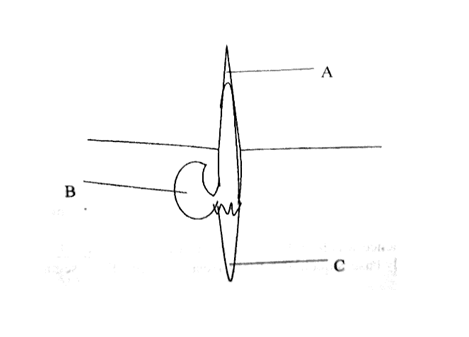
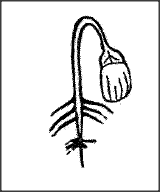
The diagram below represents a maize seedling.a) Name the structure labeled A and C (2mks)
b) State the functions of parts labeled A, B and C. (3mks)
c) Name the type of germination exhibited by maize (1mk)Hypogeal germination d) Name two conditions necessary for seed germination other than water and oxygen. (1mk)
e) What is the role of oxygen in seed germination? (1mk)It oxidizes the stored food in the seed to give energy for growth/synthesis of new materials;
0 Comments
a) State the function of Juvenile hormone in insect metamorphosis (1mk)
leads to the formation of larval utricle;
b) (i) Give a reason why most insects are serious crop pests at the larval stage (1mk)
Growth rate in rapid/fast/high and shed cuticle several times hence feed a lot to have (desired) energy;
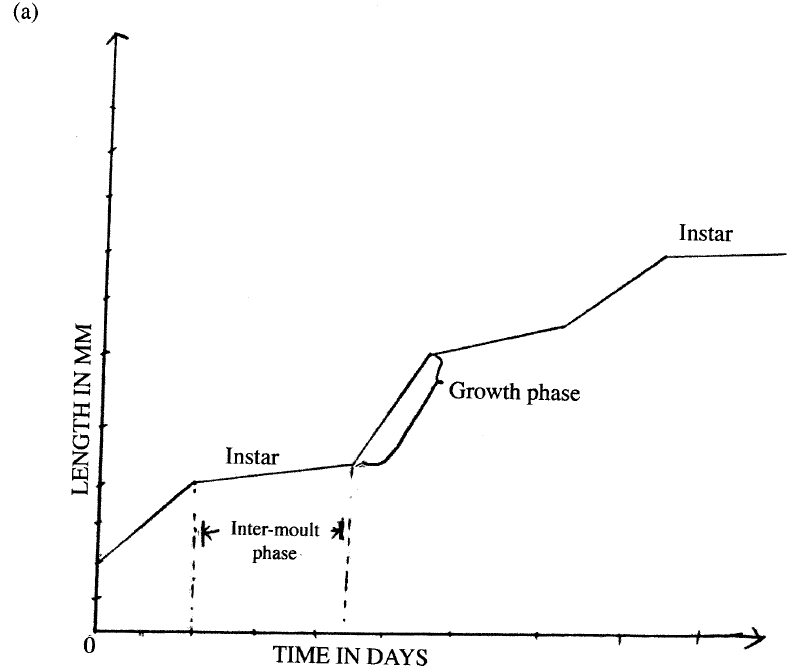
(ii) What happens at growth phase in insects growth curve (1mk)
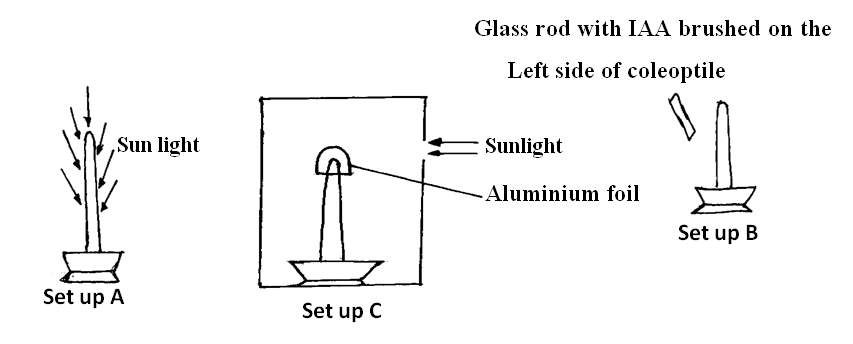
(a) What type of response was being investigated above? (1mk)Tropism/tropic response; (b) Which of the set up above would act as a control experiment? (1mk)(c) Explain what happened in set up B after 24 hours (2mks)The side brushed with IAA increased concentration of this hormone (IA; This lead to increased cell elongation/growth hence a growth harvature away from the brushed side;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN03
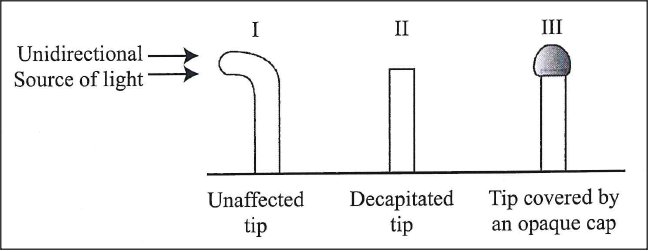
In an experiment, students treated seedlings as illustrated below.
