K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN08
Describe the role of the following organs in excretion and homeostasis.
(a) the liver (b) the skin during hot environmental conditions.
ANSWERS
(a) Regulation of blood sugar ; when blood sugar is below normal/90 mg/100 cm3 glucagon ; triggers the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver ; the glucose is released into the blood stream. When blood sugar is in excess above normal/10 mg/100cm3, insulin; causes the liver to convert glucose excess to glycogen ; which is stored.
Production of heat energy ; by increasing the rate of metabolic activities: Excretion of bile pigments ; produced due to breakdown of worn out red blood cells: Deamination/removal of amino group of excess amino acids to form urea: and detoxication/poisonous/toxic substances: (b) Sweat glands excrete urea; excess water; and salts: hence maintaining salt & water balance in the blood. Evaporation of sweat; cools the body due to loss of latent heat of vaporization; when the body temperature rises : blood vessels in the skin vasolidate: allowing more blood to flow near the skin surface: thus heat is lost to the environment radiation/convection. The eretor pili mucle relaxes hair flattens ; in a hot environment reducing insulation: hence heat is lost from the body by radiation! convection; to the environment.
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN07
How are respiratory surfaces in mammals adapted to their functions?
ANSWERS
Many to provide a large surface area: across which large amounts of gases diffuse: moist surfaces: to dissolve respiratory gases: so as to diffuse. Made of a thin membrane/epithelium/one cell thick wall ; to reduce diffusion distance;
Highly vascularized: to carry away oxygen; and bring in carbon (IV) oxide: creating a steep diffusion gradients.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN07
Describe the process of blood clotting in human beings.
ANSWERS
When a blood vessel is cut/injured platelets/thrombocytes/damaged tissue/wound is exposed to the air: they release thrombokinase/thromboplastin ; an enzyme that activates the conversion of prothrombin: to thrombin: in the presence of calcium ions: vitamin K/ phylloquinone ; is needed for the formation of prothrombin; Thrombin converts (soluble blood protein) fibrinogen ; into (the fibrous form) fibrin; which forms a mesh / network across the wound: The clot so formed prevents excessive bleeding: and entry of disease agents/pathogens/micro-organisms/microbes;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN06
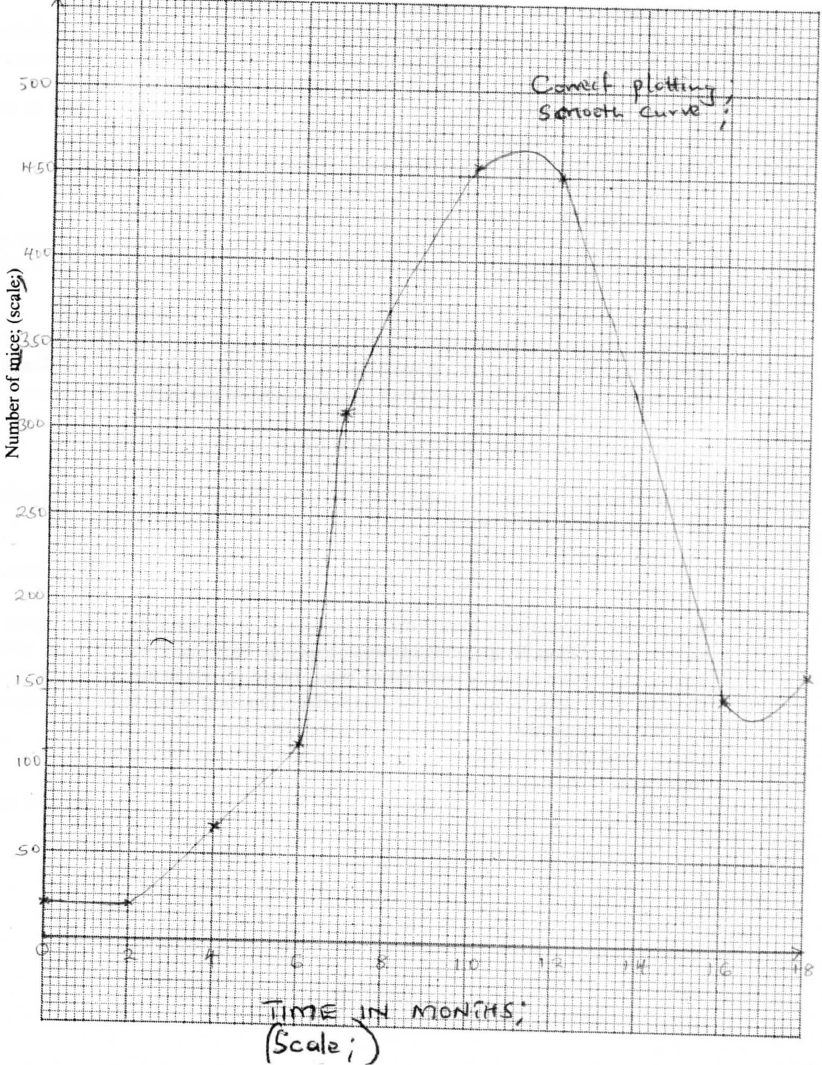
A scientist carried out an investigation to find out the population growth of mice under laboratory conditions. Twenty young mice were placed in a cage. The results obtained from the investigation were as shown in the table below.
