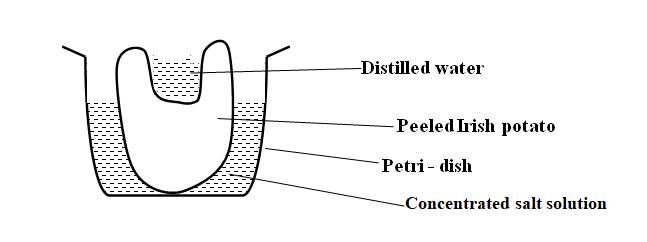
A group of students set up an experiment to investigate a certain physiological process. The set up
|
| Ions | Concentration in pond water | Concentration in cell |
| Sodium | 50 | 30 |
| Potassium | 2 | |
| Calcium | 15 | 1 |
| Chloride | 180 | 200 |
(i) Sodium ions
(ii) Potassium ions
(b) For each processes named in (a) (i) and (ii) above, state one condition necessary for the process to take place.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN11
Explain each of the following physiological observations:
(a) sportsmen release little, concentrated urine at the end of a strenuous exercise
(b) a rabbit has a higher oxygen demand than a camel
(a) sportsmen release little, concentrated urine at the end of a strenuous exercise
(b) a rabbit has a higher oxygen demand than a camel
answers
(a) during /after the exercise one sweat ; (profusely to cool the body/eliminate some nitrogenous (wastes) a lot of water is lost through this ; one is dehydrated ;(the little) water that is left in the body system (further) selectively reabsorbed in the kidney tubules (resulting in less but concentrated urine;)
(b) a rabbit has a higher surface area to volume ratio/ smaller in size hence has a bigger surface area exposed to heat loss to the environment/ lose heat faster/ its more active than the camel; hence need more oxygen to(aerobically) respire (to synthesize the needed energy to support its activity /lifestyle;
(b) a rabbit has a higher surface area to volume ratio/ smaller in size hence has a bigger surface area exposed to heat loss to the environment/ lose heat faster/ its more active than the camel; hence need more oxygen to(aerobically) respire (to synthesize the needed energy to support its activity /lifestyle;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN04
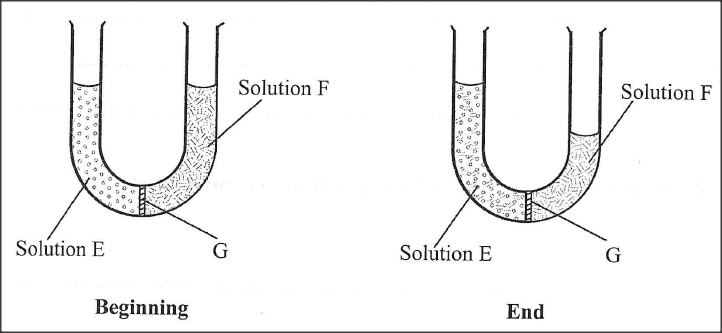
In investigating a certain physiological process, students set up the apparatus as shown below and made the observations after 30 minutes as illustrated.
(a) Name the physiological process being investigated.
(b) Account for the observation made at the end of the experiment.
(c) State the likely identity of G.
(b) Account for the observation made at the end of the experiment.
(c) State the likely identity of G.
answers
. (a) osmosis
(b) solution E is hypertonic/ had more solute molecules compared to solution F; solution F hypotonic to solution E; by osmosis water molecules move through the semi- permeable membrane G (from solution F to E); hence decreases in volume of F/ increased solution E;
(c) semi permeable membrane /visking tubing /slice of potato /pawpaw (any other permeable plant tissue) pig bladder/cellophane paper/dialysis membranes.
(b) solution E is hypertonic/ had more solute molecules compared to solution F; solution F hypotonic to solution E; by osmosis water molecules move through the semi- permeable membrane G (from solution F to E); hence decreases in volume of F/ increased solution E;
(c) semi permeable membrane /visking tubing /slice of potato /pawpaw (any other permeable plant tissue) pig bladder/cellophane paper/dialysis membranes.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN04
A group of form two students placed a fresh leaf in warm water. They observed that air bubbles formed on the surface of the leaf.
(a) What biological process were they investigating?
