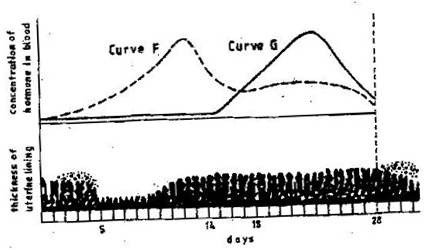
Comprehensive KCSE Questions and Answers on Reproduction in Plants and Animals1. 1989 Q5 P1 The table below shows two mammalian hormones. For each hormone, state the site of production and its function in the body. 2. 1989 Q10 P1 At what stage of mitosis do chromosomes replicate to form daughter chromatids? 3. 1990 Q5 P1 Fill in the blank spaces in statement below. After fertilization of an ovule……………………develops in to a testa and…………………………..develops into endosperm. 4. 1990 Q8 P1 State the differences between the composition of maternal blood entering the placenta and maternal blood leaving the placenta. 5. 1991 Q3 P1 After four months of pregnancy, the ovaries of a woman can be removed without terminating pregnancy. However, during the first four months of pregnancy, the ovaries must remain intact if pregnancy is to be maintained. Explain these observations. 6. 1991 Q12 P1 (a) State the type of sexual reproduction in each of the following organisms. (i) Hydra ............ (ii) Moss (funari) ............... (b)State two advantages of sexual reproduction to the survival of a species. (c)State two ways in which man has utilized vegetative reproduction in plants for his own benefits. 7. 1992 Q8 P1 Name two mechanisms that prevent self-pollination in flowers that have both male and female parts 8. 1993 Q11 P1 The diagram below represents some stages in mitosis (a) Name the stages represented by the diagrams labeled A,B and C A……………………………………………………. B…………………………………………………… C…………………………………………………… (b) State the significance of mitosis to an organism. (c) Name two regions in higher plants where cells actively undergo mitosis 7. 1995 Q16 P1 (a) Describe how insect pollinated flowers are adapted to pollination (b)Describe the role or each of the following hormones in the human menstrual cycle (i) Oestrogen (ii) Progesterone (iii) Luteinising hormone (9 marks) 8. 1996 Q2 P1 State two ways by which acquired Immune deficiency syndrome (A.I.D.S) Virus is transmitted. (2 marks) 9. 1996 Q9 P1 State three characteristics that ensure cross – pollination takes place in flowering plants (3 marks) 10. 1996 Q12 P1 Give a reason why it is necessary for frogs to lay many eggs (1 mark) 11. 1996 Q22 P1 Describe how new plants arise by asexual reproduction (20 marks) 12. 1997 Q17 P1 Figures 1 and 2 below represent reproductive organ of plants and an animal respectively. (a)Which letters in figures 1 and 2 represents the organs that produce female gametes? Figure 1……… Figure 2……… (b) What is the function of the structure labeled S? (c) Name the structure labeled W (d) Which letters in figures 1 and 2 represents the structures where fertilization takes Place (e) Which letter in figure 1 represents the structure where male gametes are produced? 7. 1998 Q8 P1 A flower was found to have the following characteristics: Inconspicuous petals Long feathery stigma Small, light pollen grains (a)What is the likely agent of pollination of the flower (b)What is the significance of the long feathery stigma in the flower? 8. 1998 Q11 P1 State two ways by which the human immune-deficiency (H.I.V) is transmitted other than through sexual intercourse? 17. 1998 Q13 P1 (a) List four differences between meiosis and mitosis (b) Which sex chromosomes are found in human? (i) Sperm cell? (ii) Ova? 18. 