|
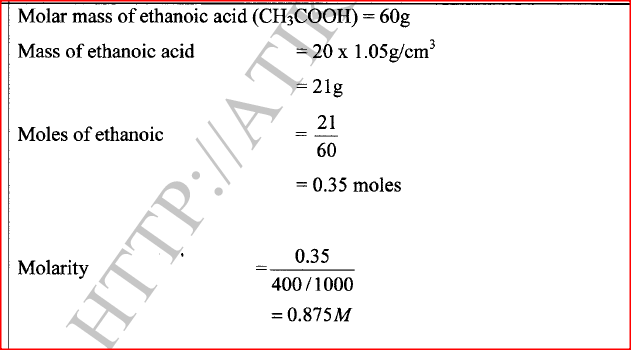
20 cm3 of ethanoic acid was diluted to 400 cm3 of solution. Calculate the concentration of the solution in moles per litre. (C = 12.0 ; H = 1.0 ; 0 =16.0) (Density of ethanoic acid = 1.05 g/cm3)
0 Comments
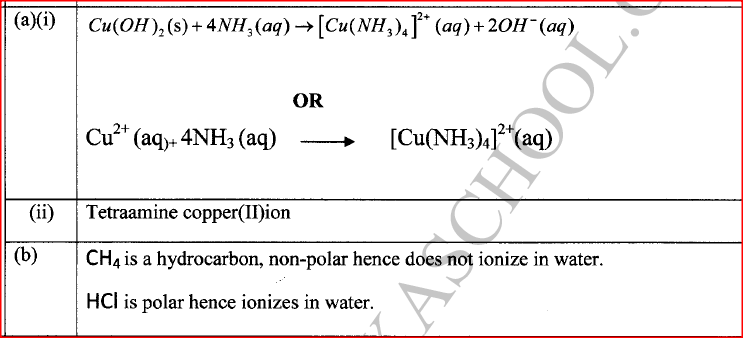
Copper(II) ions react with excess aqueous ammonia to form a complex ion.
(a) (i) Write an equation for the reaction that forms the complex ion. (ii) Name the complex ion. (b) Explain why CH4 is not acidic while HCl is acidic yet both compounds contain hydrogen.
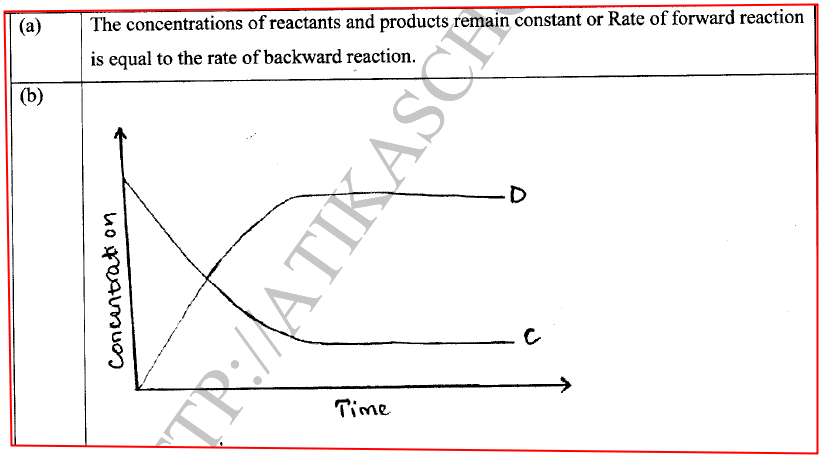
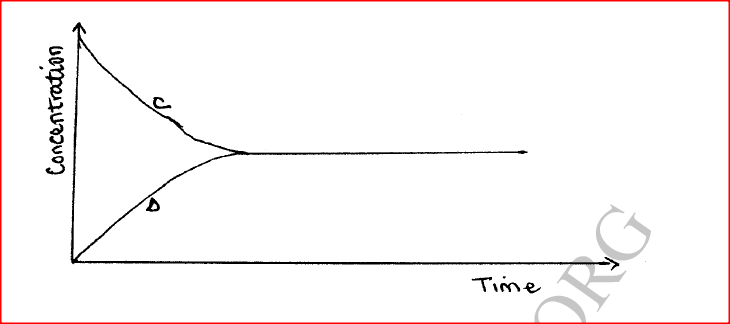
(a) State one characteristic of a reaction where equilibrium has been attained.
A sample of water is suspected to contain sulphate ions. Describe an experiment that can be carried out to determine the presence of sulphate ions.
(a) State Charles' Law.
(b) Explain why the pressure of a fixed mass of a gas increases, when the volume of the gas is reduced at constant temperature.
