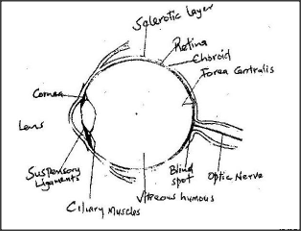
Explain structure and functions of the human eye. (20mks)
0 Comments
(a) Describe the mechanism of inhalation in man. (10mks)
External intercostals muscles contract; internal intercostals muscle relax, Rib cage move outwards; and upwards; Diaphragm muscles contract, Diaphragm flatten; volume in thoraci cavity increases; pressure reduces.
Atmospheric air enters the lungs; inflate (correct sequence to be followed) (b) Using photosynthesis theory explain the mechanics of opening of stomata. (10mks)
Guard cells have chloroplast which photosynthesis in the presence of light, to form sugar, the osmotic pressure of guard cell increases; water move from neighbouring cells into guard cells being thicker than outer walls. Causes the outer wall to stretch more resulting guard cells budging outwards.
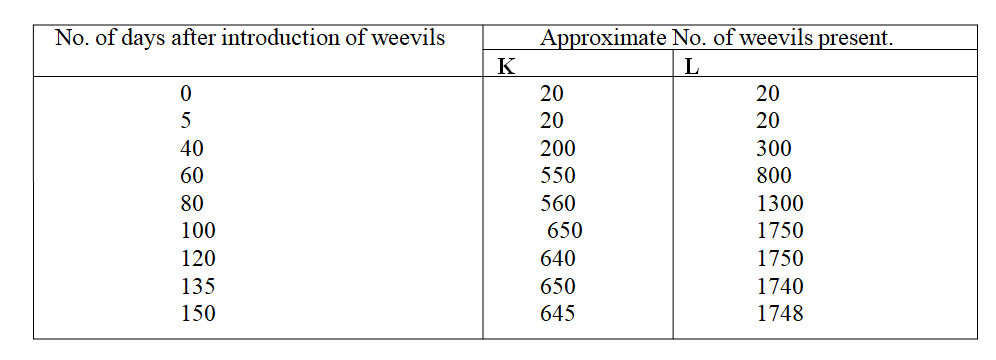
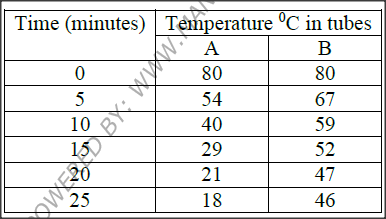
A group of students carried out a study of the population growth of flour weevils. They put 16 grams of maize flour into two equal boxes K and L respective . They then introduced equal numbers of weevils into the boxes. The boxes were kept under similar environmental conditions. The weevils were counted at intervals and the results recorded in the table below.
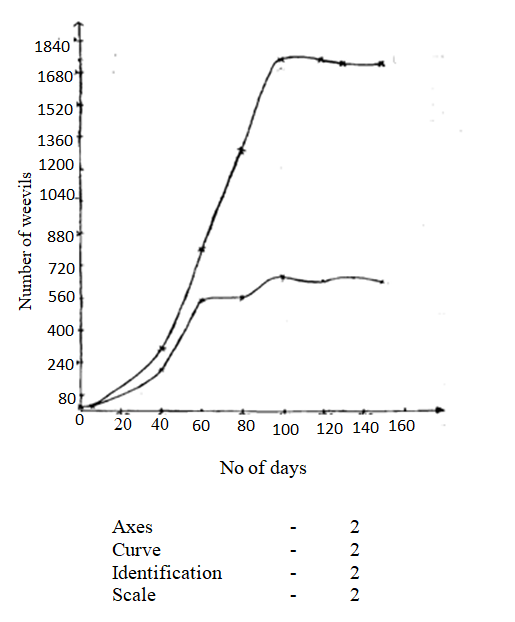
(a) Using a suitable scale ,draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table.
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