1999 Q3 P1 Explain why sexual reproduction is important in organisms 19. 1999 Q8 P1 State two disadvantages of self-pollination. 20. 2000 Q9 P1 State two advantages of metamorphosis to the life of insects. 21. 2000 Q16 P1 (a) What is the significance of sexual reproduction? (b) State three advantages of asexual reproduction 22. 2000 Q18 P1 Describe the role of hormones in the human menstrual cycle 23. 2001 Q4 P1 Name the parts of the flower that are responsible the production of gametes 24. 2001 Q18 P1 (a) Describe the process of fertilization in a flowering plant (b) State the change that take place in a flower after fertilization 25. 2002 Q13 P1 The chart below shows the number of chromosomes before and after cell division and fertilization in a mammal. a) What type of cell division takes place at Z b) Where in the body of a female does process Z occur c) On the chart, indicate the position of parents and gametes d) Name the process that leads to addition or loss of one or more chromosomes. e) State three benefits of polyploidy in plants to a farmer 26. 2002 Q17 P1 a) What structures are produced by sisal for vegetative propagation? b) Give a reason for grafting in plants c) State four advantages of vegetation propagation. 27. 2003 Q3 P1 How do the male gamete nuclei reach the ovule after pollen grains land on the stigma? 28. 2003 Q19 P1 Describe how fruits and seeds are suited to their modes of dispersal. 29. 2004 Q5 P1 During which phase of meiosis does crossing over occur. (2marks) 30. 2004 Q11 P1 Fruit formation without fertilization is called (1mark) 31. 2004 Q15 P1 a) Give the differences between the following structures in wind and insect pollinated flowers. (3marks) i) Anther ii) Pollen grains iii) Stigma (1mark) b) What is the importance of cross pollination? (1mark) c) Explain how a seed is formed after an ovule is fertilized (4marks) 32. 2005 Q15 P1 a) What is meant by the terms (i) Epigymous flower (1mark) (ii) Staminate flower? (1mark) b) How are the male parts of wild pollinated flowers adapted to their function? (4marks) 33. 2006 Q2, 9 P1 2. Name the part of the flower that develops into a) Seed b) Fruit (1mark) 9. a) State two processes which occur during anaphase of mitosis. (2marks) b) What is significance of meiosis? (2marks) 34. 2006 Q19 P1 a) Explain how the following prevent self pollination. (1mark) (i) Protoadry (ii) Self – sterility. b) Give three advantages of cross pollination. (3marks) 35. 2006 Q5 P2 The diagram below represents human foetus in a uterus. a) Name the part labeled S. (1mark) b) i)Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labeled Q. (2marks) ii) State the differences in composition of blood found in the vessels named in (b) (i) above. (2marks) c) Name two features that enable the structure labeled P carry out its function. (2marks) d) State the role of the part labeled R (1mark) 36. 2007 Q17 P1 The diagram below represents a stage during cell division (a) (i) Identify the stage of cell division (1 mark) (ii) Give three reasons for your answer in (a) (i) above (2 marks) (b) Name the structures labeled M (1 mark) 37. 2007 Q18 P1 State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction in animals (2 marks) 38. 2007 Q26 P1 State one way in which HIV / Aids is transmitted from mother to child (1mark) 39. 