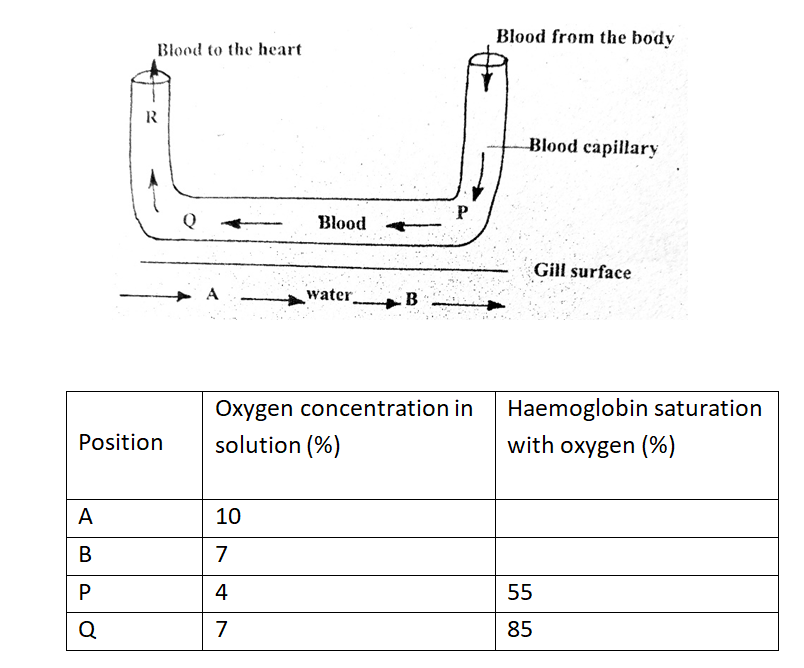
The diagram below represents the direction of flow of blood in a gill capillary. The percentage of oxygen in solution at position A, B, P, Q and R is given in the table below.a) Why is the oxygen percentage low at P? (1mk)
Blood coming from the body has supplied the tissue cells with oxygen/ oxygen has diffused out of capillary into the tissue fluid;
b) Using evidence from the data given, suggest what will happen to oxygen in the water at point B. (3mks)
Oxygen concentration at B reduces/will be at lowest; because blood at P has a lower oxygen concertation creating a diffusing gradient; From A to B there is a diffusion gradient hence at B much oxygen has diffused into the from water into the blood;
c) Name the organ into which blood coming from the capillary at Q flows. (1mk)
Heart
d) Suppose the flow of blood in the capillary illustrated above was in the opposite direction, explain the disadvantage it would have to the fish. (2mks)
Amount of exchange of respiratory gasses between blood and water would reduce; because of reduced diffusion gradient;
e) Name the principle where the blood flows in the opposite direction to another fluid. (1mk)
Counter flow system.
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN02
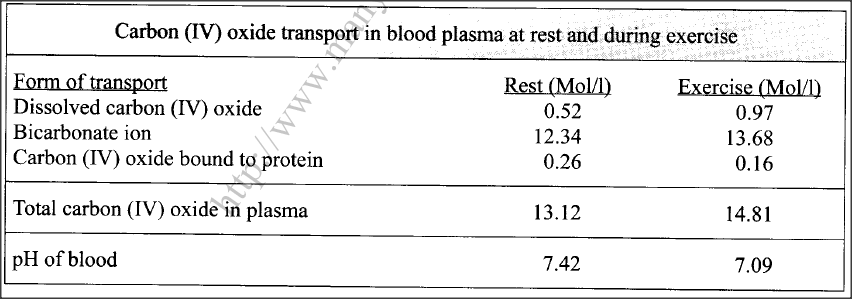
The table below shows variations in the form carbon (IV) oxide is transported in the blood at rest and during physical exercise.
(a) Explain why more carbon (IV) oxide ¡s transported in the form of bicarbonate ion.
(b)Account for the high total plasma content of carbon (IV) oxide during exercises. (c) State how one’s involvement in the exercises affects blood pH. (d) Name the protein responsible for the transport of carbon (IV) oxide in the blood.
ANSWERS
(a) Presence of carbonic anhydrase enzyme; which speeds up the conversion of carbon (IV) oxide to weak carbonic acid; which dissociates into hydrogen carbonate ion/(HCO3) (that diffuses out of the red blood cells into the blood plasma);
(b)The body needs high amount of energy; (for the exercise/muscle activity) hence high respiration rate (more oxygen intake); releasing more carbon (IV) oxide (in the blood plasma); (c)The high rate of respiration (during physical exercises coupled with normal cellular metabolism) results in the production of more carbon(IV) oxide/faster accumulation of lactic acid; lowering the blood plasma pH/making it more acidic (compared to when one is at rest); (d)Haemoglobin
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN08
State three ways in which blood capillaries are structurally adapted to their functions.