(b) Name the structures from which the air bubbles were coming from.
(c) Explain the distribution of the structures named in (b) above on the leaf surfaces of a land plant.
(a) What biological process were they investigating?
(b) Name the structures from which the air bubbles were coming from.
(c) Explain the distribution of the structures named in (b) above on the leaf surfaces of a land plant.
answers
a) Photosynthesis;/gaseous exchange in plants;
b) Stoma/somata;
c) Are more on the lower surface of terrestrial plants/fewer on the upper surface; to reduce transpiration;
b) Stoma/somata;
c) Are more on the lower surface of terrestrial plants/fewer on the upper surface; to reduce transpiration;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN21
The photograph below represents a leaf obtained from a certain plant.
Account for the observations made if the leaf was tested for starch.
answers
- Differences in distribution of chlorophyll/leaf is variegated; green patches would photosynthesize forming starch; giving blue-black colour with iodine solution unlike the regions without chlorophyll;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN15
Explain the physiological process responsible for keeping young seedlings upright.
answers
- Osmosis; water moves into the cells becoming turgid; attaining mechanical support ;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN11
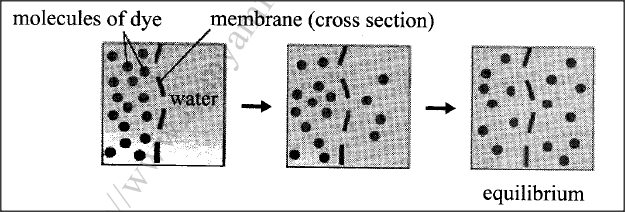
The set up below illustrates a certain physiological process.
(a) (i) Name the physiological process.
(ii) Give two examples of the process named in (a) (i) above in plants.
(b) State two ways by which the movement of dye molecules in the set up would be slowed down.
(ii) Give two examples of the process named in (a) (i) above in plants.
(b) State two ways by which the movement of dye molecules in the set up would be slowed down.
answers
a i) Diffusion;
ii) Gaseous exchange/excretion of carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen;
Translocation of materials;
Absorption/uptake of mineral ions/salts;
b. Lowering the temperature of the medium;
Increasing thickness of the membrane;
Use less dye/add more water/reducing the concentration gradient;
ii) Gaseous exchange/excretion of carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen;
Translocation of materials;
Absorption/uptake of mineral ions/salts;
b. Lowering the temperature of the medium;
Increasing thickness of the membrane;
Use less dye/add more water/reducing the concentration gradient;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN06
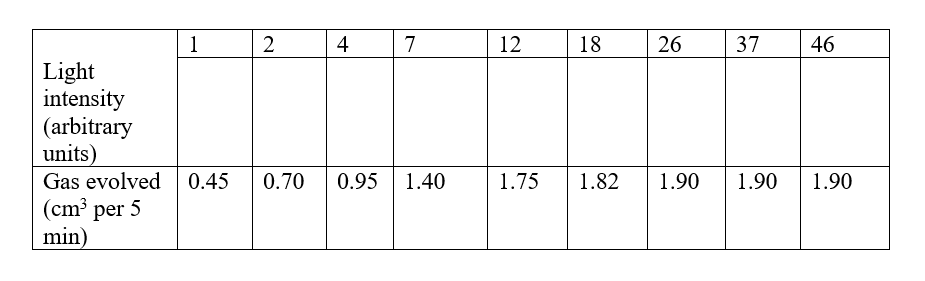
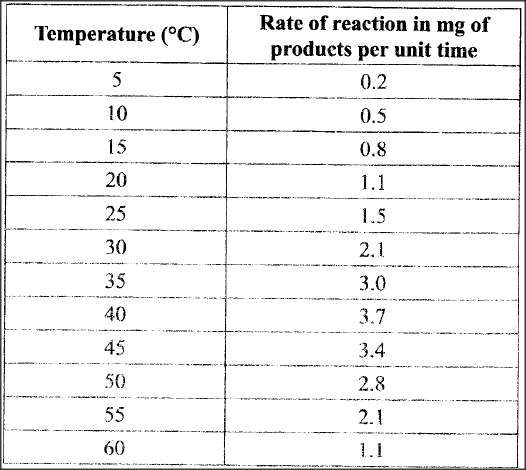
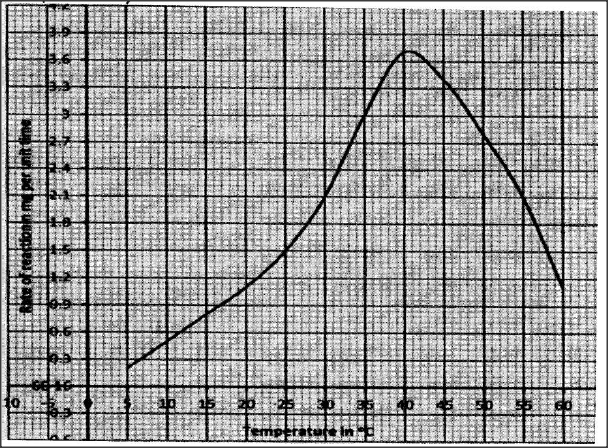
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction catalysed by an enzyme. The results are shown in the table below.