ANSWERS
(a)The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure.
(b)As the volume decreases, there is increased bombardment / collisions of the molecules against the walls of the container, hence increased pressure.
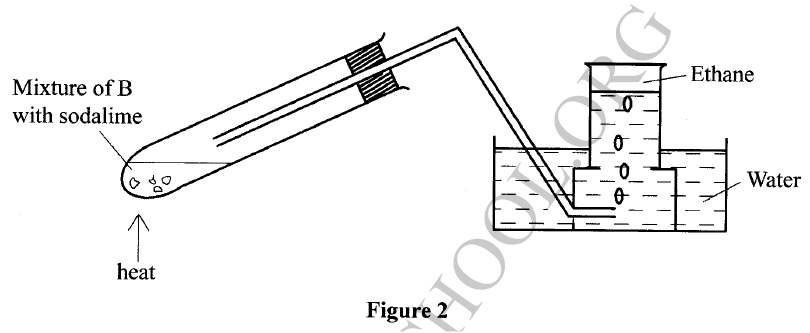
The set-up in Figure 2 was used to prepare a sample of ethane gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name B
(b) Write an equation for the complete combustion of ethane. (c) State one use of ethane.
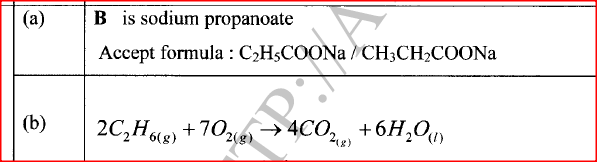
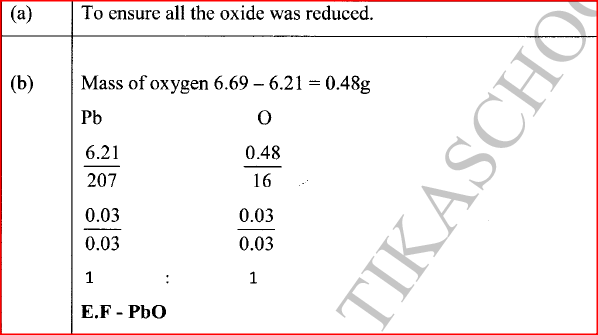
The empirical formula of lead(II) oxide was determined by passing excess dry hydrogen gas over 6.69g of heated lead(II) oxide.
(a) What was the purpose of using excess dry hydrogen gas? (b) The mass of lead was found to he 6.21g. Determine the empirical formula of the oxide. (Pb = 207.0 0 = 16.0)
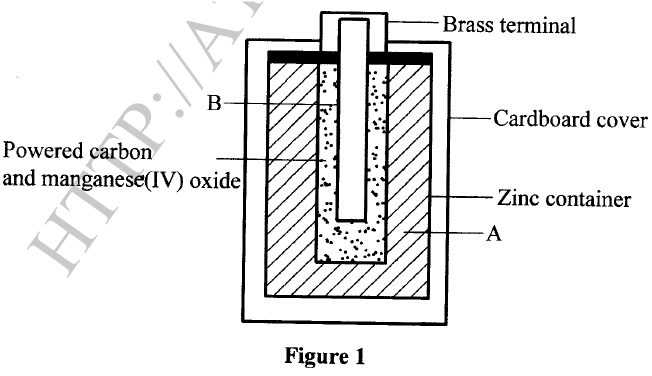
The diagram in Figure 1 shows a section of a dry cell. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name the part labelled B.
(b) The part labelled A is a paste. Give a reason why it is not used in dry form. (c) What is the purpose of the zinc container?
ANSWERS
(a)Carbon electrode (Anode) /Graphite electrode.
(b)To allow movement of ions / to have it as an electrolyte. When dry, the ions are immobile. (c)It is the cathode / negative electrode.
Calculate the values of X and Y in the following nuclear equation.
ANSWERS
Table 1 shows the atomic numbers and the first ionisation energies of three elements. The letters are not actual symbols of the elements. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) Explain the trend in first ionisation energy from A to C.
(b) Write the electronic configuration for the ion of C.
ANSWERS
(a) Ionisation energy decreases down the group 1 elements.
This is because atomic radii increases from A to C (down the group) /outermost electron is far from nucleus hence requires less energy to be lost during reaction. (b)Electron configuration of ion of C- 2.8.8 |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |


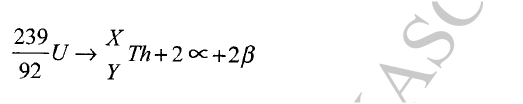


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

