GENETICS: KCSE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON TOPIC1. 1989 Q13 P1 In an experiment, a variety of garden peas having a smooth seed coat was crossed with a variety with a wrinkled seed coat. All the seeds obtained in the f generation had a smooth seed coat. The f generation was selfed. The total number of f2 generation was 7324. (a) Using appropriate letter symbols. Work out the genotype of the f1 generation (b) From the information above, work out the following for the f2 generation 2. 1990 Q2 P1 The figure below is a structural diagram of a portion from anucleic acid stand. -----S – P – S – P – S – P – S ----- C G U C (a) Giving a reason, name the nucleic acid to which the portion belongs (b) Write down the sequence of bases of a complementary strand to that show above 3. 1990 Q12 P1 A garden pea plant having green round seeds was crossed with another garden pea plant having yellow wrinkled seeds. The seeds produced in the f1 generation were all green and round (a) State the dominant traits in these plants (b) If D and d represents genes that determine seed colour, while T and T represents genes that determines seed texture; (i) Give the genotype of each parent plant (ii) Give a reason for your answer (b) (i) above (iii) Work out the genotypes of the F1 generation. (iv) In the table below, work out the progeny between the F1 generation and a plant having yellow wrinkled seeds (v) What was the phenotypic ratio of the progeny in (b) (iv) above? 4. 1991 Q13 P1 In a certain birds species, the spotted pattern of feathers is controlled by a dominant gene B, and the plain pattern by a recessive gene b. Red colour of the legs is controlled by a dominant gene R and brown colour by a recessive gene r If a homozygous spotted red legged bird was crossed with a plain feathered brown legged bird, what are:- (a) (i) The parental genotype? (ii) The gametes produced by these parents (iii) The genotypes and phenotypes of F1 generation. (b) Using a punnet square, work out the cross between two F1 individuals and show the phenotype ration of the F2 generation. 5. 1992 Q14 P1 (a)Write the base sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA) that would be coded from the DNA strands shown below. C – A – T – G – A – G – T (b) What is mutation? (c) Name two types of chromosomal mutation (d) State two factors that may cause mutation (e) What is the significance of chlasma formation during melotic cell division 6. 1993 Q12 P1 In a certain plant species, some individual plants may have only white, red or pink flowers. In an experiment a plant with white flowers was crossed with red flowers. The parent plants were pure lines. All the plants from F1 generation were pink. Using letter R to represent the gene for the red colour and letter W for white colour. (a) Work out the genotype of F1 generation. (b) If the plants from F1 generation were selfed, what would be the phenotypic ration of the F2 generation?. (c) What is the genetic explanation for the absence of plants with red and white in the flowers F1 generation? 7. 1994 Q11 P1 State two structural differences between ribonucleic acid (RNA) and Deoxyribonucleic (DNA). 8. 1995 Q9 P1 Name a disorder of human blood that is caused by mutation. 9. 1996 Q1 P1 State the function of Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule (1 mark) 10. 1996 Q18 P1 In an experiment black mice were crossed and the offspring were back and brown. The gene for black colour is dominant over that of brown colour. Using letter B to represent the gene for black colour and b to represent the gene for brown colour (a) Work out the genotypes of the F1 generation (4 marks) (b) What is the phenotype ration of the spring (1 mark) 11. 1997 Q16 P1 In a breeding experiment, plants with red flowers were crossed. The produced 123 plants with red flowers and 41 with white flowers (a) Identify the recessive character Give a reason (b) What was the genotype of the parent plants that gave rise to the plants with a red and white flowers? 12. 1998 Q12 P1 In a family with four children, three were found to have normal skin pigmentation while one was an albino. Using letter A to represent gene for normal skin pigmentation and a to represent the gene for albinism, (a) What are the genotypes of the parents? (b) Work out the genotype of (i) Normal pigmentation (ii) The albino child Genotype of normal pigmented children (c )What is the probability that the fifth child will be an albino? 13. 1999 Q7 P1 An investigation plants with red flowers were crossed with plants with white flowers. All the plants in the F1 generation had pink flowers. a) Give a reason for the appearance of pink flowers in the F1 generation. b) If the plants the F1 generation were selfed, state the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation. 14. 2000 Q12 P1 The chart below represents the result of successive crosses, staring with red- flowered plants and white flowed plants and in which both plants are pure breeding. (a) What were parental genotypes? Use letter R to represent the gene for red colour and r for white colour (b) (i) What was the colour of the flowers in the first filial generation? (ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above (c) If 480 red flowered plants were obtained in the second filial generation, how many F2 plants and white flowers? Show your working. 15. 2001 Q9 P1 Name three types of chromosomal mutations 16. 2001 Q14 P1 Tallness in pea plants is due to a dominant gene.Two tall pea plants were crossed and their F1 generation were in the ratio of 3 tall: 1 short. Using letter T to represents the gene for tallness and t for shortness give the (a) (i) Genotype of the parents (ii) Gamete of the parents (iii) Genotype ratio of the F1 generation (b) What is meant by the term testcross in genetic studies? 17. 2002 Q5 P1 State two characters that researchers select in breeding programme. 18. 2002 Q11 P1 Give an example of a sex – linked trait in humans on: Y CHROMOSOME. X CHROMOSOME. a) What is meant by the term sex – linkage? b) Name two sex – linked traits in humans. c) In Drosophila Melanogaster, the inheritance of eye colour is sex – linked. The gene of red eye is dominant. A cross was made between a homozygous red – eyed female and a white – eyed male. Work out the phenotypic ration of F1 generation. (Use R to represent the gene for red eyes). 19. 2004 Q12 P1 Across between a red flowered plant and white flowered produced plants with pink flowers. Using letter R to represent the gene for red colour, and W for white colour a) What were the parental genotypes (1 mark) b) Workout a cross between F1 plants (4 marks) c) Give the i) Phenotypic ratio of F2 plants (1 mark) ii) Genotypic ratio of F2 plants (1 mark) d) Name a characteristic in humans, which is controlled through a mammalian heart? 20. 2005 Q12 P1 In a garden with plants of same species, 705 plants had red flowers while 224 had white flowers. a) Work out the ratio of red to white flowered plants (1 mark) b) (i) Using letter R to represent the dominant gene, work out a cross between F1 offspring and a white flowered plant. (4 marks) (ii) What is the genotypic ratio from the cross in b(i) above? (1 mark) c) What is meant by the term allele? (1 mark) 21. 2006 Q2 P2 a) Name two disorders in human caused by gene mutation. (2 marks) b) Describe the following chromosomal mutations. (2 marks) a. Inversion b. Translocation. c) In mice the allele for black fur is dominant to the allele for brown fur. What percentage offspring would have brown fur form across between heterozygous black mice? Show your working. Use letter B to represent the allele for black colour. (4marks) 22. 2007 Q20 P1 (a) What is meant by the term allele? (1 mark) (b) Explain how the following occur during gene mutation: (i) Deletion (1 mark) (ii) Inversion (1 mark) (c) What is a test- cross? (1 mark) 23. 2007 Q5 P2 In maize the gene for purple colour is dominant to the gene for white colour. A pure breeding maize plant with purple grains was crossed with a heterozygous plant. (a) (i) Using letter G to represent the gene for purple colour, work out the genotype ratio of the offspring (5 marks) (ii) State the phenotype of the offspring (1 mark) (b) What is genetic engineering? (1 mark) (c) What is meant by hybrid vigour? (1 mark) 24. 2008 Q6 P1 (a) What is meant by non- disjunction? (1 mark) (b) Give two examples of continuous variation in humans (2 marks) 25. 2008 Q2 P2 A pea plant with round seeds was crossed with a pea plant that had Wrinkled seeds the gene for round seeds is dominant over that for wrinkled seeds Using letter R to represent the dominant gene state: (a) The genotype of parents if plant with round seed was heterozygous (2 marks) (b) The gametes produced by the round and wrinkled seed parents Round seed parent Wrinkled seed parent (c) The genotype and phenotype of F1 generation. Show your working (3 marks) (d) What is a test – cross? (1 mark) 26. 2009 Q5 P1 (a) What is meant by the following terms? (i) Hybrid vigour (1 mark) (ii) Polyploidy? (1 mark) (b) State two causes of chromosomal mutations (2 marks) 27. 2010 Q10 P1 State two advantages of hybrid vigour. (2 marks) 28. 2010 Q27 P1 a) What is meant by the term non-disjunction? (1 mark) b) Give an example of a genetic disorder caused by: i) Non-disjuction; (1 mark) ii) Gene mutation ( 1 mark) 29. 2010 Q5 P2 When pure breeding black guinea pigs were crossed with pure breeding white guinea pigs, the offsring had a coat with black and white patches. a) Using letter G to represent the gene for black coat colour and letter H for white coat colour, work out the genotypic ratio of F2. b) State the phenotypic ratio of F2. (1 mark) c) i) Name the term used when two alleles in heterozygous state are fully expressed phenotyically in an organism. (1 mark) ii) Give an example of a trait in human beings where the condition whose term is named in (c) (i) above expresses itself. (1 mark) 30. 2011 Q24 P1 (a) Differentiate between the following terms: (i) dominant gene and recessive gene (1 mark) (ii) Continous variation and discontinuous variation (1 mark) (b) What would be the expected results from a test cross? (2 marks) 31. 2011 Q2abc P2 In humans, hairy ears is controlled by a gene on the Y chromosome. (a)Using letter YH to represent the chromosome carrying the gene for hairy ears, work out a cross between a hairy eared man and wife. (4 marks) (b) (i) What is the probability of the girls having hairy ears? (1 mark) (ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above (1 mark) (c) Name two disorders in humans that are determined by sex-linked genes. (2 marks) 32. 2012 Q1 P2 In a certain plant species which is normally green, a recessive gene for colour (n) causes the plants to be white in colour. Such plants die at an early age. In the heterozygous state, the plants are pale green in colour but grow to maturity. (a) Give a reason for the early death of the plants with the homozygous recessive gene. (2 marks) (b) If a normal green plant was crossed with the pale green plant, what would be the genotype of the first filial generation (F1 generation)? Show your working. (4 marks) (c) If heterozygous plants were self-pollinated and the resulting seeds planted, work out the proportion of their offspring that would grow to maturity. (2 marks) 33. 2012 Q8 P1 What is the probability of a couple with blood group AB getting a child with blood group AB?
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
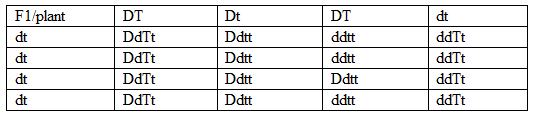
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
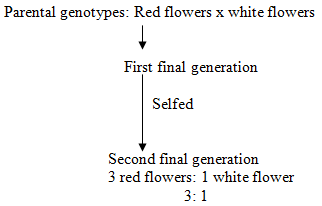
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

