Mastering KCSE Biology with Comprehensive Topical Questions and Answers
(a) Describe the mechanism of inhalation in man. (10mks)
External intercostals muscles contract; internal intercostals muscle relax, Rib cage move outwards; and upwards; Diaphragm muscles contract, Diaphragm flatten; volume in thoraci cavity increases; pressure reduces.
Atmospheric air enters the lungs; inflate (correct sequence to be followed) (b) Using photosynthesis theory explain the mechanics of opening of stomata. (10mks)
Guard cells have chloroplast which photosynthesis in the presence of light, to form sugar, the osmotic pressure of guard cell increases; water move from neighbouring cells into guard cells being thicker than outer walls. Causes the outer wall to stretch more resulting guard cells budging outwards.
0 Comments
State the importance of breathing through the nose than through the mouth. (2mks)
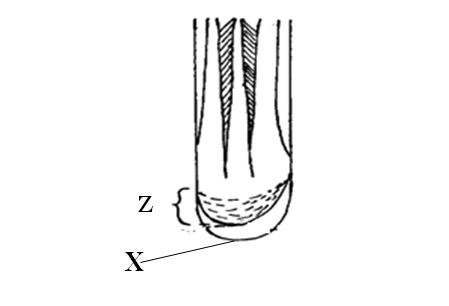
Study the diagram below and answer the following questions.(a) (i) Identify the part labelled X (1mk)
Root cap;
(iii) State the function of part X above (1mk)
Protects the root tip from mechanical damage/abrasive effects of the soil particles as it grows
(b) List down two characteristics of cells in the region labelled Z (2mks)
Gaseous Exchange Questions and Answers1. 1992 Q11 P1 The diagram below represents an organ from a bony fish. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow (a) Identify the organ and the parts labelled M, N, and P
M________________ N________________ P________________ (b) How the structures are labelled P adapted to their function? 2. 1994 Q14 P1 What are the characteristics do gills of a fish and the mouth cavity of a frog have in common that enables them to be efficient in gaseous exchange? 3. 1996 Q14 P1 (a) Describe the path taken by carbon dioxide released from the tissue of an insect to the atmosphere (3 marks) (b) Name two structures used for gaseous exchange in plants (2 marks) 4. 1998 Q4 P1 Why are gills in fish highly vascularised? 5. 1999 Q5 P1 Suggest three reasons why green plants are included in a fish aquarium. 6. 1999 Q16 P1 Describe the: a) Process of inhalation in mammals. b) Mechanisms of opening and closing of stomata in plants. 7. 2000 Q11c P1 State two ways in which the leaf is suited to gaseous exchange 8. 2001 Q10 P1 Name three sites where gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial plants. 9. 2002 Q9 P1 Name two gaseous exchange structures in higher plants. 10. 2003 Q13 P1 The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
a) Name the gas that diffuses: i) To the body cells ii) From the body cells b) Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) (i) above? c) i) What is tissue fluid? ii) What is the importance of tissue fluid? K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN22
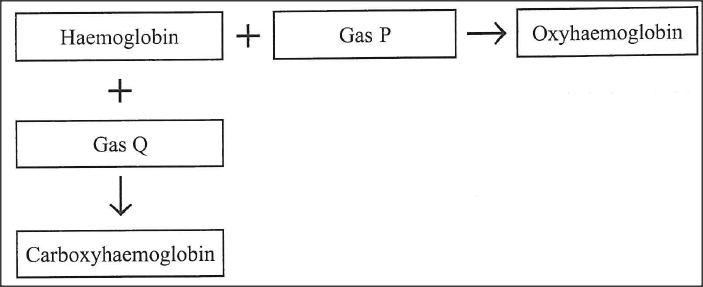
The chart below illustrates how respiratory gases are transported in the human blood.
(a) Identify gas Q.
(b) Explain the advantage oxyhaemoglobin has over carboxyhaemoglobin.
answers
(a) carbon(ii) oxide acc. CO
(b) Oxyhaemoglobin is unstable/fully dissociate, releasing oxygen to the tissues/dissociate giving haemoglobin free to take up more gaseous molecules(hence constantly supplying the much needed oxygen to the respiratory tissues); carboxyhaemoglobin is stable/binds itself on the haemoglobin molecules /does not dissociate ,hence starving the tissues/cells of the oxygen ,leading to suffocation/death
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN15
State the significance of transpiration to a plant.
