|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN08
Describe the role of the human skin in homeostasis.
answers
When body temperature is lowered below normal; arterioles in the skin constrict; blood is diverted to a shunt system; less blood flows to the skin/less heat is lost; when body temperature is raised above normal;arterioles in the skin dilate;more blood flows to the skin; more heat is lost by convection and radiation;when body temperature is lowered below normal:erector-pilli muscle s contract, hair stands erect; more air is trapped, air is a bad conductor;and insulates the body against heat loss; when body temperature is raised above normal: erectorpi11i muscles relax, hair lies on skin;less air is trapped, more heat is lost; when body temperature is lowered below normal: less fluids are absorbed by sweat glands;less sweating, less vaporisation of water;
when body temperature is raised above normal:sweat glands are more stimulated and more sweat is produced; water in sweat evaporates and takes up heat from the body;body is cooled/body temperature is lowered;
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN08
How does excretion take place in plants?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN07
Describe the process of carbohydrate digestion in human beings.
answers
In the mouth;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN07
Explain how each of the following factors affects the rate of photosynthesis:
(i) temperature; (ii) chlorophyll concentration.
answers
(i) Reactions in photosynthesis are catalysed by enzymes; at optimum temperature photosynthesis proceeds faster;
Below optimum temperature the rate of photosynthesis decreases because enzymes are inactivated by the low temperatures / above optimum the rate of photosynthesis decreases because enzymes are denatured; (ii) Chlorophyll traps energy from sunlight for photosynthesis; The higher the chlorophyll concentration the higher the rate of photosynthesis and vice versa; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN06
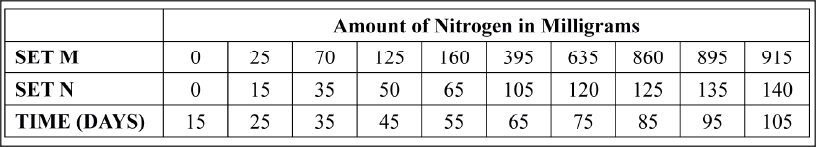
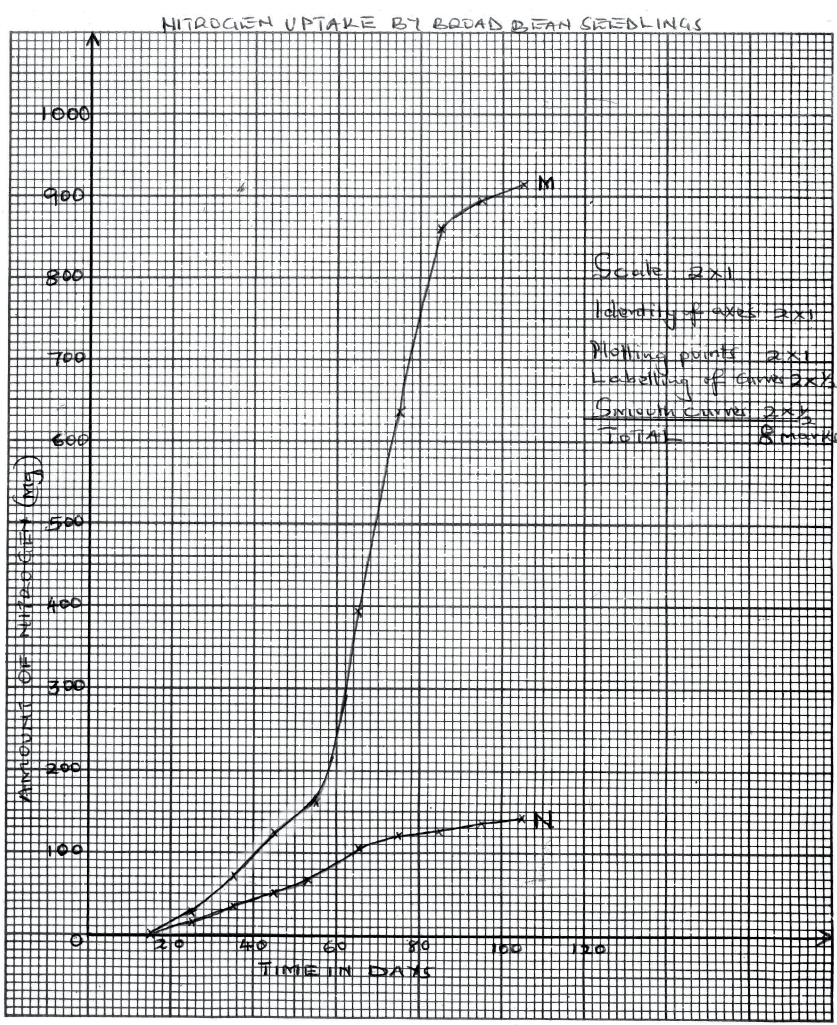
An experiment was done to determine the uptake of nitrogen from the soil by broad bean seedlings. The experiment was done with one set of seedlings M grown in the atmosphere enriched with carbon (IV) oxide and another set up of seedlings N grown in the normal atmosphere.
The amount of nitrogen in each seedling was measured in milligrams at intervals often days. The table below shows the results obtained.
(a) Using the same axis draw line graphs of nitrogen uptake by the two (M and N) sets of broad bean seedlings against time.
(b) Determine the rate of uptake of nitrogen in Set M between 65 and 85 days. (c) (i) What is the relationship between carbon (IV) oxide concentration in the air and nitrogen uptake? (ii) Account for the relationship in (c)(i) above. (d) (i) What would happen to the concentration of nitrogen in the seedlings in set M, if after 75 days the seedlings are transferred to a normal atmosphere. (ii) Explain your answer in (d)(i) above. (e) State three ways in which nitrogen fixation occurs.
answers
(c) (i) The higher the carbon UV) oxide content in air, the higher the nitrogen uptake and vice versa;
(ii) More Carbon (IV) oxide in the air makes the seedlings to photosynthesize more; hence more amino acids/protein; are formed in the dark stage; formation of amino acids/protein requires nitrogen; (d) (i) The concentration of nitrogen would remain constant; (ii) Despite decline in CO,; the nitrogen already absorbed/taken up by the plant will still remain: (iii) Lightning; By free-living bacteria/micro organisms; By Rhizobium (in root nodules of legumes); K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN05
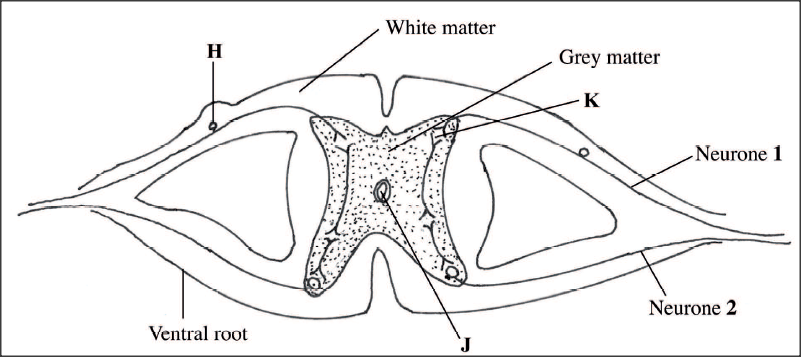
The diagram below represents the transverse section of the spinal cord.
(a) Name the part labelled H.
(b) State two functions of the fluid found in the part labelled J. (c) Give a reason for the colour of white matter. (d) Name and give the function of the enzyme found at the part labelled K. Name Function (e) On the diagram, use an arrow to show the direction of impulse transmission along the neurone labelled 1.
answers
(a) H - cell body;
(b) Has nutrients for nourishment of neurons, brain, spinal cord; Acts as a shock absorber for protection of spinal cord from mechanical damage; (c) Contains myelin sheaths (of neurons which are made up of fats that make it have a shiny white appearance); (d) Cholinesterase: Breaks down Acetyicholine; to acetic acid and choline; (e) Correct arrow on neurone 1 points towards the grey matter;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN04
Explain why people with sickle cell trait have an adaptive survival advantage over normal individuals in malaria endemic regions.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN04
Differentiate between sickle cell anaemia and sickle cell trait.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN04
How is sex determined in man?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN03
(a) Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in plants through the lenticels.
(b) Explain each of the following: (i) the tracheoles lack spiral bands of chitin; (ii) the floor of the mouth is lowered during inhalation in a bony fish.
answers
(a) O2, concentration is higher outside than inside the lenticels; O2, diffuses into lenticels; then into the cells; CO2 concentration is higher inside the lenticels than on the outside CO2 diffuses out of the lenticels into the atmosphere;
(b) (i) To provide a large surface area! make them thin; for gaseous exchange to reduce diffussion distance for respiratory gases; (ii) This increases the volume of the buccal cavity while decreasing the pressure; which forces water to rush into the mouth; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN02
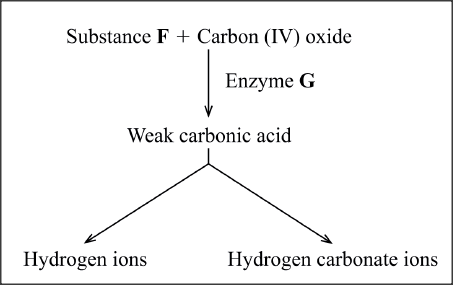
The diagram below illustrates the role played by red blood cells in the transportation of carbon (1V) oxide.
(a) Other than the carbon (IV) oxide transportation in the red blood cells, name the other form of carbon (1V) oxide transportation in humans.
(b) (i) Name substance F (ii) Name the enzyme marked C and state its role in the reaction. Enzyme Role (c) Explain why transportation of carbon (1V) oxide in red blood cells is advantageous. (d) Explain the role of calcium ions in blood clotting.
ANSWERS
(a) Carbonic acid/carbaminohaemoglobin/hydrogen carbonate;
(b) (i) Water; (ii) Carbonic acid; Role: catalyses reaction between carbon IV oxide and water to form (weak) carbonic acid; (c) Prevents accumulation of acidity/maintains pH of blood since hydrogen ions combine with haemoglobin to form Haemoglobin acids; Faster; due to the catalytic effect of carbonic anhydrase; (d) Activates thromboplastin; thrombokinase to neutralize heparin/convert prothrombin to thrombin; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN01
(a) State four characteristics of fruits dispersed by animals.
(b) State two roles of each of the following hormones in menstruation: (i) luteinising hormone; (ii) oestrogen.
ANSWERS
(a)
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN27
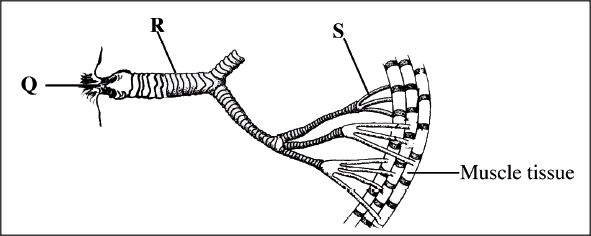
The diagram below shows the gaseous exchange system of a locust.
(a) Name the structure labelled Q.
(b) State the function of the part labelled R. (c) How is the part labelled S structurally adapted to its function?
ANSWERS
(a) Spiracle;
(b) Keep the trachea open for air passage; (c) Lacks spiral bands of chitin /to make it thin; for diffusion of gases; Moist; to dissolve respiratory gases; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN26
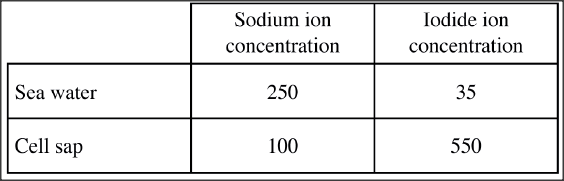
The table provided shows the concentration of sodium and iodine in sea water and cell sap of a plant.
(a) (i) Name the process through which the plant cells take up sodium ions.
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above. (b) If the plant was sprayed with a chemical that inhibits respiration: (i) which of the two ions uptake will be affected’? (ii) give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above.
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Diffusion;
(ii) Sea water contains a higher concentration of sodium ions than the cell sap; (b) (i) Iodide ions; (ii) Sea water has a lower concentration of iodide ions than the cell. The plant requires energy to take up the iodide ions (by active transport);
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN25
State two roles of luteinising hormone in human reproduction.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN24
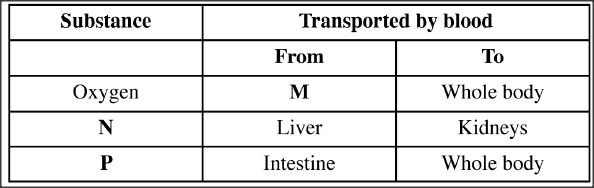
The table provided shows the transportation of substances in the human body.
Name the substances represented by
M N P
ANSWERS
M - lungs;
N - Urea, ammonia. ; P - Digested food. water; mineral ions; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN23
Below is an illustration of a cross section of a plant root showing the transportation of substances in the plant.
(a) Name the substances transported along the paths labelled K and L.
K L (b) Give a reason for your answer in L above.
ANSWERS
(a) K - Photosynthetic products/manufactured foods example vitamins/alicose/proteins/sucrose/maltose/fructose/lipids/nitrates;
L - Water and mineral salts; (b) The substances are moved into the star shaped xylem;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN22
Why are some bacteria able to resist the effect of antibiotics?
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN22
Name two vestigial structures in human beings.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN21
Name the type of skeleton that makes tip each of the following animals:
(a) locust (b) bird.
ANSWERS
(a) Exoskeleton;
(b) Endoskeleton; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN20
State one function of each of the following cell organelles:
(a) golgi bodies (b) lysosomes.
ANSWERS
(a) Packaging of substances/glycoproteins/ transportation of glycoproteins;
Secretion of synthesized proteins and carbohydrates; Formation of lysosomes/modification of carbohydrates to form glycoproteins; (1 mark) (b) Digestion of food/Breakdown large molecules; Destroy worn out organdies or cells/tissue;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN19
Why is a burning charcoal stove in a poorly ventilated room likely to cause death of the inhabitants?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN18
Explain why four months after fertilisation, ovaries can be removed from a human female, without terminating pregnancy.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN18
Explain why mammalian testes are located to hang outside the body
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN17
Give a reason why the image is not formed when light is focused on the blind spot.
ANSWER
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

