|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN08
Describe how water moves from the soil to the leaves in a tree.
answers
Water exists as a thin film in the soil between soil particles. The concentration cell sap is greater than that of the surrounding solution in the soil; Thus drawing water molecules across the cell wall and membrane into the root hair cells; by osmosis; water drawn into the root hair cell dilutes the cell sap/ makes it less concentration than that in the adjacent cell into the cortex cells. (By osmosis); across the endosperm by active transport; into the xylem vessels (of the root); Then conduct the water up into the xylem (vessels) of the stem; into xylem of leaves. Water is pushed/ rises up the stem by root pressure ( in the xylem vessels) water would rise by capillary; cohesion, and adhesive forces; water moves as a continuous an uninterrupted water column in the xylem (vessel) up the tree to the leaves. As water vaporizes from the spongy mesophyll cells; their cells sap becomes more concentrated than adjacent water flows into the cells from other surroundings cells; which in turn takes in water from xylem vessels within the leaf veins. This creates a pull / suction force/ transpiration pull that pulls a stream of water from xylem vessel in the stem and roots; the transpiration pull maintains continuous column of water from the roots into the leaves (transpiration stream).
2 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN07
Describe how human kidney functions
answers
The afferent arteriole which is the branch of renal artery supplies blood to glomerulus; The afferent arteriole has a wider diameter than the afferent arteriole; this causes high pressure; leading to ultra filtration. The walls of the blood capillaries are one cell thick hence glucose, amino acids, (vitamins, hormones) salts, (creatinine) urea and water filter into Bowman’s Capsule to form glomerular filtrate; White blood cells/ red blood cells and plasma proteins such as (Globulin, fibrinogen, platelets) are too large to pass through the capillaries: the filtrate flow into the proximal convoluted tubule; where amino acids (vitamin) and all glucose are selectively reabsorbs back into the blood stream. Many mitochondria provides energy for re- absorption of these substances against concentration gradient/ by active transport. The Glomerular filtrate flow into loop of henle. Water in descending loop moves by osmosis into the blood capillaries; sodium chloride is actively pumped from the ascending arm of loop henle into the blood capillaries. The glomerular filtrate flow into the distal convoluted tubule, water is absorbed from distal convoluted tubule into blood capillaries; the glomerular filtrate flows into collection tube/ duct from where more water is reabsorbed into the blood stream.
Antidiuretic hormone influences the amount of water reabsorbed ( depending on osmotic pressure of blood); The glomerular filtrate from collecting duct now referred to as urine; is emptied into pelvis. The urine passes though pelvis and ureter into bladder out of the body through urethra. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN06
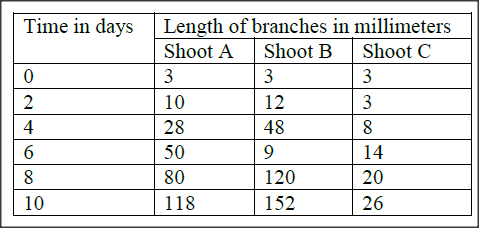
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of hormones on growth of lateral buds of three pea plants
The shoots were treated as follows: Shoot A – Apical bud was removed. Shoot B – Apical bud was removed and gibberellic acid placed on the cut shoot. Shoot C – Apical bud was left intact. The length of the branches developing from lateral buds were determined at regular intervals. The results obtained are as shown in the table below.
a) Using the same axes, draw graphs to show the lengths of branches against time.
b)i) What was the length of the branch in shoot B on the 7th day? ii) What would be the expected length of the branch developing from shoot A on the 11th day? c) Account for the results Obtained in the experiment d) Why was shoot C included in the Experiment? e) What is the importance of gibberellic acid in agriculture? f) State two physiological processes that are brought about by the application of gibberellic acid on plants.
answers
(b) (i) 105 + 1 (mm)
(ii) 134 – 140 (mm) (c) Graph A: The tip of the shoot which was removed contained indole acetic acid (IAA); which causes apical dominance/ inhibits growth/ development of more lateral buds; hence lateral buds sprouted/grew. Graph B; the gibberellic acid which was added on the cut. Promotes formation of lateral branches of stems, hence the fast growth of branches on shoot b. Graph C; The shoot tip which remained intact contains IAA which inhibits growth/ development of lateral buds; hence little change of length of lateral branches. (d) Control (e) Increase productivity (f) Promote cell division, and cell elongation K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN05
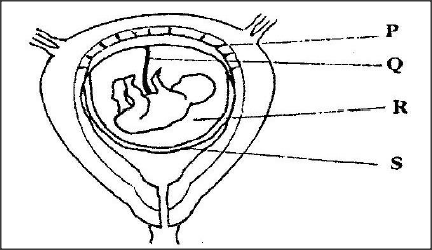
The diagram below represents human foetus in a uterus.
a) Name the part labeled S.
b) i) Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labeled Q. ii) State the differences in composition of blood found in the vessels named in (b)(i) above. c) Name two features that enable the structure labeled P carry out its function. d) State the role of the part labeled R
answers
(a) Chorion
(b) (i) Arteries; veins (ii) More food nutrients; more oxygen in veins less food nutrients more excretory products in arteries (c) Highly vascular zed; large surface area Presence of secretory cells (d) Cushion/ absorb shock K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN04
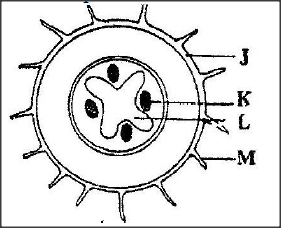
The diagram below represents a traverse section through a plant organ
A. From which plant organ was the section obtained?
B. Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. C. Name the parts labeled J,K and L. D. State two functions of the part labeled M.
answers
(a) Root
(b) Presence of root hairs Presence of endodermis Xylem star shaped at centre Phloem at arms of the xylem (c) J- Epidermis K- Phloem L – Xylem (d) - Absorption of water Absorption of minerals salts Give three reasons for loss of energy from one trophic level to another in the food chain.19/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN03
Give three reasons for loss of energy from one trophic level to another in the food chain.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN03
Distinguish between pyramid of numbers and pyramid of biomass.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN02
In mice the allele for black fur is dominant to the allele for brown fur. What percentage offspring would have brown fur form across between heterozygous black mice? Show your working. Use letter B to represent the allele for black colour.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN02
Describe the following chromosomal mutations.
a. Inversion b. Translocation.
answers
(i) Occurs when chromatids/ chromosomes break at 2 places and when rejoining the Middle piece rotates and joins in an inverted position.
(ii) Occurs when a section of chromatid break off and becomes attached to another chromatid of another chromosome.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN02
Name two disorder in human caused by gene mutation.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP2QN01
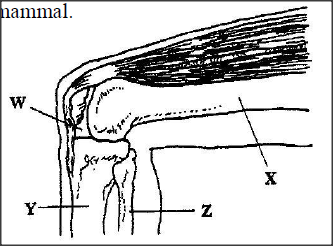
The diagram below represents bones at a joint found in the hind limb of a mammal.
a) Name the bones labeled XY and Z
b) i) Name the substance found in the place labeled W. ii) State the function of the substance named in (b) (i) above. c) Name the structure that joins the bones together at the joint. d) State the differences between ball and socket joint and the one illustrated in the diagram above. e) Name the structure at the elbow that performs the same function as the same function as the patella.
answers
(a) X- Femur
Y- Tibia Z- Fibula (b) (i) Synovial fluid (ii) Lubrication of the joint/ shock absorption Distribution of pressure (c) Ligament (d) Ball and socket joint allows movement in all planes while the illustrated allows movement in one plane only. Accept 3600 for all planes 1800 for one plane. (e) Olecranon process.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN27
Name the end products of the light stage in photosynthesis.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN26
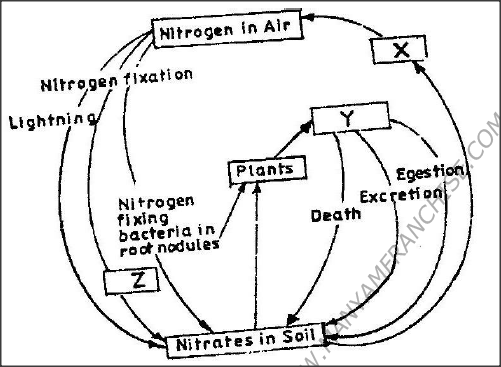
The chart below represents a simplified nitrogen cycle.
What is represented by X,Y, and Z?
answers
X- Denitrifying bacteria/ denitrification
Y- Animals/ Herbivores; accept primary consumers Z- Nitrogen fixing bacteria ( in soil) accept Azotobacter. A dog weighing 15.2kg requires 216kj while a mouse weighing 50g requires 2736kj per day. Explain.19/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN25
A dog weighing 15.2kg requires 216kj while a mouse weighing 50g requires 2736kj per day. Explain.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN24
State four ways in which respiratory surfaces are suited to their function.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN23
State the function of each of the following parts of human ear.
a) Ear ossicles b) Cochlea c) Semi circular canals d) Eustachian tube.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN22
State two functional differences between the rods and cones in the human eye.
answers
Rodes Cones
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN22
State the function of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN21
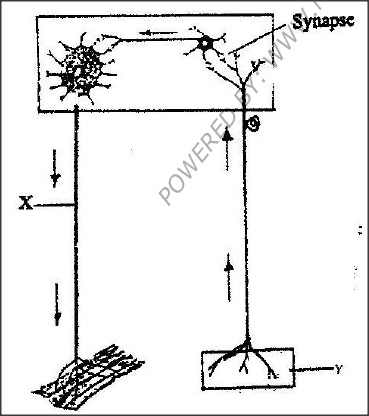
The diagram below represents a reflex are in human.
a) Name the parts labeled X and Y
b) Name the substance that is responsible for the transmission of an impulse across the synapse.
answers
(a) X- motor neurone- accept of motor neurone rej. Axon alone
Y- Sense organ/ receptor (b) Acetyl; chlorine/ noradrenaline ( Nerepinephrine)
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN20
State three biological importance of tropisms plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN20
What name is given to response to contact with surface exhibited by tendrils and climbing stems in plants?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN19
Give three advantages of cross pollination.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN19
a) Explain how the following prevent self pollination.
(i) Protoadry (ii) Self – sterility.
answers
(i) Protoandry – Male reproduction organ/ anthers androecia/ stamens mature earlier than female reproduction organ/ carpels/ stigma/ pistil/ gynoecium.
(ii) Self sterility- pollen grains are sterile to stigma of some plants/ flowers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN18
How does substrate concentration affect the rate of enzyme action?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN18
State two functions of bile juice in the digestion of food.
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

