|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
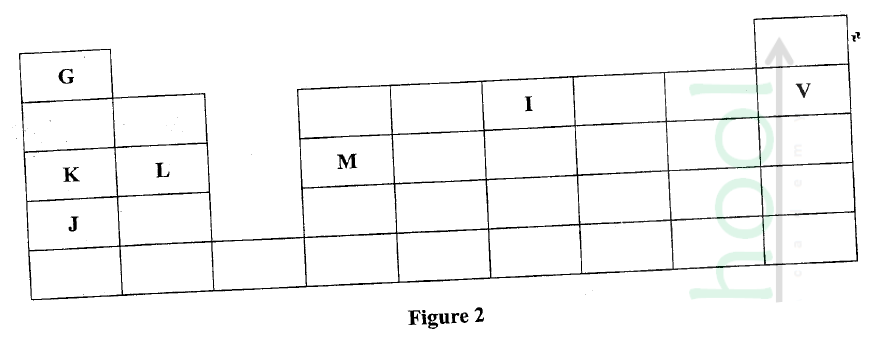
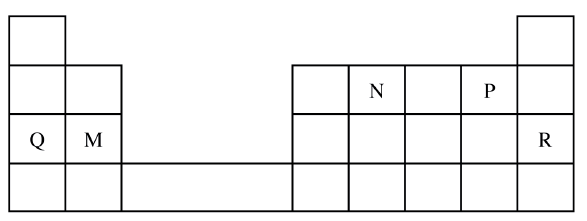
Figure 2 is a section of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements.
(a) (i) Select elements which belong to the same chemical family.
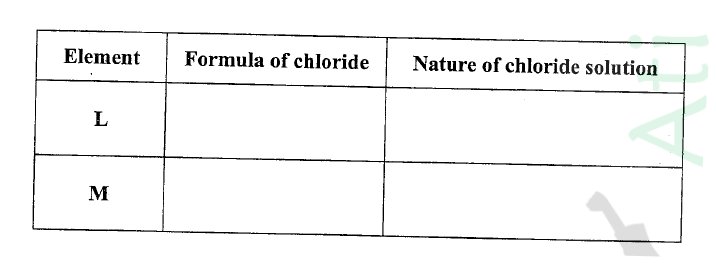
(ii) Write the formulae of ions for elements in the same period. (b) The hrst ionisation energies of two elements K and M at random are 577 kJ/mol and 494 kJ/mol (i) Write equations for the 1ˢᵗ ionisation energies for elements K and M and indicate their energies. (iii) Write the formula of the compound formed when L and I react. (iv) Give one use of elemcnt V. (c) (i) State anothcr group that G can be placcd in Figure 1. Explain. (ii) How do the reactivity of elements J and K compare? Explain. (d) (i) Elements L and M form chlorides. Complete the following table by writing the formulae of each chloride and state the nature of the solutions.
(ii) The chloride of element M vapourises easily while its oxide has a high melting point. Explain.
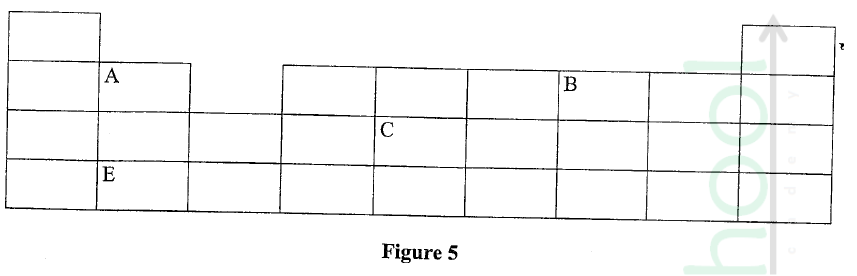
Figure 5 represents a grid that is part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
(a) Write the electron arrangement of element C.
(b) On the grid provided, show with a tick (✓) the position of element D whose atomic number is 18. (c) Element E is more reactive than A. Explain.
ANSWERS
(a) 2.8.4
(b) period 3, group 8 (c) E has a bigger atomic radius than A / the valence electrons of element E are further from the nucleus, hence loosely held by the positive nucleus and requires less energy to be removed during reaction. OR A has a smaller atomic radius than E / the valence electrons of element A are closer to the nucleus, hence strongly held by the positive nucleus and requires more energy to be removed during a reaction.
(a) Element U has atomic number 12 while element V has atomic number 16. How do the melting points of their oxides compare? Explain.
ANSWERS
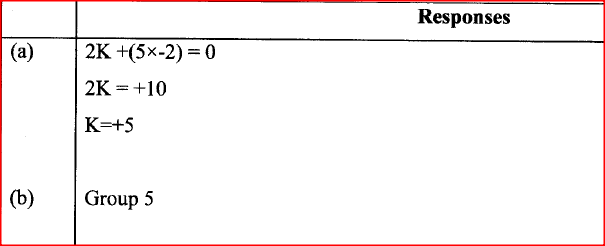
An oxide of element K has the formula K2O5.
