State the functions of the following parts in a cell: Nucleolus, Smooth endoplasmic reticulum30/10/2021 a) State the functions of the following parts in a cell (2mks)(i) Nucleolus
Manufacture/synthesis of ribosomes;
(ii) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Transport of lipido
(b) Name an organelle that would be found in large numbers in cells of secretory glands (1mk)
Golgi bodies/Golgi apparatus;
0 Comments
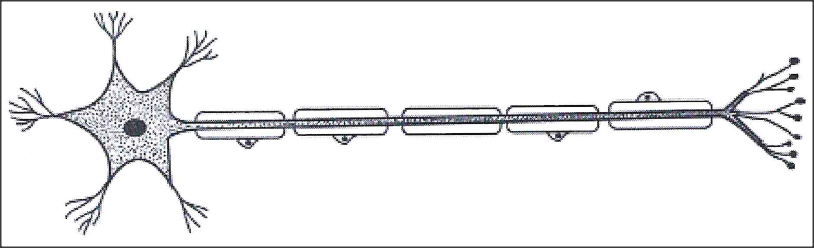
(a) State the functions of the following(i) Nerve cells (2mks)
(ii) Plasma (2mks)
(b) Give the functions of the following organ systems(i) Excretory system (2mks)
(ii) Endocrine system (2mks)
Identify the part of the light microscope which serve each of the functions described below9/9/2021
Identify the part of the light microscope which serve each of the functions described below
(i) Making rough focus (1mk)
Name the causative organism of the following diseases
(i) Malaria (1mk)
Name the organelle that is likely to be found in abundance in:(a) an enzyme secreting cell (1mk) ……………Golgi bodies (b) Cells producing lipid related secretions (1mk) …………………Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (c) Areas where the cells have raptured (1mk) ………………Lysosomes K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2019PP1QN03
The diagram below illustrates a specialised cell obtained from a certain tissue.
(a) Name the cell.
(b) State two ways in which the cell is structurally adapted to its function.
answers
(a) nerve cell/motor neuron; acc neuron
(b) longer axon to transmit impulses/delivers action potential along way; has numerous dendrites for receiving/delivering /transmitting impulse; myelin sheath for faster transmission of impulse/insulation of axon; Schwan cell for secretion of myelin sheath; node of ranvier to enhance speed of transmission of impulse; cell body has nucleus for controlling nerve impulse transmission. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN06
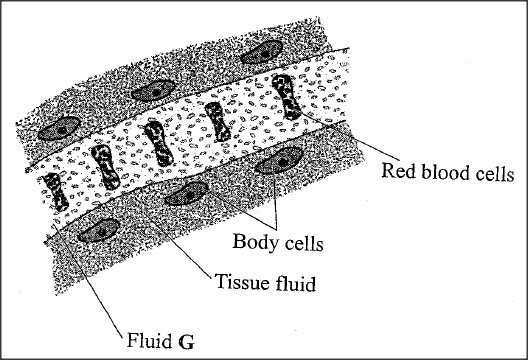
The diagram below illustrates tissue fluid and cells surrounding a capillary.
(i)Name fluid G.
(ii) Give two ways by which fluid G is different from tissue fluid.
answers
(i) (Blood) plasma;
(ii) Has (more large) proteins/blood platelets; High (hydrostatic) pressure/low pressure of tissue fluid; Has red blood cells; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2018PP1QN01
(a) Name the cell organelle found in abundance in the white blood cells.
(b) Give a reason for your answer in (a) above.
answers
a)Lysosomes/golgi apparatus;
b)White blood cells fight pathogens to protect the body, the lysosomes contain lytic enzymes which destroy pathogens;/golgi apparatus synthesize lysosomes which contain lytic enzymes that destroy parthogens; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN03
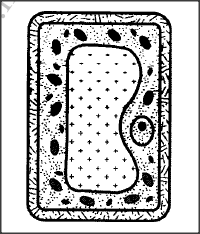
The diagram below illustrates the appearance of a plant cell after it had been put in a certain solution.
(a) Explain the appearance of the cell at the end of the treatment.
(b) Explain the results obtained if a red blood cell is subjected to the same treatment. (c) Explain why transfusion with distilled water is not recommended for a dehydrated patient.
answers
(a) The cell is turgid; its cell sap was hypertonic (compared to the solution in which it was placed); by osmosis, water moved into the cell across its cell semi-permeable membrane, (swelling and becoming turgid);
(b)The red blood cell lacks the cell wall; water molecules move across its semi-permeable membrane by osmosis; into its hypertonic medium (inside the cell),cell contents/cytoplasm swelling and bursting haemolyses; (c)Would haemolyse; due, to lowering of the osmotic pressure of the blood below normal; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN01
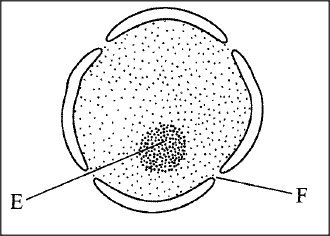
The diagram below represents a nucleus.
(a) Name the structures labelled E and F.
(i) E F (ii) State the function of F. (iii) With reference to the nucleus, state one difference between an animal and a bacterial cell. (b) Name the plant cell organelle: (i) that stores chlorophyll (ii) responsible for intracellular digestion. (c) State two main functions of the vacuole in the amoeba.
ANSWERS
(a) E—Nucleolus;
F — Nuclear pore/nucleopore; ii. Facilitates movement of materials in and out of the nucleus; iii. Nuclear material in the bacterial cell is not enclosed within a membrane /prokaryotic, while in animal cell it is enclosed eukaryotic; (b) i. Chloroplast; ii. Lysosome; (c) i. Feeding (food vacuole); ii. Osmoregulation (contractile vacuole); iii. Excretion/removal of wastes; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP1QN02
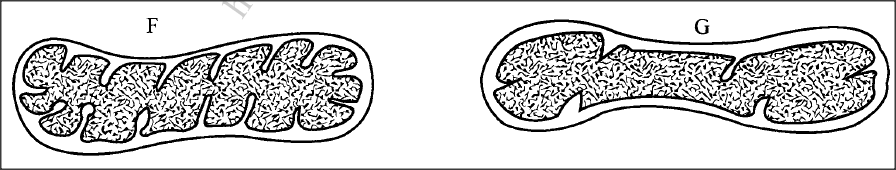
Below are diagrams of a cell organelle obtained from different organs of an animal
(a) (i) For each organelle state an organ in the urinary system where it is likely to be found.
F G (ii) Give a reason for your answers in (a) (i) on page 2. (b) Name the part of the chloroplast where the following reactions occur: (i) Carbon(IV) oxide fixation (ii) Photolysis
answers
(a) (i) F - Kidney;
G - Bladder/Ureter/Urethra; ii) Kidney - active re-absorption of solutes requires more energy; organelle F has more cristae for attachment of more respiratory enzymes producing more energy; Bladder/ureter/urethra does not require as much energy/organelle G has less number of cristae hence fewer respiratory enzymes attached/less energy produced; (b) i) Stroma; ii) Grana/granurn;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN08
State three functions of Golgi apparatus.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2014PP1QN20
State one function of each of the following cell organelles:
(a) golgi bodies (b) lysosomes.
ANSWERS
(a) Packaging of substances/glycoproteins/ transportation of glycoproteins;
Secretion of synthesized proteins and carbohydrates; Formation of lysosomes/modification of carbohydrates to form glycoproteins; (1 mark) (b) Digestion of food/Breakdown large molecules; Destroy worn out organdies or cells/tissue; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN09
State one way in which each of the following is structurally adapted to its function:
(a) neurone; (b) mitochondrion.
answers
a)Presence of myelin sheath for insulationlincreases transmission; Axon for transmission of impulses;
Large cell body controls activites of cell; Nerve endings/dendrites receives impulses from receptors cells; Node of Ranvier speeds up impulse transmission. (b) Inner membrane highly folded/cristae to increase S A for attachment of (respiratory) enzymes. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2013PP1QN02
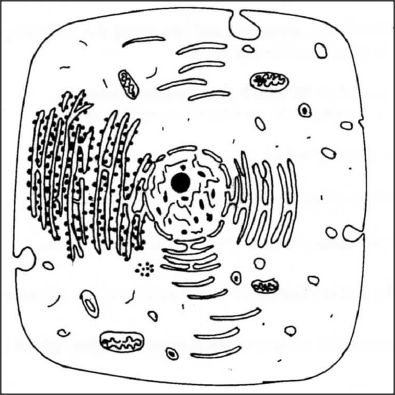
The diagram below represents a cell as seen under an electron microscope.
(a) Based on the diagram, state whether it represents an animal cell or a plant cell.
(b) Give two reasons for your answer in 2(a) above. (c) Why is the palisade layer a tissue?
answers
(a) Animal cell;
(b) Has cell membrane only/has no cell wall; Has numerous small vacuoles; Has central nucleus; (c) Consists of many similar cells performing the same function; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN30
Name the organelle that is involved in each of the following:
(a) manufacture of lipids (b) formation of lysosomes
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN27
What is the function of contractile vacuoles in amoeba?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN03
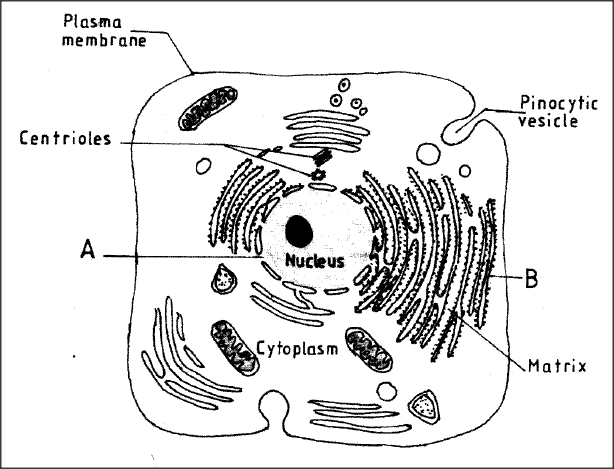
The figure below is a fine structure of a generalised animal cell as seen under an electron microscope.
(a) Name the parts labelled A and B.
A B (b) How is the structure labelled B adapted to its function?
answers
(a) (i) A - nucleopore;
B - Rough Endoplastic Reticulum; (b) Surface covered with ribosomes; for protein synthesis; Has interconnected channels: for transportation of proteins;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN09
State two ways in which chloroplasts are adapted to their function.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN03
State the functions of:
(a) Ribosomes; (b) Lysosomes.
answers
(a) Protein synthesis
(b) Destroys worn out organdies and micro-organism; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2010PP1QN01
State the name given to the study of:
(a) the cell; (b) microorganisms.
answers
(a) Cytology;
(b) Microbiology;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN26
How are the mitochondria adapted to their functions?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2009PP1QN07
State the function of the following cell organelles
(a) Ribosome (b) Lysosomes
ANSWERS
(a) site for protein synthesis
(b) Break down worn out cells/ organelles / food materials K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN19
The diagram below represents a tissue obtained from an animal
(a) Identify the tissue
(b) State the functions of the tissue named ( a) above
ANSWERS
(a) Cardiac muscle
(b) Contraction of the heart
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2008PP1QN12
State two functions of the endoplasmic reticulum
ANSWERS
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