(a) On the grid provided, draw a graph of the number of mice against time.
GRAPH PAPER (b) Account for the changes in mice population between (i) O to 2 months (ii) 2 to 6 months (iii) 6 to 10 months (iv) 10 to 12 months. (c) (i) Between which two months was the population change greatest? (ii) Calculate the rate of population change over the period in (c)(i) above. (d) What change in population would be expected if the investigation was continued to the 19th month? (e) To obtain the observed results state two variables that were kept constant during the investigation.
answers
(b) (i) No change in population/population is constant: mice still maturing/have not given birth:
(ii) Slow/gradual population growth; few mice have reached sexual maturity; (iii) Faster/rapid rate of population growth/exponential; Many mice sexually matured/reproducing/enough food/space/no competition birth rate higher than death/no diseases: (iv) Population decline; Competition is high / food is limiting / space is limiting/accumulation of toxic waste/disease (outbreak) deathrate higher than birth rate. (c) (i) 6 and 8; (ii) 310-115 = 195 mice per month; (d) Population would increase; (e) Food; space ; cage size; water; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN05
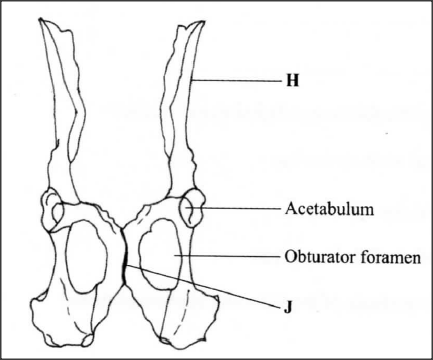
The diagram below represents a mammalian pelvic girdle.
(a) How are the structures labelled H and J adapted to their function?
(i) H (ii) J (b) State the function of obturator foramen. (c) (i) Name the bone that articulates with the pelvic girdle at acetabulum. (ii) Name the type of joint formed by the acetabulum and the bone named in (c)(i) above. (d) Name the bone formed by the fusion of caudal vertebrae inhuman beings.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN04
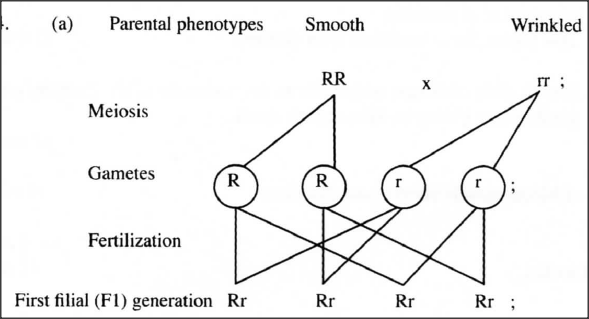
In an investigation, a variety of pea plants grown from seeds with smooth coats were crossed with plants grown from seeds with wrinkled coats. All the seeds obtained in the first filial (F1) generation had smooth seed coats.
(a) Using the letter R to represent the gene for smooth seed coat, work out the genotype of the F1 generation. Show your working.
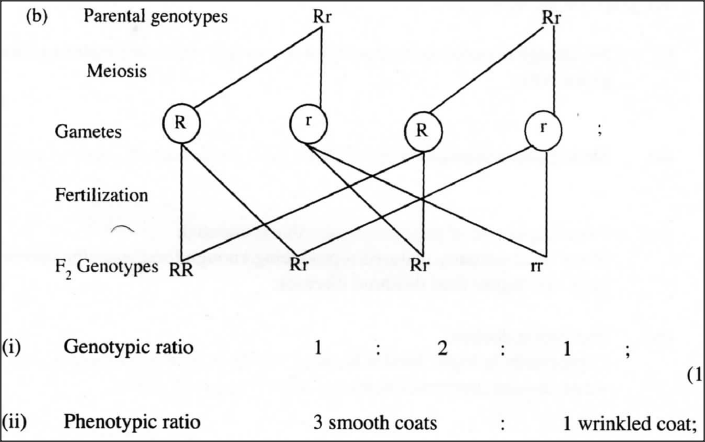
(b) If the F1 generation was sel fed, determine the phenotypic ratio of the second filial (F,) generation. Show your working. (c) If the total number of seeds in the F, generation was 14 640, calculate the number of seeds with wrinkled coats. Show your working. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN03
(a) Explain the importance of the following in photosynthesis:
(i) light; (ii) carbon(IV) oxide; (iii) chlorophyll.