(a) On the grid provided plot the rate of reaction against temperature.
(b) When was the rate of reaction 2.6 mg of product per unit time?
(c) Account for the shape of the graph between:
(i) 5°C and 40°C
(ii) 45°C and 60°C
(d) Other than temperature name two ways in which the rate of reaction between 5°C and 40°C could be increased.
(e)(i) Name one digestive enzyme in the human body which works best in acidic condition.
(ii) how is the acidic condition for the enzyme named in (e) (I) above attained’?
(f) The acidic condition in (e) (iii) above is later neutralized.
(i) Where does the neutralization take place?
(ii) Name the substance responsible for the neutralization.
(b) When was the rate of reaction 2.6 mg of product per unit time?
(c) Account for the shape of the graph between:
(i) 5°C and 40°C
(ii) 45°C and 60°C
(d) Other than temperature name two ways in which the rate of reaction between 5°C and 40°C could be increased.
(e)(i) Name one digestive enzyme in the human body which works best in acidic condition.
(ii) how is the acidic condition for the enzyme named in (e) (I) above attained’?
(f) The acidic condition in (e) (iii) above is later neutralized.
(i) Where does the neutralization take place?
(ii) Name the substance responsible for the neutralization.
answers
(b) 330C and 51.5 (± 0.50C)
32.5 - 33.5 and 51.0 – 52.0
(c) (i) 5°C and 40° C
As temperature is increased rate of reaction is increased/ more products are formed (per unit time) because enzymes become more active
(ii) 45° C and 60° C
As temperature increase rate of reaction decreases less/products are formed (unit per time) because enzymes become denatured by high temperatures above 40, hence cannot act on substrate.
(d) Increase in enzyme and substance concentration
Use of co-factors and co-enzymes
(e) (i) Pepsin,
Chymosin
Renin
(ii) Wall of stomach/ gastric gland/ oxyntic/ pariental/ cell produced Hydrochloric
(f) (i) Duodenum
(ii) Bile juice/ e.g. NaHCO3
32.5 - 33.5 and 51.0 – 52.0
(c) (i) 5°C and 40° C
As temperature is increased rate of reaction is increased/ more products are formed (per unit time) because enzymes become more active
(ii) 45° C and 60° C
As temperature increase rate of reaction decreases less/products are formed (unit per time) because enzymes become denatured by high temperatures above 40, hence cannot act on substrate.
(d) Increase in enzyme and substance concentration
Use of co-factors and co-enzymes
(e) (i) Pepsin,
Chymosin
Renin
(ii) Wall of stomach/ gastric gland/ oxyntic/ pariental/ cell produced Hydrochloric
(f) (i) Duodenum
(ii) Bile juice/ e.g. NaHCO3
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN05
A freshly obtained dandelion stem measuring 5cm long was split lengthwise to obtain two similar pieces. The pieces were placed in two different solutions of different concentrations in petri dishes (L1 and L2) for 20 minutes. The appearance after 20 minutes is as shown.
(a) Account for the appearance of the pieces in solutions L1 and L2
(b) Suite the significance of the biological process involved in the experiment.
(b) Suite the significance of the biological process involved in the experiment.
answers
(a) L1 - Inner cells gained water by Osmosis; hence increased in length; epidermal cells did not gain water because they are covered by a water proof cuticle leading to curvature.
L2 - Inner cells lost water by osmosis; leading to (flaccidity) decrease in length; epidermal cells did not lose water due to waterproof leading to curvature
(b) Absorption of water by the roots
Opening and closing of the stomata
L2 - Inner cells lost water by osmosis; leading to (flaccidity) decrease in length; epidermal cells did not lose water due to waterproof leading to curvature
(b) Absorption of water by the roots
Opening and closing of the stomata
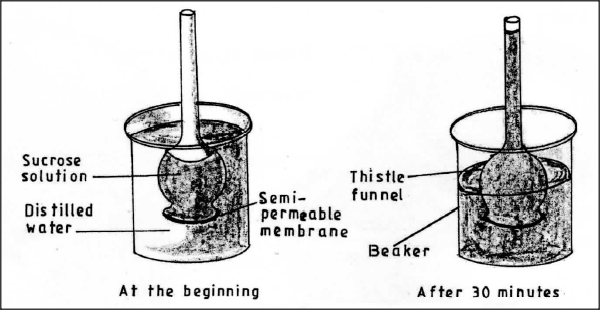
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN06
Students set up an experiment as illustrated below.
(a) Name the physiological process that resulted in the observations made after 30 minutes.
(b) State the importance of the physiological process investigated in plants.
(c) Explain the observations made after 30 minutes.
(b) State the importance of the physiological process investigated in plants.
(c) Explain the observations made after 30 minutes.
answers
(a) Osmosis;
(b) Absorption of water from the soil; opening and closing of stoma; feeding in insectivorous plants; support (in seedlings, leaves,herbaceous plants);
Movement of water from cell to cell in plants.
(c) The thistle funnel gained water by osmosis; because the sucrose solution was hypertonic;
(b) Absorption of water from the soil; opening and closing of stoma; feeding in insectivorous plants; support (in seedlings, leaves,herbaceous plants);
Movement of water from cell to cell in plants.
(c) The thistle funnel gained water by osmosis; because the sucrose solution was hypertonic;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN10
What is meant by each of the following terms?
(i) Crenated cell.
(ii) Flaccid cell.
(i) Crenated cell.
(ii) Flaccid cell.
ANSWERS
(i) Crenated cell is a shrunk animal cell that has lost water by osmosis;
(ii) Flaccid cell is a flabby /shrunk plant cell that has lost waster by osmosis;
(ii) Flaccid cell is a flabby /shrunk plant cell that has lost waster by osmosis;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN10
Explain two roles of diffusion in human beings.
ANSWERS
- Absorption of materials e.g. diffusion of digested food into the blood stream;
- Gaseous exchange e.g. CO2,/O2, diffuses from capillaries into the alveoli.
- Excretion of nitrogenous wastes; e.g. urea diffuses from blood capillaries into the elimination sites.
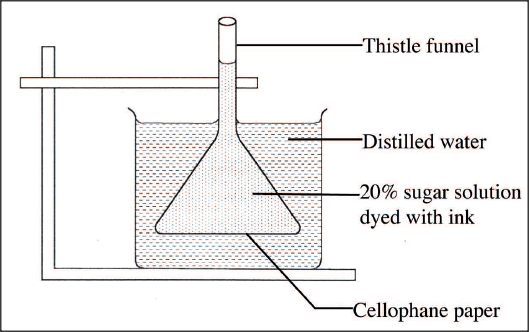
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN05
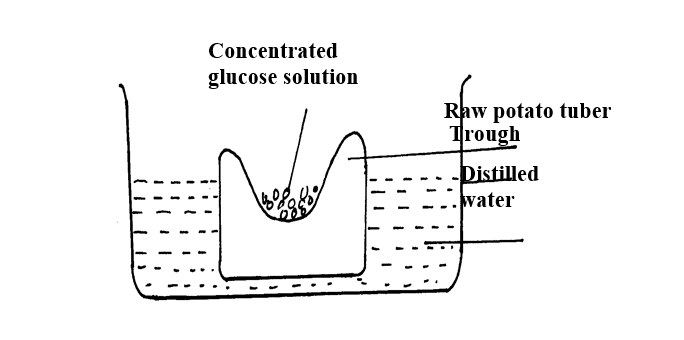
The diagram below shows a set up for an experiment to demonstrate a certain physiological process.
(a) What nature of solution is represented by 20% sugar solution?
(b) Explain the observation made on the set up after one hour.
(b) Explain the observation made on the set up after one hour.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN30
State two ways in which osmosis is significant to plants.
answers
- Absorption of water; support;
- Opening and closing of stomata;
- Feeding in insectivorous/plants;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN05
Describe how turgor pressure builds up.
answer
- As the cell gains water by osmosis; the sap/cellvacuole enlarges; pushing the cytoplasm outwards; exerting pressure on the cell wall;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN01
Explain how an increase in temperature affects the rate of active transport.
answers
- The rate of active transport increases with increase intemperature up to the optimum temperature;
- Further increase in temperature slows down the rate of active transport until it stops because it denatures enzymes;
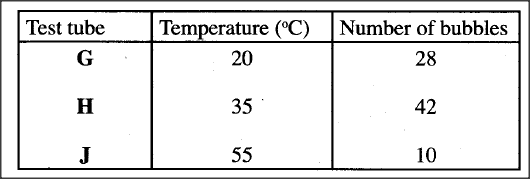
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN03
(a) In an investigation, equal amounts of water was placed in. three test-tubes labelled G, H and J. Pondweeds of equal length were dropped in each test tube. The test-tubes were then placed in identical conditions of light and carbon (IV) oxide at different temperatures for five minutes. After the five minutes, the bubbles produced in each test-tube were counted for one minute. The results were as shown in the table below.
(i) Name one requirement for this process that is not mentioned in the investigation.
(ii) Name the gas produced in this investigation.
(iii) Account for the results in test-tubes H and J.
(b) State two ways in which the human intestinal villus is adapted to its function.
(ii) Name the gas produced in this investigation.
(iii) Account for the results in test-tubes H and J.
(b) State two ways in which the human intestinal villus is adapted to its function.
answers
(a) (i) chlorophyll;
(ii) oxygen; (1 mark)
(iii) Test tube H is at optimum temperature for enzyme activity; hence high rate of
photosynthesis/more bubbles. In test tube J most enzymes have been denaturedby the high temperature; hence low rate of photosynthesis/fewer bubbles.
(b) — The villus epithelium is thin; for faster diffusion of dissolved food substances;
— The epithelium has goblet cells; which produce mucus to lubricate food passage;
— They have microvilli; which further increase their surface area for absorption;
Have lacteal; for absorption of fatty acid & glycerol/transportation of lipids;
Highly vascularised; for absorption of digested food.
(ii) oxygen; (1 mark)
(iii) Test tube H is at optimum temperature for enzyme activity; hence high rate of
photosynthesis/more bubbles. In test tube J most enzymes have been denaturedby the high temperature; hence low rate of photosynthesis/fewer bubbles.
(b) — The villus epithelium is thin; for faster diffusion of dissolved food substances;
— The epithelium has goblet cells; which produce mucus to lubricate food passage;
— They have microvilli; which further increase their surface area for absorption;
Have lacteal; for absorption of fatty acid & glycerol/transportation of lipids;
Highly vascularised; for absorption of digested food.
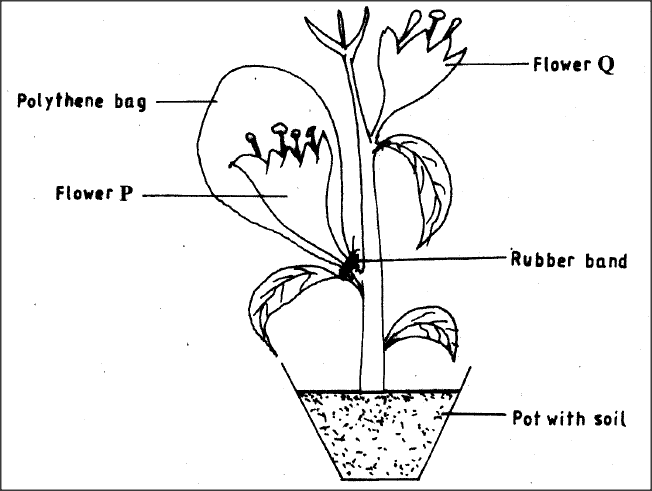
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN16
The diagram below represents an experimental set-up used by students to investigate a certain process.
Flower Q produced seeds while P did not. Account for the results.
answers
- The plant/flower is self sterile/not successfully self pollinated; covering prevents pollination; in flower P. Flower Q received pollen from other plants/cross pollination;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN13
State three factors that affect the rate of diffusion.
answers
Temperature; surface area; distance that particles have to travel; diffusion/concentration gradient; size/density of particles; surface area to volume ratio; thickness of membrane; medium of diffusion
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN07
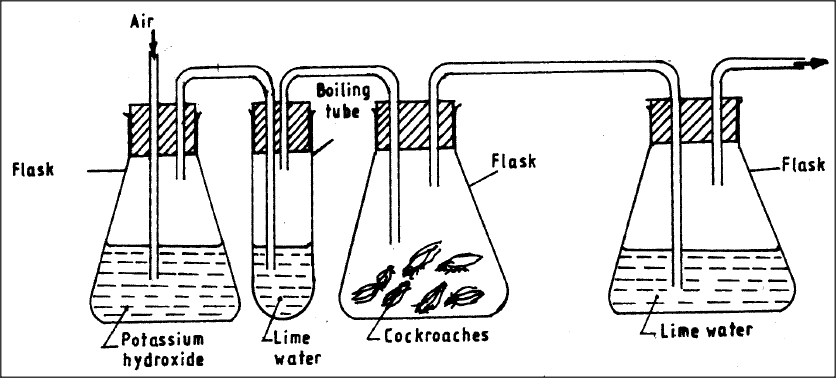
The diagram below represents a set-up that students used in an investigation.
(a) Name the physiological process that was being investigated.
(b) State the role of potassium hydroxide in flask K.
(c) Account for the observation in boiling tube L and flask N.
L .
N
(b) State the role of potassium hydroxide in flask K.
(c) Account for the observation in boiling tube L and flask N.
L .
N
answers
(a) Respiration/aerobic respiration;
(b) Flask K Potassium hydroxide removes Carbon IV Oxide from atmospheric air;
(c) L - Lime water remains clear because Carbon (IV) Oxide has been removed;
Flask N lime water forms a white precipitate because the respiring cockroaches produce Carbon (IV) Ovide;
(b) Flask K Potassium hydroxide removes Carbon IV Oxide from atmospheric air;
(c) L - Lime water remains clear because Carbon (IV) Oxide has been removed;
Flask N lime water forms a white precipitate because the respiring cockroaches produce Carbon (IV) Ovide;
Archives
December 2024
January 2024
November 2023
January 2023
December 2022
September 2022
August 2022
April 2022
March 2022
November 2021
October 2021
September 2021
November 2020
October 2020
August 2020
July 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
September 2019
August 2019
October 2015
Categories
All
1995
1996
1997
1998
1999
2000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
Animals
Bilharzia
BIOLOGY ESSAY
Blood Cells
Cell Physiology
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
Chromosomes
Circulatory System
Classification
Co-ordination
DASHBOARD
Diffusion
Diseases
DNA
Ecology
Evolution
Excretion And Homeostasis
Form 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 3 Level
Form 4
FUNGI
Gaseous Exchange
Genetics
GERMINATION
Growth And Development
HIV/AIDS
HORMONES
Introduction To Biology
Kidney
Malaria
METABOLISM
Nutrition
Nutrition In Animals
Nutrition In Plants
Osmosis
Oxygen
Paper 1
Paper 2
PAPER 3
Photosynthesis
PHOTOTROPISM
PLANT CELLS
POLLINATION
Reception
Reception_Response And Coordination In Plants And Animals
Reproduction In Animals
Reproduction In Plants And Animals
Respiration
Response And Co Ordination
REVISION KIT
Section A
SECTION B
Section C
Sodium
Support And Movement In Plants And Animals
TAXONOMY
TERM 1
TERM 2
The Cell
Theory Of Inheritance Of Acquired Characteristics
Transplant In Plants
Transport In Plants And Animals
TOPICS
FORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