(a) Describe the mechanism of inhalation in man. (10mks)
External intercostals muscles contract; internal intercostals muscle relax, Rib cage move outwards; and upwards; Diaphragm muscles contract, Diaphragm flatten; volume in thoraci cavity increases; pressure reduces.
Atmospheric air enters the lungs; inflate (correct sequence to be followed) (b) Using photosynthesis theory explain the mechanics of opening of stomata. (10mks)
Guard cells have chloroplast which photosynthesis in the presence of light, to form sugar, the osmotic pressure of guard cell increases; water move from neighbouring cells into guard cells being thicker than outer walls. Causes the outer wall to stretch more resulting guard cells budging outwards.
State the importance of breathing through the nose than through the mouth. (2mks)
Name two types of active immunity (2mks)
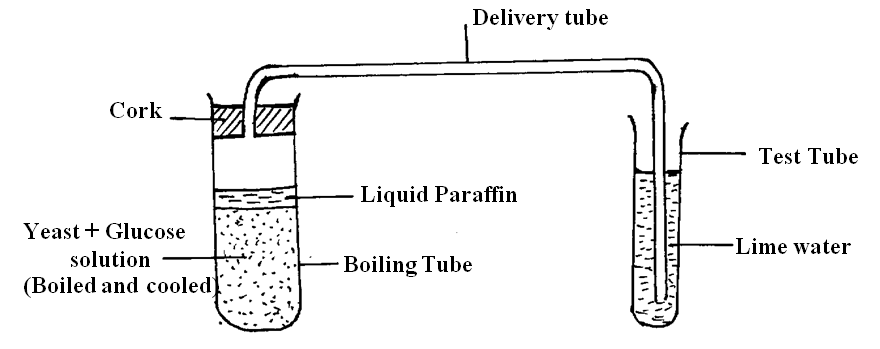
(a) Which process was being investigated? (1mk)
Anaerobic respiration
Rej: Respiration alone (b) Why was it necessary to boil the glucose solution? (1mk)
To expel all the dissolved oxygen;
(c) Write a word equation representing the chemical reaction taking place above in the boiling tube (1mk)State two physiological mechanisms of controlling the human body temperatures during a hot day1/11/2021 (a) State two physiological mechanisms of controlling the human body temperatures during a hot day (2mks)
b) Name two ways in which loop of Henle is adapted to its function (2mks)
a) List down two differences between closed and open circulatory systems (2mks)Open system
Closed system
b) Name two ways in which heart muscles are special (2mks)
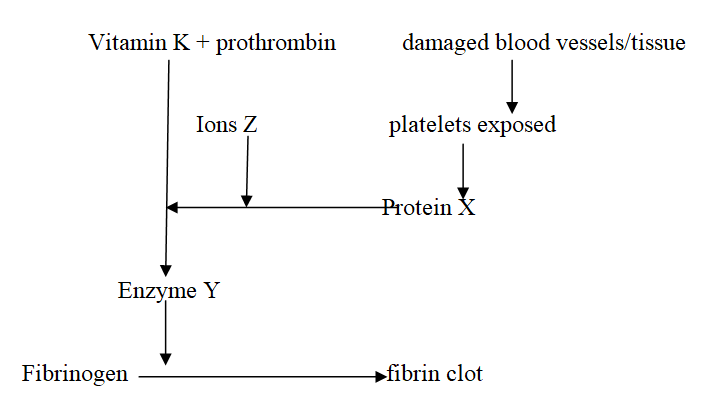
The scheme below illustrates the blood clotting process;(a) Identify the following; (2mks)(i) Protein X
Thromboplastin / thrombokinase;
(ii) Enzyme Y
Thrombin;
(b) State down the role of ions Z in the scheme above (1mk)
Activates conversion ofinactive prothrombin to active thrombin;
(iii) Name a trait in humans determined by multiple alleles (1mk)
Blood groups;
Set-u A
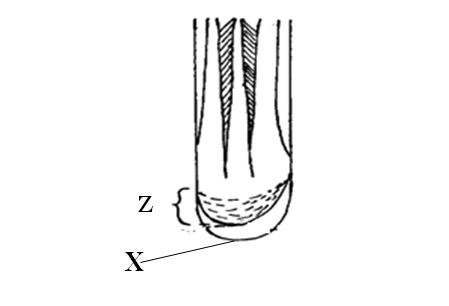
Study the diagram below and answer the following questions.(a) (i) Identify the part labelled X (1mk)
Root cap;
(iii) State the function of part X above (1mk)
Protects the root tip from mechanical damage/abrasive effects of the soil particles as it grows
(b) List down two characteristics of cells in the region labelled Z (2mks)
(a) Why is osmosis regarded as a special case of diffusion (1mk)
Involves the movement of water molecules from a region where they are highly concentrated to a region where they are lowly concentrated through a semi-permeable membrane.
(b) List down two importance of active transport in animals (2mks)
List down the processes responsible for; (2mks)(i) The formation of glomerular filtrateultra filtration (ii) Absence of glucose and amino acids in urine.Reabsorption;
Gaseous Exchange Questions and Answers1. 1992 Q11 P1 The diagram below represents an organ from a bony fish. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow (a) Identify the organ and the parts labelled M, N, and P
M________________ N________________ P________________ (b) How the structures are labelled P adapted to their function? 2. 1994 Q14 P1 What are the characteristics do gills of a fish and the mouth cavity of a frog have in common that enables them to be efficient in gaseous exchange? 3. 1996 Q14 P1 (a) Describe the path taken by carbon dioxide released from the tissue of an insect to the atmosphere (3 marks) (b) Name two structures used for gaseous exchange in plants (2 marks) 4. 1998 Q4 P1 Why are gills in fish highly vascularised? 5. 1999 Q5 P1 Suggest three reasons why green plants are included in a fish aquarium. 6. 1999 Q16 P1 Describe the: a) Process of inhalation in mammals. b) Mechanisms of opening and closing of stomata in plants. 7. 2000 Q11c P1 State two ways in which the leaf is suited to gaseous exchange 8. 2001 Q10 P1 Name three sites where gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial plants. 9. 2002 Q9 P1 Name two gaseous exchange structures in higher plants. 10. 2003 Q13 P1 The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
a) Name the gas that diffuses: i) To the body cells ii) From the body cells b) Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) (i) above? c) i) What is tissue fluid? ii) What is the importance of tissue fluid? K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN08
Explain the effect of increased physical activity on the following organ systems:
(a) heart (b) lungs (c) kidneys (d) skin.
answers
(a) Heart
-Increased heart beat/ rate/cardiac frequency; increase blood pressure; pumping more blood to the muscles/Peripheral blood vessels; at a faster rates; supplying oxygen; Nutrients; for continued oxidation/respiration; to yield energy needed to sustain the (vigorous) contraction/relaxation of muscles during the physical activity; carbon (iv) oxide /Lactic acid/other Nitrogenous wastes/Metabolic wastes produced during the process are also eliminated/ transported to the relevant excretory organs for elimination; the wastes ,if left to accumulate Can also intoxicate/poison cells/cause muscle cramps/pain/fatigue; (b) Lungs -Panting /increased breathing rates; cause the lungs to expand/increase in volume to take in more air/oxygen; and deflate to expel more carbon (iv) oxide; more oxygen is taken in (during exercise) to sustain the process of muscle respiration/to produce the required energy (for constant muscle contraction and relaxation);
Kidneys also maintain the blood plasma pH; and osmotic balance; by elimination excess hydrogen ions(H+) that accumulate to production of Lactic acid/CO2 during the exercise; To maintain the osmotic balance kidneys conserve sodium ions (Na+); and reabsorb water (in the kidney tubules); Leading to reduction in the volume of urine produced; During exercise the kidney tend to filter out urine releasing more in the urine; (d) Skin - Due to increased muscle activity during physical exercise are sweats(more); Eliminating Nitrogenous wastes/ excess water; through the skin/sweat pores) cooling the body; After (water in) sweat evaporates the increased internal body temperature also leads to dilation of superficial blood vessels (vasodilation)/ blood flowing near the skin; leading to loss of excess heat (to the atmosphere) by radiation/ convection; the hair on the skin surface also lie Flat to allow for loss of heat( to the environment) by radiation/convection; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN02
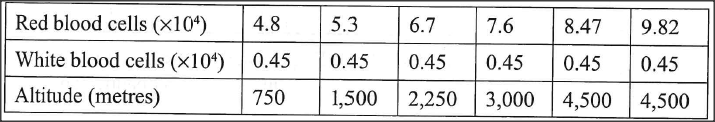
The table below shows results of blood cell counts per mm3 of blood from a sample of people living at different altitudes.
(a) Explain the relationship between:
(i) red blood cells count and the altitude; (ii) white blood cells count and the altitude. (b) Explain why chances of nose-bleeding increase with altitude in humans.
answers
(a) i) Number of red blood cells increase with altitude; to increase oxygen carrying capacity (by haemoglobin molecules in blood); since oxygen concentration is lower at higher altitude;
ii) white blood cells serve to protect the body against harmful microorganisms/pathogens; thernadites of pathogen of the body to microbial attack is not dependent on the altitude (to be countered by the white blood cell); hence 6 the number of white blood cell count is constant at whatever altitude; (b) Atmospheric Pressure decreases with the increase in altitude; the imbalance between the (outer) atmospheric pressure at high altitude and the internal blood pressure (generated by the heart) results in (one) nose bleeding at high altitudes/ internal blood pressure is higher than the (outer) atmospheric pressure.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN23
State three homeostatic roles of the liver.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN22
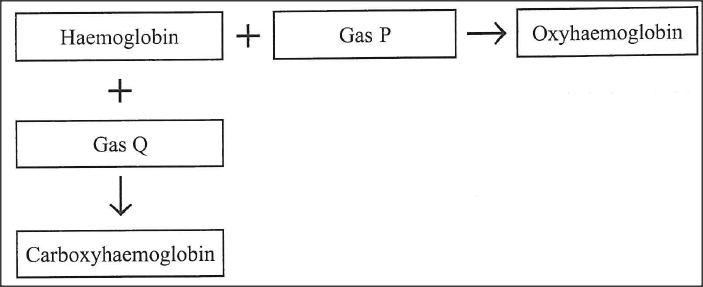
The chart below illustrates how respiratory gases are transported in the human blood.
(a) Identify gas Q.
(b) Explain the advantage oxyhaemoglobin has over carboxyhaemoglobin.
answers
(a) carbon(ii) oxide acc. CO
(b) Oxyhaemoglobin is unstable/fully dissociate, releasing oxygen to the tissues/dissociate giving haemoglobin free to take up more gaseous molecules(hence constantly supplying the much needed oxygen to the respiratory tissues); carboxyhaemoglobin is stable/binds itself on the haemoglobin molecules /does not dissociate ,hence starving the tissues/cells of the oxygen ,leading to suffocation/death K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN20
State how each of the following features enhance efficient movement of fish in water:
(a) Scale (b) body shape
answers
(a) faces towards the back/overlap/points backwards to provide a smooth surface for easier movement in water/are stony/ covered with mucus for easier /smooth movement in water/ reduce friction making
(b) streamlined body shape to reduce friction / pointed(stuff) head for easier penetration / passage in water.;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN15
State the significance of transpiration to a plant.
answers
(b) enable the plant to get rid of excess water
Creates a suction force /help in the uptake of water /mineral/salts from the soil Maintains turgor in plants/turgidity in cells Cools the plant K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN12
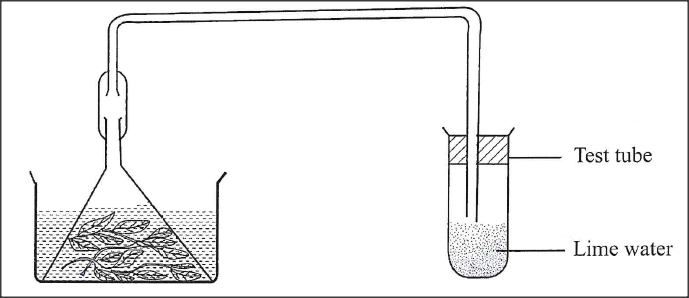
While investigating a certain metabolic process in plants, students set up the apparatus as shown be low in a classroom and monitored it for 48 hours.
(a) Identify the metabolic process under investigation.
(b) Account for the observations made in the test tube at the end of the investigation.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN08
State the role of each of the following in the mammalian respiratory system:
(a) mucus (b) cartilage rings (c) epiglottis
answers
.(a) trap foreign particles (from the inhaled /entering air); moisten the (inhaled/incoming) air (for efficient gaseous exchange);
(b) keep the wind pipe /trachea open / not to collapse (to allow for continuous flow of air); (c) acts as a valve / flap between the larynx and the oesophagus to permit air to enter the air way to the lungs and food particles to pass into the gut / oesophagus: acc prevent food particles from entering the trachea /air passage during swallowing; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN06
(a) Name the respiratory structure in the amoeba.
(b) Give a reason for your answer in (a) above.
answers
(a) cell membrane/plasma membrane /plasmalemma;
(b) has a large surface area to volume ratio
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN05
Explain why significantly increasing the blood pH slows down the rate of selective reabsorption of materials in the kidney tubules.
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |

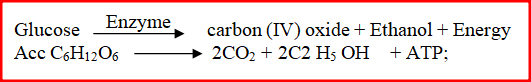









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

