. Explain this observation. (F=19.0;Ne=20.0)
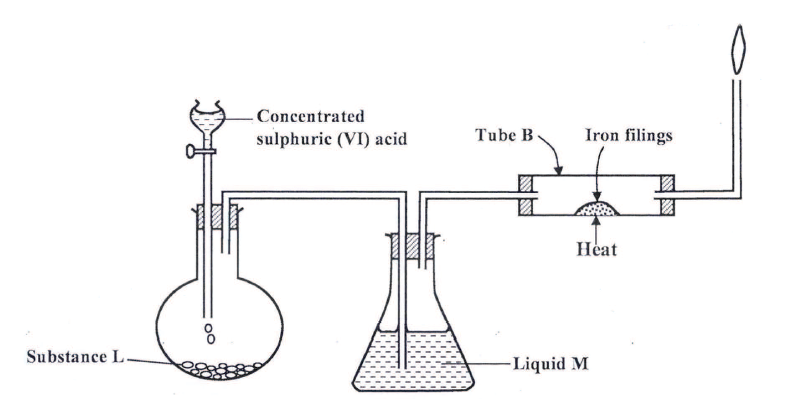
(a) The set up below was used to prepare dry hydrogen chloride gas, and investigate its effect on heated iron filings.
(i). Name substance L
(ii) Name liquid M (iii) What will be observed in tube B? (iv) Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in tube B. (v) Why is the gas from tube B burnt? (b) (i) Explain the following observations: I) A white precipitate is formed when hydrogen chloride gas is passed through aqueous silver nitrate. II) Hydrogen chloride gas fumes in ammonia gas. (ii) State two uses of hydrogen chloride gas (c) The diagram below is a representation of an industrial process for the manufacture of a bleaching powder.
(i) Name substance Q.
(ii)When the bleaching powder is added to water during washing, a lot of soap is used. Explain
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Sodium chloride / potassium chloride /rock salt.
(ii) Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (iii) Grey solid turns green
(i) I The gas reacts with silver nitrate to form insoluble silver chloride
II Both gases form ammonium chloride which is white. (ii) To make hydrochloric acid. Manufacture of ammonium chloride. Manufacture of PVC. Making chloroethene /vinyl chloride
A gas jar full of chlorine water was inverted over water and allowed to stand for sometime
a)State and explain two observations made in the gas jar after some time.
b) Write the equation for the reaction between chlorine and hot concentrated potassium hydroxide
a)What is meant by the term radical?
b) The table below contains atoms that form common radicals. Complete the table to show radicals formed from various atoms.
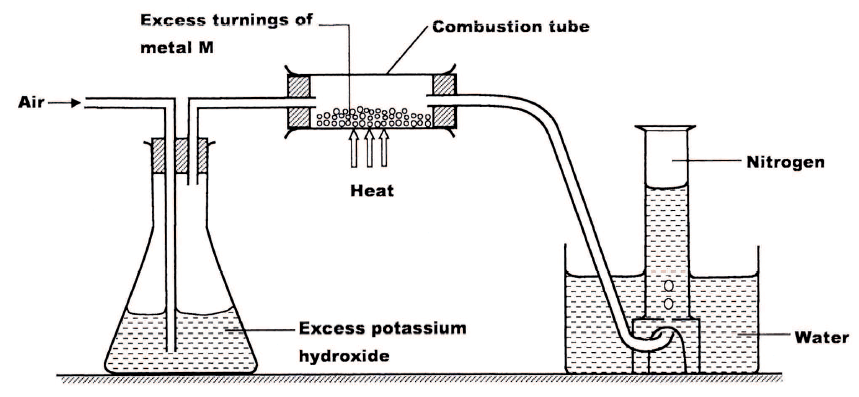
A student used the set up below to prepare a sample of nitrogen gas.
a) State the function of potassium hydroxide in the set up
b) Give a suitable metal M for use in the combustion tube c) Give a reason why the nitrogen gas obtained is not pure.
ANSWERS
(a) It absorbs carbon (IV) oxide present in the air.
(b) Copper /Cu(S) (c) It has rare noble gases which have not been removed / Argon.
a) Name a suitable solvent for extracting an indicator form flowers:
b) Give a reason why the solvent named in (a) above is used
ANSWERS
(a) Acetone / ethanol / propanone / propanol.
(b) The solvent dissolves the organic compound indicator present in the flowers / it is an organic solvent.
Cotton is a natural polymer. State one advantage and one disadvantage of this polymer.
