State the role of light in photosynthesis (1mk)Photolysis/provides energy required for splitting water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen gas;
1 Comment
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN09
Below is a photograph of Brassica oleracea, Sukuma wiki leaf.
(a)State two observable features that adapt the leaf to gaseous exchange.
(b) Explain the relationship between photosynthesis and aerobic respiration within the leaf.
answers
.(a) broad leaf blade /lamina; that expose more stomata for gaseous exchange; acc broad leaf alone
(b) photosynthesis (within the leaf in the presence of light energy) yield simple carbohydrates /glucose /sugars which form the main substrate during aerobic respiration (producing energy (ATP) During the process of respiration carbon iv oxide produced is intern used as a raw material in photosynthesis; During photosynthesis water is broken down yielding oxygen which is needed/ used in (cellular) (aerobic respiration); K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN06
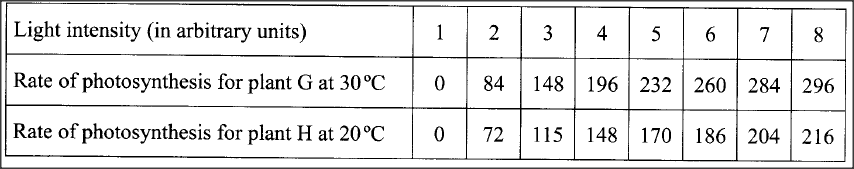
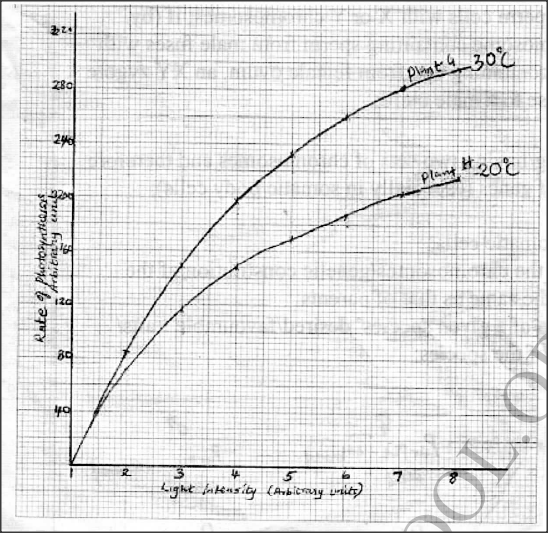
In an investigation, two potted plants G and H belonging to the same species were exposed to increasing light intensities at different temperatures, 30°C and 20°C respectively. The rate of photosynthesis was measured for each plant and results recorded as shown in the table below:
(a) On the same axis, plot graphs of rate of photosynthesis against light intensity for plants G and H.
(b) State the aim of the investigation. (c) Account for the difference in the rate of photosynthesis in the two plants. (d) Account for the difference in the rate of photosynthesis in the two plants between the following light intensities: (i) 1—4 units (ii) 4—8 units. (e) (i) Predict the rate of photosynthesis at light intensity of 16 units. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (e) (i) above. (f) State one internal and one external factor that could be limiting in the investigation.
answers
b) To investigate/compare the effect of (varying) light intensity/temperature on the rate of photosynthesis;
c) Rate of photosynthesis is higher in plant G (than H); (Photosynthesis being an enzymatic process), enzymes were subjected to favourable/optimal temperatures (of 30°C): hence more activated, unlike in plant H where temperatures were lower (20C); d) (i) 1-4 units Rapid increase in rate of photosynthesis increases with the increase in light intensity; due to increase in light energy for photosynthesis/formation of more ATP molecules; (ii) 4 — 8 units Slower/gradual increase in the rate of photosynthesis as the light intensity increases: because other factors become limiting/some chlorophyll molecules start bleaching; e) i) Slight increase/no significant increase/remains constant; ii) The optimum light intensity has been exceeded/some chlorophyll could be destroyed; f) Internal factor — Chlorophyll/enzyme concentration; External factor — Carbon (IV) oxide concentration/amount of water; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN04
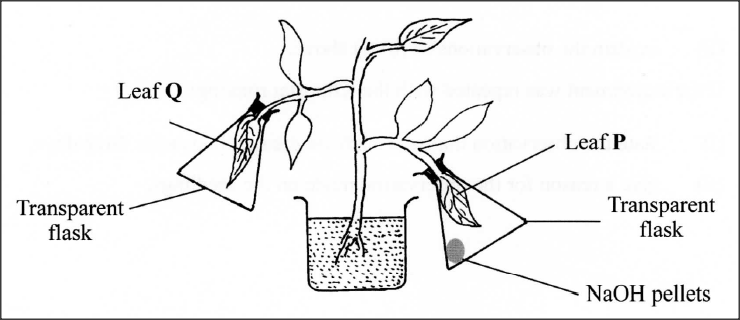
In an experiment to investigate a factor affecting photosynthesis, a potted plant which had been kept in the dark overnight was treated as shown in the diagram below and exposed to light.
(a) Why was the potted plant kept in the dark overnight’?
(b) Which factor was being investigated in the experiment? (c) (i) Which test did the students perform to confirm photosynthesis in the leaves labelled P and Q? (ii) State the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q. P Q (iii) Explain the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q. P Q (d) What was the purpose of leaf Q in the experiment?