(i) Account for the observations made in seedling I.
(ii) Explain the similarity in the end results made in seedlings II and III. (iii) State the likely treatment that would make seedlings II and III respond like seedling I.
answers
(i) Positive phototropism/tip bends towards light; light causes migration of auxins (produced at the tip) to the darker sides; (of the shoot) resulting in faster division of cells/ elongation/growth on the darker /opposite side of the shoot hence bending towards light
(ii) both seedlings remain upright; ( erect) seedling II does not have tip while seedling III the tip has been covered by opaque material preventing light causing unequal distribution of auxins; . uniform/even distribution of auxins) (iii) Fitting a gar block treated with auxins at the decapitated end of seedling II; Removing the opaque material covering the tip of seedling III/ replacing the opaque cap with a transparent one; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP2QN01
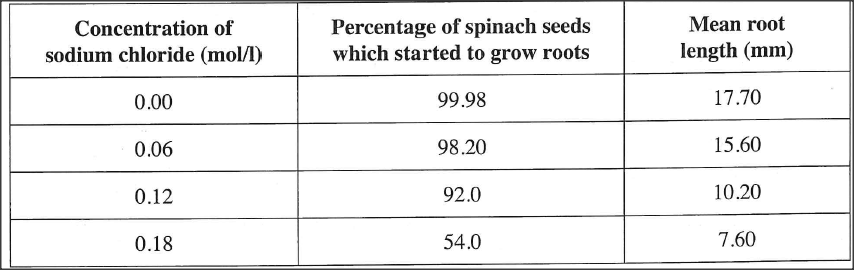
In an experiment to investigate the effect of sodium chloride on the growth rate in a spinach seedling, seeds were treated with different concentrations of sodium chloride. The results are as recorded in the table below.
(a) From the results in the table above, explain the effect of increasing the concentration of sodium chloride.
