The Inter-relationship between Living and Non-living Things
The Inter-relationship between Living and Non-living Things
In the intricate web of nature, there exists a profound inter-relationship between living and non-living things. These two components of the ecosystem are interconnected and rely on each other for survival and sustainability. Let's explore this relationship in more detail:
0 Comments
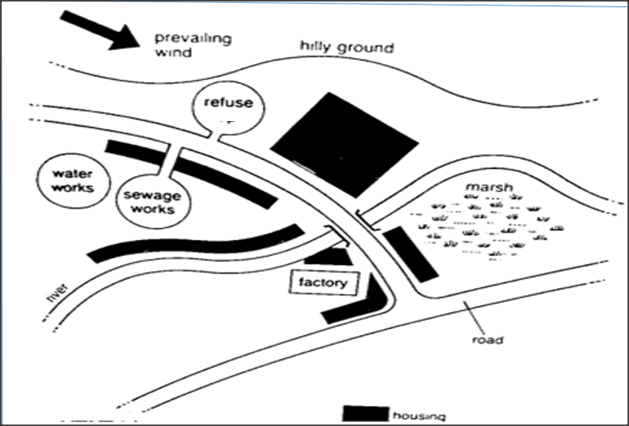
Below is a diagram of a poorly planned town showing some building and facilitiesa) Giving evidence from the diagram, state two likely sources of water pollution. (2mks)