answers
(b) enable the plant to get rid of excess water
Creates a suction force /help in the uptake of water /mineral/salts from the soil Maintains turgor in plants/turgidity in cells Cools the plant K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN08
State the role of each of the following in the mammalian respiratory system:
(a) mucus (b) cartilage rings (c) epiglottis
answers
.(a) trap foreign particles (from the inhaled /entering air); moisten the (inhaled/incoming) air (for efficient gaseous exchange);
(b) keep the wind pipe /trachea open / not to collapse (to allow for continuous flow of air); (c) acts as a valve / flap between the larynx and the oesophagus to permit air to enter the air way to the lungs and food particles to pass into the gut / oesophagus: acc prevent food particles from entering the trachea /air passage during swallowing; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN09
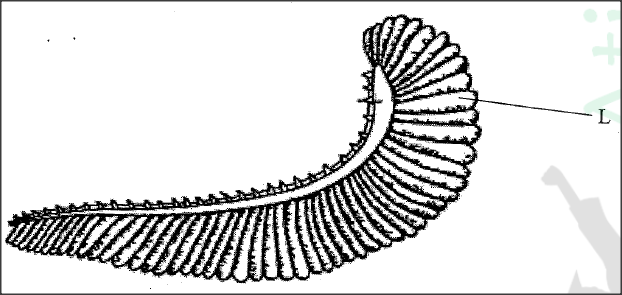
The diagram below represents an organ in a bony fish
(a) Name the organ.
(b) Describe how air in water reach the capillaries inside structure L.
ANSWERS
a) Gill;
b) Fish mouth opens lowering pressure in buccal cavity and water rushes in; mouth closes increasing pressure that forces water into the gill cavity/opercular cavity; O2 rich water flows over the gills in a counter current direction to capillary blood flow; causing O2 to diffuse into the gill capillaries;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN10
State two structural adaptations of leaves that maximize efficiency in gaseous exchange
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN10
State the effect of movement of the diaphragm muscles during inhalation in mammals.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN04
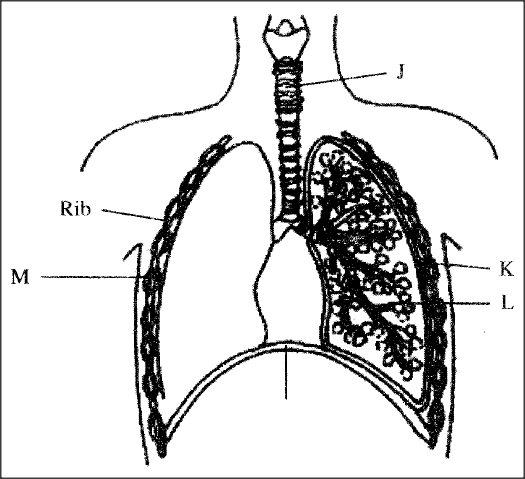
The diagram below represents some gaseous exchange structures in humans.
(a)Name the structures labeled K, L and M.
(b) How is the structure labeled J suited to its function? (c) Name the process by which inhaled air moves from the structure labeled L into blood capillaries. (d) Give the scientific name of the organism that causes tuberculosis in humans.
ANSWERS
(a) K- Pleural membranes
L- Alveolus M- Intercostal muscles (b) Has C- shaped cartilage rings that support it preventing it from collapsing and allow free flow of air Inner lining has mucus secreting cells that trap fine dust particles and microorganisms Inner lining has hair like structures called cilia that enhance upward movement of the mucus to the larynx (c) Diffusion (d) Mycobacterium tuberculosis (underline separately). Explain why it is not advisable to be in a poorly ventilated room with a burning charcoal stove.30/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN019
Explain why it is not advisable to be in a poorly ventilated room with a burning charcoal stove.
answer
Charcoal in limited supply of air produces carbon(ii) oxide, which combines with haemoglobin forming Carboxylhaemoglobin which is a stable compound and does not dissociate easily, reducing capacity of the haemoglobin to carry oxygen leading to suffocation hence death
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN09
What is the effect of contraction of the diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN09
Name two structures for gaseous exchange in aquatic plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN01
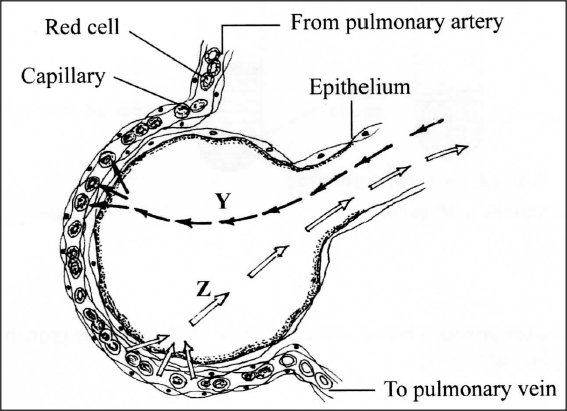
The diagram below illustrates a blood capillary surrounding a structure for gaseous exchange in human beings.