(a) Determine the oxidation number of K. (b) To which group of the periodic table does K belong?
Table 1 shows the atomic numbers and the first ionisation energies of three elements. The letters are not actual symbols of the elements. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) Explain the trend in first ionisation energy from A to C.
(b) Write the electronic configuration for the ion of C.
ANSWERS
(a) Ionisation energy decreases down the group 1 elements.
This is because atomic radii increases from A to C (down the group) /outermost electron is far from nucleus hence requires less energy to be lost during reaction. (b)Electron configuration of ion of C- 2.8.8
(a) Write an equation to show the effect of heat on the nitrate of:
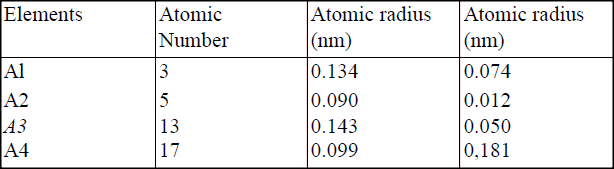
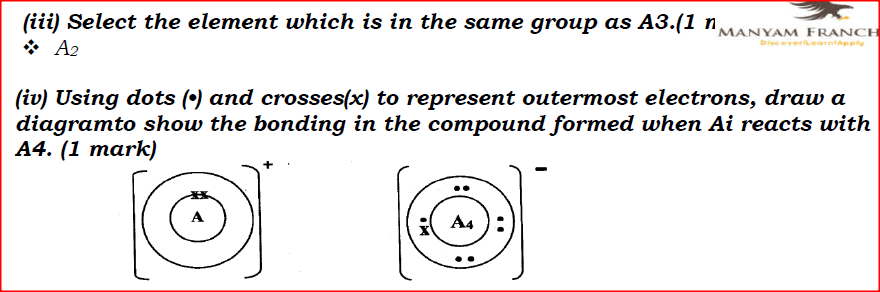
(i) Potassium (ii) Silver (b) The table below gives information about elements Ai, A2, A3, and A4 i) In which period of the periodic table is element A2? Give a reason.
(ii) Explain why the atomic radius of:
I. Ai is greater than that of A2; II. A4 is smaller than its ionic radius. (iii) Select the element which is in the same group as A3. (iv) Using dots (•) and crosses(x) to represent outermost electrons, draw a diagramto show the bonding in the compound formed when Ai reacts with A4.
The atomic number of sulphur is 16. Write the electron arrangement of sulphur in the following:
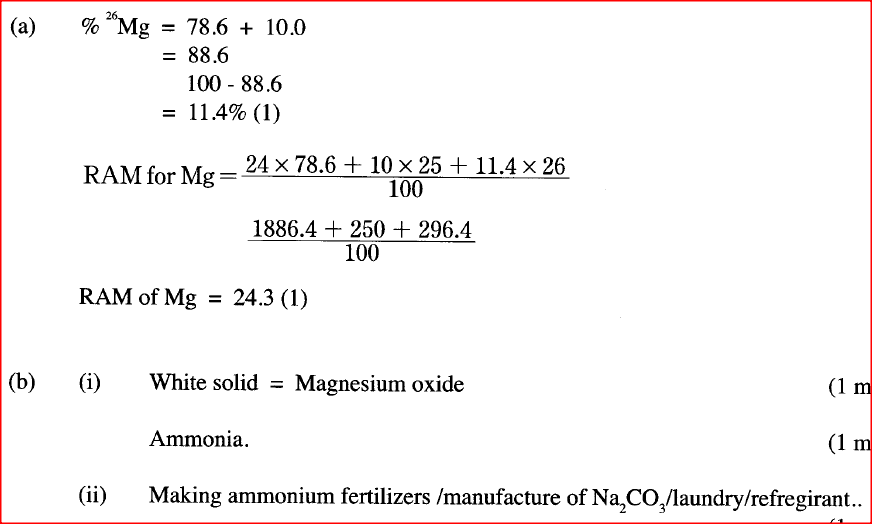
(b) When magnesium burns in air, it forms a white solid and a grey-green solid.
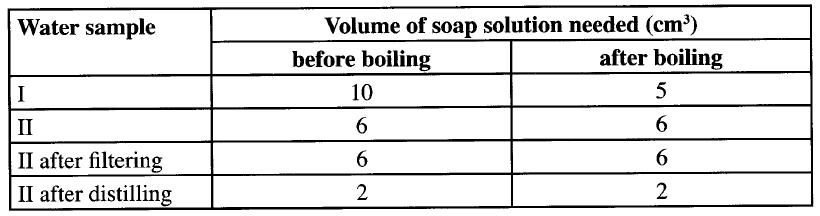
When a few drops of water are added to the mixture, a gas that turns red litmus paper blue is evolved. Identify the (i) white solid. (ii) gas evolved and state its use. (I) Name of gas (II) Use of the gas. ; (c) Two different samples of water (I and II) were tested with soap solution. Sample II was further subjected to two other processes before adding soap. 20 cm3 of each sample of water was shaken with soap solution in a boiling tube until a permanent lather was obtained. The results are shown in the table below
(i) Identify the water sample that had temporary hardness. Explain your answer.