b) State three ways that the positioning of the refuse pit and sewage works pose danger to the residence of the town. (3mks)
c) Residents living close to the marsh are likely to suffer from malaria. Explain. (1mk)
d) Suggest two control measures to overcome water pollution in the area. (2mks)
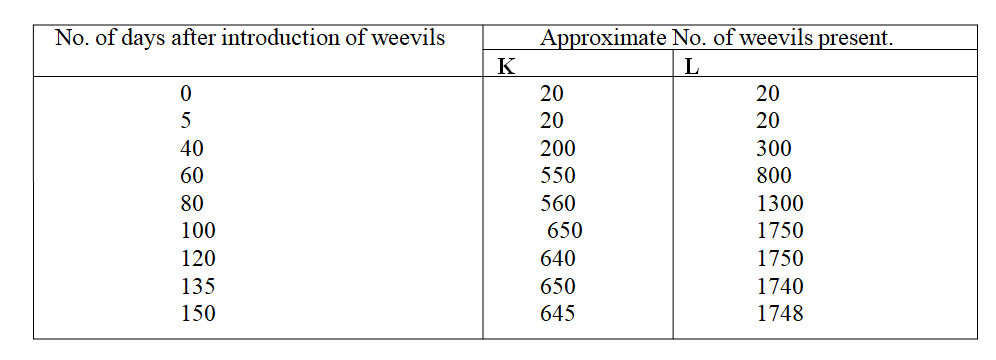
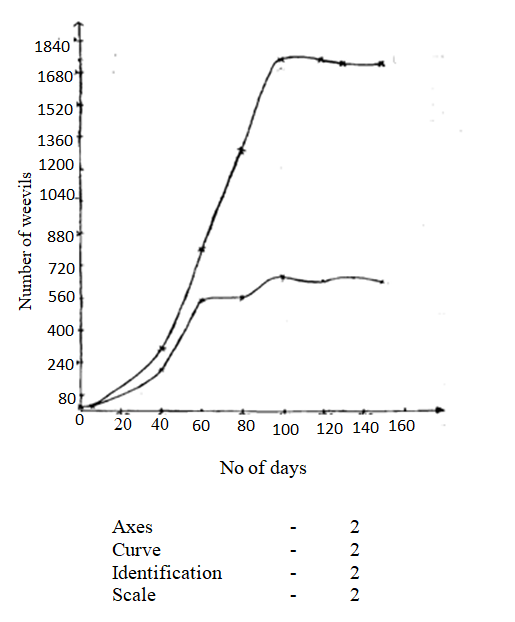
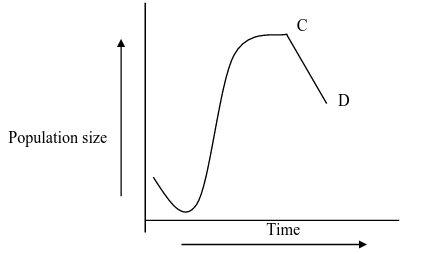
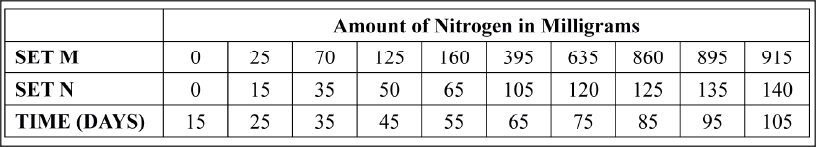
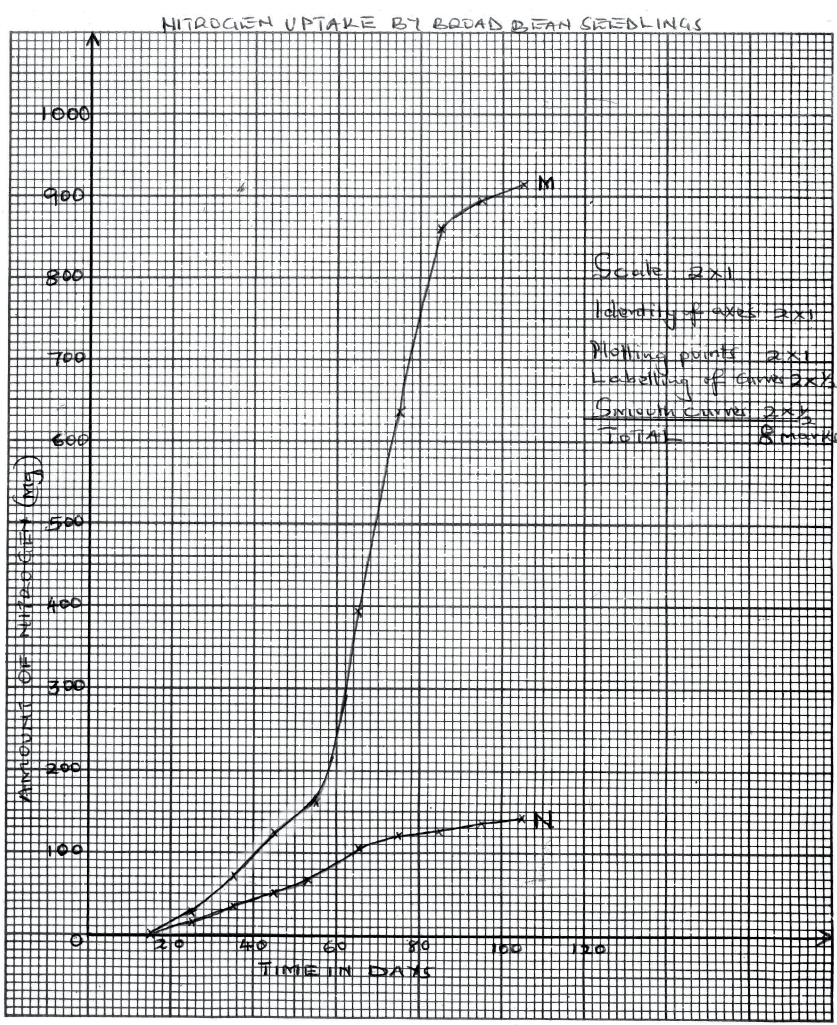
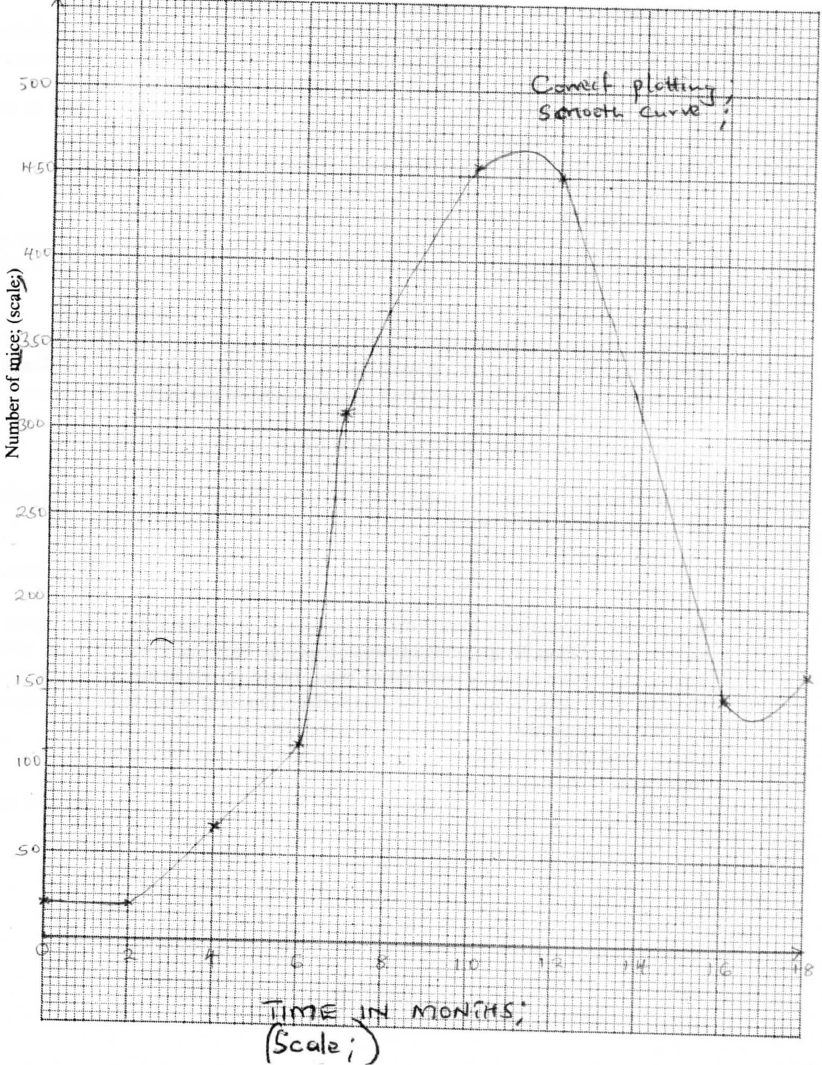
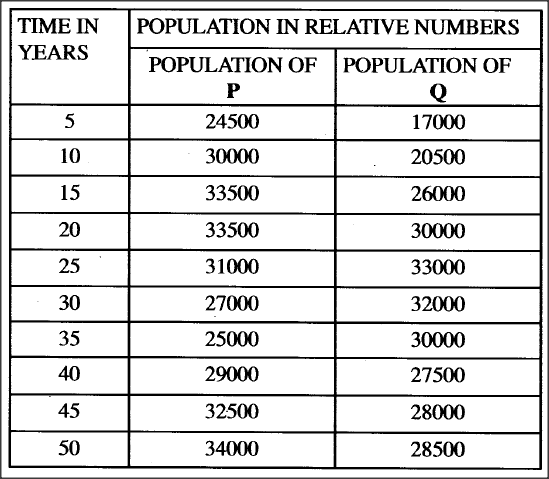
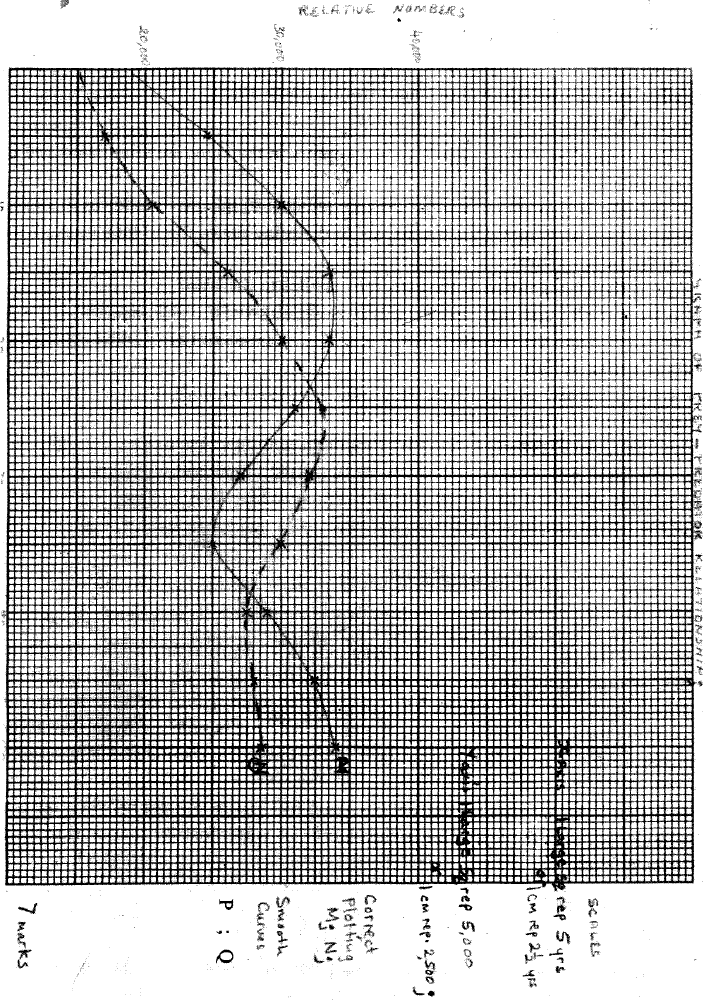
A group of students carried out a study of the population growth of flour weevils. They put 16 grams of maize flour into two equal boxes K and L respective . They then introduced equal numbers of weevils into the boxes. The boxes were kept under similar environmental conditions. The weevils were counted at intervals and the results recorded in the table below.
(a) Using a suitable scale ,draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table.
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |













 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

