|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
The Versatile Applications of Sulphur: From Fertilizers to PharmaceuticalsSulphur has a wide range of industrial uses due to its unique properties. Some common industrial uses of sulphur include:
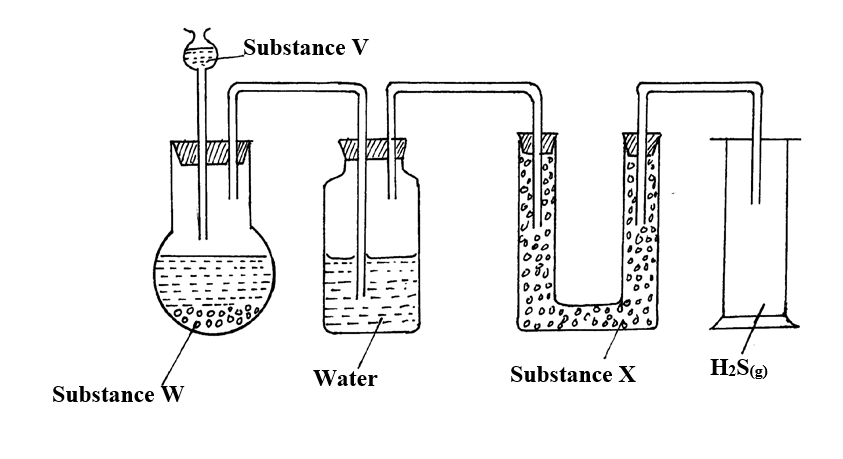
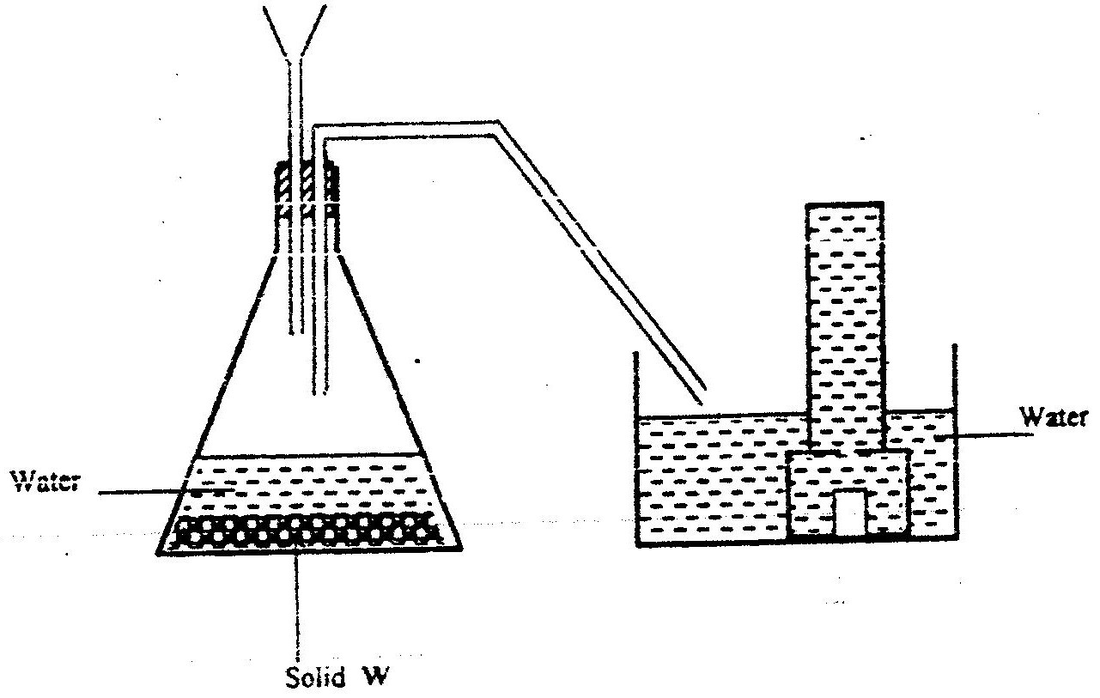
The apparatus shown below were used for the preparation of hydrogen sulphide gas in the laboratory13/10/2021
a) Name;i) Substance V (1mk)
V is Dilute hydrochloric Acid
ii) Solid X (1mk)
W is Iron (ii) Sulphide
b) Write an equation for the preparation of hydrogen sulphide (1mk)c) What property of the gas enables it to be collected by the method shown in the diagram? (1mk)
It is denser than air
d) What is the purpose of the water in the second flask? (1mk)
To absorb acid vapour (HCl)
e) What precaution should be taken when preparing the gas? (1mk)
The gas should be prepared in a fume chamber or in the open
f) Explain the observations made when dry hydrogen sulphide is exposed to wet Lead (II) acetate paper (2mks)
Black colour observed; black lead (ii) sulphide is formed.
