PHYSICS HIGH SCHOOL NOTES FOR KCSE PREPARATIONS
RECTILINEAR PROPAGATION AND REFLECTION AT PLANE SURFACES.IntroductionObjects that produce their own light are known as luminous objects i.e. the sun, torch lamps etc. objects that do not produce their own light are called non-luminous objects i.e. the moon. Opaque objects are those which do not allow light to pass through them.Translucent materials are those which allow light to pass through them but we cannot see through them i.e. church glass and bathroom glass. Transparent materials are those which allow light to pass through them and we can see through them i.e. window panes, car windows etc. A ray is the direction of the path followed by light. A beam is a group of rays travelling together.
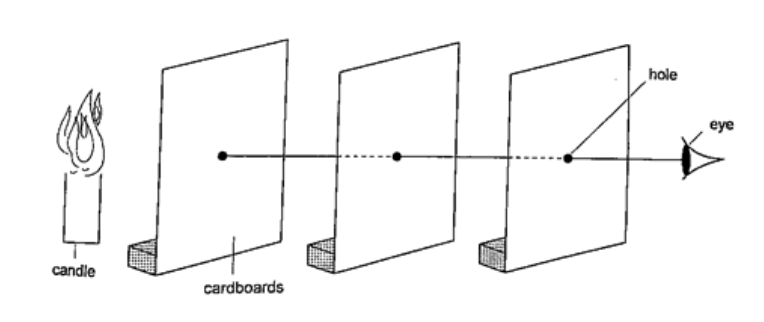
Experiment: light travels in straight lines
Procedure
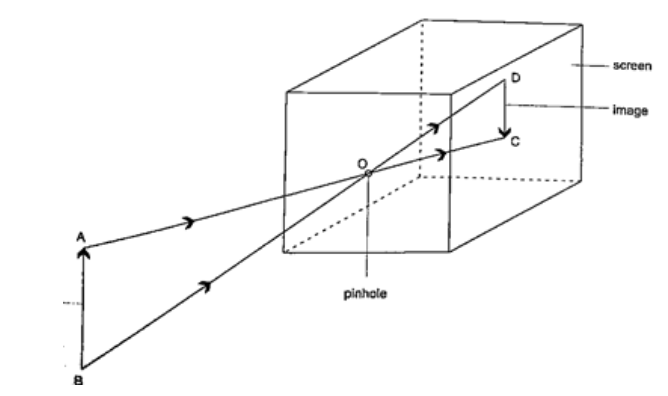
DiscussionWhen one cardboard is displaced or moved slightly the flame cannot be seen at the other end. This shows that light travels in a straight line. This principle is applied in the following,Pinhole cameraIt consists of a closed box with a small hole on one face and a screen of tracing paper/ frosted glass on the opposite face as shown. An image will be formed on the screen. Since light travels from one point of the object through the hole an image will be formed on the opposite screen of the box.If the object is near the hole it is magnified while diminished if away from the hole. Magnification is therefore the ration of the image to object height, expressed as, Magnification
= height of image/ height of object or
= distance of image from pinhole/ distance of object from pinhole
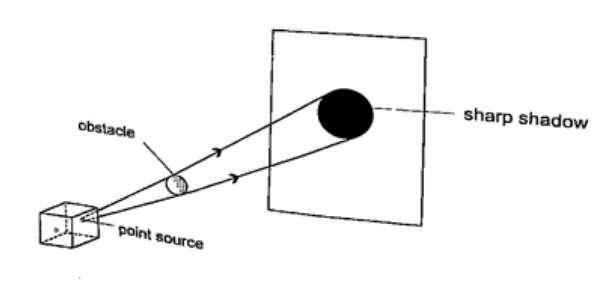
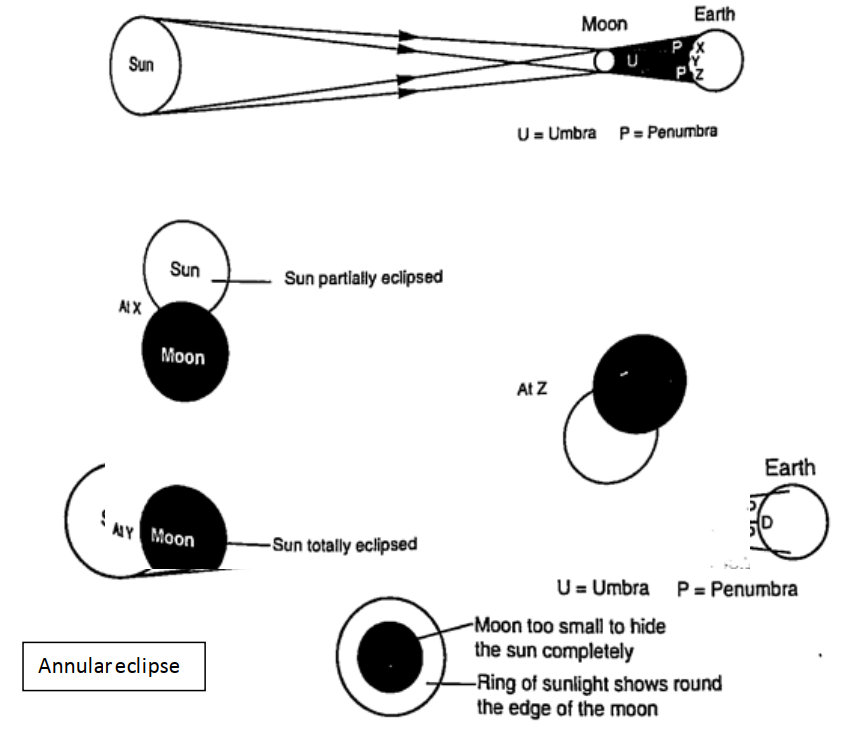
