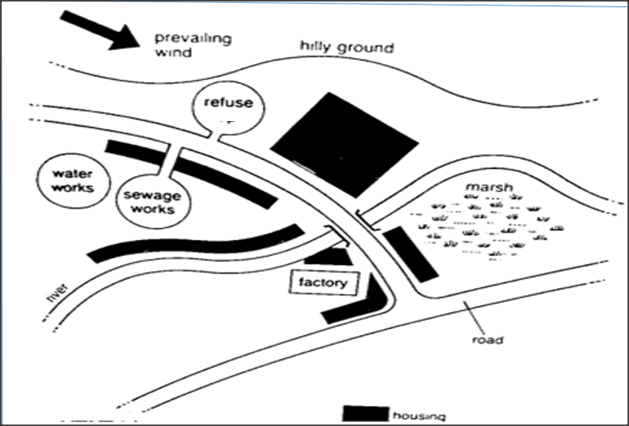
Below is a diagram of a poorly planned town showing some building and facilitiesa) Giving evidence from the diagram, state two likely sources of water pollution. (2mks)
b) State three ways that the positioning of the refuse pit and sewage works pose danger to the residence of the town. (3mks)
c) Residents living close to the marsh are likely to suffer from malaria. Explain. (1mk)
d) Suggest two control measures to overcome water pollution in the area. (2mks)
0 Comments
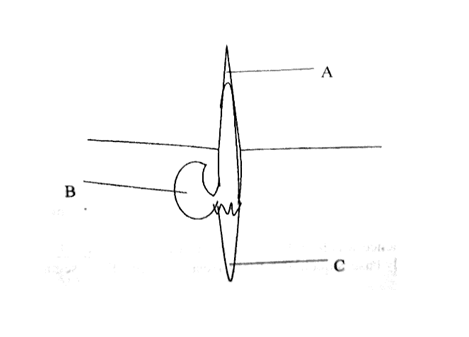
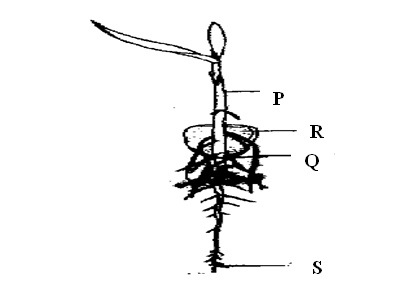
The diagram below represents a maize seedling.a) Name the structure labeled A and C (2mks)
b) State the functions of parts labeled A, B and C. (3mks)
c) Name the type of germination exhibited by maize (1mk)Hypogeal germination d) Name two conditions necessary for seed germination other than water and oxygen. (1mk)
e) What is the role of oxygen in seed germination? (1mk)It oxidizes the stored food in the seed to give energy for growth/synthesis of new materials;
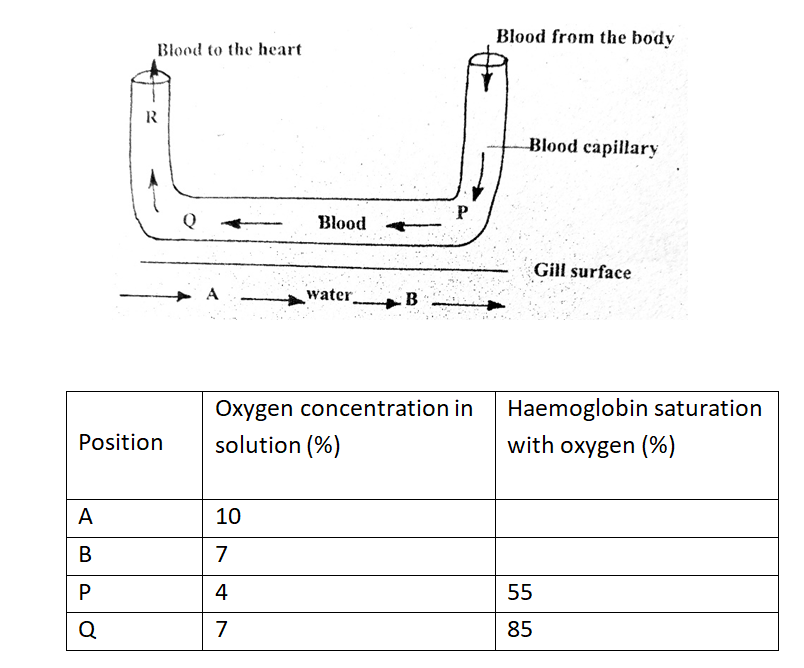
The diagram below represents the direction of flow of blood in a gill capillary. The percentage of oxygen in solution at position A, B, P, Q and R is given in the table below.a) Why is the oxygen percentage low at P? (1mk)
Blood coming from the body has supplied the tissue cells with oxygen/ oxygen has diffused out of capillary into the tissue fluid;
b) Using evidence from the data given, suggest what will happen to oxygen in the water at point B. (3mks)
Oxygen concentration at B reduces/will be at lowest; because blood at P has a lower oxygen concertation creating a diffusing gradient; From A to B there is a diffusion gradient hence at B much oxygen has diffused into the from water into the blood;
c) Name the organ into which blood coming from the capillary at Q flows. (1mk)
Heart
d) Suppose the flow of blood in the capillary illustrated above was in the opposite direction, explain the disadvantage it would have to the fish. (2mks)
Amount of exchange of respiratory gasses between blood and water would reduce; because of reduced diffusion gradient;
e) Name the principle where the blood flows in the opposite direction to another fluid. (1mk)
Counter flow system.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2017PP2QN02
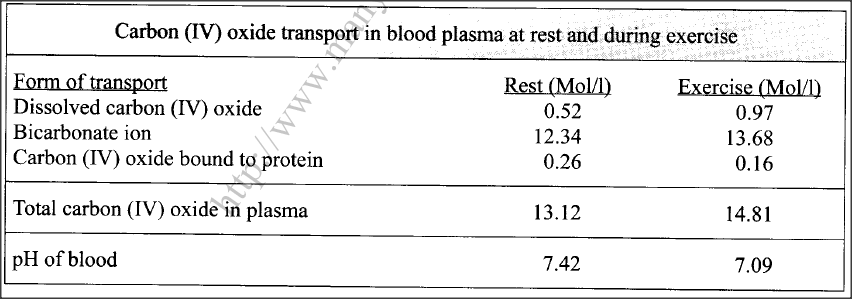
The table below shows variations in the form carbon (IV) oxide is transported in the blood at rest and during physical exercise.