(b) Apart from a ruler, state two other equipment one would need to determine the rate of growth in the roots. (c) With a reason, state one other part of the seedling the students would focus on to determine the effect of sodium chloride on growth. (d) State the likely effect on the seedling of increasing the concentration of sodium chloride to 2.20mol/l
answers
(a) Increased Nacl concentration/having more Nacl ions decreases water potential/decrease osmotic potential/ increase osmotic pressure/makes water potential more negative outside the seed/seedling in the surrounding solution to be hypertonic to the cell sap in the seedling ; seeds cells take in water by osmosis) are dehydrated/lose water molecules to the surrounding solution , reducing the growth enzyme activity; have reduced growth rates;
(b) Threads(wire/string) Books; Pen; Marker (pen); Dye/water proof ink/ bloating paper/tissue paper (c) Rate of growth/ increase in length of shoot tip/apex it is a region of (active) cell division/growth (d) The seedling will be (dehydrated) /lose water (hence) wither/die/dry K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN06
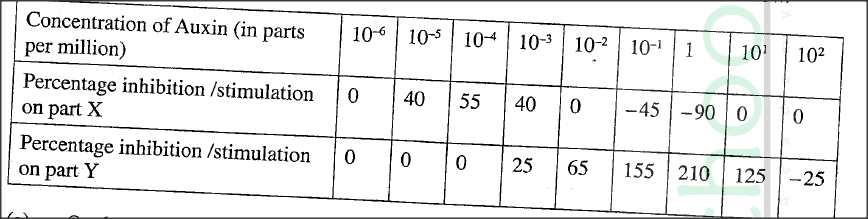
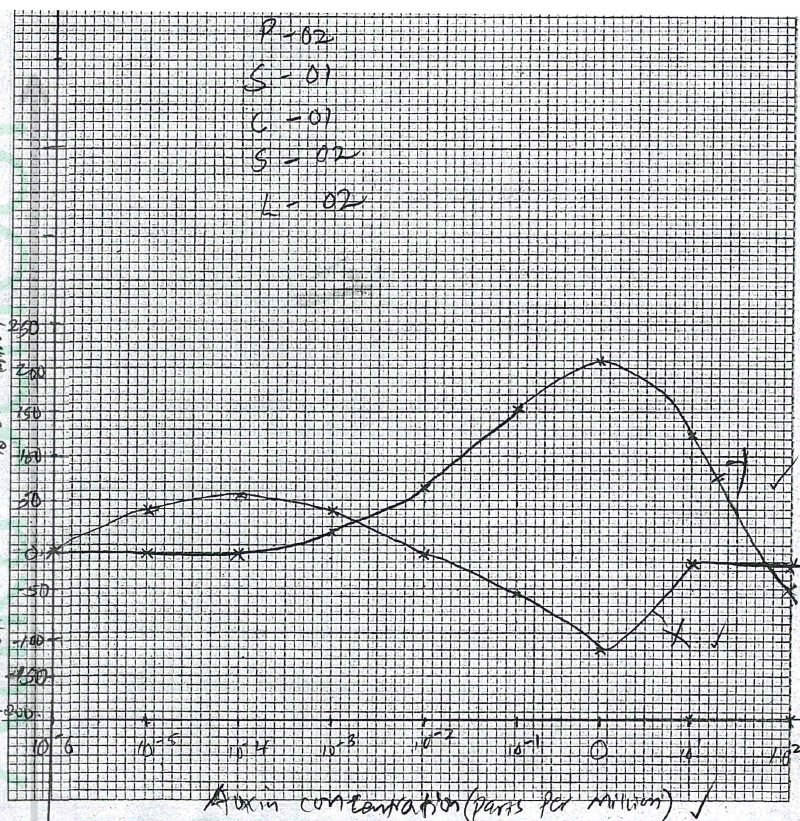
The effect of auxin concentration on growth response of two parts of a plant, X and Y was investigated over a period of time. The results were tabulated as shown in the table below.
(a) On the same axis, draw line graphs of the effect on growth of the two parts, X and Y (percentage inhibition or stimulation) against the concentration
(b) With reasons, name the two parts of the plant, X and Y. X Reason Y Reason (c) From the graph identify: . (i) the point at which the percentage stimulation was the same for both X and Y. (ii) the optimum concentration of auxins required for part Y (d) State three ways in which the effects of auxins on plants is applied in flower farming. (e) Distinguish between simple and conditioned reflex action
answers
b) X—root;
Reason Low auxin concentration stimulates (rapid/faster) cell division and elongation/growth in roots; High concentration of auxins inhibits growth in roots; Y—shoot; Reason Low auxin concentration has little effect on the growth of shoots/shoots are stimulated to grow with high auxin concentration (up to a given optimum); c) i. 33%±2; ii. 1.0 parts per million; (d)Faster maturity of flowers/earlier flower formation/flowering; Prunning/decapitating shoot tips to allow sprouting of lateral buds, hence more yield; Keeping flowers fresh; Stimulate formation/development of (adventitious) roots; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN23
State two characteristics of living things illustrated in the photograph below.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN14
The diagram below illustrates a germinating seedling.
