Mastering KCSE Biology with Comprehensive Topical Questions and Answers
|
What is the significance of transpiration in plants? (3mks)
0 Comments
(a) What are meristems? (1mk)Regions of plants where active cell division and differentiation takes place. (b)(i) What is the role of cork-cambium in secondary growth? (1mk)Form the bark of the stem (ii) Name the meristem that is responsible for increase in length of stems (1mk)apical meristem K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN28
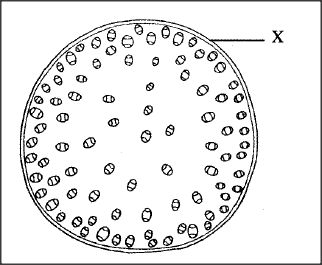
The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ
(a) Name the plant organ from which the section was obtained.
(b) (î) Name the class to which the organism from which section was obtained belongs. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above. (c) Name the part labeled X
answers
(a) Stem
(b) (i) Monocotyledonae (ii) Vascular bundles are scattered and not arranged in a ring Absence of pith/ cambium (c) Epidermis K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN23
Below is an illustration of a cross section of a plant root showing the transportation of substances in the plant.
(a) Name the substances transported along the paths labelled K and L.
K L (b) Give a reason for your answer in L above.
ANSWERS
(a) K - Photosynthetic products/manufactured foods example vitamins/alicose/proteins/sucrose/maltose/fructose/lipids/nitrates;
L - Water and mineral salts; (b) The substances are moved into the star shaped xylem;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN25
State one adaptation of xylem vessels to their function.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN07
Explain how the following forces contribute to the movement of water up the xylem vessels:
(a) cohesion; (b) adhesion.
answers
(a) Water molecules cling to each other maintaining a continuous column of water/preventing the break of water column;
(b) Water molecules cling to the sides of the xylem vessel walls;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN18
Why are plants able to accumulate most of their waste products for long?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN04
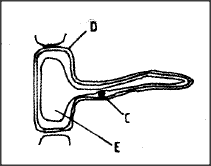
The diagram below shows a specialized plant cell.
(a) (i) Name the cell.
(ii) Name the parts labelled D and E. D E (b) State the function of the part labelled C.
answers
(a)(i) Root hair cell;
(ii) D—cell wall; E — cellsap vacuole; (b) Controls the functioning of the cell; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN02
The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ.
(a) Name the plant organ from which the section was obtained.
(b) (i) Name the class to which the plant organ was obtained. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b)(i) above. (c) Name the part labelled X.
answers
(a) Stem:
(b) (i) Monocotyledonae; (ii) Vascular bundles scattered/not arranged in a ring (c) Epidermis; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN05
Name a support tissue in plants thickened with
(i) Cellulose (ii) Lignin
answers
(i) Collencyma
(ii) Xylem/ tracheid/ vessels/ schlerencyma
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN05
what happens when a wilting young plants is well watered
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN29
Explain why the rate of transpiration is reduced when humidity is high
answers
State two ways in which aerenchyma tissues in aquatic plants are adapted to their function23/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN25
State two ways in which aerenchyma tissues in aquatic plants are adapted to their function
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN15
Name the type of movement that occurs within a plant cell
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN14
Name a support tissue in plants that is not thickened with lignin
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN06
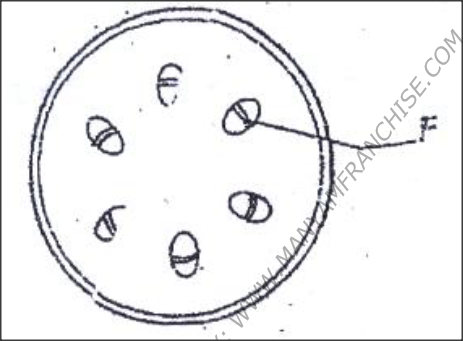
The diagram below shows a section through a plant organ
(a) (i) Name the class of the plant which the section was obtained
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above (b) State the functions of the part labeled F
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Dicotyledonous; Rej: Dicotyledonous
(ii) Vascular bundles arranged in a ring / presence of vascular (b) (Divides to) give rise to secondary thickening (growth/ increase in growth/ diameter/ width of stem/ gives rise to new/ additional xylem and phloem tissues K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN01
Name the tissues in plants responsible for:
(a) Transport of water and mineral salts (b) Transport of carbohydrates (c) Primary growth
ANSWERS
(a) xylem
(b) Phloem (c) Apical meristems
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2007PP1QN09
State two ways in which the root hairs are adapted to their function
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN08
Describe how water moves from the soil to the leaves in a tree.
answers
Water exists as a thin film in the soil between soil particles. The concentration cell sap is greater than that of the surrounding solution in the soil; Thus drawing water molecules across the cell wall and membrane into the root hair cells; by osmosis; water drawn into the root hair cell dilutes the cell sap/ makes it less concentration than that in the adjacent cell into the cortex cells. (By osmosis); across the endosperm by active transport; into the xylem vessels (of the root); Then conduct the water up into the xylem (vessels) of the stem; into xylem of leaves. Water is pushed/ rises up the stem by root pressure ( in the xylem vessels) water would rise by capillary; cohesion, and adhesive forces; water moves as a continuous an uninterrupted water column in the xylem (vessel) up the tree to the leaves. As water vaporizes from the spongy mesophyll cells; their cells sap becomes more concentrated than adjacent water flows into the cells from other surroundings cells; which in turn takes in water from xylem vessels within the leaf veins. This creates a pull / suction force/ transpiration pull that pulls a stream of water from xylem vessel in the stem and roots; the transpiration pull maintains continuous column of water from the roots into the leaves (transpiration stream).
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN04
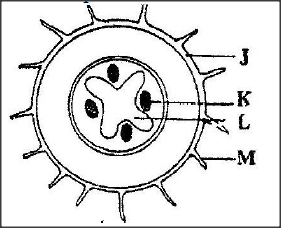
The diagram below represents a traverse section through a plant organ
A. From which plant organ was the section obtained?
B. Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. C. Name the parts labeled J,K and L. D. State two functions of the part labeled M.
answers
(a) Root
(b) Presence of root hairs Presence of endodermis Xylem star shaped at centre Phloem at arms of the xylem (c) J- Epidermis K- Phloem L – Xylem (d) - Absorption of water Absorption of minerals salts
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN03
Name two tissues in plants which are thickened with lignin.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN14
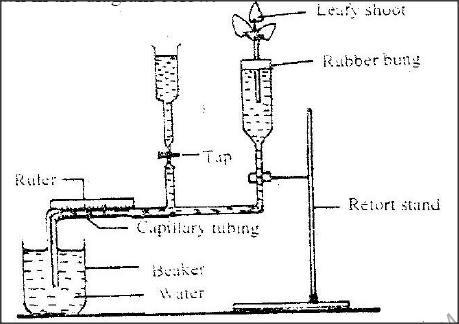
A set up that was used to investigate certain process in plants is shown in the diagram below.
a) What process was being investigated?
b) (i) State two precautions that should be taken when setting up the experiment. (ii) Give a reason for each precaution stated in b(i) above. c) State three environmental factors that influence the process Under investigation.
answers
a) Transpiration
b)i) The leafy shoot should be from herbaceous plant Cut off the last few centimeters of the stalk under water All the air in the capillary tubule should be expelled Jelly should be applied around the stem around the rubber bung. The end of the capillary fusing should rest in beaker of water. ii) Avoid air bubbles. For continuity of the flow of water Jelly should not touch the xylem vessels because it might block they xylem. To avoid introduction of air bubbles in the xylem. For continuity of water uptake. c) Temperature Humidity Wind Atmospheric pressure Light intensity Availability of water
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN10
How are the xylem vessels adapted for support?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN09
Name the:
a) Material that strengthens xylem tissue. b) Tissue that is removed when the bark of a dicotyledonous plant is ringed.
answers
a) lignin
b) Phloem |
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed