|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN19
Explain how a biotic factors affect plants
answers
Wind.
In windy conditions the rate of transpiration increases; wind disperses fruits/ seeds; is an agent of pollination; acc. Spores for seed. Temperature Changes in temperatures affects the rate of photosynthesis and other biochemical reactions/ metabolic reactions/ enzymatic reactions/ enzymatic reactions, temperature increases rate of transpiration; Lights Plants need light for photosynthesis, some plants need light for flowering/ photoperiodism/ seeds like lettuce require light for germination. Humidity When humidity is low, the rate of transpiration increases; PH Each plant requires a specific pH to grow well/ acidic/ alkalinity/ neutral; Salinity Plants with salt tolerant tissues grow in saline area, plants in estuaries adjust to salt fluctuations; Topography North facing slopes in temperature lands have more plants than south facing slope Plants on windward side have stunted/ distorted growth; Comparisons of mountains and valleys Description of other areas with other topographies e.g. River valley rainfall/ water - Fewer plants in areas/ semi arid and - Water is needed for germination/ is a raw material for photosynthesis/ dissolves/ minerals salts/ provides turgidity for support/ fruits/ seeds Pressure; Variation in atmospheric pressure affect availability of CO+2+ which affects photosynthesis and low pressure increase rate of transpiration; and affect amount of oxygen; for respiration Mineral salts/ trace elements - Affects distribution of plants in the soils - Plants thrive well where there are mineral salts in the soil Plants living in the soil deficient in particular mineral element have special methods obtaining it; for example legumes obtaining from nitrogen by fixation or carnivorous.
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN18
How is the mammalian skin adapted to its functions?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN17
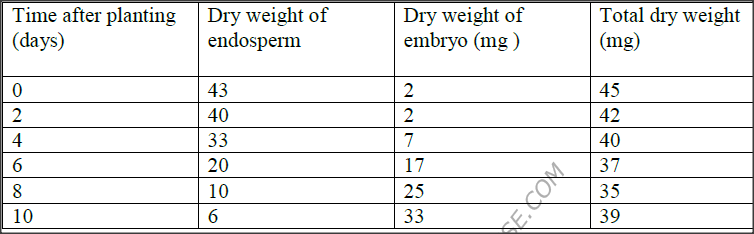
During germination and growth of a cereal, the dry weight of endosperm, the embryo and total dry weight were determined at two – day intervals. The results are shown in the table below.
a) Using the same axes, draw graphs of dry weigh of endosperm, embryo and the total dry weight against time
b) What is the total dry weight on day 5? c) Account for: i) Decrease in dry weight of endosperm from day 0 to 10 ii) Increase in dry weight of embryo from day 0 day 10 iii) Decrease in total dry weight from day 0 to day 8 iv) Increase in total dry weight after day 8 d)Dormancy. i) Within a seed ii) Outside the seed e) Give two characteristics of meristematic cells
answers
(b) 38.5 (mg); Acc. + 0.5 ( i.e. 38 – 39)
(c) (i) Hydrolysis of starch into simple sugars; which are translocated to the embryo; Respiration/ to give energy/ heat/ gases Acc. Simple sugar oxidized (ii) New materials are synthesized from protein); bringing about growth of embryo; acc new cells/ protoplasm synthesized (iii) The rate of respiration is faster than that of synthesis of materials for growth (iv) First leaf (carried out photosynthesis) leading to growth (d) (i) Presence of absiscic acid/ germination inhibitors; Embryo not fully developed Absence of hormones/ enzymes that stimulate germination Impermeable seed coat; rej hard seed coat Acc. Inactive enzymes/ hormones/ absence of gibberellins/ cytokinins. (ii) – Unsuitable / unfavourable temperature - absence of light - lack of water - lack of oxygen (c) Dense cytoplasm - Thin cell wall - Absence of vacuoles ( cell sap)
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN16
Outliner three roles of active transport in the human body
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN16
how do the following factors affect the rate of diffusion?
i) Diffusion gradient ii) Surface area volume ratio iii) Temperature
answers
(i) The higher diffusion gradient between ( two points) the rate of diffusion; acc converse.
(ii) The higher the surface area:: Volume ratio, the faster is the rate of diffusion ; acc converse (iii) Increasing temperature increases the rate of diffusion; acc converse.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN16
What is diffusion
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN15
a) Give the differences between the following structures in wind and insect pollinated flowers.
i) Anther ii) Pollen grains iii) Stigma b) What is the importance of cross pollination? c) Explain how a seed is formed after an ovule is fertilized
answers
(i) anther Insect Wind
Small short anther firmly Large/ long anthers/ loosely attached to Attached to elements filaments (ii) Large heavy/ spiky small/ light/ smooth (iii) Small/ sticky Long feathery (b) Source of variation/ hybrid acc. Production of hybrid K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN14
What is meant by the following terms? Give an example in each case.
i) Homologous structures ii) Example iii) Vestigial structures Example
answers
(i) Have a common ( embryonic) origin modified to perform different functions; vertebrae for limb/ pentadactyl limb
Example Vertebrate fore limb/ pretadactyl limb; acc beaks of birds ( fee of birds/ mouthparts in insects. (ii) Have different (embryonic) origins ( but have evolved) to perform similar functions. (iii) Are greatly reduced in size and therefore caused to function Acc. Third digit of wing of bird Halteres in flies Presence of hind limb ( buds) in python Human ear muscles Example Human appendix / kiwi ( flightless bird) with reduced wings/ vestigial wings in flies human hair/ presence of hind limbs in python; reduced pelvic girdle of whale.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN14
What is the difference between Darwinian and Lamarckian theories of evolution?
answers
Lamarckian
Inheritance of acquired characteristics/ Environment induces production of inheritable character which is then inherited.while Darwinian Inheritance of genetically acquired characteristics/ character happens to appear spontaneously which then gives advantage to organisms therefore better- adaptable characters are then inherited by natural selection. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN13
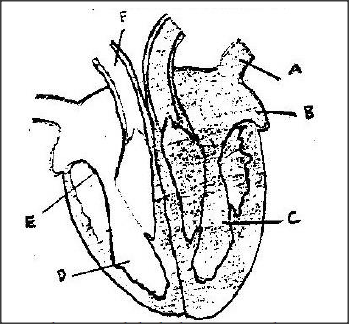
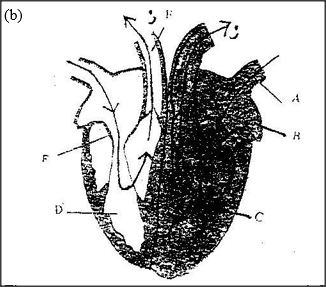
The diagram below shows a vertical section through a mammalian heart.
a) Name the parts labeled A,B,E and F
b) Use arrows to show the direction in which blood flows in the heart. c) Give a reason why the wall of chamber C is thicker than chamber D
answers
(a) A Pulmonary vein
B Left atrium I auricle E Tricuspid valve F Pulmonary artery
(b) The left ventricle ‘C’ pumps blood a longer distance to all parts of the body; while the right ventricle ‘D’ pumps blood to a shorter distance/ to the lungs; therefore the left ventricle has thicker walls to generate exert more pressure.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN12
Across between a red flowered plant and white flowered produced plants with pink flowers.
Using letter R to represent the gene for red colour , and W for white colour a) What were the parental genotypes b) Workout a cross between F1 plants c) Give the i) Phenotypic ratio of F2 plants ii) Genotypic ratio of F2 plants d) Name a characteristic in humans, which is controlled through a mammalian heart?
answers
(a) RR WW
(b) Parental genotypes R W Gametes R W X WW R W Fertilization Offsprings RR RW RW WW (c) (i) Phenotypic ration Red Pink White 1 2 1 (ii) 1RR : 2RW; 1WW (d) (ABO) blood grouping; blood groups;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN11
Fruit formation without fertilization is called
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN10
How are the xylem vessels adapted for support?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN09
Name two mineral elements that are necessary in the synthesis of chlorophyll.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN08
Name the class in the phylum arthropoda which has the largest number of individuals?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN07
State the function of the organelles:
a) Lysosomes b) Golgi apparatus
answers
a) Stores hydrolytic enzymes for destruction of worn out organelles / cells/ tissues / digestion of bacteria. / pathogens;
Acc. Digestion of food / accept autolysis. b) processing / packaging synthesized and transporting of packaged cell materials;. Production of lysosomes/ secretions of packaged material; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN06
The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in a defective eye.
a) Name the defect:
b) Explain how the defect named in (a) above can be corrected
answers
a) Myopia/ shortsightedness / short sight
b) Concave lens / divergent lends; to diverge the rays so that the image is focused on the retina Acc. Concave.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN05
During which phase of meiosis does crossing over occur.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN04
Other than carbon dioxide, name other products of anaerobic respiration
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN03
How is aerechyma tissue adapted to its function
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN02
Distinguish between natural and acquired immunity
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN01
State the function of the cartilage named in (a) above
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN01
Name the cartilage found between the bones of the vertebral column
answer
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