g) State the observation that would be made when hydrogen sulphide gas is bubbled through acidified Potassium dichromate (VI) solution (1mk)
h) Explain why it is not advisable to dispose off hydrogen sulphide gas by burning (1mk)SO2 is formed causing acid rain a) Explain why sulphur is soluble in ethanol but hot in water (1mk)
b) Explain how a pure sample of sodium chloride can be obtained from a mixture of the two (1mk)
One of the allotrope s of sulphur is rhombic sulphur.
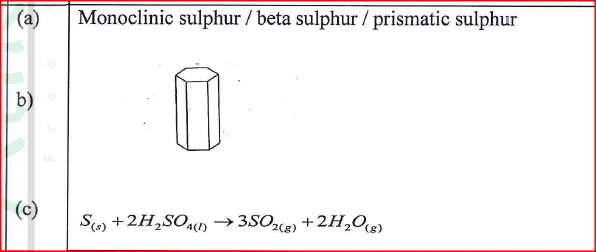
(a) Name the other allotrope of sulphur. (b) Draw a diagram to show the shape of the allotrope named in (a) above. (c) Write an equation for the reaction between concentrated sulphur(VI) acid and sulphur
Hydrogen sulphide is a highly toxic and flammable gas. It is normally prepared in a fume chamber.
(a) Name two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. (b) One of the uses of hydrogen sulphide is to produce sulphur as shown in the following equation: 2H2S(g) + S02 (g) -> 3S(s) + 2H20(1) Identify the reducing agent in this reaction and give a reason for your answer. (c) Other than production of sulphuric (VI) acid, state one commercial use of sulphur.
ANSWERS
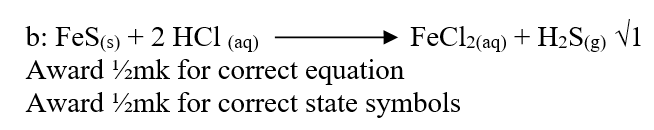
(a)Iron (II) sulphide or conc sulphide / copper sulphide (Accp formula: Fes/ HCl)
Hydrochloric acid or lead (II) sulphide/ HNO3 (b)Hydrogen sulphide The sulphur changes from -2 to zero/ (it reduces SO2 to S) i.e. +4 to 0 / sulphur lost e’s in the H2S to form sulphur (c)Vulcanization of rubber Manufacture of sulphur drugs Manufacture of gun powder/ match sticks / explosives/ fungicides
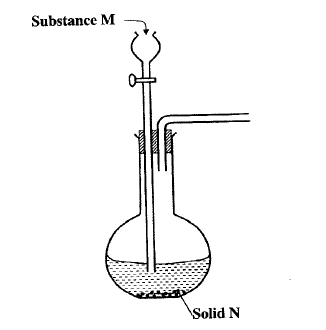
The set up below can be used to generate a gas without heating. This occurs when substance M reacts with solid N.
a i) Complete the table below giving the names of substance M and solid N if the gasses generated are chlorine and sulphur (IV) oxide.
(ii) Complete the diagram above to show how a dry sample of sulphur (IV) oxide can be collected
(b) Describe two chemical methods that can be used to test the presence of sulphur (IV) oxide. (c) Other than the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid, state two uses of sulphur (IV) oxide.
ANSWERS
(b) Presence of SO2
- Use of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) which turns from orange to green. - Bubble gas through acidified potassium manganate (VII) which decolourises /changes i.e from purple to colourless. - Iron (III) sulphate solution - yellow/brown changes to green - Bromine water colour changes from yellow/brown / orange to colourless (c) - Fumigation - Bleaching agent - Preservative . - Disinfectant - Antioxidant
(a) One of the allotropes of sulphur is rhombic sulphur, name the other allotrope.
(b) Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid reacts with ethanol and copper. State the property of the acid shown in each case. (i) Ethanol .................... (ii) Copper ....................
