Mastering KCSE Biology with Comprehensive Topical Questions and Answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN03
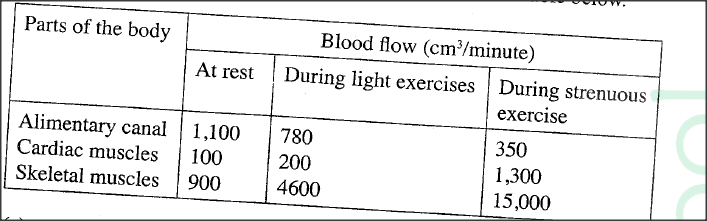
The amount of blood flowing tough certain pans in the mammalian body at different activity levels was measured and results tabulated as Shows in the table below.
(a) Account for:
(i) the high blood flow through the cardiac and skeletal muscles during strenuous exercises. (ii) the results obtained for the alimentary canal at rest. (b)Name two waste materials excreted by both the skin and the kidneys.
answers
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN25
Desert kangaroo rats spend most of their time in underground burrows,
(a) Name this type of behavioral activity (b) Explain the significance of this behaviour to the organism.
answers
(a) Aestivation;
(b) Reduced metabolic activity; hence low rate of respiration; minimizing water loss/dessication (to the environment);
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN08
Describe how the mammalian eye is structurally adapted to its function.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN23
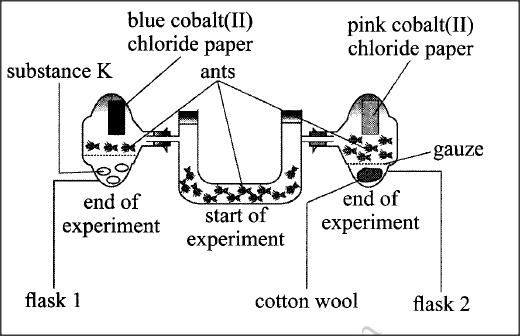
The diagram below represents a set up during an experiment.
(a) (i) What was, the experiment investigating?
(ii) State the likely identity for substance K (iii) Explain your answer in (a) (ii) above (b) Account for the observations made in flask 2.
answers
a.) i) To investigate how ants respond to moisture/water hydrotaxis (varied environments with/without moisture water);
ii) Silica gel/anhydrous calcium chloride pellets/pyrogallic acid/dehydrating drying agent; iii) The colour of cobalt (II) chloride paper remained blue/all the moisture water vapour was absorbed/There was no water/moisture in the flask to change the colour of cobalt(II) chloride paper; b.) (More) ants were attracted) moved into the flask; due to the presence of moisture/water vapour; (evidenced by the change of cobalt (II) chloride paper to pink) K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN12
Explain the survival values of the following tropic responses to plants.
(a) Geotropism (b) Phototropism
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN07
Using a relevant example in each case, describe simple and conditional reflex actions.
answers
Simple reflex action eg. withdrawal of finger from a sharp object/ hot object; its an automatic response to a specific stimulus; when the finger touches sharp object/ hot object, the pain receptors/ thermoreceptors in the skin are stimulants; and trigger off a nerve impulse; the nerve impulse is transmitted via the senses neurone; to the grey matter of the spinal cord/ CNS/ brain; the impulse is then transmitted via synapse; to the relay neurone; and then through another synapse; to the motor neurone; and then through another synapse; to the motor neurone; the impulse is then transmitted to the effector muscles in the hand; ace - efferent neurone for motor neurone Afferent neurone for sense neurone intermediate/ associative/ connector/interauncial neurone - for relay. The effector muscles/ biceps contract; and the finger is withdrawn from the hot object/ sharp object;
Conditioned reflex action - salivation in a dog/ human being (ace. any other relevant example) student in response to sound; it is an automatic response evoked from an animal by unrelated stimulus; substituted for the one which normally elicits the response; it develops from a past experience; and involves modification of behaviour/involves learning; it weakens with time; and must be reinforced by repeating the related stimulus; the dog/ student salivates when the bell (for meals) rings; because they have learnt to associate the ringing of the bell at meal time with food; everytime it rings (accept use of other relevant examples) they are offered food. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN05
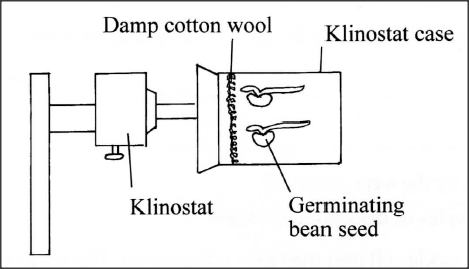
In an experiment to investigate a plant response, the set up shown in the diagram below was used.
(a) Name the type of response that was being investigated.
(b) If the Klinostat was not rotating: (i) state the observations that would be made on the seedlings after three days; (ii) explain the observations in (b) (i) above. (c) If the experiment was repeated with the Klinostat rotating: (i) state the observation that was made on the seedlings after three days; (ii) give a reason for the observation made on the seedlings.
ANSWERS
(a) Geotropism/Gravitropism;
(b) (i) The shoot tip/plumule curved upwards; root tip/radicle curved downwards; (ii) Auxins migrated downwards to lower side; Higher concentration on the lower side; caused more growth on the lower side than on the upper side in shoots inhibited growth on the lower side than on the upper side in the roots; (c) (i) The seedling will continue growing horizontally; (ii) There was even distribution of auxins (on the tips); K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN20
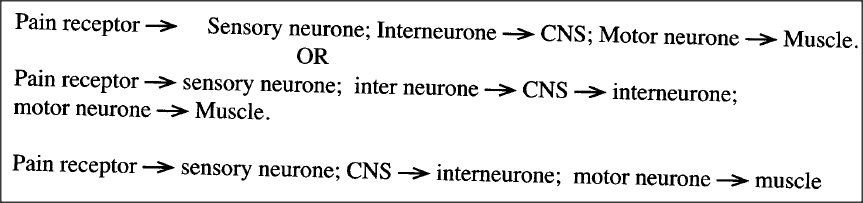
Below are components of a simple reflex pathway:
List the components in their proper sequence during the transmission of a nerve impulse.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN14
Name two types of involuntary muscles in mammals.
b)State the location of each of the muscles named in (a) above.
answers
Cardiac muscles - heart K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN05
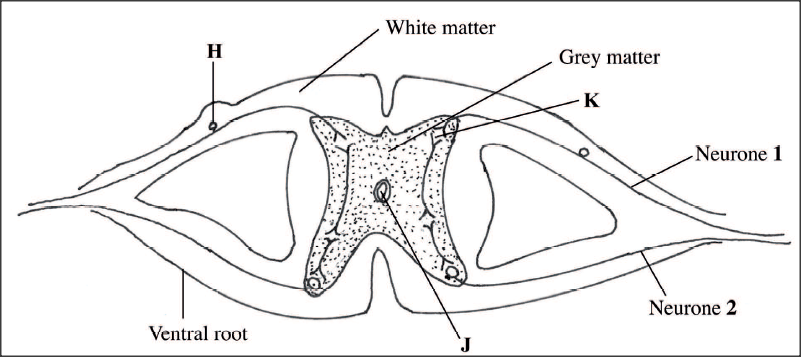
The diagram below represents the transverse section of the spinal cord.
(a) Name the part labelled H.
(b) State two functions of the fluid found in the part labelled J. (c) Give a reason for the colour of white matter. (d) Name and give the function of the enzyme found at the part labelled K. Name Function (e) On the diagram, use an arrow to show the direction of impulse transmission along the neurone labelled 1.
answers
(a) H - cell body;
(b) Has nutrients for nourishment of neurons, brain, spinal cord; Acts as a shock absorber for protection of spinal cord from mechanical damage; (c) Contains myelin sheaths (of neurons which are made up of fats that make it have a shiny white appearance); (d) Cholinesterase: Breaks down Acetyicholine; to acetic acid and choline; (e) Correct arrow on neurone 1 points towards the grey matter;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN17
Give a reason why the image is not formed when light is focused on the blind spot.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN16
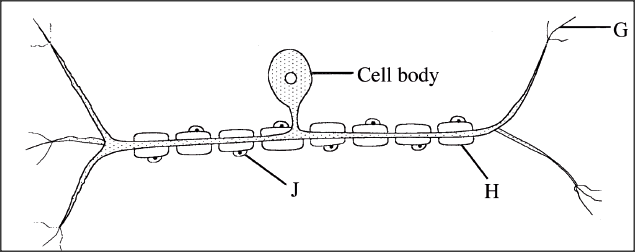
The diagram below illustrates a nerve cell.
(a) Name the type of nerve cell illustrated.
(b) Give a reason for your answer in (a) above (c) identify the part labelled J (d) State one function of each of the parts labelled G and H. (i) G (ii) H
ANSWERS
(a) Sensory neurone;
(b) Cell body is located off the axon/tied outside the CNS; (c) Schwann cell; (d) (i) Receipt/transmits impulses to neighbouring neurons in the CNS from sense organs; (ii) Insulates the axon/accept dendron for axon; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN13
State one function of each of the following parts of a mammalian eye:
(a) eye lashes (b) lachrymal glands.
ANSWERS
(a) Trap foreign particles entering the eye;
Produce fluid/tears; (b) Moistens the cornea; Wash foreign materials out of the eye; Antiseptic / kills harmful microorganisms; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN11
State three differences between tactic and tropic responses.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN02
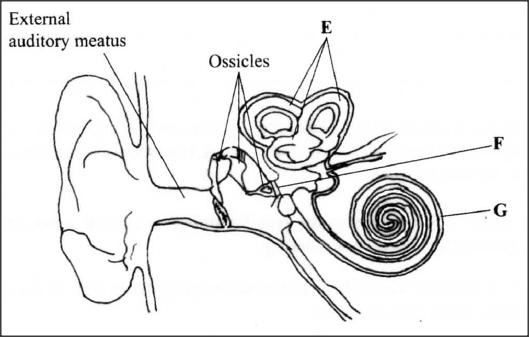
The diagram below represents the human ear.
(a) Name the parts labelled E, F and G.
E F. (b) How is each of the following adapted to its function? (i) External auditory meatus; (ii) Ear ossicles. (c) Name one defect of the human ear.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN23
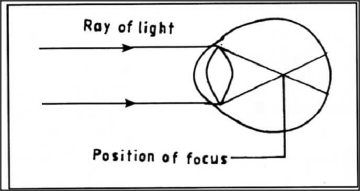
The diagram below illustrates a defect in the eye.
Explain how the defect illustrated above can be corrected.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN07
Using a relevant example in each case, describe simple and conditional reflex actions.
ANSWERS
Simple reflex action - withdrawal of finger from a sharp object.
Is an automatic response to a specific stimulus; When the finger touches a sharp object, pain receptors in the skin; are stimulated and trigger off a nerve impulse; The nerve impulse is transmitted via the sensory neuron; to the grey matter of the spinal cord; The impulse is then transmitted via a synapse; to the relay neuron; and then through another synapse; to the motor neuron; The impulse is then transmitted to the effector muscles in the hand; These effector muscles contract; and the finger is withdrawn from the hot object; Conditioned reflex action Is an automatic response evoked from an animal by unrelated stimulus; substituted for the one which normally elicits the response; It develops from past experience; and involves modification of behaviour through learning; It weakens with time; and must be reinforced by repeating the unrelated stimulus; Students salivate when the bell for lunch rings; because they have learned to associate the ringing of the bell at lunchtime with food; from experience; every time it rings, they are offered food;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN09
State the importance of negative phototaxis to termites.
answer
Describe how accommodation in the human eye is brought about when focusing on a near object.25/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN08
Describe how accommodation in the human eye is brought about when focusing on a near object.
answers
Light rays from a near object are more diverged and need to bend more; in order to be focused properly on the retina; ciliary muscles contract; suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary muscles relax; the lens becomes thicker; increasing its curvature/becomes more convex; light from the object is refracted more; in order to be focused/more sharply on the retina to form an image.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN28
What is a tropic response?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP2QN04
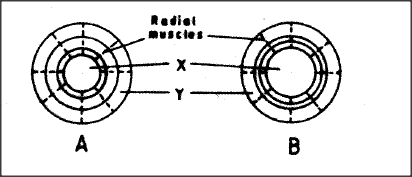
The diagram below shows how the iris and pupil of a human eye appear under different conditions..
(a) Name the structures labelled X and Y.
X Y (b) (i) State the condition that leads to the change in appearance shown in the diagram labelled B. (ii) Describe the changes that lead to the appearance of the iris and pupil as shown in the diagram labelled B. (iii) What is the significance of the changes described in (b) (ii) above?
ANSWERS
(a) X Pupil;
Y Circular muscles; (b) (i) Dull/dim light/low light intensity; (ii) Circular muscles (in iris) relax; while radial muscles contract; the pupil becomes bigger; allowing more light to enter the eye; (iii) Allows one to visualize objects/see under dim light; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN26
State one survival value for each of the following in plants:
(a) Thigmotropism in stems; (b) Geotropism in roots.
answers
(a) Provides support;
Enables plants to grow towards light; Any one (b) In search of nutrients Anchorage; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN06
State one function for each of the following:
(a) Cerebellum; (b) Medulla oblongata.
answers
(a) Co-ordinates balance;
(b) Controls heart beat/blood pressure/breathing rate; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP2QN04
(a) (i) Explain the changes that take place in the pupil and iris of a human eye when a person moves from a dark room to a room with bright light
(ii) What is the significance of the changes explained in (a) above (b) How does the human eye obtain nutrients? (c) Explain why images that form on the blind spot are not perceived
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed