Navigating the Stages of System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)The stages of the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) are outlined in the documents provided. Here is a summary of the stages as mentioned in the documents:
0 Comments
Understanding the Importance of Problem Recognition and Definition Stage in System DesignProblem recognition and definition is a crucial step in the process of designing a new system. It involves identifying and understanding the issues or challenges that exist within the current system or business processes. From the documents provided, the following points can be derived regarding problem recognition and definition:
Key Considerations in Designing a New System for Effective Organizational ManagementManagement may consider designing a new system when the following needs arise:
Exploring the Additional Purposes of Information Systems in OrganizationsThe purpose of an information system is to support and improve the day-to-day operations in a business and the decision-making process. From the documents provided, we can derive the following purposes of an information system:
What are the key activities that happen in requirements specificationsIn the requirements specification stage of the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle), there are several key activities that take place. Here are the key activities mentioned in the documents:
The Role of Information Systems in Organizations: Necessity and Benefits of Developing New SystemsAn information system is an arrangement of people, data processes, and information that work together to support and improve the day-to-day operations in a business and the decision-making process. It is the complete apparatus for handling all aspects of information within an organization. This includes people, procedures, technological, and other resources that collect, transform, and disseminate information in the organization.
The purposes of an information system in an organization are:
Developing new information systems is necessary due to various circumstances such as new opportunities to improve internal processes and service delivery, problems hindering goal achievement, and directives for change. Name the stage of program development cycle when: (3 marks)A user guide would be written.…………………………………………………………………………………….. Documentation A programmer dry-runs the code.…………………………………………………………………………………….. Testing and Debugging System charts would be drawn.…………………………………………………………………………………….. Program Design Mention any two advantages of running both the manual system and the computerized simultaneously19/7/2023 Mention any two advantages of running both the manual system and the computerized simultaneously.
Identify two main risks of direct changeover during system implementation.
Give two disadvantages of Direct changeover over Parallel running.
Briefly explain the terms parallel running and direct changeover as used in system implementation19/7/2023 Briefly explain the terms parallel running and direct changeover as used in system implementation
Give two importance of feedback mechanism in systems
Advantages of questionnaire over interview
(a) List and describe four strategies for converting from an old system to a new system. (4mks)
(b) (i) Distinguish between private data and confidential data (2mks)
(ii) What can be done to stop illegal access to a computer laboratory by unauthorized people (3mks)
(c) (i) List four areas that would be considered in the requirement specification. (4mks)
(ii) Name any two areas covered in feasibility report during system analysis and design. (2mks)
Explain three functions of an information system in an organisation.
(b) Explain two benefits that a company would gain from using batch processing method for data processing
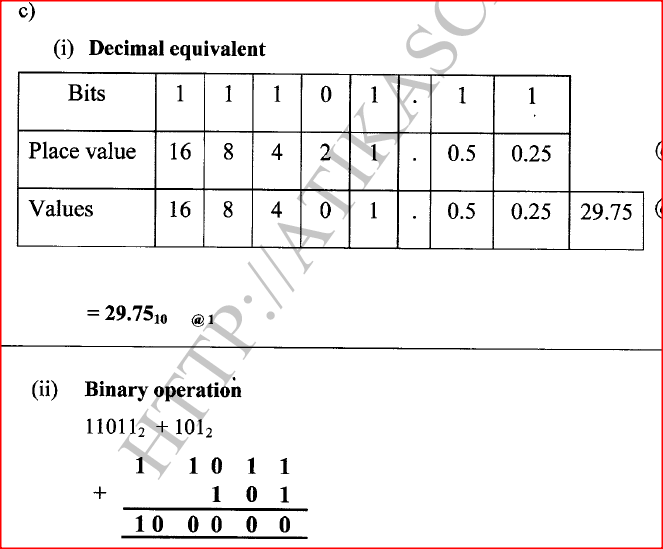
(c) (i) Convert the number 11101.1 12 to its decimal equivalent.
(ii) Perform the following binary operation 110112 + 1012
RESPONSES
a) Functions of information system in an organization.
A school has been advised to employ a database administrator. State three responsibilities of this personnel in the school.
(b) Explain two ways in which computers can be used in the transport industry.
(c) Mary was advised to partition a hard disk for her computer. Explain two reasons that may have necessitated this. (d) Explain a reason for conducting each of the following studies in systems development: (i) Schedule feasibility; (ii) Technical feasibility.
RESPONSES
a) Possible responsibilities of a database admin in a school
Describe three arithmetic errors that may occur during computerised data processing.
(b) Arnold a programmer intends to create a user input interface screen for a system. State three factors that he should consider.
(c)With the aid of an example in each case describe the following types of maintenance. (i) adaptive; (ii) perfective; (iii) corrective.
RESPONSES
a) Arithmetic errors
Truncation error
(i) Adaptive
An organisation intends to replace an existing system by carrying out the process in stages.12/1/2021 An organisation intends to replace an existing system by carrying out the process in stages.
(a) Name this implementation strategy;
Technical feasibility:
Explain two uses of a system documentation in system development.
Uses of system documentation
With the aid of a diagram. describe time sharing mode as used in computer data processing.
(b) A company’s management has opted to use computers to process data. State four factors that the management needs to consider when selecting the company data processing mode.
(c) Explain the purpose of each of the following in system documentation: (î) user manual; (ii) sample data: (iii) table descriptions.
RESPONSES
(a) Time-sharing mode
This is a processing mode in which a central processor serves two or more users with different requirements. The processor time is divided equally among the tasks in the queue. A user whose task requirements are more than is apportioned is send back to the queue. For example, four jobs requiring times t1, t2, t3 and t4 to complete is apportioned equal time in each round until when they are done.
(b) Factors to consider when selecting data processing mode
Give two differences between a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and a Commandline Interface.
(a) Report or documentation
(b )Disk/master file/database a) Distinguish between Computer Aided Instruction (CAI) and Computer Aided Learning (CAL). (4 marks)
b)(i) State four activities that may be carried out when disposing off an old system in an organization. (4 marks)
ii) State four ways of getting user specifications during systems design. (4 marks)
A) State four outcomes that may result from using incorrect requirement specifications during systems development. (4 marks)
B) A school opted to use direct change over approach when installing a new system. |
Categories
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