ANSWERS
(a) Monoclinic sulphur /Beta sulphur! Prismatic sulphur
(b) (i) Dehydrating property (ii) Oxidising property
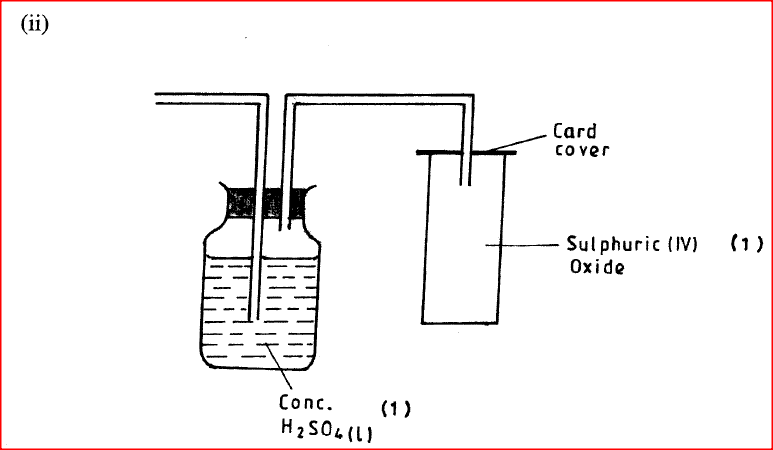
Sulphur(IV) oxide is prepared in the laboratory using the set-up in Figure 3. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Identify substance F. (1 mark)
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the flask. (1 mark) (c) State the purpose of liquid G. (I mark)
In the contact process, during the production of sulphur (VI) oxide, a catalyst is used.
Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is preferred to platinum.
ANSWERS
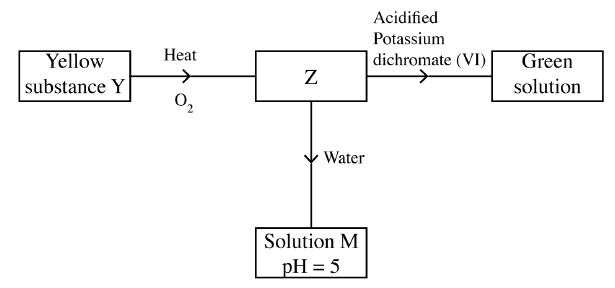
Study the flow chart below and answer the questions t hat follow.
Identify Z and M.
Z……………………… M……………………
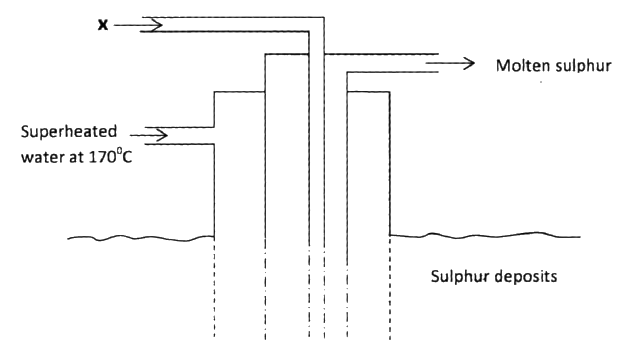
(a) The diagram below shows the frasch process used for extraction of sulphur
Use it to answer the question that follows
(i) Identify X
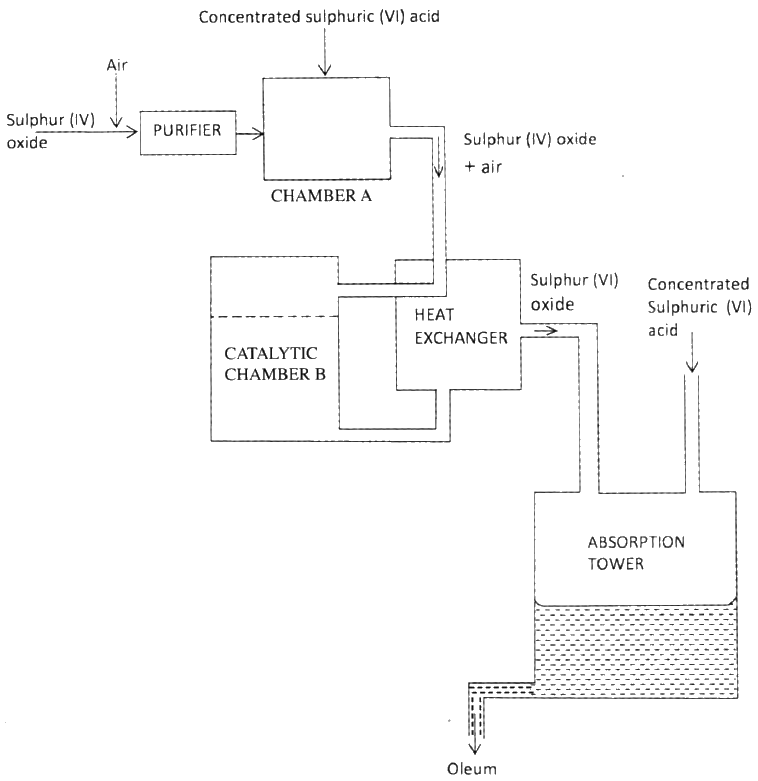
(ii) Why is it necessary to use superheated water in this process (iii) State two physical properties of sulphur that makes it possible for it to be extracted by this method (b) The diagram below shows part of the process in the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow
(I) Write an equation for the formation of sulphur (IV) oxide from sulphur
(II) What is the role of concentrated sulphur (VI) acid in chamber A? (III) Name two catalysts that can be used in the catalytic chamber B. (IV) State two roles of the heat exchanger (c) Explain one way in which sulphur (IV) oxide is a pollutant (d).what observation will be made when a few drops of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid are added to crystals of sugar? Explain your answer
ANSWERS
(a)(i)Hot compressed air
(ii)To melt the sulphur and maintain it in molten state (iii)low melting point of sulphur - insolubility of sulphur in water - less dense than water (b)(i)S + O2 → SO2 (ii)To dry the SO2 and air (iii)Vanadium (v) oxide and platinum or titanium (iv)it provides the reactants (SO2 and O2) with enough energy to react - it removes heat from the product hence preventing decomposition or conserves heat, or recycles heat or reduces cost of production. (c)- contributes to acid rain which corrodes buildings OR - causes aquatic solutions to be acidic hence affecting aquatic life etc. - poisonous/toxic (d)Turns black conc H2SO4 removes hydrogen and oxygen from the sugar molecule leaving only carbon which is black . Dehydration of sugar forms carbon which is black.
a) What would be observed if sulphur (IV) oxide is bubbled through acidified potassium manganate (VII)
