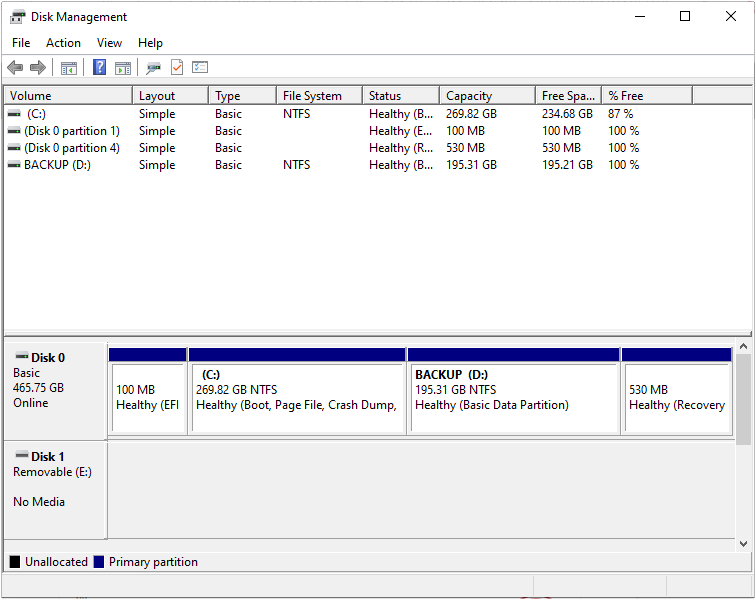
PROCESS FOR PARTITIONING WINDOWS 10To partition a hard drive with Windows 10, you can follow these steps:
Note: Partitioning a hard drive will erase all data on it, so make sure to back up any important files before proceeding.
0 Comments
|
Categories
All
AuthorAtika School Team Archives
March 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