2007 Q3 P2 (a)What is meant by the following terms (i) Protandry (1 mark) (ii) Self sterility? (1 mark) (b)The diagram below shows a stage during fertilization in a plant (i) Name the parts labeled Q, R, and S (3 marks) (ii) State two functions of the pollen tube (2 marks) (c) On the diagram label the micropyle (1 mark) 40. 2008 Q8 P1 The diagram below shows a stage in mitosis in a plant cell (a) Name the stage of mitosis (1mark) (b) Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above (2 marks) (c) Name the part of the plant from which the cell used in preparation was Obtained (1 mark) 41. 2008 Q1 P2 The figure shows changes that take place during menstrual cycle in human (a) Name the hormone whose concentrations are represented by curves F and G ( 2 marks)
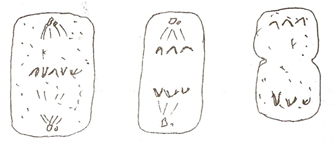
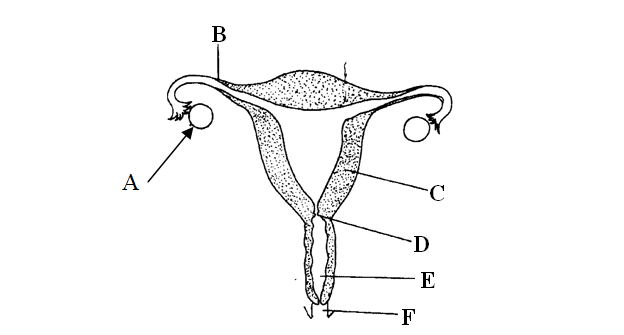
(b) State the effects of the hormones named in (a) above on the lining of the uterus ( 2 marks) (c) (i) Name the hormone which is released by the pituitary gland in high concentration on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle ( 1 mark) (ii) State two functions of the hormone named in (c) (I ) above (2 marks) (d) State the fertile period during the menstrual cycle (1 mark) 42. 2009 Q8 P1 (a) Pregnancies continues if the ovary of an expectant mother is removed after 4 months explain ( 2 marks) (b) What is the role of the testes in the mammalian reproductive systems? (2 marks) 43. 2009 Q7 P2 How are flowers adapted to wind and insect pollination? (20 marks) 44. 2010 Q22 P1 What is the function of the following structure in the human reproductive organ? a) Fallopian tubes. (1 mark) b) Epididymis. (1 mark) c) Scrotal sac (1 mark) 45. 2010 Q7 P2 Describe the process of fertilization in flowering plants. (20 marks) 46. 2011 Q26 P1 Name the gamete cells that are produced by the ovaries (1mark) 47. 2012 Q15 P1 What name is given to a group of hormones that controls the development of secondary sexual characteristics in a human male? (1mark) 48. 2012 Q16 P1 The diagram below represents an experimental set-up used by students to investigate a certain process. Flower Q produced seeds while P did not. Account for the results. (3marks) 49. 2012 Q17 P1 Name two substances that leave the foetal blood through the placenta. (2marks) 50. 2012 Q25 P1 State the role of the following hormones in the life cycle of insects: (2marks) Ecdsone hormone; …… Juvenile hormone…… The diagram below represents female reproductive system;(a) Name the part labelled ;A ,B ,C and D. (4mks)A:
ovary
B:
Oviduct/fallopian tube
C:
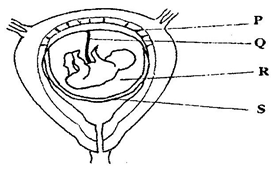
Uterus/uterine wall
D:
D - Cervix
(b) State two functions of structure A. (2mks)
Produce ova femme hormones/ Estrogen and progesterone.
(c) How is part C adapted to its functions? (1mk)
(d) Of what significance is part E to reproduction? (1mk)
Copulation/Achieve orgasm in Human male followed by ejaculation birth canal
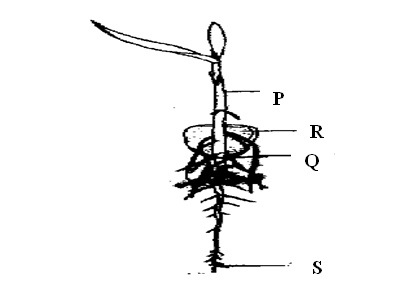
The diagram below represents a maize seedling.(a) Name the parts labeled P and Q. (2mks)P:
Coleoptile/plumule sheath;
Q:
Root
(b) State the function of the part labeled R. (1mk)
Storage of food/enzyme/to provide food to the seedling
(c) Give three adaptations of the structure labeled S to its functions. (3mrks)
(d) What is the role of air in germination of the above seedlings? (2mks)
Air contains oxygen for respiration/oxidation to produce energy.