(b) In an experiment, sulphur (IV) oxide was dissolved in water to form solution L. (i) What would be observed if a few drops of barium nitrate solution were immediately added to solution L? (ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction that occurred between solution L and aqueous barium nitrate in (b) (i) above.
When a sample of concentrated sulphuric acid was left in an open beaker in a room for two days, the volume was found to have increased slightly
Expected Answer
(a) Hygroscopy
(b) Drying of gases ║drying agent
When the oxide of element H was heated with powdered carbon the mixture glowed and carbon dioxide was formed. When the experiment was repeated using the oxide of element J, there was no apparent reaction.
Expected Answer
(a) Electrolysis of fused or molten oxide
(b) JCH║J, carbon, H
A certain matchstick head contains potassium chlorate and sulphure. On striking the two substances react to produce sulphure dioxide and potassium chloride. Explain the environmental effect of using such matches in large numbers.
Expected Answer
SO2 which is poisonous is released in the air. Acid rain which may cause corrosion will be formed
Acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution is decolourised when sulplur (IV) oxide is bubbled through it. The equation for the reaction is given below.
2H2O(1) + 5S02(g) + 2KMnO4(aq) —►K2SO4(aq) + 2MnSO4(aq)+ 2H2SO4(aq) (a) Which reactant is oxidised? Explain. (b) Other than the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid, state one other use of sulphur (IV) oxide.
When a solid sample of sulphur is heated in a test tube, it changes into a liquid, which flows easily. On further heating, the liquid darkness and does not flow easily. Explain these observations.
Expected Response
Solid sulphur is made of S8 rings. It melts into aliquid of S8 rings, On further heating the rings open up to form long chains of sulphur atoms, which then entangle making it viscous and dark, or sulphur melts into S8 molecules. The molecules join up to form long chain which entangle making it viscous and dark
a) The diagram below shows a set –up used by as a student in an attempt to prepare and collect oxygen gas
c) The reaction between sulphur dioxide and oxygen to form trioxide in the contact process in exothermic. Factory manufacturing sulphuric acid by contact process produces 350kg of sulphur trioxide per day (conditions) for the reaction catalyst. 2 atmospheres pressure and temperatures between. (400 – 5000C) i) What is meant by an exothermic reaction? ii) How would the yield per day of sulphur trioxide be affected Temperatures lower than 40000C are used? Explain.
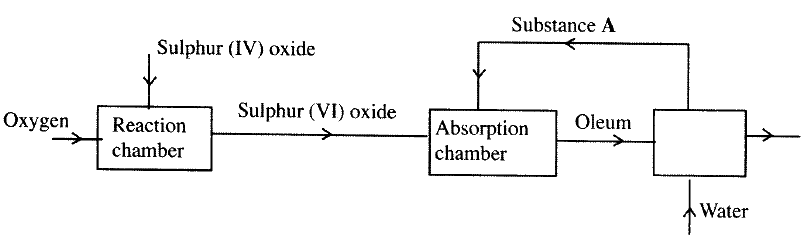
The flow chart below shows some of the processes involved in large scale production of sulphuric (VI) acid. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
a) Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale
(b) (i) Name substance A. (ii)Write an equation for the process that takes place in the absorption chamber. (c) Vanadium (V) oxide is a commonly used catalyst in the contact process. (i) Name another catalyst which can be used for this process. (ii) Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is the commonly used catalyst. (d) State and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals of copper (II) sulphate in a bearer. (e) The reaction of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with sodium chloride produces hydrogen chloride gas. State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid , illustrated in this reaction. (f) Name four uses of sulphuric (VI) acid
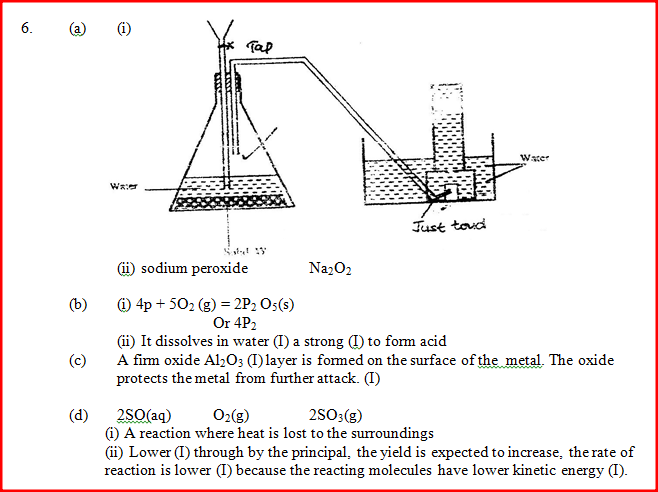
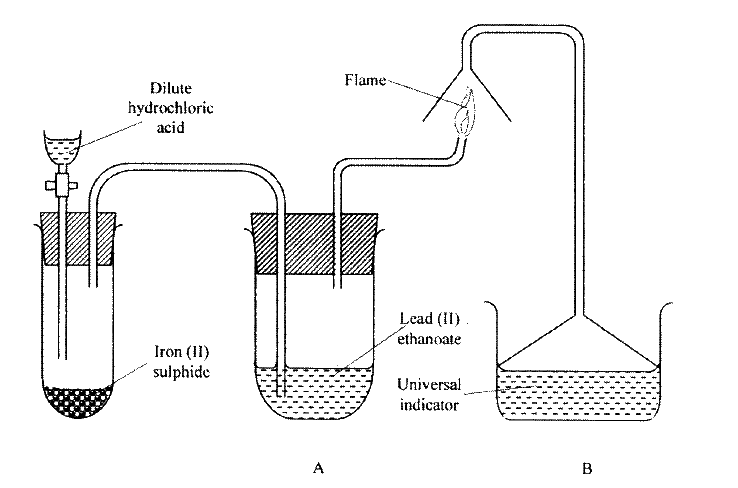
The set up below was used to prepare a gas and study some of its properties. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) State and explain the observations made in the:
(i) tube labelled A; (ii) beaker labelled B. (b) State one precaution that should be taken when carrying out this experiment.
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Black solid is deposited.
(ii) The indicator turns red. (b) The experiment should be done in fume chamber or in open air.
Hydrogen sulphide is a highly toxic and flammable gas. It is normally prepared in a fume chamber
.a) Name two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. b) One of the uses of hydrogen sulphide is to produce sulphur as shown in the following equation; 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) → 3S(s) + 2H2O(l) Identify the reducing agent in this reaction and give a reason for your answer. c) Other than production of sulphuric(IV) acid, state one commercial use of sulphur.
ANSWERS
(a) Iron (II) Sulphide
Hydrochloric acid (b)Reducing agent, hydrogen sulphide The sulphur changes from -2 to zero (c) Vulcanization of rubber Manufacture of sulphur drugs
In an attempt to prepare sulphur dioxide gas, dilute sulphuric acid was reacted with barium sulphuric. The yield of sulphur dioxide was found to be negligible explain
Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide react as shown in the equation below
SO2(g) + NO2(g) → SO3(g) + NO(g)
(i) Using the oxidation numbers of either sulphur or nitrogen, show that this is a redox reaction
(ii) Identify the reducing agent
State and explain the observation that would be made when a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid are added to a small sample of hydrated copper (II) sulphate
|
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |




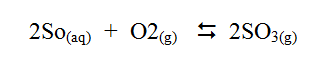




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