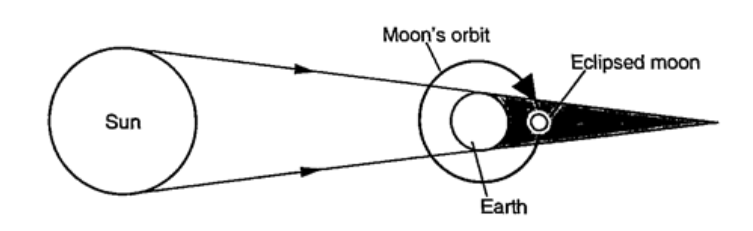
ShadowsShadows are formed when an opaque object is placed between a source of light and a screen. When the shadow is big a dark patch at the centre is formed (umbra) while a surrounding lighter patch called penumbra is formed.EclipsesEclipse of the sun (solar eclipse)This occurs when the moon is between the earth and the earth. The shadow of the moon falls on the earth’s surface. Sometimes the distance is large for the shadow to reach the earth and when this happens an annular eclipse occurs.
Eclipse of the moonIt is also known as lunar eclipse and occurs when the earth is between the sun and the moon. The shadow of the earth falls on the moon.Examples1. Calculate the height of a building 300 m away from a pinhole camera which produces an image 2.5 cm high if the distance between the pinhole and the screen is 5.0 cm.Solution
Object distance = 300 m, image height = 2.5 cm, image distance = 5.0 cm. Object height/ image height = object distance/ image distance Object height = (30,000 × 2.5) / 5.0 = 15,000 cm = 150 m. 2. The length of a pinhole camera is 25.0 cm. An object 2.0 cm is placed 10.0 m from the pinhole. Calculate the height of the image produced and its magnification. Solution
Image height = (image distance × object height) / object distance
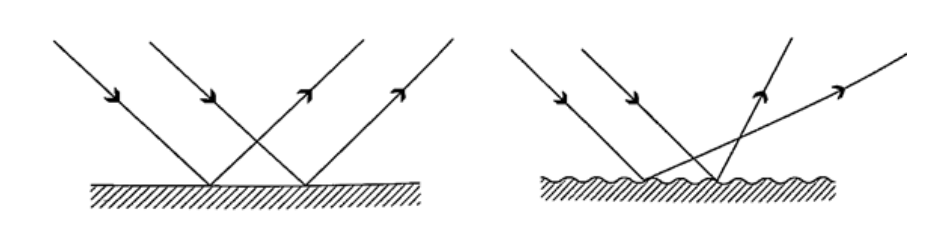
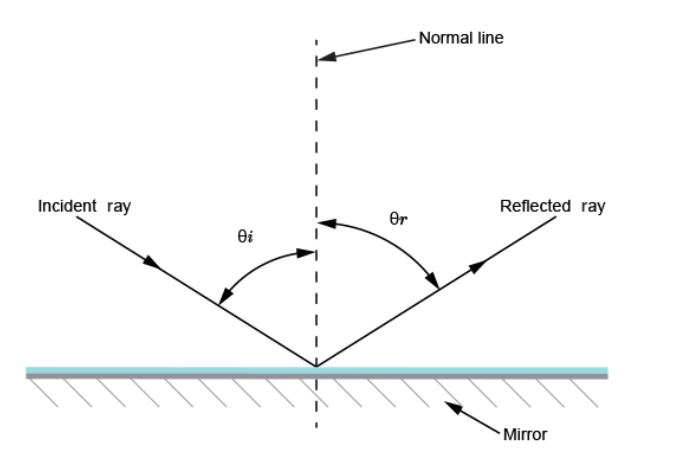
= (25 ×200) / 10 = 500 cm or 5 m. Magnification = image distance / object distance = 25 /10 = 2.5 Reflection from plane surfacesDiffuse and regular reflectionRegular reflection occurs when a parallel beam of light falls on a plane mirror band reflected as a parallel beam. They occur on polished surfaces. A diffuse reflection occurs on rough surfaces where a parallel beam of light is reflected in all directions.THE THREE LAWS OF REFLECTIONAny mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave.The three laws of reflection are
