|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN19
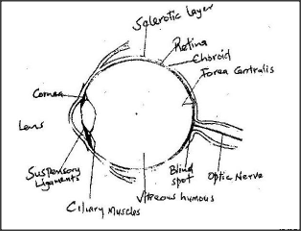
How is the human eye adapted to its function?
answers
Adaptations of the eye.
The presence of:-
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN18
Describe how gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial Plants.
answers
Gaseous exchange in terrestrial plants.
Gaseous exchange in plants involves two main respiratory gases: carbon IV oxide and oxygen. During daytime green plants take in carbon IV oxide for photosynthesis and oxygen for respiration. During photosynthesis oxygen is given out as a by product and released to the atmosphere. In plants such as the flowering plants stomata in the leaves and lenticels in the woody stems and pneumatophores/breathing roots in aquatic woody plants provide the surface for gaseous exchange. Gaseous exchange taken place by diffusion across the respiratory surface. Stomata These are located mainly in the leaves and in younger parts of the stem. The opening and closing of stomata is controlled. Mainly by the intensity of light. They are normally open during the day and closed during the night. Several theories explaining the mechanism of stomata opening and closing have been put forward. 1. Photosynthetic theory Guard cells have chloroplasts. During daylight, they carry out photosynthesis producing surges. The surges increase the osmotic pressure of the cell sap. This causes water to more into guard cells from the neighboring epidermal cells by osmosis. The results is an expansion and increase in turgidity of the guard cells causing the stomata to open. In darkness photosynthesis stops. The sugar in the guard cells is converted to starch. This lowers the osmotic pressure of guard cells causing the to lose water to neighboring cells by osmosis. The guard cells become flaccid and the stomata close. The guard cells become flaccid and the stomata close. 2. Starch – sugar interconversion: The enzymatic conversion of starch to sugar proceeds more readily in an alkaline environment(high PH).The conversion of sugar to starch occurs more readily in an acidic environment (low Ph).During the night, when photosynthesis is not taking place, carbon dioxide accumulates in leaf cells it combines with water to form carbonic acid. This lower the PH in the guard cells leading to conversion of sugar to starch this decreases the osmotic pressure in the guard cells causing them to lose water to the neighboring epidermal cells. The guard cells become flaccid and the stomata close. During daylight, when photosynthesis is taking places, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the leaf cells, raising their PH, and favouring the conversion of starch to sugar. This increases the osmotic pressure in the guard cells causing them to take in is an expansion and increase in turgidity of the guard cells causing the stomata to open. 3. Potassium Ion (K+) mechanism When guard cells are exposed to light, their chloroplasts manufacture ATP. The ATP drives at K+ pump in the cell membrane of the guard cells. This causes an active uptake of K+ into the guard cells from surrounding epidermal cells. Accumulation of K+ in guard cells increases the osmotic pressure of their cell sap. This causes water to move into the guard cells from neighbouring epidermal cells by osmosis. The result is an expansion and increase in turgidity of the guard cells causing the stomata to open. -At the onset of darkness, chloroplast stop making ATP and its concentration in guard cells falls rapidly stopping K+ pump, K+ migrate from the guard cells Causing them to lose water to the neighbouring cells by osmosis. The guard cells become flaccid and the stomata close. -Water molecules are pumped into the guard cells from adjacent epidermis cells. -A small extent of gaseous exchange takes place in the stem through structures called lenticels. These are small gaps in the bark usually circular or oval & slightly raked on the bark surface. The cells in these area are thin walled and loosely packed leaving air space which communicates with air spaces in the cortex. Hence 02 for respiration is taken up & C02 is given out. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN17
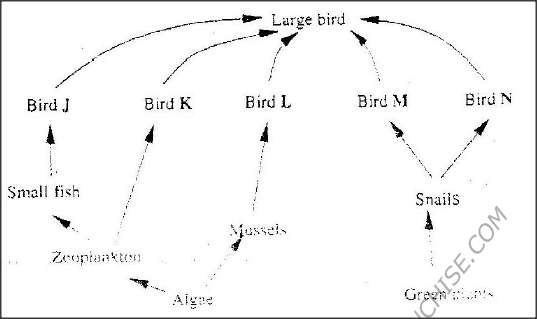
After an ecological study of feeding relationships students Constructed the food web below.
a) Name the process through which energy from the sun is incorporated into the food web.
b) State the mode of feeding of the birds in the food web c) Name two ecosystems in which the organisms in the food web live d) From the information in the food web, construct a food chain with the large bird as a quarternary consumer. e) What would happen to the organisms in the food web if bird N migrated? f) Not all the energy from one trophic level is available to the next level. Explain g) (i) Two organisms which play a role in the ecosystems are not included in the food web. Name them. (ii) State the role played by the organisms named in g(i) above. h) i) State three human activities that would affect the ecosystems. ii) Explain how the activities stated in h(i) above would affect the ecosystems.
answers
a)Photosynthesis
b)Heterotrophic – holozoic c) Small fish pond / dam, rain forests. d) Algae Zoo plankton small fish bird large bird. e)-Snails would increase in number -Bird M would increase in number. -Green plants would decrease in number f) The energy to be passed on from one trophic level to the next is contained in food materials. Most of the food taken in by consumers passed on from one trophic level to the next is consumers passes through the digestive track as undigested matter that is removed as faeces. The digested materials are absorbed in to the bloodstream and conveyed to various tissues of the body. Most of the absorbed food materials are used in respiration, to Produce is lost as heat during sweating, evaporation and transpiration in plants. g)i) Scavengers e.g. vultures Decomposers e.g. bacteria ii) Scavengers feed on dead bodies of herbivores and carnivore / the consumers. -Decomposers act upon the remains of the producers, consumers, & Scavengers causing decay, to release inorganic materials, which are later re-used by producers to make new organic compounds. h) i) -Deforestation -Overgrazing -Soil erosion -Hunting, poaching -Over fishing -Poor waste disposal // Environmental pollution ii) Deforestation Lack of trees leads to reduced number producers in an ecosystem. Overgrazing Many animals eat away and trample the vegetation hence reducing / depleting the number of producers. -Lead to gully erosion hence carrying away some of the underground and crawling animals (Consumers) Name two modern methods of food preservation and for each state the biologic principle behind it.18/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN16
Name two modern methods of food preservation and for each state the biologic principle behind it.
answers
b) Refrigeration
It inactivates disease causing organisms/micro-organisms. Irridation –The radiation kills/destroys the micro-organism. Pasteurization (for milk only) Canning-Kills the micro – organisms.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN16
Name two organisms that cause food spoilage
answers
a) - Fungus
-Bacteria K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN15
a) What is meant by the terms
(i) Epigymous flower (ii) Staminate flower? b) How are the male parts of wild pollinated flowers adapted to their function?
answers
a)i) A flower whose ovary is situated below the other floral parts.
ii) A flower with only the male reproductive parts parts (male flower) b) Larger anthers. Anther loosely attached Flexible filament Small, smooth and light pollen grains K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN14
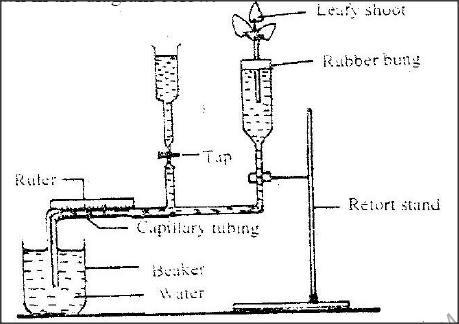
A set up that was used to investigate certain process in plants is shown in the diagram below.
a) What process was being investigated?
b) (i) State two precautions that should be taken when setting up the experiment. (ii) Give a reason for each precaution stated in b(i) above. c) State three environmental factors that influence the process Under investigation.
answers
a) Transpiration
b)i) The leafy shoot should be from herbaceous plant Cut off the last few centimeters of the stalk under water All the air in the capillary tubule should be expelled Jelly should be applied around the stem around the rubber bung. The end of the capillary fusing should rest in beaker of water. ii) Avoid air bubbles. For continuity of the flow of water Jelly should not touch the xylem vessels because it might block they xylem. To avoid introduction of air bubbles in the xylem. For continuity of water uptake. c) Temperature Humidity Wind Atmospheric pressure Light intensity Availability of water K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN13
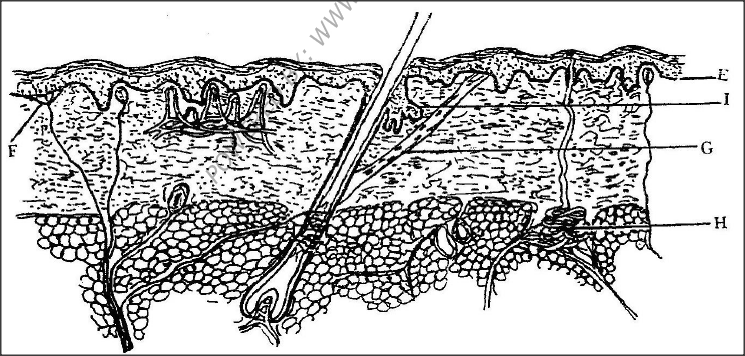
The diagram below shows a section through the mammalian skin.
a) Name the parts labeled E, F and G.
E ………………………………………… F ………………………………………… G ………………………………………… b) State two functions in each case of substance secreted by the structures labeled. (i) H ………………………………… (ii) I ………………………………….
answers
a) E – Malpighian layer
F – Nerve cell G – Erector pili muscle b)i) H – Excretion of waste products of metabolism from the body e.g. excess. Water, mineral salts traces of urea, lactic acid etc. Temperature regulation in the body brings a cooling effect through Loss of excess heat by evaporation of water. Keeps the hair and epidermis flexible and water proof Contains antiseptic substances for protection against bacteria. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN12
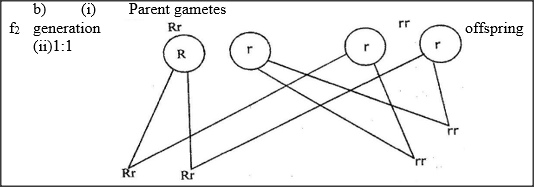
In a garden with plants of same species, 705 plants had red flowers while 224 had white flowers.
a) Work out the ratio of red to white flowered plants b) (i) Using letter R to represent the dominant gene, work out a cross between F1 offspring and a white flowered plant. (ii) What is the genotypic ratio from the cross in b(i) above? c) What is meant by the term allele? K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN11
The diagram below represents a part of the rib cage.
a) Name the parts labeled W, Y and Z.
W …………………………………………………… Y ……………………………………………………. Z …………………………………………………….. b) How does the part labeled Z facilitates breathing in?
answers
a) W – Spinal column / reutebral column
Y – Sternum Z – Intercostal muscles. b) The external intercostals muscles contract while the internal intercostals. Muscles relax. This movement pulls the ribs upwards and outwards. The diaghragm muscles contracts (flattens).The thoracic volume increase while the pressure reduces, leading to atmospheric air rushing into the lungs through the nose and trachea hence inflating the lungs.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN10
Name the organism that causes amoebic dysentery.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN09
Why would carboxyhaemoglobin lead to death?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN08
Name three factors in seeds that cause dormancy.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN07
State the importance of osmosis in plants.
answers
Name the substance which accumulates in muscles when respiration occurs with insufficient oxygen.18/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN06
Name the substance which accumulates in muscles when respiration occurs with insufficient oxygen.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN05
To which class does an animal with two body parts and four Pairs of legs belong?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN04
What is meant by
a) Organic evolution b) Continental drift?
ABSWERS
a)It is the process through which ancient simpler forms of life under went gradual series of small changes for many million years, to give rise to the modern species of life // accepts as a theory formed one large single land mass, which later broke up into parts which drifted from one another forming the present day continents.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN03
What is the role of the vascular bundles in plant nutrition?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN02
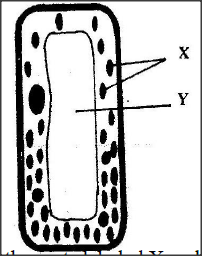
The diagram below represents a cell.
(a) Name the parts labeled X and Y
X …………………………………….. Y …………………………………….. (b) Suggest why the structures labelled X would be more on one side than the other.
ANSWERS
a) X – Chloroplast
Y – Cell vacuole / sap vacuoles b) To receive maximum amount of light.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2005PP1QN01
Apart from hearing, state another function of the human ear.
ANSWER
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

