|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN08
How is a mammalian heart structurally adapted to its function?
ANSWERS
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN07
Explain the various ways in which seeds and fruits are adapted to dispersal.
ANSWERS
Wind - dispersed seeds / fruits are light / small to be carried by air currents;
Some seeds / fruits have developed hairy structure feather-like projections; wing like structure which increase their surface area to be blown about /carried away by wind; open capsules; borne on long stalks, which are swayed by wind scattering seeds. Water - dispersed fruits / seeds are also light; to float on water; Some, (like coconuts) have fibrous /spongy mesocarps to trap air; making them buoyant/floating on water; Others (like the water lily) produce seeds whose seed coats trap air bubbles; making them float on water; Some have water-proof seed testa / pericarp; remain afloat without soaking /sinking immediately they are released from parent plants; Animal - dispersed fruits have developed hooks; to stick on (the fur of passing) animals; In some cases, fruits are succulent, brightly coloured / scented; to attract animals, birds; The seed coats (of some seeds) are hard; and resistant to the digestive enzymes; hence passing out through the gut undigested; Self dispersal by explosive mechanism; Fruits have sutures/lines of weakness; which split open when drying scattering seeds. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN06
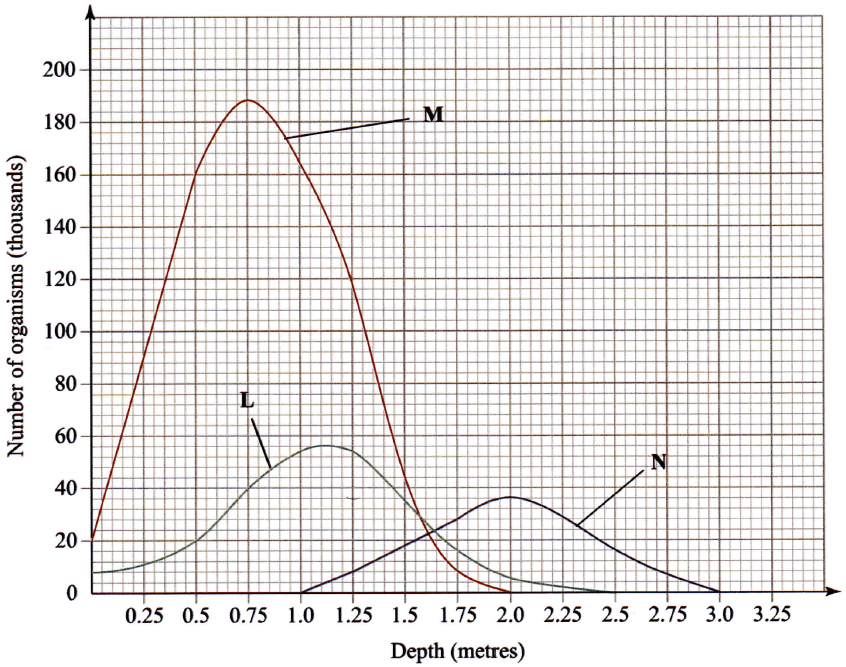
The graph below shows the relative numbers of three main species of organisms in a pond.
(a) Giving a reason for your answer, which of the species is a
(i) producer? Reason (ii) secondary consumer? Reason (b) State the depths at which each of the populations labelled L, M and N is at its optimum. L M N (c) (i) Which method may have been used to determine the population of organisms labelled N in the pond? (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (c) (j) above. (iii) State the assumptions made when using the method in (c) (i) above. (d) State two reasons why primary productivity in the pond decreases with depth. (e) Explain the ecological importance of fungi to plants. (f) Why is flooding likely to lead to a cholera outbreak?
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Producer - M
Reason Largest in number hence source of food for the other species Abundant on the water surface to trap light for photosynthesis; (ii) Secondary consumer - N Reason - Smaller in number than L and M (b) L -1.125m; M- 0.75m; N- 2.00m; (c) (i) Capture - Recapture (method) /Capture - mark - release - recapture; (ii) Animals are highly mobile; (iii) No migration during the period of survey/study; No deaths/variation/reproductiori in population during the period; Method of marking does not affect the animal behaviour; Marked/released animals will freely mix with others in the pond; Released/marked animals will have enough time to mix with the others; There is uniform/random distribution of animals within the period. (d) Decrease in light intensity as depth increases; Decrease in temperature as depth increases; (e) Breakdown of organic materials/decompose/rot/decay of materials; to release plant nutrients; (f) Flood water may mix with human waste contaminated with cholera bacteria; The flood water may then contaminate food / water sources; The contaminated water/food causes cholera infection when ingested; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN05
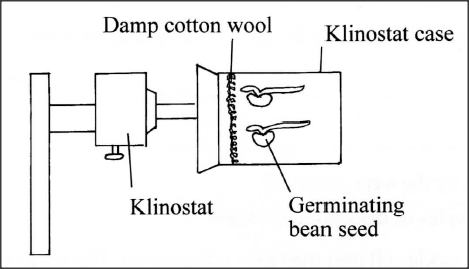
In an experiment to investigate a plant response, the set up shown in the diagram below was used.
(a) Name the type of response that was being investigated.
(b) If the Klinostat was not rotating: (i) state the observations that would be made on the seedlings after three days; (ii) explain the observations in (b) (i) above. (c) If the experiment was repeated with the Klinostat rotating: (i) state the observation that was made on the seedlings after three days; (ii) give a reason for the observation made on the seedlings.
ANSWERS
(a) Geotropism/Gravitropism;
(b) (i) The shoot tip/plumule curved upwards; root tip/radicle curved downwards; (ii) Auxins migrated downwards to lower side; Higher concentration on the lower side; caused more growth on the lower side than on the upper side in shoots inhibited growth on the lower side than on the upper side in the roots; (c) (i) The seedling will continue growing horizontally; (ii) There was even distribution of auxins (on the tips); K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN04
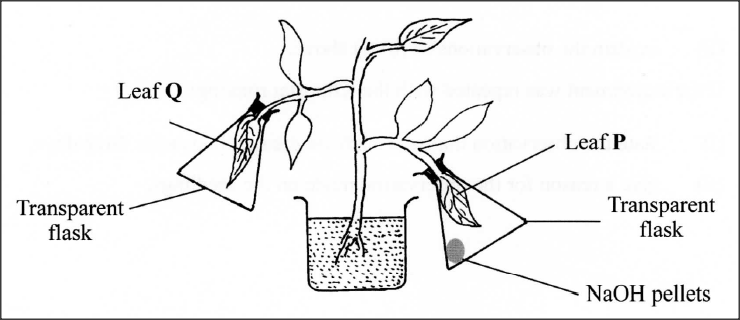
In an experiment to investigate a factor affecting photosynthesis, a potted plant which had been kept in the dark overnight was treated as shown in the diagram below and exposed to light.
(a) Why was the potted plant kept in the dark overnight’?
(b) Which factor was being investigated in the experiment? (c) (i) Which test did the students perform to confirm photosynthesis in the leaves labelled P and Q? (ii) State the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q. P Q (iii) Explain the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q. P Q (d) What was the purpose of leaf Q in the experiment?
ANSWERS
(a) To destarch/remove starch from the leaves;
(b) Carbon (IV) Oxide/CO2; (c) (i) Test for starch; (ii) p - Retained the colour of iodine solution/brown/yellow; Q - Turned blue-black/black/dark-blue; (iii) P - Did not photosynthesize /no starch is formed because Sodium Hydroxide pellets absorbed Carbon (IV) Oxide; Q - Photosynthesized /starch was formed because Carbon (IV) Oxide was in the flask; (d) Control (experiment);
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN03
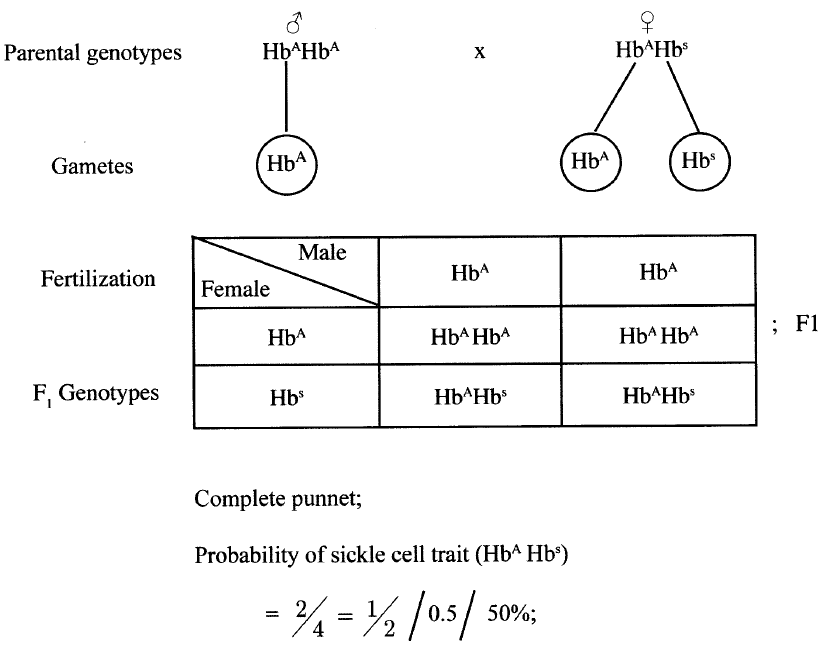
A female with sickle cell trait marries a normal man. The allele for sickle cell is HbS and the normal allele is HbA. Determine the probability that their first born will have the sickle cell trait. Show your working..
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN03
State two examples of discontinuous variation.
ANSWERS
(i) Sex;
(ii) ABO blood group system/Rhesus factor; (iii) Ability to roll tongue; (iv) Free or attached earlobe; (v) Presence/ absence of hair in the nose! on the ear pinna; (vi) Finger prints; ability to taste PTC (phenythiocarbamide) PTV (phenylthio urea) (vii) Winglength in prosophila; (viii) Size of abdomen in drosophila; (ix) Eye colour in prosophila; (x) Smooth/wrinkled seed coats in pea plants; (xi) Green/yellow seed coats/seed coat colour in pea plants; (xii) Polymorphism/melanic and non melanic forms in moths.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN03
What is meant by the term genetics?
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN02
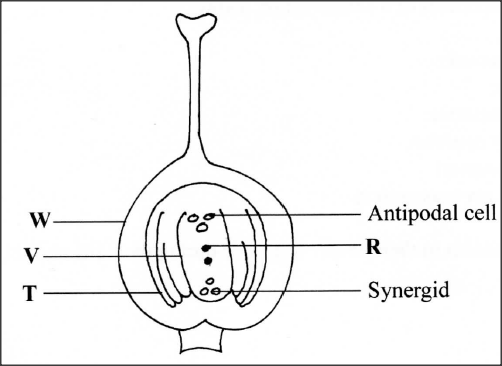
The diagram below illustrates the structure of the female part of a flower.
(a) Name the part labelled W.
(b) Describe what happens when the pollen tube enters the structure labelled V. (c) What do the structures labelled R and T develop into after fertilization? R T
ANSWERS
(a) W - ovary wall/ovary;
(b) Tip of pollen tube bursts open; one of the nuclei fuses with the egg cell nucleus; to form a diploid zygote; while the remaining male nucleus fuses with the polar nuclei; to form a triploid endosperm nucleus; (c) R - Endosperm/primary endosperm; T - testa/seed coat; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN01
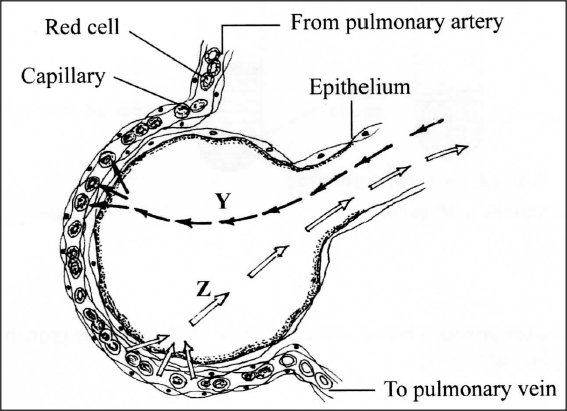
The diagram below illustrates a blood capillary surrounding a structure for gaseous exchange in human beings.
(a) Name the gaseous exchange structure.
(b) Identify the gases labelled Y and Z. Y Z (c) How does the gas labelled Y reach the inside of the blood capillary? (d) How does cigarette smoking lead to lung cancer?
ANSWERS
.(a) Alveolus;
(b) Y - oxygen/O2; Z - Carbon (IV) Oxide/CO2; (c) Oxygen concentration is lower in the blood capillary than in the alveolus; oxygen diffuses; through the epithelium and endothelium of capillary wall, plasma into the red blood cells where it combines with haemoglobin. (d) Cigarettes/tobacco contains tar; tar contains carcinogenic substances; which trigger cancer K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN20
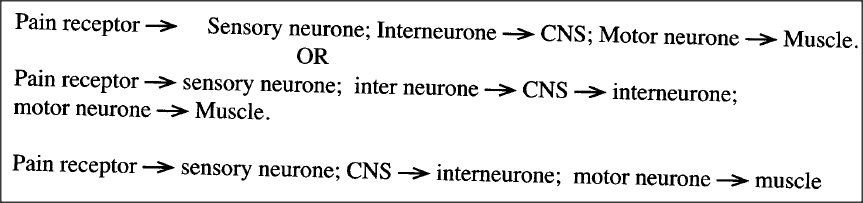
Below are components of a simple reflex pathway:
List the components in their proper sequence during the transmission of a nerve impulse.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN19
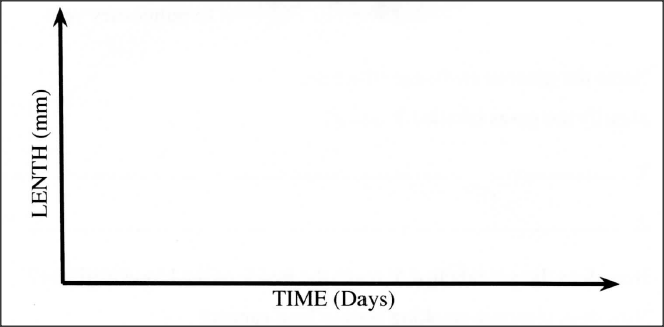
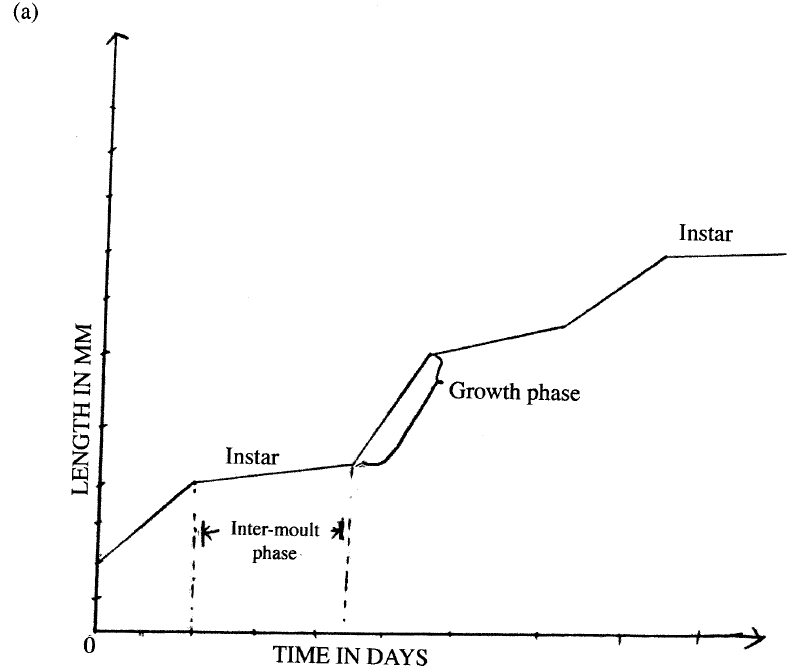
(a) Using the axes provided below, sketch a curve to illustrate the growth pattern observed in the phylum arthropoda.
(b) Explain the growth pattern observed observed in arthropods.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN18
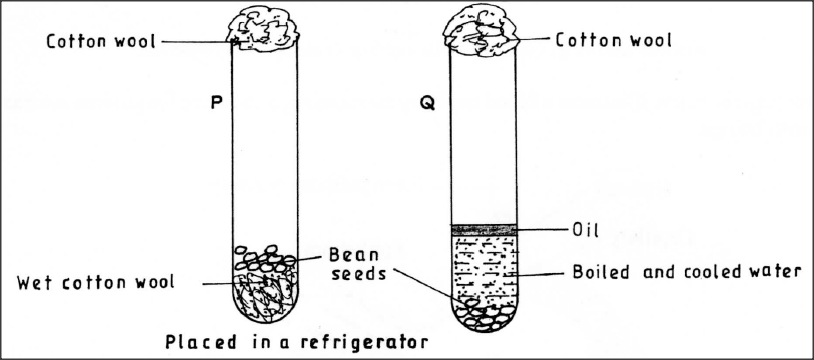
The diagram below shows an experimental set-up to investigate the conditions necessary for germination. Test tube P was placed in a refrigerator while Q was left at room temperature. The set-ups were observed regularly for two weeks but no germination occurred.
Explain the observations in P and Q.
P Q
answers
P - the low temperature/freezing temperature inactivated enzymes;
Q - Boiling eliminated oxygen; oil layer prevented entry of oxygen necessary for respiration during growth;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN17
What happens to the glucose synthesized during photosynthesis?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN17
How is a human stomach adapted to
(i) protein digestion? (ii) churning?
answers
(i) Has gastric glands; that secrete gastric juice;
(ii) Thick muscular wall; that contract and relax;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN16
State four structural differences between millipedes and centipedes.
answers
Millipedes Centipedes
Cylindrical body Dorso - ventrally flattened Head has two clumps of many simple eyes Head has a pair of simple eyes Each segment has two pairs of walking Each segment has a pair of waking legs legs (except the first thoracic segment) Head has a pair of short antennae; Head has a pair of long antennae. No poison claws Has poison claws Three body parts - head short, throrax, Two body parts - head and trunk and trunk Has anterior genital aperture Has aposterior genital aperture Has 9 - 100 segments Has 15 - 21 segments K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN15
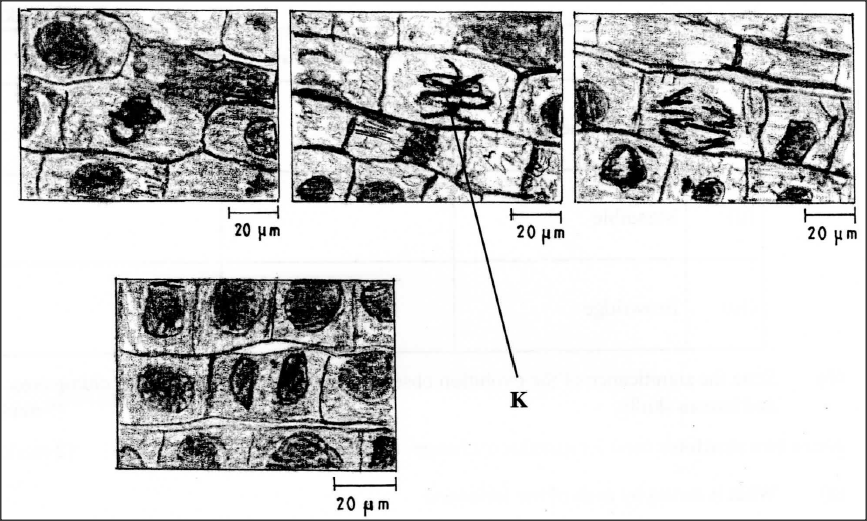
The photomicrographs below show the various stages of cell division in a certain plant.
(a) (i) Name the type of cell division illustrated.
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above. (b) (i) Name the stage of cell division labelled K. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above.
answers
(a) (i) Mitosis;
(ii) Formation of two daughter cells. (b) (i) Metaphase; (ii) Chromosomes are at the equator
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN14
Name two types of involuntary muscles in mammals.
b)State the location of each of the muscles named in (a) above.
answers
Cardiac muscles - heart
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN13
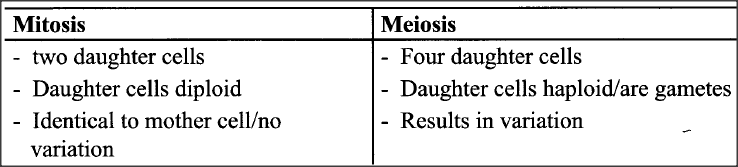
State three differences between the end products of mitosis and meiosis.K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN12
(a) What is meant by each of the following:
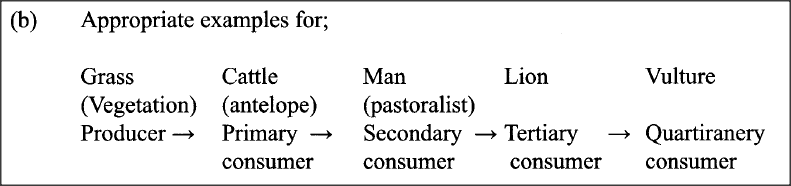
(i) pyramid of biomass? (ii) pyramid of numbers’? (b) During an ecological visit to the Savanna Grassland, students were able to see lions, antelopes, vultures and pastoralists grazing their cattle. Construct a food chain with four consumer levels to illustrate the energy flow in the ecosystem.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN11
Name two structures used for gaseous exchange in plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN10
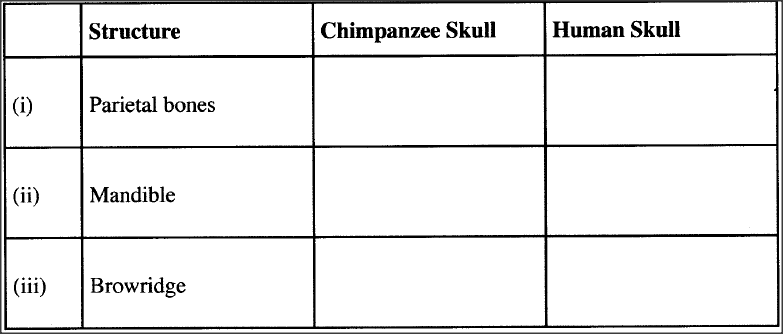
The diagram below illustrates the skulls of adult human and chimpanzee.
(a) State one difference between the two skulls in the following structures:
(b) State the significance of the evolution observed on the parietal bone in the chimpanzee and human skulls.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN09
The diagram below shows an experimental set up to investigate a certain physiological process in plants.
(a) State the aim of the experiment.
(b) State the role of the following in the experiment: (i) potassium hydroxide; (ii) aluminum foil. (c) Account for the expected colour change in tube F.
answers
(a) To show that carbon (TV) oxide is produced during respiration in plants;
(b) (i) Absorb carbon (IV) oxide from the (incoming) air; (ii) Exclude light / to prevent photosynthesis; (c) No colour change in tube F / no observable colour change. Carbon (IV) oxide removed/absorbed from air by potassium hydroxide.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN08
State two control measures for malaria.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN08
Name the organism that:
(î) causes malaria; (ii) transmits malaria.
answers
(i) Plasmodium spp/malariae, vivax, Ovale, falseparum;
(ii) Anopheles female mosquito; |
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