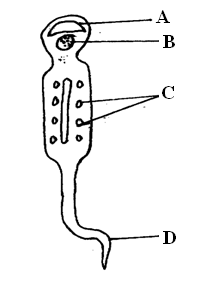
The diagram below shows a specialized cell from a human being.(a) Identify the cell. (1mk)
Sperm cell/spermatozoon;
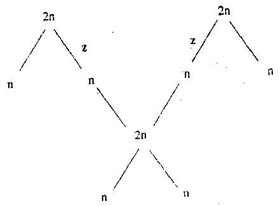
(b) Name the parts labelled A,B, and C. (3mks)A:
A crosome;
B:
Nucleus
C:
Mitochondria
(c) State the functions of the part labeled D. (1mk)
Propels the sperm forward
(d) A student observed cells under a microscope and counted six (6) cells a cross the diameter of view. The diameter of field of view was found to be 1.25mm. Calculate the length of one of the cells observed. ( Answer in micrometer). (3mks)
a) Identify the type of asexual reproduction exhibited by yeast cells (1mk)
Budding;
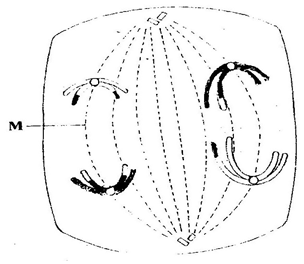
b) List down the functions of the following parts; (3mks)i) Testis
ii) Fallopian tube
iii) Urethra
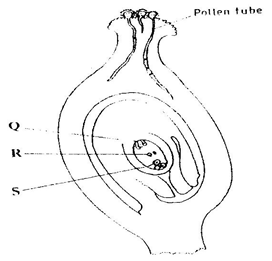
Passage of urine/sperms/semen;
State three ways how HIV and AIDS is transmitted in human population (3mks)
Discuss the adaptations of the reproductive system of a male mammal to its function
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN16
State two benefits of mutation in living organisms.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN13
A female human being was found to have an extra sex chromosome in her cells.
(a) Give the total number of chromosomes in the female individual’s cells.
(b) Explain the possible cause of this condition. (c) State two physical characteristics observed in the female individual with such a condition.
answers
(a) 47
(b)Non-disjunction/failure of homologous chromosome to separate/segregate (in anaphase I) or failure of sister chromosome to separate/segregate (in anaphase II); resulting in an extra X sex chromosome, X chromosome in a cell having XXX instead of XX; (c) infertile / ovary abnormalities; Taller than average female; Development delays; (more pronounced) signs of obesity; Flat feet Abnormally curved fingers; Widely spaced eyes; Abnormally shaped breast bone;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN07
Describe the role of hormones in the human menstrual cycle.
answers
After/at the onset of menstruation, (the anterior lobe of) the pituitary gland; secretes follicle stimulating hormone (FSH); the FSH causes the Graafian follicle; to develop into the ovary; and stimulate the ovary tissues to secrete oestrogen hormone; Oestrogen brings about repair/healing of the endometrium/uterine wall; its concentration increases to a level which stimulates the (anterior) pituitary gland; to secrete lutenizing hormone (L.H.) and stops further secretion of FSH;
The L.H. stimulates the maturation of the Graafian follicle; LH also stimulates the Graafian follicle to release an ovum into the (funnel of the) fallopian tube/causes ovulation; it also stimulates the remains of the Graafian follicle to form a yellow body/corpus luteum (in the ovary; The corpus luteum is stimulated by the L.H. to produce progesterone; Progesterone then stimulates the thickening of the endometrium/inner lining of the uterine wall; in readiness for implantation; as progesterone level increases, it inhibits (the pituitary gland) from secreting FSH; further increase in progesterone level inhibits the pituitary gland from secreting L.H. This causes the corpus Luteum to degenerate; this reduces the amount of progesterone; the sudden drop in secretion of progesterone causes the endometrium to slough off/menstruation occurs; and the cycle is repeated;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN07
Describe the mode of reproduction in a named fungus.
