Describe how accommodation in the human eye is brought about when focusing on a near object.25/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN08
Describe how accommodation in the human eye is brought about when focusing on a near object.
answers
Light rays from a near object are more diverged and need to bend more; in order to be focused properly on the retina; ciliary muscles contract; suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary muscles relax; the lens becomes thicker; increasing its curvature/becomes more convex; light from the object is refracted more; in order to be focused/more sharply on the retina to form an image.
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN08
Describe the exoskeleton and its functions in insects.
answers
The exoskeleton is made of chitin; chitin is not evenly distributed; hence it allows for movement; exoskeleton is secreted by the epidermal cells; when still soft it allows for growth of the insect; when in contact with the air it hardens limiting growth; It is shed regularly; thus regulating the growth of insects. It also supports the internal structures; Because it is hard; it protects; internal organs from mechanical damage. It is water proof; preventing water loss/dessication; of the insect. It also provides a surface for attachment of muscles;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN07
Explain how the human skin brings about cooling of the body on a hot day.
answers
Erector pilli muscle relax; and hair lie flat; trapping less air; thus reducing insulation;
Blood capillaries under the skin vasodilate; and more blood is brought under the skin; increasing heat loss; sweat glands release more sweat to the skin surface; the sweat take away heat from the body when it evaporates;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN07
Explain how structural features in terrestrial plants affect their rate of transpiration.
answers
Plants in arid, semi-arid and desert habitats have leaves covered with thick/waxy cuticles; that are waterproof/impermeable to water; allowing for reduced rate of transpiration; Sunken stomata; in some desert/semi arid areas plants have water vapour accumulating in the pits; reducing rate of transpiration (as the moisture in the pit is carried away by wind.) Most plants have few or no stomata on the upper surface of leaf; the fewer the stomata the less the water lost from the plant. Some plants have small stomata/stomatal size decrease when guard cells are flaccid; thus reducing transpiration rate. Plants with small/folding leaves; expose less surface area; hence reduce the rate of transpiration. Leaves with shinny surfaces; reflect light resulting
reduced leaf temperatures; thus reducing the rate of transpiration. Some plants have leaves covered with hairs/scales; which trap a layer of moisture; the leaf surface reducing rate of transpiration. Mesophyte have a thin layer of cuticle; to facilitate high transpiration rate; brad lenses exposing large area to transpiration; Many stomata on both leaf surfaces provide many apartunes to enhance transpiration.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN06
Explain how the osmotic pressure in the human blood is maintained at normal level.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN06
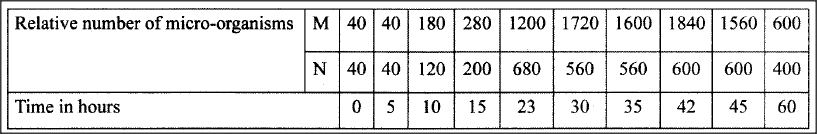
An experiment was carried out to investigate the population of a certain micro-organism. Two petri-dishes were used. Into the petri-dish label led M, 60cm3 of a culture medium was placed while 30cm3 of the same culture medium was placed in petri-dish labelled N. Equal numbers of the micro-organisms were introduced in both petri-dishes. The set-ups were then incubated at 35°C. The number of micro-organisms in each petri-dish was determined at irregular intervals for a period of 60 hours. The results were as shown in the table below.
(i)On the same axes, draw the graphs of relative number of micro-organisms against time on the grid provided.
(ii) After how many hours was the difference between the two populations greatest? (iii) Work out the difference between the two populations at 50 hours. (iv) With a reason state the effect on the population of micro-organisms in petri-dish M if the temperature was raised to 60°C after 20 hours. (v) Account for the shape of the curve for population in petri-dish N between 46 hours and 59 hours.
answers
(ii) 42 hours;
(iii) Graph M at 50 hrs is 1220 ± 20. Graph N at 50 hrs is 540 ± 20 (2 m 1220-540=680±4; (iv) Population growth stops; . High temperatures kill the microorganisms/denature enzymes; (v) 46 hours to 59 hours death rate of the microorganisms is higher, than their population growth rate; due to exhaustion of nutrients; and accumulation of toxic wastes; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN05
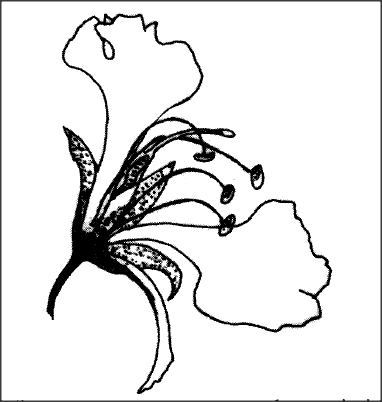
The diagram below represents a flower.
(i) On the diagram, name two structures where meiosis occurs.
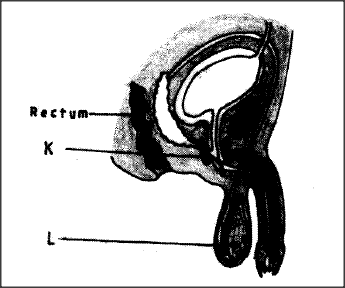
(ii) How is the flower adapted to prevent self-pollination? (ii) How is the flower adapted to prevent self-pollination? (b) The diagram below represents a human reproductive organ.
(i) Explain two adaptations of the structure labelled L to its functions.
(ii) Explain the role of the gland labelled K.
answers
(a) (i) Anthers; Ovary;
(ii) Anthers are below the stigma to minimise self pollination;
production; it has many, long and coiled seminiferous tubules to increase the surface area for production/storage of sperms; (ii) K produces an alkaline fluid that neutralizes acid in the vagina; this fluid contain nutrients for the sperms; and also activates sperms; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN04
The diagram below represents a section of the human brain.
(i)Name the structures labelled P and R.
P R (ii) State two functions of the part labelled Q. (b) (i) Name two reproductive hormones secreted by the pituitary gland in women. (ii) State one function of each of the hormones named in (b)(i) above.
answers
(a) (i) - is cerebral hemisphere/cerebrum;
R - medulla oblongata; (ii) Muscular co-ordination; maintaining body posture; manual/motar dexterity; (b) (i) Follicle stimulation hormone; luteinizing hormone; oxytocin; prolactin; (ii) FSH - stimulates secretion of oestrogen; stimulates development of the Graafìan follicle; LH - Brings about ovulation; causes development of corpus luteum; Oxytocin - causes contraction of uterus; causes expulsion of milk from mammary glands; Prolactin - stimulates milk production/secretion;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN03
How are the pneumatophores adapted to their function?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN03
Describe how oxygen in the alveolus reaches the red blood cells.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN03
Name the causative agents for the following respiratory diseases.
(i) Whooping cough. (ii) Pneumonia.
answers
(a) (i) Bordetella pertussis;
(ii) Streptococcus pneumoniae; (iii) Micoplasma pneumoniae;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN02
Explain how comparative embryology is an evidence for organic evolution.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN02
Name two disorders in humans that are determined by sex-linked genes.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN02
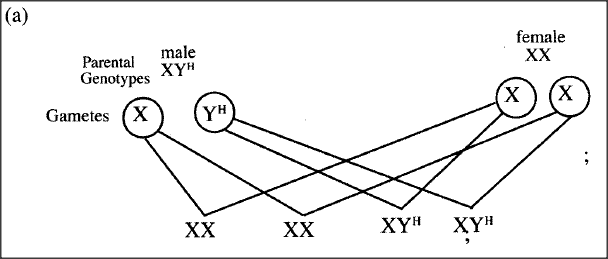
In humans, hairy ears is controlled by a gene on the Y Chromosome.
(a) Using letter Y^H to represent the chromosome carrying the gene for hairy ears, work out a cross between a hairy eared man and his wife. (b) (i) What is the probability of the girls having hairy ears? (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b(i) above. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN01
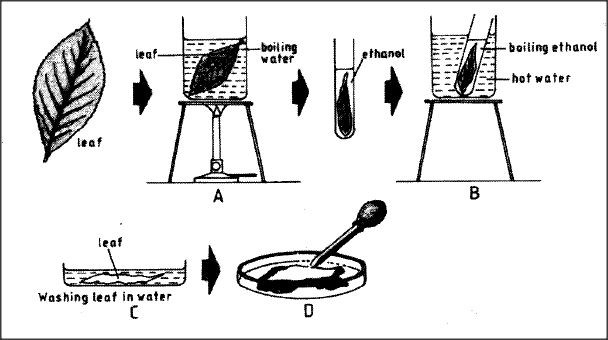
The set-up below illustrates a procedure that was carried out in the laboratory with a leaf plucked from a green plant that had been growing in sunlight.
(i) What was the purpose of the above procedure?
(ii) Give reasons for carrying out steps A, B and C in this procedure. A B C (iii) Name the reagent that was used at the step labelled D. (iv) State the expected result on the leaf after adding the reagent named in (iii) above.
ANSWERS
(i) - Testing a leaf for the presence of starch;
(ii) - A - kill the leaf/break down cells/stop enzymatic activity; B - Removal of chlorophyll; C - Soften leaf/makes leaf less brittle; (iii) Iodine solution; (iv) Areas where starch is present stain blue/blue black;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN29
State four reasons why water is significant in seed germination.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN28
State two ways by which auxins regulate growth in seedlings.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN28
What is a tropic response?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN27
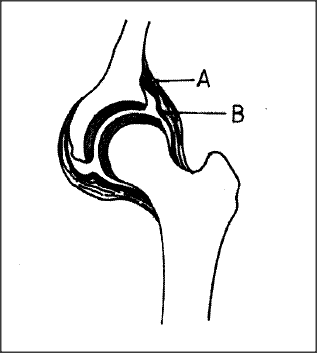
The diagram below represents features of a joint in a mammal.
(a)Name the part labelled A.
(b) State the function of the part labelled B.
ANSWERS
(a) Ligament;
(b) Secretes synovial fluid; contains/holds the synovial fluid in place;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN26
Name the gamete cells that are produced by the ovaries.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN25
State one economic importance of each of the following plant excretory products.
(a) Tannin. (b) Quinine. (c) Caffeine.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN24
What would be the expected results from a test cross?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN24
Differentiate between the following terms:
(i)dominant gene and recessive gene: (ii) continuous variation and discontinuous variation.
ANSWERS
(i) Dominant gene expresses itself phenotypically in both its homozygous and heterozygous states while recessive gene can only express itself phenotypically in the homozygous state;
(ii) Continuous variation is a characteristic for which there is a continuum or range while discontinuous variation is a characteristic for which there are discrete categories or units; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN23
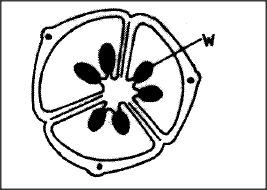
The diagram below represents a transverse section of an ovary from a certain flower.
a) (i)Name the structure labelled W.
(ii)Name the type of placentation illustrated in this diagram. (b) Give an example of a plant whose flowers have the type of placentation named in (a)(ìi) above.
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Ovule;
(ii) Axile placentation; (b) Orange or any correctly named citrus plant;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN22
State the difference in content of oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide in the air that enters and leaves the human lungs.
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