(a) Name the type of germination illustrated in the diagram
(b) Describe how the type of germination named in (a) above is brought about.
answers
(a) Epigeal;
(b) Hypocotyl elongates faster than the epicotyl; pushing cotyledons above the ground; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN14
The photograph below illustrates a germinating seedling.
(a) Name the type of germination illustrated in the photograph.
(b) Explain the function of each of the parts labelled G and H. G H
answers
a. Epigeal;
b. G- Elongates to expose the foliage leaves to light photosynthesis H- Stores food (for growth); For photosynthesis (it is green); Protects plumule during germination; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN05
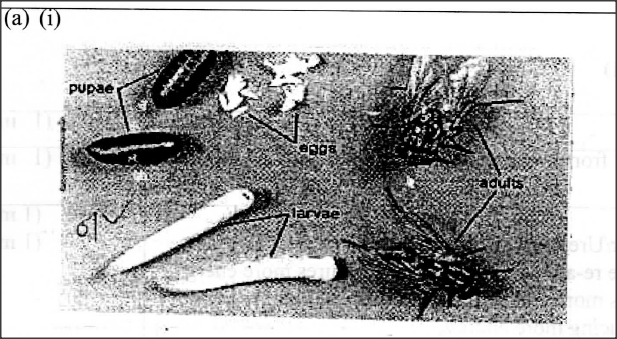
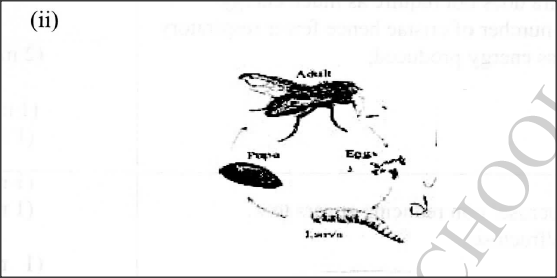
The photograph illustrates a housefly at various stages of its development.
(a) (i) On the photograph, name the stages of the life cycle.
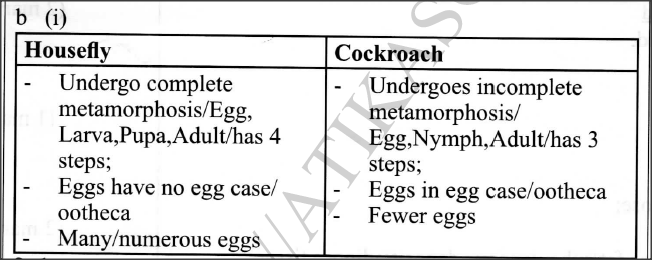
(ii) Using arrows, link the stages of the life cycle in the correct order. (b) (i) State two differences between the life cycles of a housefly and that of a cockroach. (ii) State one advantage of the life cycle of a cockroach to itself.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN15
What is seed dormancy
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN19
(a) Using the axes provided below, sketch a curve to illustrate the growth pattern observed in the phylum arthropoda.
(b) Explain the growth pattern observed observed in arthropods.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN18
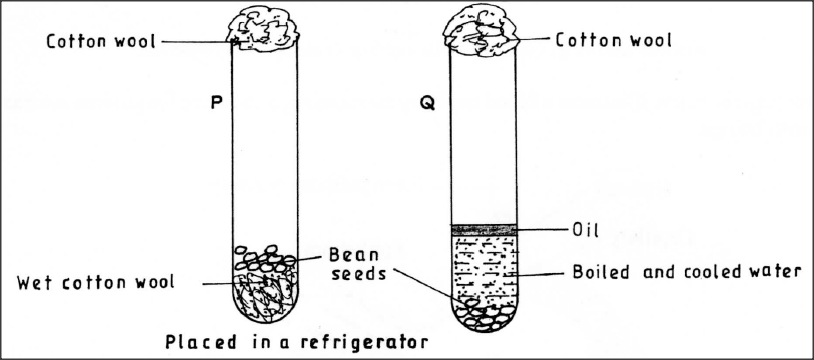
The diagram below shows an experimental set-up to investigate the conditions necessary for germination. Test tube P was placed in a refrigerator while Q was left at room temperature. The set-ups were observed regularly for two weeks but no germination occurred.