ANSWER
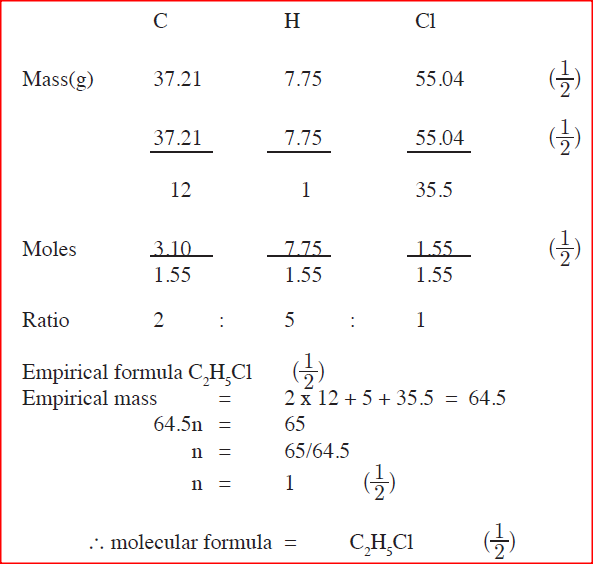
An organic compound had the following composition 37.21% carbon, 7.75% hydrogen and the rest chlorine. Determine the molecular formula of the compound, given that
the molecular mass of the compound is 65. (C=12.0; H=1.0; CL=35.5)
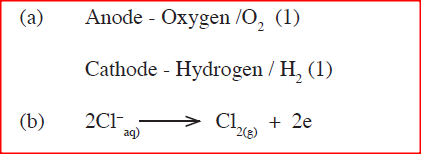
(a) A student electrolyzed dilute sodium chloride solution using inert carbon electrodes. Name the products at:
i)Anode : ii)Cathode: (b) If the experiment was repeated using concentrated sodium chloride instead of dilute sodium chloride solution, write the half equation at the anode.
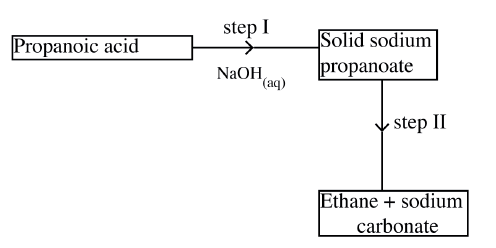
Study the flow chart below and answer the question the follow.
a) Name the process in step I.
b) Identify the reagent in step II. c) Give one use of ethane
ANSWERS
(a) Step 1 is neutralisation.
(b) Step II is soda lime/ mixture of NaOH and CaO. (e) Fuel/making ethene/making hydrogen gas.
The set up below was used to separate a mixture of methanol and propanol. Study it and answer the question that follow.
a) State the function of X
b) Which liquid will collect first in the beaker? give a reason.
ANSWERS
Given that the atomic number of Y is 13 and that of Z is 9:
a)Write the electronic arrangement of Y and Z; b) Draw the dot (.) and cross(x) diagram for the compound formed by Y and Z
In the contact process, during the production of sulphur (VI) oxide, a catalyst is used.
Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is preferred to platinum.
ANSWERS
Draw a set up that can be used to separate a mixture of sand and iodine
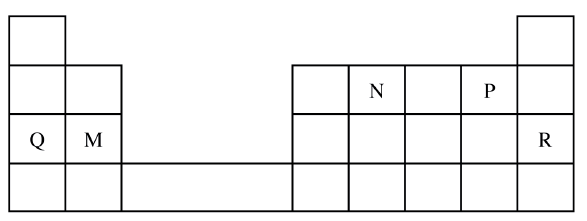
Use the part of the periodic table given below to answer the questions that follow (Letters are not the actual symbols of the elements)
a) Identify the element that forms giant covalent structures
b) Identify one element that does not form compounds c) Write the formula for the nitride of M
In an experiment on rates of reaction, potassium carbonate was reacted with dilute sulphuric (Vi) acid
(a)What would be the effect of an increase in the concentration of the acid on the rate of the reaction? (b) Explain why the rate of reaction is found to increase with temperature.
ANSWERS
(a) Rate increases.
(b) Temperature increases the kinetic energy of the particles increasing the number of collisions.
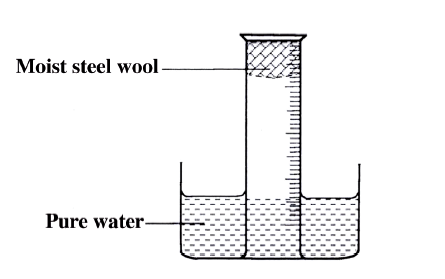
A measuring cylinder fitted with moist steel wool was inverted in a trough of water as shown in the diagram below
(a)State and explain the observations made on the;
i) Moist steel wool after four days. ii) Water level in the measuring cylinder after four days. (b) What would be the effect of using steel wool moistened with salty water?