answers
Rhizopus/mucor/mould; reproduce asexually; by sporulation; spores develop from a single cell forming sporangium; which bursts on maturity releasing spores; which are dispersed by air currents/wind germinating; to form new generation/ form a mycelium (if it lands on a suitable medium); Or
Yeast/Saccharomyces/Schizosaccharomyces; reproduce asexually;by budding; parent cell forms an outgrowth/projection/bud; this is followed by division of the nucleus into two; one of the nuclei moves into the bud; which grows and develops into a new cell; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP2QN02
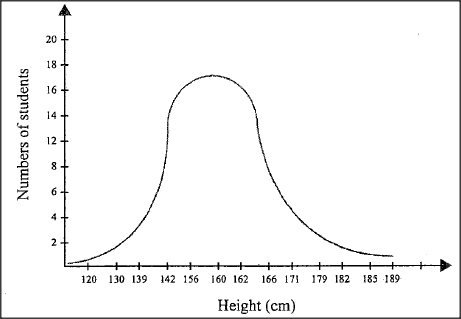
Below is a graphical representation of students’ height in a classroom.
(a) Name the type of curve illustrated.
(b) (i) State the type of variation represented by the curve. (ii) State two meiotic processes that lead to variation among organisms. (iii) Explain the role of variation in organisms. (c) Explain the need for genetic counselling in present day health facilities.
answers
a) Normal distribution curve;
b) i. Continuous (variation); ii. Independent assortment; Crossing over; iii. Organisms/individuals with advantageous traits/variations are favoured/selected by nature; and survive to reproduce/pass on/propagate the advantageous/favourable traits to their off-spring; Or Variation ensures propagation of desirable/favourable traits; to the future generations/off-spring, ensuring improved/quality population; c) Provides information/advice to individuals/families/communities about genetic disorders; Helps identify/test/advice families/communities on possible risks of genetic disorders; Provides supportive services/serves as patient advocates/refer individuals/families to relevant health professionals;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
State the significance of diploidy.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
(i) Define the term diploidy.
(ii) Name the type of cell division that gives rise to diploid cells. (iii) Name the type of cells in which the process named in (b) (ii) above Occurs.
answers
i. State of being/having two sets of chromosomes and therefore two copies of genes (especially in somatic/body cells);
ii. Mitosis; iii. Body cells/somatic cells;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN04
Explain how the sex of a male child is determined in human beings.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN30
State two advantages of hybrid vigour
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN10
State two functions of the placenta in mammals.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN10
State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction in animals.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN07
Explain how the following prevent self-pollination.
(i) Protandry (ii) Self- sterility.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN07
Explain the various ways in which seeds and fruits are adapted to dispersal.
ANSWERS
Wind - dispersed seeds / fruits are light / small to be carried by air currents;
Some seeds / fruits have developed hairy structure feather-like projections; wing like structure which increase their surface area to be blown about /carried away by wind; open capsules; borne on long stalks, which are swayed by wind scattering seeds. Water - dispersed fruits / seeds are also light; to float on water; Some, (like coconuts) have fibrous /spongy mesocarps to trap air; making them buoyant/floating on water; Others (like the water lily) produce seeds whose seed coats trap air bubbles; making them float on water; Some have water-proof seed testa / pericarp; remain afloat without soaking /sinking immediately they are released from parent plants; Animal - dispersed fruits have developed hooks; to stick on (the fur of passing) animals; In some cases, fruits are succulent, brightly coloured / scented; to attract animals, birds; The seed coats (of some seeds) are hard; and resistant to the digestive enzymes; hence passing out through the gut undigested; Self dispersal by explosive mechanism; Fruits have sutures/lines of weakness; which split open when drying scattering seeds. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP2QN02
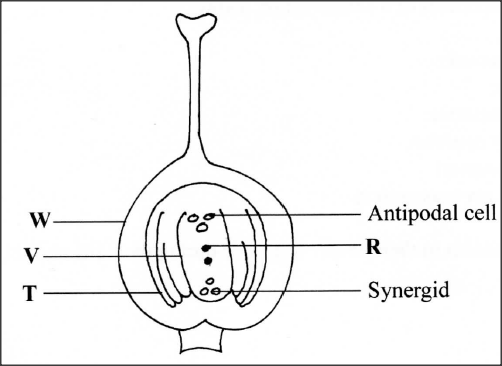
The diagram below illustrates the structure of the female part of a flower.
