|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN20b
Describe how the cervical, lumbar and sacral vertebrae are suited to their functions.
answers
Cervical vertabrae
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN20
Name three types of skeletons found in multicellular animals
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN19
Describe the role of hormones in the growth and development of plants.
answers
Indole acetic acid/IAA/ Auxins
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN18
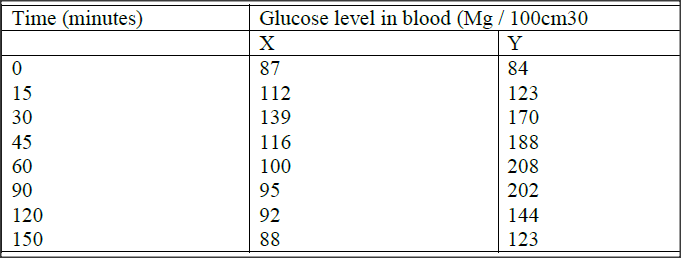
Two person X and Y drunk volumes of concentrated solution of glucose. The amount of glucose in their food was determined at intervals. The results are shown in the table below:
a) On the grid provided, plot graphs of glucose level in blood against time on the same axes.
b) What was the concentration of glucose in the blood of X and Y at the 20th minute? X = 120 + -3) Y = 140 +-3) c) Suggest why the glucose level in person X stopped rising after 30 minutes while it continued rising in person Y. d) Account for the decrease in glucose level in person X after 30 minutes and person Y after 60 minutes (3 minutes) e) Name the compound that stores energy released during oxidation of glucose. f) Explain what happens to excess amino acids and development of plants.
answers
(a) – For exchanged axis award maximum 3 marks for points x identity
The scale must however be correct. For graphs on separate axis mark both and award the highest mark. (a) Axis = 2 (b) Scale = 1 (c) ( plotting) = 1 (d) curves) = 1 (b) X = 120 + -3) Y = 140 + -3 (c) Person X is capable of regulating glucose while person y is likely to be diabetic. X – Insulin (d) X insulin released, excess glucose is converted into glycogen ( in liver) must be mentioned if insulin is not mentioned Y Insulin not released, thus the decline is due to glucose being released in urine. (e) A.T.P / Adenosine triphosphate (f) Deaminated; resulting in formation of ammonia Ammonia combines with CO2 to form urea ( and H20); Urea is passed out in Urine carbohydrate group is oxidized/ stored as glycogen
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN17
State four advantages of vegetation propagation.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN17
Give a reason for grafting in plants
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN17
What structures are produced by sisal for vegetative propagation?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN16
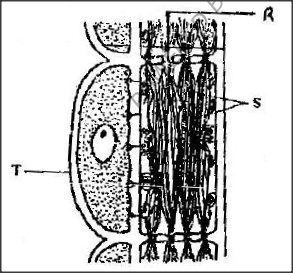
The diagram below represents part of phloem tissue.
a) Name the structures labeled R and S and the cell labeled T.
R S Cell labeled T b) State the function of the structure labeled S c) Explain why xylem is a mechanical tissue
answers
(a) R. Sieve pore
S- cytoplasmic strand, cytoplasmic filaments rej. Proto plasmic strand) Cell labeled T (b) Translocation (L is tied with structures) (c) Thickened and lignified. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN15
Ascaris lumbricoides in an example for an endo – parasite
a) The name Ascaris refers to b) State the habitat of the organism c) State three ways in which the organism is adapted to living in its habitat.
answers
(a) Genus
(b) Ileum/ colon/ duodenum/ intestines/ of humans or intestines of pig (c) Lack of elaborate elementary canal ( simple guts) can tolerate raw corn Thick cuticle pellicle, reject the outer covering lays many eggs Mouthparts for sucking partly digested food
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN14
Distinguish between divergent and convergent evolution giving example in each case.
answers
Divergent basic structural form is modified to serve different functions; e.g. vertebrate forelimbs, break structure in birds/ feet in birds’ convergent different structures are modified to pass or similar functions e.g. wings and birds and insects/ eye of human and octopus, vertebrates for humans e.g. squeal, legs of vertebrae and insects .
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN14
State two ways in which Home sapiens differs from Homo habilis
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN14
What is organic evolution
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN13
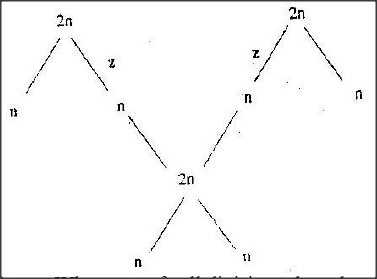
The chart below shows the number of chromosomes before and after cell division and fertilization in a mammal.
a) What type of cell division takes place at Z
b) Where in the body of a female does process Z occur c) On the chart, indicate the position of parents and gametes d) Name the process that leads to addition or loss of one or more chromosomes. e) State three benefits of polyploidy in plants to a farmer
answers
a) Meiosis
b) Ovary c) parent must be the 2n top; any ‘n’ is a gamete d) Non – dysfunctions e) increased yields / highbred Vigor, Resistance decreases Resistance to drought. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN12
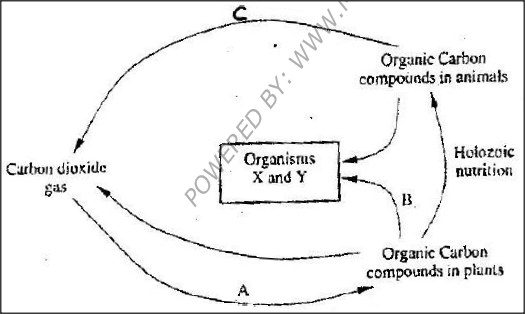
The chart below represents a simplified carbon cycle.
(a)Name the process labeled A, B, and C
A B C b) Name the organisms X and Y X Y c) State the importance of carbon cycle in nature
answers
a) A A photosynthesis
B Decomposition / decay C Respiration b) X Bacterial Y Fungi c) Regulate the CO2 in the atmosphere. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN11
Give an example of a sex – linked trait in humans on:
Y CHROMOSOME. X CHROMOSOME.
answers
Y CHROMOSOME
Tuft and hair sprouting from pinna / baldness; hairy pinna; X CHROMOSOME Colour blindness / haemophilia.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN10
What happens to excess fatty acids and glycerol in the body?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN09
Name two gaseous exchange structures in higher plants.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN08
Which type of joint is found at the articulations of
a) Pelvic girdle and femur b) Humerus and ulna
answers
a) Ball and socket
b) Hinge Explain why the carrying of wild animals is higher than that for cattle in a given piece of land.17/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN07
Explain why the carrying of wild animals is higher than that for cattle in a given piece of land.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN06
In what form is oxygen transported from the lungs to the tissues?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN05
State two characters that researchers select in breeding programme.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN04
During germination and early growth, the day weight of the endosperm decreases while that of the embryo increases. Explain.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN03
Give one example of a metallic co – factor
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN03
State the function for co-factors in cell metabolism
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2002PP1QN02b
Name the bacteria found in the root nodules of leguminous plant
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