ANSWERS
(a) To destarch/remove starch from the leaves;
(b) Carbon (IV) Oxide/CO2; (c) (i) Test for starch; (ii) p - Retained the colour of iodine solution/brown/yellow; Q - Turned blue-black/black/dark-blue; (iii) P - Did not photosynthesize /no starch is formed because Sodium Hydroxide pellets absorbed Carbon (IV) Oxide; Q - Photosynthesized /starch was formed because Carbon (IV) Oxide was in the flask; (d) Control (experiment);
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN17
What happens to the glucose synthesized during photosynthesis?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN07
Explain how each of the following factors affects the rate of photosynthesis:
(i) temperature; (ii) chlorophyll concentration.
answers
(i) Reactions in photosynthesis are catalysed by enzymes; at optimum temperature photosynthesis proceeds faster;
Below optimum temperature the rate of photosynthesis decreases because enzymes are inactivated by the low temperatures / above optimum the rate of photosynthesis decreases because enzymes are denatured; (ii) Chlorophyll traps energy from sunlight for photosynthesis; The higher the chlorophyll concentration the higher the rate of photosynthesis and vice versa; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP2QN03
(a) Explain the importance of the following in photosynthesis:
(i) light; (ii) carbon(IV) oxide; (iii) chlorophyll.
(b) Name one appropriate food substance for each of the following enzymes:
(i) ptyalin (ii) pepsin (c) State the cause and two symptoms of Ben-ben. Cause Symptoms
answers
(a) (i) Provides energy needed to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen/photolysis;
Provides energy for formation of ATP molecules (which is used in dark stage) (ii) Combines with hydrogen ions to make glucose; (iii) Used to trap light energy; (b) (i) Starch; (ii) Protein; (c) (i) Lack of vitamin B1/thiamine; (ii) . Stunted growth; Paralysis of legs/arms/limbs/damage to peripheral nerves; Heart failure Swelling of feet/oedema Gastrointestinal disturbances/loss of appetite/constipation/diarrhoea/vomiting; Weight loss/muscle wasting Pale skin K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN18
Explain how the following factors affect the rate of photosynthesis:
(a) Concentration of carbon (iv) oxide (b) Light intensity
ANSWERS
(a) Rate of photosynthesis increases as CO2 concentration increases up to a certain level/ optimum level and ( vise versa)Reverse:
b)The rate of photosynthesis decreases with decrease in CO2 concentration until it stop rate of photosynthesis increases as the light intensity up to an optimum level (and vice versa) K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP2QN03
The equation below represents a process that takes place in plants
6CO2 + 6H2O→C6H12O6 + 602 (a) Name the process (b) State two conditions necessary for the process to take place (c) State what happens to the end- products of the process
answers
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Light (energy) Chlorophyll (c) Oxygen – used in respiration, oxidation Released into the atmosphere Glucose – used in respiration Converted to sucrose or starch for storage Used in formation of sturdiness allulose cell wall/ cytoplasm K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN24
Name the sites where light and dark reactions of photosynthesis take place
Light reaction Dark reaction
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN16
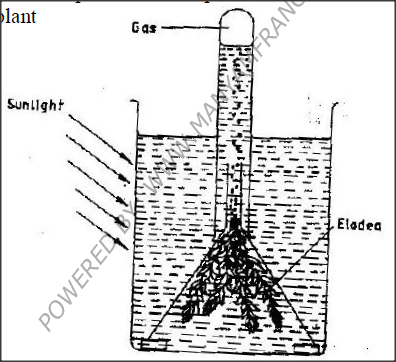
The diagram below represents a set up that was used to investigate certain process in a plant
(a) State the process that was being investigated
(b) State a factor that would affect the process
ANSWERS
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Carbon (iv) Oxide/ Temp/ chlorophyll
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2007PP1QN06
Describe what happens during the light stage of photosynthesis
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2006PP1QN27
Name the end products of the light stage in photosynthesis.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2004PP1QN09
Name two mineral elements that are necessary in the synthesis of chlorophyll.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2003PP1QN10
How are leaves of submerged adapted plants for photosynthesis?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 1998PP1QN14
In an experiment to investigate a factor affecting photosynthesis, a leaf of a potted plant which had been kept in the dark overnight was covered with aluminum foil as shown in the diagram below
The set up was kept in sunlight for three hours after which a food test was carried out on the leaf.
(a) Which factor was being investigated in the experiment? (b) What food test was carried out? (c) (i) State the results of the food test (ii) Account for the results in c (i) above (d) Why was it necessary to keep the plant in darkness; before the experiment?
ANSWERS
(a) Light; Rej: light intensity
(b) Test for starch (c) (i) The covered part of the leaf remain brown/yellow/ retain color of iodine, and the uncovered parts turned blue/ black; rej blue alone black alone. (ii) Starch was formed in the covered part of the leaf (because of the presence); while starch was not formed in the covered part of the leaf ( because of lack light) (d) To destarch the leaf; (a) State the role of light in the process of photosynthesis.(b) Name one end product of dark reaction in photosynthesis.ANSWERS
(a) To split water/ Photosynthesis/hydrous |
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

