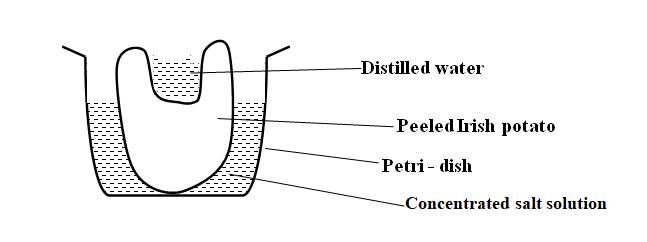
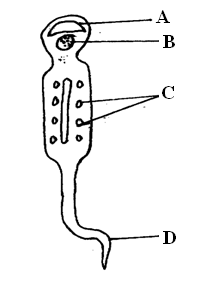
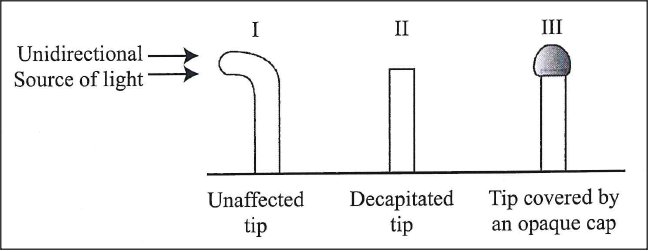
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN02
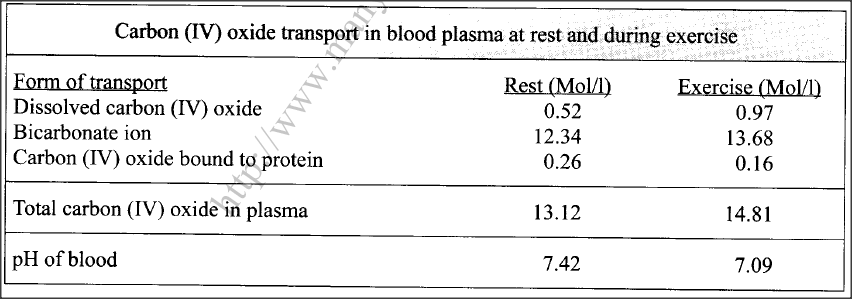
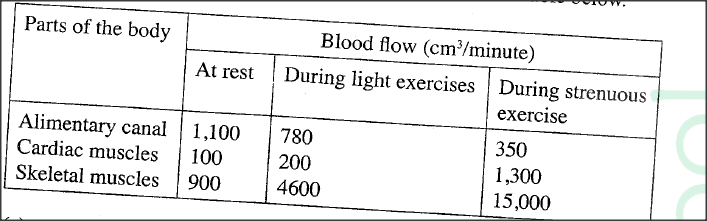
The table below shows variations in the form carbon (IV) oxide is transported in the blood at rest and during physical exercise.
(a) Explain why more carbon (IV) oxide ¡s transported in the form of bicarbonate ion.
(b)Account for the high total plasma content of carbon (IV) oxide during exercises. (c) State how one’s involvement in the exercises affects blood pH. (d) Name the protein responsible for the transport of carbon (IV) oxide in the blood.
ANSWERS
(a) Presence of carbonic anhydrase enzyme; which speeds up the conversion of carbon (IV) oxide to weak carbonic acid; which dissociates into hydrogen carbonate ion/(HCO3) (that diffuses out of the red blood cells into the blood plasma);
(b)The body needs high amount of energy; (for the exercise/muscle activity) hence high respiration rate (more oxygen intake); releasing more carbon (IV) oxide (in the blood plasma); (c)The high rate of respiration (during physical exercises coupled with normal cellular metabolism) results in the production of more carbon(IV) oxide/faster accumulation of lactic acid; lowering the blood plasma pH/making it more acidic (compared to when one is at rest); (d)Haemoglobin
0 Comments
Explain why certain bacteria and other pathogens become resistance to drugs after some time3/11/2021 (a) What is mutation? (2mks)
Mutation is a sudden/spontaneous change; in the genetic make up of an organism
(b) Explain why certain bacteria and other pathogens become resistance to drugs after some time. (2mks)
bacterial that survive the drug will undergo mutation: to produce bacteria which are resistance to the prevailing condition/drug. (2mks)
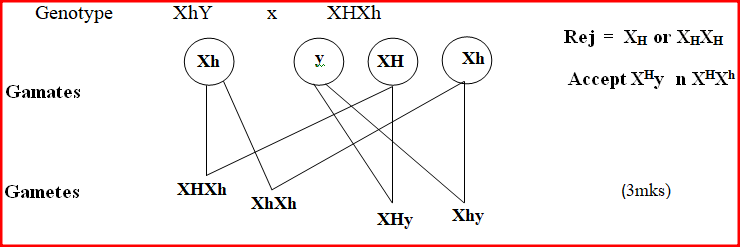
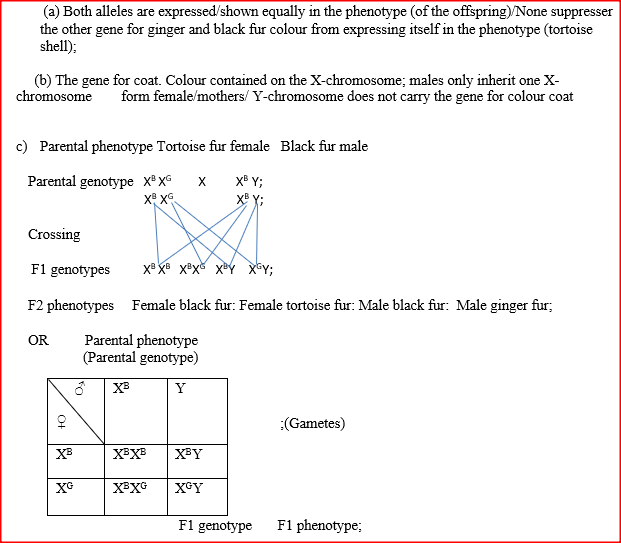
(c) Work out a cross between a Haemophiliac man married to a carrier woman for Haemophilia.
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