(b) Name one appropriate food substance for each of the following enzymes:
(i) ptyalin (ii) pepsin (c) State the cause and two symptoms of Ben-ben. Cause Symptoms
answers
(a) (i) Provides energy needed to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen/photolysis;
Provides energy for formation of ATP molecules (which is used in dark stage) (ii) Combines with hydrogen ions to make glucose; (iii) Used to trap light energy; (b) (i) Starch; (ii) Protein; (c) (i) Lack of vitamin B1/thiamine; (ii) . Stunted growth; Paralysis of legs/arms/limbs/damage to peripheral nerves; Heart failure Swelling of feet/oedema Gastrointestinal disturbances/loss of appetite/constipation/diarrhoea/vomiting; Weight loss/muscle wasting Pale skin K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN02
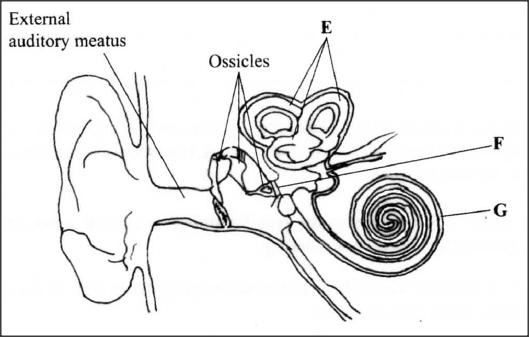
The diagram below represents the human ear.
(a) Name the parts labelled E, F and G.
E F. (b) How is each of the following adapted to its function? (i) External auditory meatus; (ii) Ear ossicles. (c) Name one defect of the human ear.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN01
The diagram below represents a plant in the division Bryophyta.
(i) Name the parts labelled B and D.
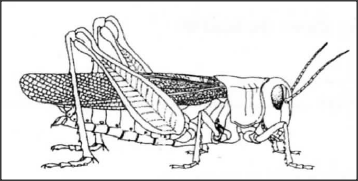
B D (ii) State one function for each of the parts labelled A and C. A C (b) The diagram below represents a member of the kingdom Animalia.
(i) Name the phylum to which the organism belongs.
(ii) Using observable features in the diagram, give three reasons for the answer in b(i).
answers
(a) (i) B Seta/stalk;
D Rhizoid: (ii) A Production of spores/sporulation; C Photosynthesis; (b) (i) Arthropoda; (ii) Segmented body; Jointed appendages; Presence of exoskeleton
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN30
State two ways in which osmosis is significant to plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN29
State two functions of pelvic girdle in mammals.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN28
Name the bone that allows the head to:
(i) nod; (ii) turn side ways
answers
(i) Atlas;
(ii) Axis allows movement in all planes;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN28
State two features of a ball and socket joint.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN27
State the importance of moulting to an insect.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN27
State two differences between complete and incomplete metamorphosis.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN26
Name two sex linked traits in human beings.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN26
What is meant by the term sex linked genes?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN25
State one adaptation of xylem vessels to their function.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN24
Explain three protective functions of mammalian blood.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN23
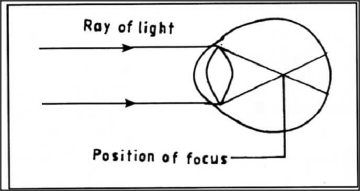
The diagram below illustrates a defect in the eye.
Explain how the defect illustrated above can be corrected.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN22
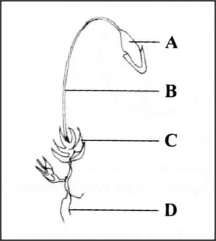
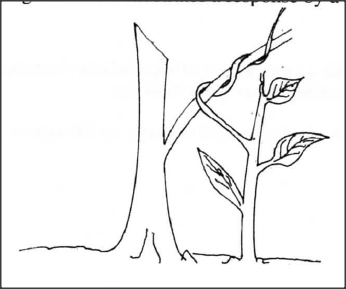
The diagram below illustrates a response by a certain plant.
(a) Name the type of response.
(b) Explain how the response illustrated above occurs.
answers
(a) Thigmotropism/Haptotropism;
(b) Part of the tendril in contact with support causes migration of auxins to the opposite side; leading to faster cell division/growth on the side not in contact with the support: This causes the tendril to curl around the support;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN21
What is meant by the term organic evolution?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN21
Explain the role of continental drift in evolution.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN20
Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN19
State three factors in seeds that cause dormancy.
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

