|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN19
Describe how fruits and seeds are suited to their modes of dispersal.
answers
Water dispersed fruit / seeds
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN18
Describe the functions of the various parts of the human eye.
answers
Sclerotic layer – (made up of collagen fibres thus) protects the eye maintains shape of eyeball.
Cornea
Eyelids
Lens – Refracts light rays / focuses light on retina Vitrerous aqueous humour once. Aqueous Humour – Nourishes cornea / lens Refracts light Irus – ( pigmented thus) – gives the eye its colour / absorbs light controls amount of light entering the eye / adjusts size of pupil impulses. Pupil – light enters the eyes through pupil. Retina – has photoreceptor cells / rods / cones / image formation ;l generates impulses. Fever / yellow spot – visual acuity / most sensitive part of retina with only cones. Blind spot – point where nerve fibre emerges from the optic nerve / where the optic nerve leaves the eye / point where blood vessels & nerve fibres enter the eye. Optic nerve – transmit impulses to brain. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN17
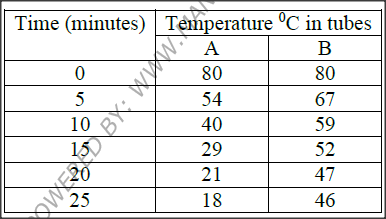
Some students used a model to demonstrate the effect of sweating on human body temperature. Two boiling tubes A and B were filled with hot water. The temperature of water in the tubes was taken at the start of the experiment and then at 5 minutes interval. The surface of tube A was continuously wiped with a piece of cotton wool soaked in methylated spirit. The results obtained are shown in the table below.
a) On the same axes, plot graphs of temperature of water in the tubes against time.
b) At what rate was the water – cooling in tube A? c) Why was tube B included in the set up? d) Account for the rate of cooling in tube A. e) State two processes of heat loss in tube b. f) What would be the expected results if tube A was insulated? g) What would the insulation be comparable to in: i) Bird ii) Mammals? h) Name the structures in the human body that detect: i) External temperature changes ii) Internal temperature changes
answers
b) 80 – 18 = 62; 2.48C /Min
2.5 25 c) Control d) Rate was faster in tube A; because the film of methylated sprit evaporated; removing heat from the tube; e) Convection ; radiation f) Lower rate of heat loss; g) i) birds Feather ii) Mammals? Fur h) i) external temperature changes Temperature ii) Internal temperature changes Hypothalamus
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN16
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN16
a) What is meant by:
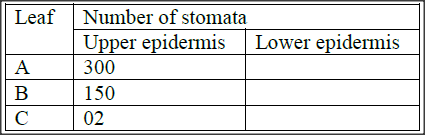
i) Autecology ii) Synecology? b) The number and distribution of stomata on three different leaves are shown in the table below:
Suggest the possible habitat of the plants from which the leaves were obtained
Leaf Habitat A B C (c) State the modifications found in the stomata of leaf C.
answers
a) i) study of a single species within a community / ecosystem /habitat / environment.
ii) Synecology? Study of natural communities within an ecosystem b) Leaf Habitat A aquatic / fresh water B Forest; Terrestrial C Arid / semi arid; desert. c) Sunken Hairy Reserved rhythm Small stomatal pore
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN14
Explain the role of antidiuretic hormone when there is excess water in the human body.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN15
A response exhibited by a certain plant tendril is illustrated below.
a) i) Name the type of response
ii) Explain how the response named in (a)(i) above occurs b) What is the importance of tactic responses to microscopic plants? c) State four applications of plant hormones in agriculture.
answers
a) i) Thigmotropism / haptotropism
ii) Contact with support; causes migration of auxine to enter the side; causing faster growth on the side away from centre of surface (causing tendrils curl around support.) b) Escape injurious stimuli / seek favorable habitats; move towards light / stimuli. c) Induce foot growth in stem cutting
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN14
Explain how marine fish regulate their osmotic pressure.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN13
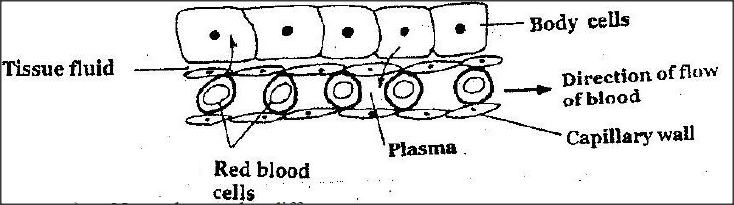
The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
a) Name the gas that diffuses:
i) To the body cells ii) From the body cells b) Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) (i) above? c) i) what is tissue fluid? ii) What is the importance of tissue fluid? d) Name the blood vessel with the highest concentration of: i) Glucose ii) Carbon dioxide
answers
a) i) Oxygen
ii) Carbon dioxide b) Oxyhaemoglobin c) i) The blood plasma except blood cells and proteins; that has filtered out of the capillaries. ii) It is a medium of exchange of substances/ materials between capillaries and body cells; supply nutrients to cells / supply oxygen to cells / remove waste products from cells. d) i) Hepatic portal vein ii) Pulmonary artery K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN12c
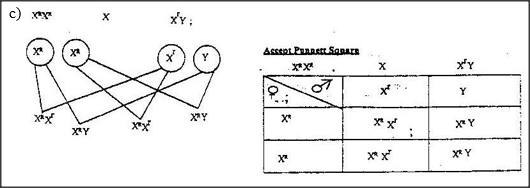
In Drosophila Melanogaster, the inheritance of eye colour is sex – linked. The gene of red eye is dominant. A cross was made between a homozygous red – eyed female and a white – eyed male. Work out the phenotypic ration of F1 generation. (Use R to represent the gene for red eyes).
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN12b
Name two sex – linked traits in humans.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN12
What is meant by the term sex – linkage?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN10
How are leaves of submerged adapted plants for photosynthesis?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN11.
Name the causative agent of typhoid.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN09
Name the:
a) Material that strengthens xylem tissue. b) Tissue that is removed when the bark of a dicotyledonous plant is ringed.
answers
a) lignin
b) Phloem
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN08
State a function of the large intestine in humans
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN07
The diagram below represents regions of a root tip.
a) Name the tow regions above X in ascending order
b) State the function of the part labeled X
answers
a) Zone of cell division Acc cell multiplication
Zone of cell elongation / enlargement; Acc expansion for elongation b) To protect root tip
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN06.
Distinguish between analogous and homologous structures.
answers
Analogous structures – structures which (appear similar and ) perform similar functions but have different origins.
Homologous structures – structures which have a common origin but (have evolved to ) perform different functions. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN05
A bone obtained from a mammal is represented by the diagram below.
a) Name the bone.
b) Which bones articulate with the bone shown in the diagram at the notch?
answers
a) Ulna
b) radius; Humerus;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN04
What is the role of the bacteria named in (a) above?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN04
Name the bacteria found in root nodules of leguminous plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN03
How do the male gamete nuclei reach the ovule after pollen grains land on the stigma?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN02
Name the phylum whose members possess notochord
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN01
A process that occurs in plants is represented by the equation below.
C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + Energy (Glucose) (Ethanol) (Carbon dioxide) a) Name the process. b) State the economic importance of the process named in (a) above
answers
a) Anaerobic respiration / fermentation; Acc. Alcohol production/ drawing dough.
b) Brewing/ Banking. |
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