(ii) Explain why the results for sample II are different after distilling but remain unchanged after filtering. (iii) State two disadvantages of using both water samples for domestic purposes.
Study the information in Table 3 and use it to answer the questions that follow.
A crystal of iodine, heated gently in a test tube gave off a purple vapour.
(a) Write the formula of the substance responsible for the purple vapour. (b) What type of bond is broken when the iodine crystal is heated gently? (c) State one use of iodine.
ANSWERS
(a)Formula of Iodine I2
(b)Weak Van der Waals (c)Antiseptic
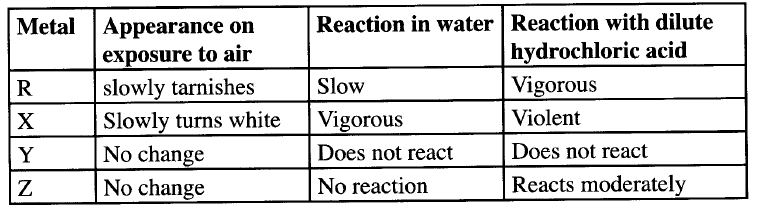
The table below shows behaviour of metals R, X, Y and Z. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
a) Arrange the metals in the order of reactivity starting with the most reactive
b) Name a metal which is likely to be i X ii Y
ANSWERS
(a) Reactivity series starting with the most reactive
X R Z Y (b) X could be potassium Y could be copper
a)What is meant by the term radical?
b) The table below contains atoms that form common radicals. Complete the table to show radicals formed from various atoms.
Use the part of the periodic table given below to answer the questions that follow (Letters are not the actual symbols of the elements)
a) Identify the element that forms giant covalent structures
b) Identify one element that does not form compounds c) Write the formula for the nitride of M
The electronic structures for elements represented by letters A,B,C,D are
A=2 .8.6 B 2.8.2 C 2. 8. 1 D 2. 8. 8. a) Select the element which forms:
Distinguish between ionisation energy and electron affinity of an element.
ANSWERS
What name is given to elements which appear in group (II) of the periodic table?
ANSWER
The table below gives the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in substances X, Y and Z. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Which letter represents an ion?
(b) Which of the substances are isotopes? Give a reason.
ANSWERS
(a) Y
(b) Y and Z They have the same number of protons (8) but different atomic masses.
The atomic numbers of phosphorus, sulphur and potassium are 15, 16 and 19 respectively. The formulae of their ions are P3-,S2- and K+. These ions have the same number of electrons.
a) Write the electron arrangement for the ions. b) Arrange the ions in the order of increasing ionic radius starting with the smallest. Give a reason for the order.
a) What is meant by the terms: i. element ii. atomic number
b) The formula for a chloride of titanium is TiCl3. What is the formua of its sulphate?
ANSWERS
(i) Element — substance that consists of one type of atoms.
(ii) Atomic number — number of protons in an atom. Ti3(S04)2
ANSWERS
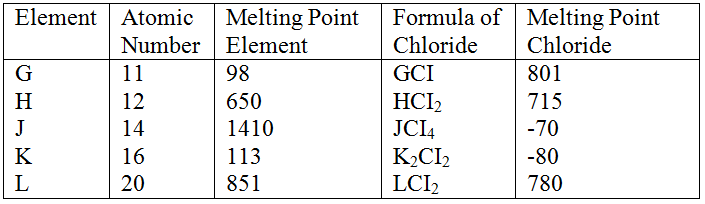
(a) Study the information below and answer the questions that follow:
The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements
|
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
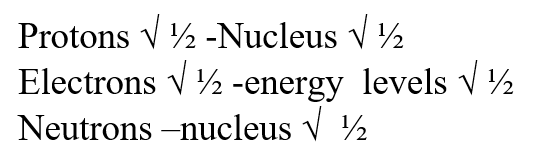



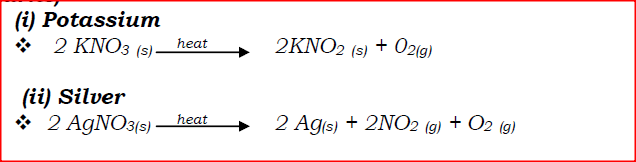









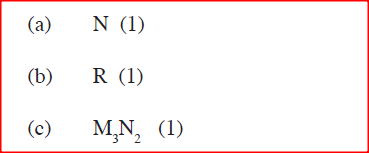





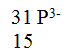




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