(a) Name the gaseous exchange structure.
(b) Identify the gases labelled Y and Z. Y Z (c) How does the gas labelled Y reach the inside of the blood capillary? (d) How does cigarette smoking lead to lung cancer?
ANSWERS
.(a) Alveolus;
(b) Y - oxygen/O2; Z - Carbon (IV) Oxide/CO2; (c) Oxygen concentration is lower in the blood capillary than in the alveolus; oxygen diffuses; through the epithelium and endothelium of capillary wall, plasma into the red blood cells where it combines with haemoglobin. (d) Cigarettes/tobacco contains tar; tar contains carcinogenic substances; which trigger cancer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN11
Name two structures used for gaseous exchange in plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN07
How is a guard cell structurally adapted for gaseous exchange?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN03
(a) Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in plants through the lenticels.
(b) Explain each of the following: (i) the tracheoles lack spiral bands of chitin; (ii) the floor of the mouth is lowered during inhalation in a bony fish.
answers
(a) O2, concentration is higher outside than inside the lenticels; O2, diffuses into lenticels; then into the cells; CO2 concentration is higher inside the lenticels than on the outside CO2 diffuses out of the lenticels into the atmosphere;
(b) (i) To provide a large surface area! make them thin; for gaseous exchange to reduce diffussion distance for respiratory gases; (ii) This increases the volume of the buccal cavity while decreasing the pressure; which forces water to rush into the mouth; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN27
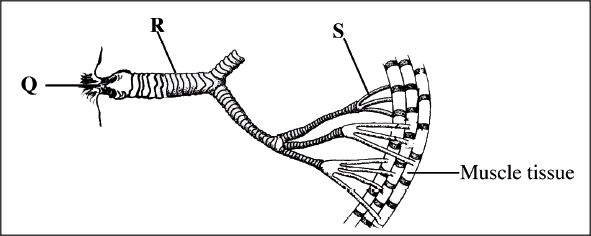
The diagram below shows the gaseous exchange system of a locust.
(a) Name the structure labelled Q.
(b) State the function of the part labelled R. (c) How is the part labelled S structurally adapted to its function?
ANSWERS
(a) Spiracle;
(b) Keep the trachea open for air passage; (c) Lacks spiral bands of chitin /to make it thin; for diffusion of gases; Moist; to dissolve respiratory gases;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN19
Why is a burning charcoal stove in a poorly ventilated room likely to cause death of the inhabitants?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN12
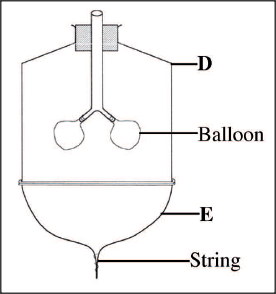
The diagram below represents a model used to demonstrate breathing in mammals.
(a) Name the mammalian structure represented by the parts labelled D and E.
(i) D . (ii) E (b) State the observation made when the string is pulled downwards. (c) Explain the observation in (b) above.
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Rib-cage/chest cavity;
(ii) Diaphragm; (b) The balloons are inflated; (c) Pulling down the string increases the volume of D, hence decreasing the pressure inside: The low pressure causes external atmospheric air to rush in and inflate the balloons;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN07
How are respiratory surfaces in mammals adapted to their functions?
ANSWERS
Many to provide a large surface area: across which large amounts of gases diffuse: moist surfaces: to dissolve respiratory gases: so as to diffuse. Made of a thin membrane/epithelium/one cell thick wall ; to reduce diffusion distance;
Highly vascularized: to carry away oxygen; and bring in carbon (IV) oxide: creating a steep diffusion gradients.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN10
How are lenticels adapted for gaseous exchange?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN05
Explain the mechanism of stomatal opening.
answers
The osmotic pressure of guard cells increase when sugar is manufactured during photosynthesis/starch is converted to sugar in low acidity/potassium moves into guard cells during the day; water enters guard cells from the surrounding cells by osmosis; because the guard cells are bean shaped with thin outer walls and thick inner walls, the thin outer walls expand faster as the cell becomes turgid; thus the thick inner wall curves; causing the stomatal aperture to open.
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed