|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN08
Describe how the mammalian heart is structurally adapted to its function.
answers
0 Comments
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN07
Using a relevant example in each case, describe simple and conditional reflex actions.
answers
Simple reflex action eg. withdrawal of finger from a sharp object/ hot object; its an automatic response to a specific stimulus; when the finger touches sharp object/ hot object, the pain receptors/ thermoreceptors in the skin are stimulants; and trigger off a nerve impulse; the nerve impulse is transmitted via the senses neurone; to the grey matter of the spinal cord/ CNS/ brain; the impulse is then transmitted via synapse; to the relay neurone; and then through another synapse; to the motor neurone; and then through another synapse; to the motor neurone; the impulse is then transmitted to the effector muscles in the hand; ace - efferent neurone for motor neurone Afferent neurone for sense neurone intermediate/ associative/ connector/interauncial neurone - for relay. The effector muscles/ biceps contract; and the finger is withdrawn from the hot object/ sharp object;
Conditioned reflex action - salivation in a dog/ human being (ace. any other relevant example) student in response to sound; it is an automatic response evoked from an animal by unrelated stimulus; substituted for the one which normally elicits the response; it develops from a past experience; and involves modification of behaviour/involves learning; it weakens with time; and must be reinforced by repeating the related stimulus; the dog/ student salivates when the bell (for meals) rings; because they have learnt to associate the ringing of the bell at meal time with food; everytime it rings (accept use of other relevant examples) they are offered food. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN06
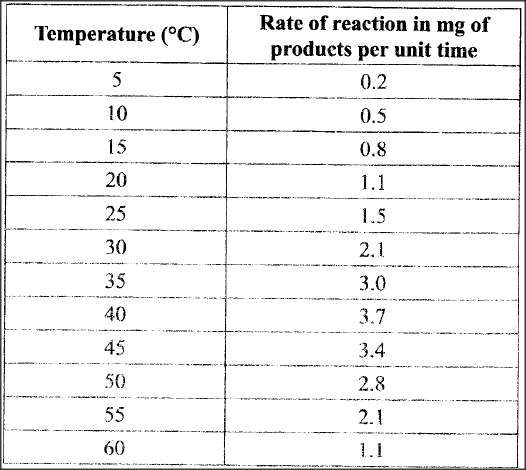
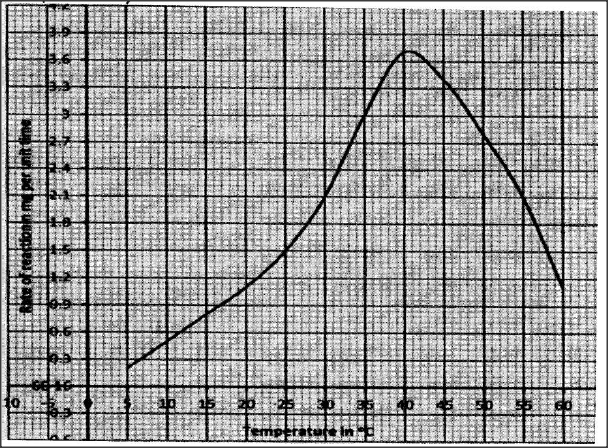
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction catalysed by an enzyme. The results are shown in the table below.
(a) On the grid provided plot the rate of reaction against temperature.
(b) When was the rate of reaction 2.6 mg of product per unit time? (c) Account for the shape of the graph between: (i) 5°C and 40°C (ii) 45°C and 60°C (d) Other than temperature name two ways in which the rate of reaction between 5°C and 40°C could be increased. (e)(i) Name one digestive enzyme in the human body which works best in acidic condition. (ii) how is the acidic condition for the enzyme named in (e) (I) above attained’? (f) The acidic condition in (e) (iii) above is later neutralized. (i) Where does the neutralization take place? (ii) Name the substance responsible for the neutralization.
answers
(b) 330C and 51.5 (± 0.50C)
32.5 - 33.5 and 51.0 – 52.0 (c) (i) 5°C and 40° C As temperature is increased rate of reaction is increased/ more products are formed (per unit time) because enzymes become more active (ii) 45° C and 60° C As temperature increase rate of reaction decreases less/products are formed (unit per time) because enzymes become denatured by high temperatures above 40, hence cannot act on substrate. (d) Increase in enzyme and substance concentration Use of co-factors and co-enzymes (e) (i) Pepsin, Chymosin Renin (ii) Wall of stomach/ gastric gland/ oxyntic/ pariental/ cell produced Hydrochloric (f) (i) Duodenum (ii) Bile juice/ e.g. NaHCO3 K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN05
A freshly obtained dandelion stem measuring 5cm long was split lengthwise to obtain two similar pieces. The pieces were placed in two different solutions of different concentrations in petri dishes (L1 and L2) for 20 minutes. The appearance after 20 minutes is as shown.
(a) Account for the appearance of the pieces in solutions L1 and L2
(b) Suite the significance of the biological process involved in the experiment.
answers
(a) L1 - Inner cells gained water by Osmosis; hence increased in length; epidermal cells did not gain water because they are covered by a water proof cuticle leading to curvature.
L2 - Inner cells lost water by osmosis; leading to (flaccidity) decrease in length; epidermal cells did not lose water due to waterproof leading to curvature (b) Absorption of water by the roots Opening and closing of the stomata K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN04
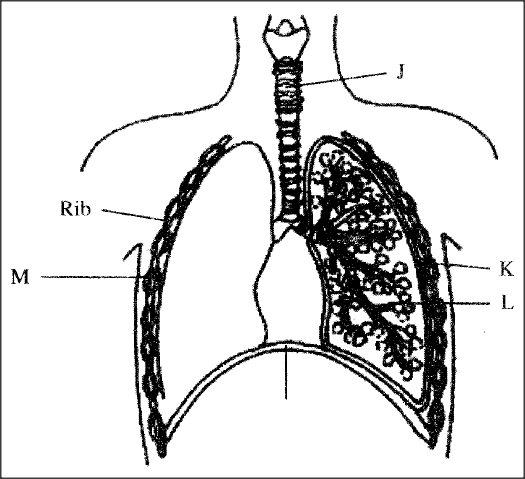
The diagram below represents some gaseous exchange structures in humans.
(a)Name the structures labeled K, L and M.
(b) How is the structure labeled J suited to its function? (c) Name the process by which inhaled air moves from the structure labeled L into blood capillaries. (d) Give the scientific name of the organism that causes tuberculosis in humans.
ANSWERS
(a) K- Pleural membranes
L- Alveolus M- Intercostal muscles (b) Has C- shaped cartilage rings that support it preventing it from collapsing and allow free flow of air Inner lining has mucus secreting cells that trap fine dust particles and microorganisms Inner lining has hair like structures called cilia that enhance upward movement of the mucus to the larynx (c) Diffusion (d) Mycobacterium tuberculosis (underline separately). K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN03
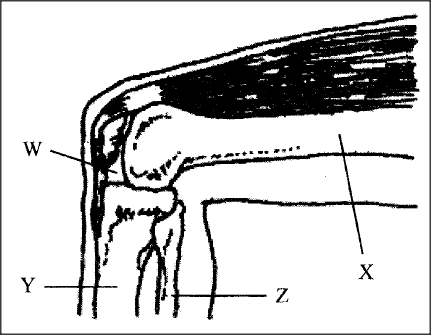
The diagram below represents bones at a joint found in the hind limb of a mammal.
(a) Name the bones labeled X, Y and Z
X Y Z (b) (i) Name the substance fi)und in the place labeled W. (ii) State the function of the substance named in (b) (î) above. (c) Name the structure that joins hones together at the joint. (d) State the difference between ball and socket joint and the one illustrated in the diagram above. (e) Name the structure at the elbow that performs the same function as the patella.
ANSWERS
(a) X- Femur
Y- Tibia Z- Fibula (b) (i) Synovial fluid (ii) Lubrication of the joint/ shock absorption Distribution of pressure (c) Ligament (d) Ball and socket joint allows movement in all planes while the illustrated allows movement in one plane only. Accept 360 for all planes 180 for one plane (e) Olecranon process
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN02
Explain why people with sickle cell trait have an adaption survival advantage over normal individuals in malaria endemic regions.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN02
Differentiate between sickle cell anaemia and sickle cell trait.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN02
How is sex determined in man?
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP2QN01
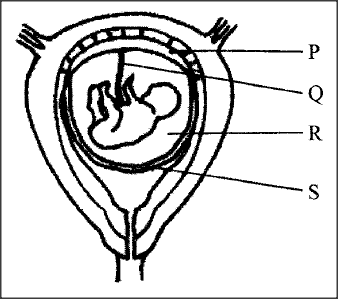
The diagram below represents a human foetus in a uterus.
(a) Name the part labeled S.
(b) (i) Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labaled Q. (ii) State the difference in composition of blood found in the vessels named in (b) (i) above. c)Name two features that enable the structure labeled P to carry out its function. (d) State the role of the part labeled R.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN30
State two advantages of hybrid vigour
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN29
Name two tissues in plants that provide mechanical support
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN29
State a characteristic that is common to all cervical vertebrae
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN28
The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ
(a) Name the plant organ from which the section was obtained.
(b) (î) Name the class to which the organism from which section was obtained belongs. (ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above. (c) Name the part labeled X
answers
(a) Stem
(b) (i) Monocotyledonae (ii) Vascular bundles are scattered and not arranged in a ring Absence of pith/ cambium (c) Epidermis
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN27
Name the opening to the chamber of the heart of an insect.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN27
Name an organism which has a single circulatory system.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN27
What is single circulatory system?
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN26
State the functions of the following parts of a microscope.
(a) Objective Lens (b) Diaphragm
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN24
How does nutrition as a characteristic of living organisms differ in plants and animals?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN23
State two functions of saliva.,
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN23
Name one salivary gland in humans.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN22
State three characteristics of the class Crustacea.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN21
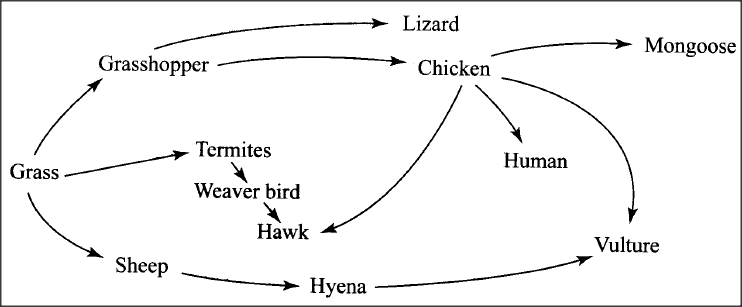
The figure below illustrates a food web in a certain ecosystem.
From the food web:
(a) Draw the shortest food chain (b) Identify the organism with the highest: (i) number of predators (ii) biomass
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2016PP1QN20
State three factors that contribute to the deceleration phase in the population curve of an organism.
answers
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