(a) Name the part labelled W.
(b) Describe what happens when the pollen tube enters the structure labelled V. (c) What do the structures labelled R and T develop into after fertilization? R T
ANSWERS
(a) W - ovary wall/ovary;
(b) Tip of pollen tube bursts open; one of the nuclei fuses with the egg cell nucleus; to form a diploid zygote; while the remaining male nucleus fuses with the polar nuclei; to form a triploid endosperm nucleus; (c) R - Endosperm/primary endosperm; T - testa/seed coat; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN15
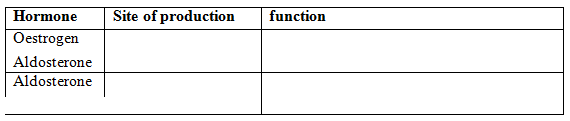
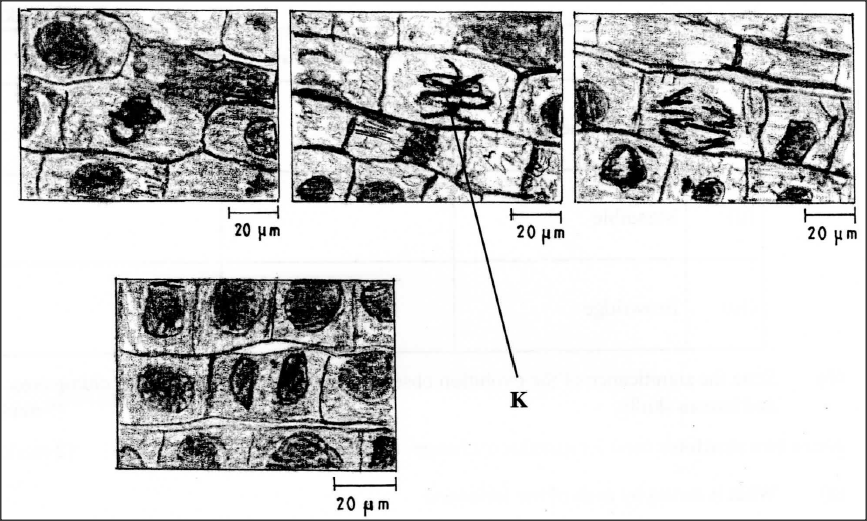
The photomicrographs below show the various stages of cell division in a certain plant.
(a) (i) Name the type of cell division illustrated.
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above. (b) (i) Name the stage of cell division labelled K. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above.
answers
(a) (i) Mitosis;
(ii) Formation of two daughter cells. (b) (i) Metaphase; (ii) Chromosomes are at the equator
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2015PP1QN13
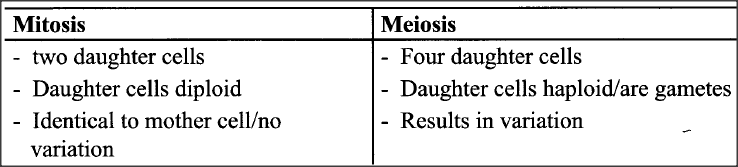
State three differences between the end products of mitosis and meiosis.K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP2QN01
(a) State four characteristics of fruits dispersed by animals.
(b) State two roles of each of the following hormones in menstruation: (i) luteinising hormone; (ii) oestrogen.
ANSWERS
(a)
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN25
State two roles of luteinising hormone in human reproduction.
ANSWERS
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