ANSWERS
(a) (i) It turned brown /blue/violet/green.
(ii) The water level rose up the gas jar/occupy space left by reacted 02 (b) The brown colour would be more since the salt accelerates rusting/rust faster.
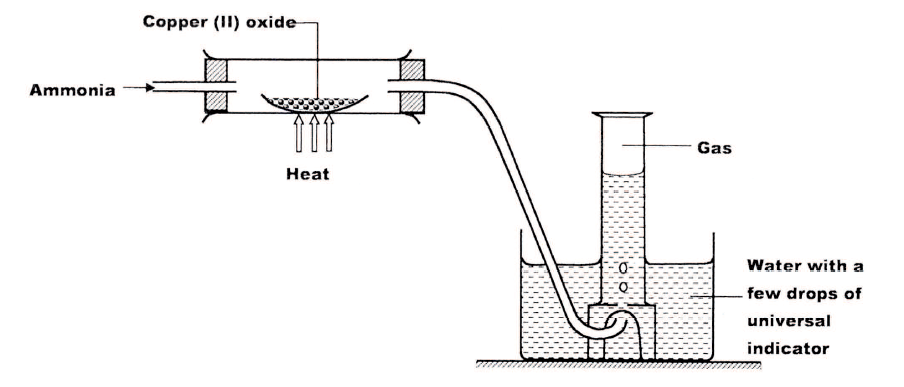
Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow
(a)Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and copper (II) oxide.
(b) During the experiment, the colour of the contents in the water trough changed. State the colour change observed and give an explanation.
When 20cm3 of 1 M sodium hydroxide was mixed with 20cm3 of 1 M hydrochloric acid, the temperature rose by 6.70C Assuming the density of the solution is 1 g/cm3 and the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.2Jg-1k-1.
(a) Calculate the molar heat of neutralization; (b) When the experiment was repeated with 1 M ethanoic acid, the temperature changes was found to be lower than that with 1 M hydrochloric acid. Explain.
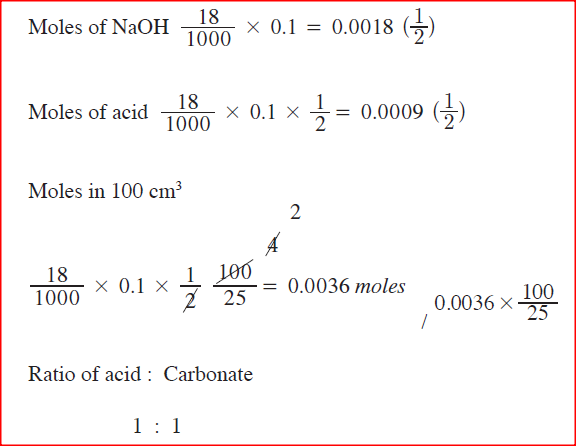
100cm3 of 0.005 M sulphuric (VI) acid were placed in a flask and a small quantity of anhydrous sodium carbonate added. The mixture was boiled to expel all the carbon (IV) oxide. 25cm3 of the resulting solution required 18cm3 of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution to neutralize it.
Calculate the mass of sodium carbonate added. (Na = 23.0; O=16.0; C=12.0) |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |




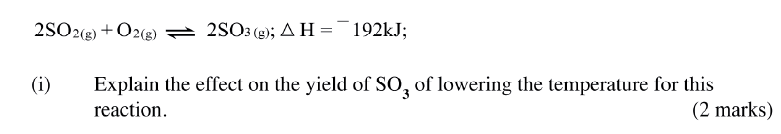
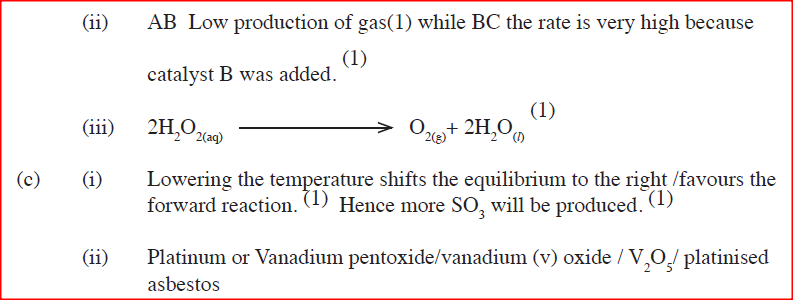














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