(a) Explain why more carbon (IV) oxide ¡s transported in the form of bicarbonate ion.
(b)Account for the high total plasma content of carbon (IV) oxide during exercises. (c) State how one’s involvement in the exercises affects blood pH. (d) Name the protein responsible for the transport of carbon (IV) oxide in the blood.
ANSWERS
(a) Presence of carbonic anhydrase enzyme; which speeds up the conversion of carbon (IV) oxide to weak carbonic acid; which dissociates into hydrogen carbonate ion/(HCO3) (that diffuses out of the red blood cells into the blood plasma);
(b)The body needs high amount of energy; (for the exercise/muscle activity) hence high respiration rate (more oxygen intake); releasing more carbon (IV) oxide (in the blood plasma); (c)The high rate of respiration (during physical exercises coupled with normal cellular metabolism) results in the production of more carbon(IV) oxide/faster accumulation of lactic acid; lowering the blood plasma pH/making it more acidic (compared to when one is at rest); (d)Haemoglobin BIOLOGY REVISION KITS FORM 3 TERM 1 PAPER 2 MODEL26092022001
Explain structure and functions of the human eye. (20mks)
(a) Describe the mechanism of inhalation in man. (10mks)
External intercostals muscles contract; internal intercostals muscle relax, Rib cage move outwards; and upwards; Diaphragm muscles contract, Diaphragm flatten; volume in thoraci cavity increases; pressure reduces.
Atmospheric air enters the lungs; inflate (correct sequence to be followed) (b) Using photosynthesis theory explain the mechanics of opening of stomata. (10mks)
Guard cells have chloroplast which photosynthesis in the presence of light, to form sugar, the osmotic pressure of guard cell increases; water move from neighbouring cells into guard cells being thicker than outer walls. Causes the outer wall to stretch more resulting guard cells budging outwards.
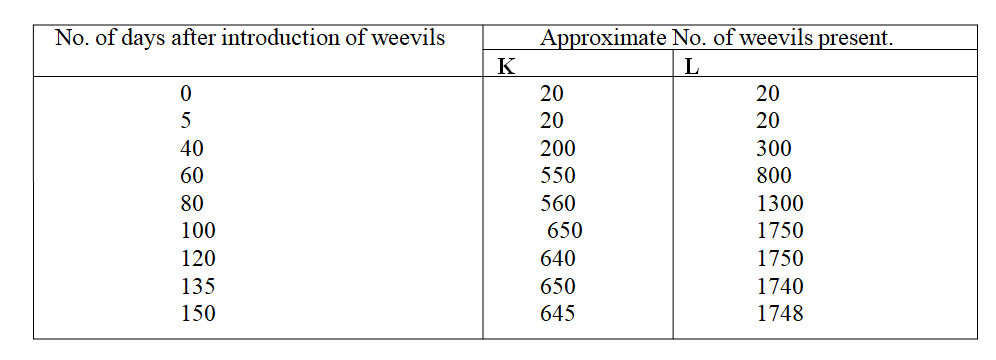
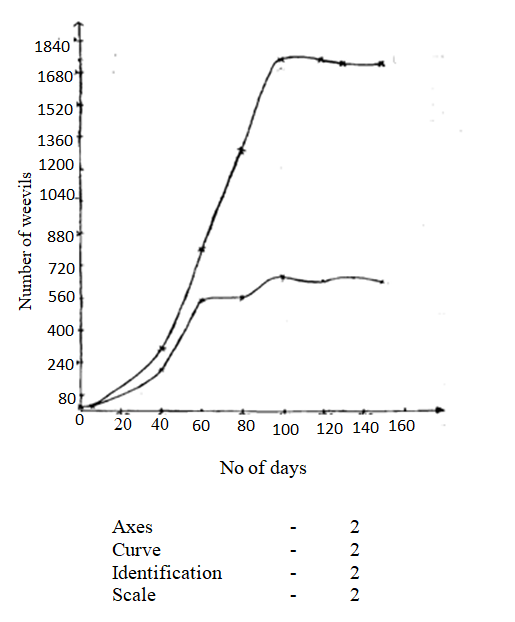
A group of students carried out a study of the population growth of flour weevils. They put 16 grams of maize flour into two equal boxes K and L respective . They then introduced equal numbers of weevils into the boxes. The boxes were kept under similar environmental conditions. The weevils were counted at intervals and the results recorded in the table below.
(a) Using a suitable scale ,draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table.
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
||||||
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