Explain the observations in P and Q.
P Q
answers
P - the low temperature/freezing temperature inactivated enzymes;
Q - Boiling eliminated oxygen; oil layer prevented entry of oxygen necessary for respiration during growth;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN02
What is meant by the term seed dormancy?
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN19
State three factors in seeds that cause dormancy.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN25
State the role of the following hormones in the life cycle of insects:
ecdysone hormone; . juvenile hormone.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN24
State four characteristics of apical meristem cells.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN20
State three aspects that can be used to estimate growth in seedlings
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN29
State four reasons why water is significant in seed germination.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP2QN01
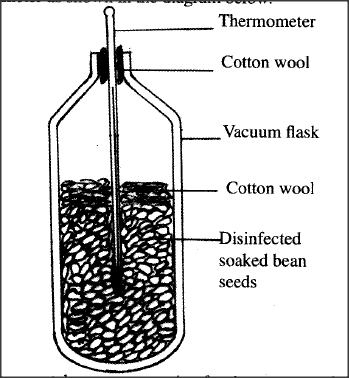
In an experiment, disinfected soaked bean seeds were put in a vacuum flask which was then fitted with a thermometer as shown in the diagram below.
The temperature readings were taken every morning for three consecutive days.
(a) Which process was being investigated? (b) (i) What were the expected results? (ii) Account for the answer in (b)(i) above, (c) Why were the seeds disinfected? (d) Why was a vacuum flask used in the set-up? (e) How would a control for this experiment be set?
answers
(a) Respiration;
(b) (i) Increase/rise in thermometer reading/temperature; (ii) Carbohydrates/starch/glucose in germinating seeds is broken down/oxidised to get energy; some of the energy is released as heat; (which increases temperature reading). (c) To kill bacteria/fungi/microorganisms; that would cause decay/decomposition/respiration of the beans; (d) To conserve heat/prevent heat loss to surroundings; (e) Use similar set-up but with dead and disinfected beans seeds/ use dead disinfected bean seeds/use dry bean seeds;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN30
What is meant by the term apical dominance?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN11
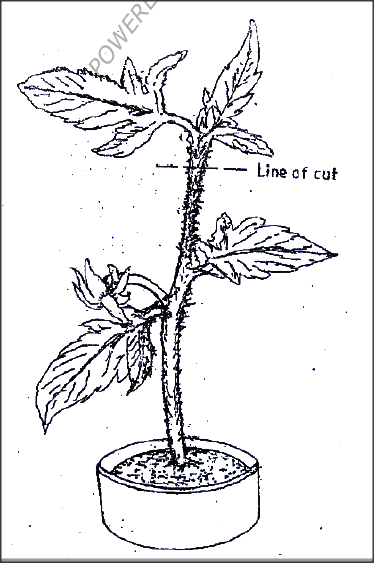
In an experiment the shoot tip of a young tomato plant was decapitated as shown in the diagram below
(a) State the expected results after 2 weeks
(b) Give a reason for your answer in (a) above
ANSWERS
(a) auxiliary/ lateral buds spront/ bronches will be formed
(b) Decapitation removes the hormone/ ouxins /IAA which is produced in the terminal bud/ the stem tip; abseul/ removal of the hormone/ auxins/ IAA promote branch/ development of auxiliary lateral buds. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN04
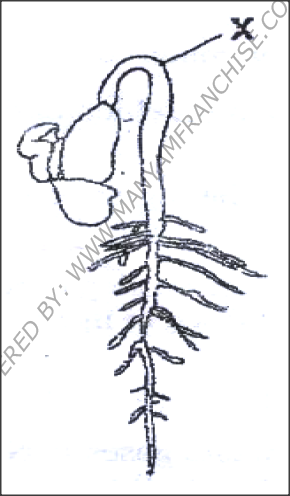
The diagram below represents a stage during germination of a seed
(i) Name the type of germination illustrated in the diagram
(ii) State the role of the part labeled x during germination of the seed
ANSWERS
(i) Epigeal
(ii) Protection of the delicate plumule; pulls the cotyledons above the ground |
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

