K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN02
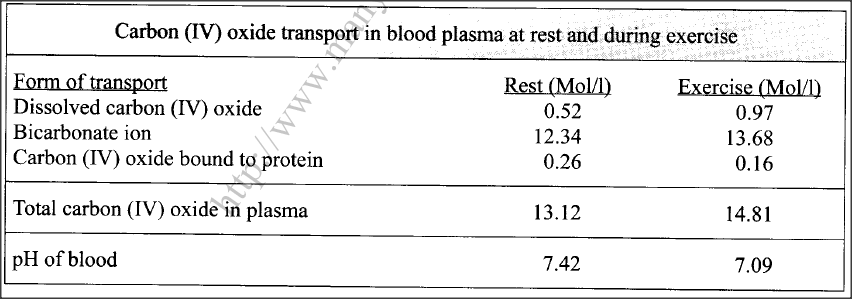
The table below shows variations in the form carbon (IV) oxide is transported in the blood at rest and during physical exercise.
(a) Explain why more carbon (IV) oxide ¡s transported in the form of bicarbonate ion.
(b)Account for the high total plasma content of carbon (IV) oxide during exercises. (c) State how one’s involvement in the exercises affects blood pH. (d) Name the protein responsible for the transport of carbon (IV) oxide in the blood.
ANSWERS
(a) Presence of carbonic anhydrase enzyme; which speeds up the conversion of carbon (IV) oxide to weak carbonic acid; which dissociates into hydrogen carbonate ion/(HCO3) (that diffuses out of the red blood cells into the blood plasma);
(b)The body needs high amount of energy; (for the exercise/muscle activity) hence high respiration rate (more oxygen intake); releasing more carbon (IV) oxide (in the blood plasma); (c)The high rate of respiration (during physical exercises coupled with normal cellular metabolism) results in the production of more carbon(IV) oxide/faster accumulation of lactic acid; lowering the blood plasma pH/making it more acidic (compared to when one is at rest); (d)Haemoglobin
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN08
Describe how the mammalian eye is structurally adapted to its function.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN07
Explain the importance of protecting the forest ecosystem with reference to the following:
(a) climate change (b) biodiversity (c) biotechnology (d) water conservation (e) pollution.
answers
a) Climate change
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN06
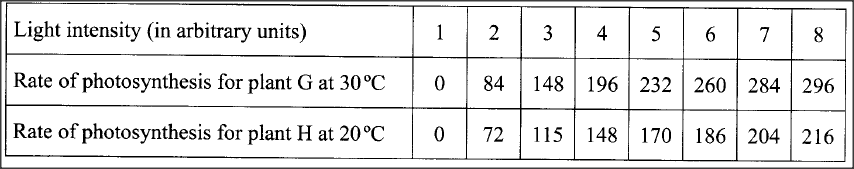
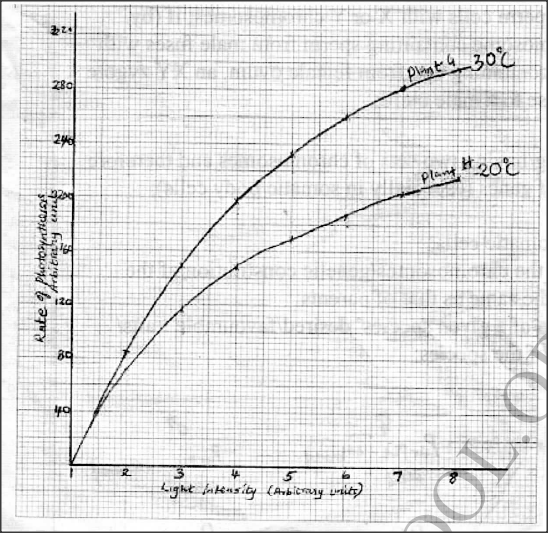
In an investigation, two potted plants G and H belonging to the same species were exposed to increasing light intensities at different temperatures, 30°C and 20°C respectively. The rate of photosynthesis was measured for each plant and results recorded as shown in the table below:
(a) On the same axis, plot graphs of rate of photosynthesis against light intensity for plants G and H.
(b) State the aim of the investigation. (c) Account for the difference in the rate of photosynthesis in the two plants. (d) Account for the difference in the rate of photosynthesis in the two plants between the following light intensities: (i) 1—4 units (ii) 4—8 units. (e) (i) Predict the rate of photosynthesis at light intensity of 16 units. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (e) (i) above. (f) State one internal and one external factor that could be limiting in the investigation.
answers
b) To investigate/compare the effect of (varying) light intensity/temperature on the rate of photosynthesis;
c) Rate of photosynthesis is higher in plant G (than H); (Photosynthesis being an enzymatic process), enzymes were subjected to favourable/optimal temperatures (of 30°C): hence more activated, unlike in plant H where temperatures were lower (20C); d) (i) 1-4 units Rapid increase in rate of photosynthesis increases with the increase in light intensity; due to increase in light energy for photosynthesis/formation of more ATP molecules; (ii) 4 — 8 units Slower/gradual increase in the rate of photosynthesis as the light intensity increases: because other factors become limiting/some chlorophyll molecules start bleaching; e) i) Slight increase/no significant increase/remains constant; ii) The optimum light intensity has been exceeded/some chlorophyll could be destroyed; f) Internal factor — Chlorophyll/enzyme concentration; External factor — Carbon (IV) oxide concentration/amount of water;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN05
State how in-breeding leads to reduced hybrid vigour
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN05
State two advantages of using genetically modified varieties in bean farming.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN05
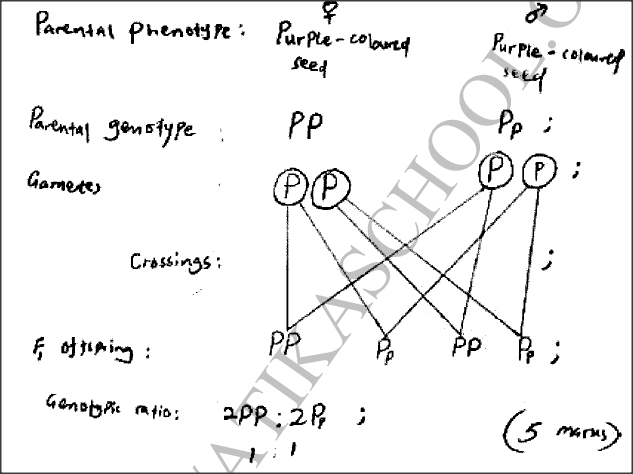
In beans, the gene for purple colour is dominant over the gene for white colour. A pure breeding bean plant with purple colour was crossed with a heterozygous bean plant.
Using the letter P to represent the gene for purple colour, work out the genotypic ratio of the offspring. Name the hormone responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in human males.1/7/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
Name the hormone responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in human males.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
State the significance of diploidy.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
(i) Define the term diploidy.
(ii) Name the type of cell division that gives rise to diploid cells. (iii) Name the type of cells in which the process named in (b) (ii) above Occurs.
answers
i. State of being/having two sets of chromosomes and therefore two copies of genes (especially in somatic/body cells);
ii. Mitosis; iii. Body cells/somatic cells;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
Explain how the sex of a male child is determined in human beings.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN03
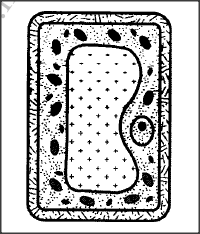
The diagram below illustrates the appearance of a plant cell after it had been put in a certain solution.
(a) Explain the appearance of the cell at the end of the treatment.
(b) Explain the results obtained if a red blood cell is subjected to the same treatment. (c) Explain why transfusion with distilled water is not recommended for a dehydrated patient.
answers
(a) The cell is turgid; its cell sap was hypertonic (compared to the solution in which it was placed); by osmosis, water moved into the cell across its cell semi-permeable membrane, (swelling and becoming turgid);
(b)The red blood cell lacks the cell wall; water molecules move across its semi-permeable membrane by osmosis; into its hypertonic medium (inside the cell),cell contents/cytoplasm swelling and bursting haemolyses; (c)Would haemolyse; due, to lowering of the osmotic pressure of the blood below normal; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN01
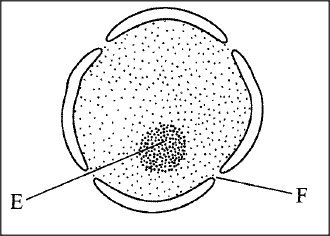
The diagram below represents a nucleus.
(a) Name the structures labelled E and F.
(i) E F (ii) State the function of F. (iii) With reference to the nucleus, state one difference between an animal and a bacterial cell. (b) Name the plant cell organelle: (i) that stores chlorophyll (ii) responsible for intracellular digestion. (c) State two main functions of the vacuole in the amoeba.
ANSWERS
(a) E—Nucleolus;
F — Nuclear pore/nucleopore; ii. Facilitates movement of materials in and out of the nucleus; iii. Nuclear material in the bacterial cell is not enclosed within a membrane /prokaryotic, while in animal cell it is enclosed eukaryotic; (b) i. Chloroplast; ii. Lysosome; (c) i. Feeding (food vacuole); ii. Osmoregulation (contractile vacuole); iii. Excretion/removal of wastes; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN23
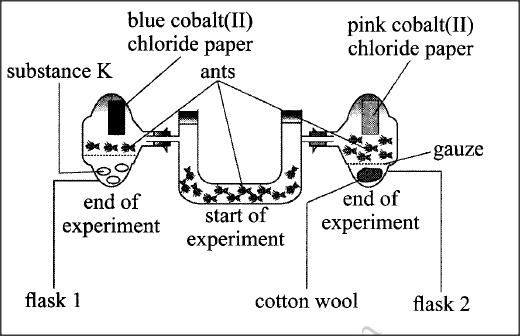
The diagram below represents a set up during an experiment.
(a) (i) What was, the experiment investigating?
(ii) State the likely identity for substance K (iii) Explain your answer in (a) (ii) above (b) Account for the observations made in flask 2.
answers
a.) i) To investigate how ants respond to moisture/water hydrotaxis (varied environments with/without moisture water);
ii) Silica gel/anhydrous calcium chloride pellets/pyrogallic acid/dehydrating drying agent; iii) The colour of cobalt (II) chloride paper remained blue/all the moisture water vapour was absorbed/There was no water/moisture in the flask to change the colour of cobalt(II) chloride paper; b.) (More) ants were attracted) moved into the flask; due to the presence of moisture/water vapour; (evidenced by the change of cobalt (II) chloride paper to pink)
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN22
State two ways by which plants manage their solid wastes.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN21
The photograph below represents a leaf obtained from a certain plant.
Account for the observations made if the leaf was tested for starch.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN20
State three methods of fossil formation.
answers
i. Petrification/change into rock;
ii. Entire organism or parts preserved; iii. Impressions (e.g. casts/moulds); K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN19
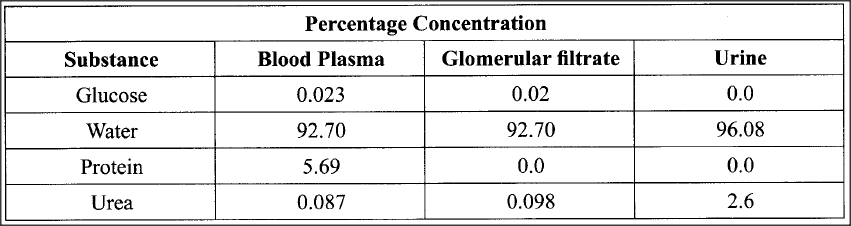
The table below shows the percentage concentration of certain substances in blood plasma, glomerular filtrate and urine in a human being at a particular time.
(a) Explain the likely impact on the composition of urine in case of the following:
(i) Vigorous physical exercises (ii) a meal rich in proteins (b) Name the processes responsible for: (i) Presence of glucose in the glomerular filtrate (ii) absence of glucose in urine
answers
a. i) Less water and urea; since sorne is excreted/eliminated through the skin (as sweat);
ii) increased amount of urea in the urine; due to deamination of amino acids (from proteins); b. i) ultra filtration; ii) Selective reabsorption; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN18
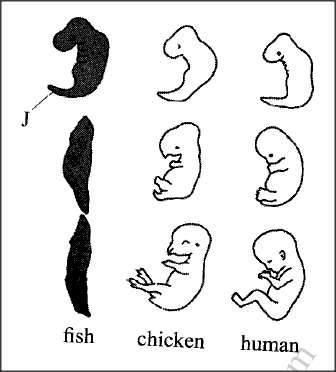
Below are diagrams representing developmental stages of three different vertebrates.
(a) State the evidence of evolution illustrated by the vertebrates in the diagram.
(b) Suggest why the structure labelled J has been retained throughout the evolution of fish. (c) State two major advantages evolution has given humans Over most of the other animals.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN17
How is the surface area increased in the mammalian small intestines?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN16
The following are text messages on a celiphone that represent gene mutation.
(a) Identify the type of gene mutation represented in each case
I II (b) State Mendel’s First Law. (c) State two disadvantages of genetically modified plant products.
answers
a. I — Deletion;
II- Inversion; b. The characteristics /traits of an organism are determined by internal factors/ genes (which occur in pairs). Only one of the genes can be carried in a gamete/ passed onto the next generation; c. Most have lost most of the original (desirable) qualities e.g taste; Poor/undesirable qualities are perpetuated through subsequent generations; Products’ qualities are irreversible- can’t get original species/qualities;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN15
Explain the physiological process responsible for keeping young seedlings upright.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN14
The photograph below illustrates a germinating seedling.
(a) Name the type of germination illustrated in the photograph.
(b) Explain the function of each of the parts labelled G and H. G H
answers
a. Epigeal;
b. G- Elongates to expose the foliage leaves to light photosynthesis H- Stores food (for growth); For photosynthesis (it is green); Protects plumule during germination; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN12
Explain the survival values of the following tropic responses to plants.
(a) Geotropism (b) Phototropism
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