Images formed by reflection from plane surfacesCharacteristics of images formed in a plane mirror
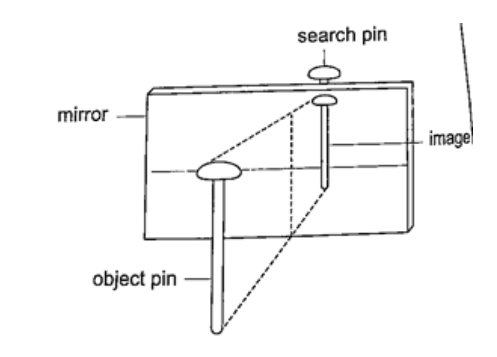
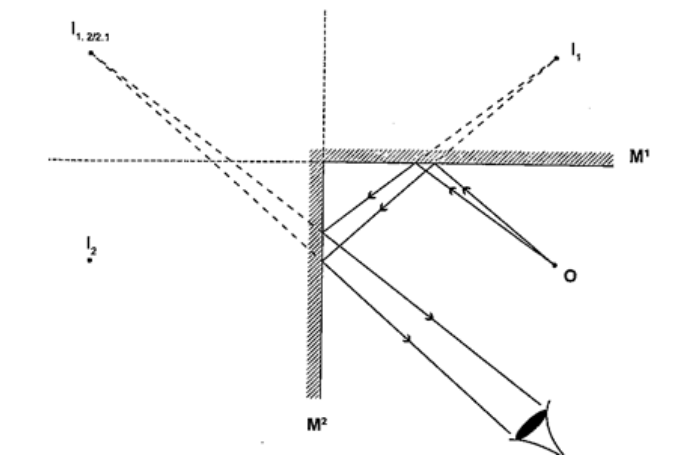
Location of an image by the non-parallax methodParallax is the apparent relative motion of two objects due to the movement of the observer. It only occurs when the objects are at a distance from one another. This can be used to find the position of images in plane mirrors.Experiment: To find the position of an image of a pin by non-parallax method Procedure
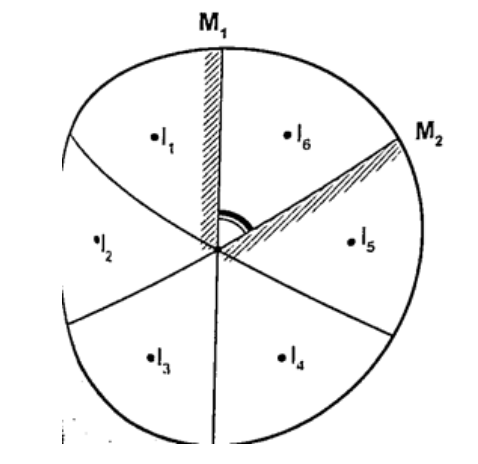
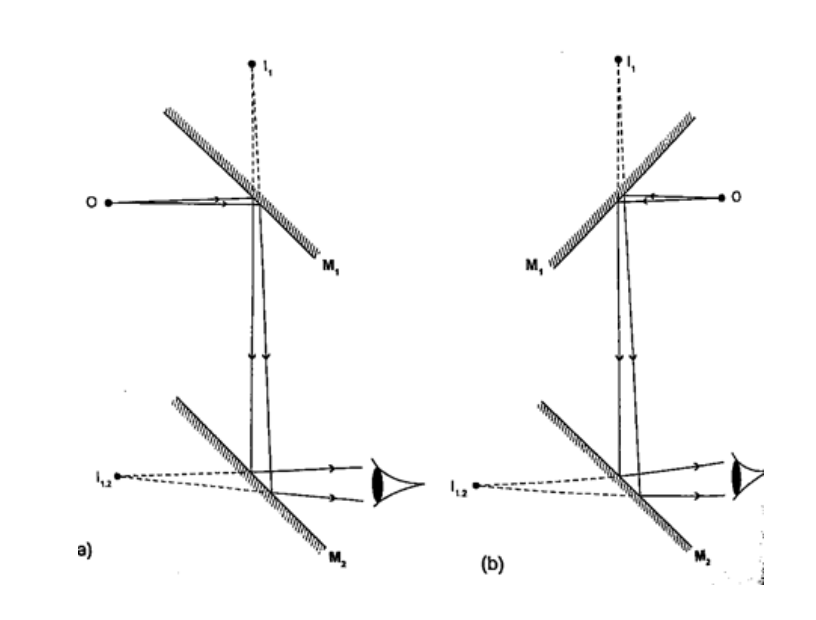
Mirrors at an angleWhen mirrors are placed at an angle several images are obtained depending on the angle between them. If the angle is 600 the images formed will be five. We use the following formula to find the number of images
n = (3600 / θ) – 1 When mirrors are parallel then the images formed are infinite. KaleidoscopeIt applies the principle of mirrors at an angle. Consists of two mirrors arranged at an angle of 600 to one another inside a tube. The bottom has a ground-glass plate with brightly coloured glass for allowing light. When one observes through the tube five images are seen.The periscopeThis consists of two mirrors arranged at an angle of 450 as shown. This principle is used in periscopes (prisms) and telescopes.
1 Comment
Brian mbuvi
27/2/2023 20:36:46
Very good and important
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
Physics notes form 1 to 4
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed