Mastering KCSE Biology with Comprehensive Topical Questions and Answers
|
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN08
Using a relevant example, describe how an allergic reaction occurs in a human being.
ANSWERS
An allergic reaction is a hypersensitive response; to an antigen by the body immune
system; The body immune system responds by overproducing antibodies; against harmless antigens; The antigen-antibody reaction occurs on the surface of body cells; which burst open; and release histamines; Histamines cause inflammation/itching! swelling/pain, et.c; which damage the body; Allergic people are hypersensitive to materials like dust/pollen grains/some foods/some drugs/some pollutants,
1 Comment
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN07
Using a relevant example in each case, describe simple and conditional reflex actions.
ANSWERS
Simple reflex action - withdrawal of finger from a sharp object.
Is an automatic response to a specific stimulus; When the finger touches a sharp object, pain receptors in the skin; are stimulated and trigger off a nerve impulse; The nerve impulse is transmitted via the sensory neuron; to the grey matter of the spinal cord; The impulse is then transmitted via a synapse; to the relay neuron; and then through another synapse; to the motor neuron; The impulse is then transmitted to the effector muscles in the hand; These effector muscles contract; and the finger is withdrawn from the hot object; Conditioned reflex action Is an automatic response evoked from an animal by unrelated stimulus; substituted for the one which normally elicits the response; It develops from past experience; and involves modification of behaviour through learning; It weakens with time; and must be reinforced by repeating the unrelated stimulus; Students salivate when the bell for lunch rings; because they have learned to associate the ringing of the bell at lunchtime with food; from experience; every time it rings, they are offered food; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN06
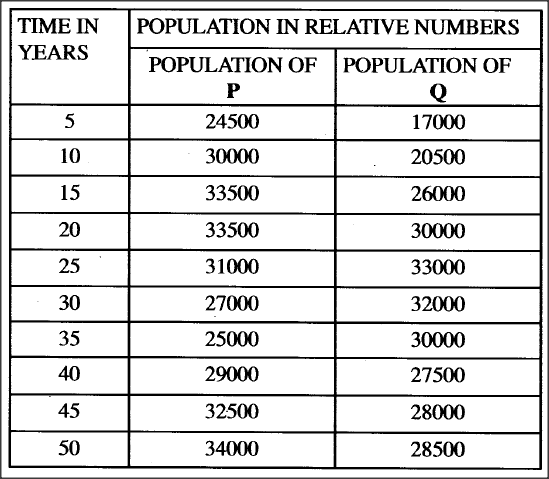
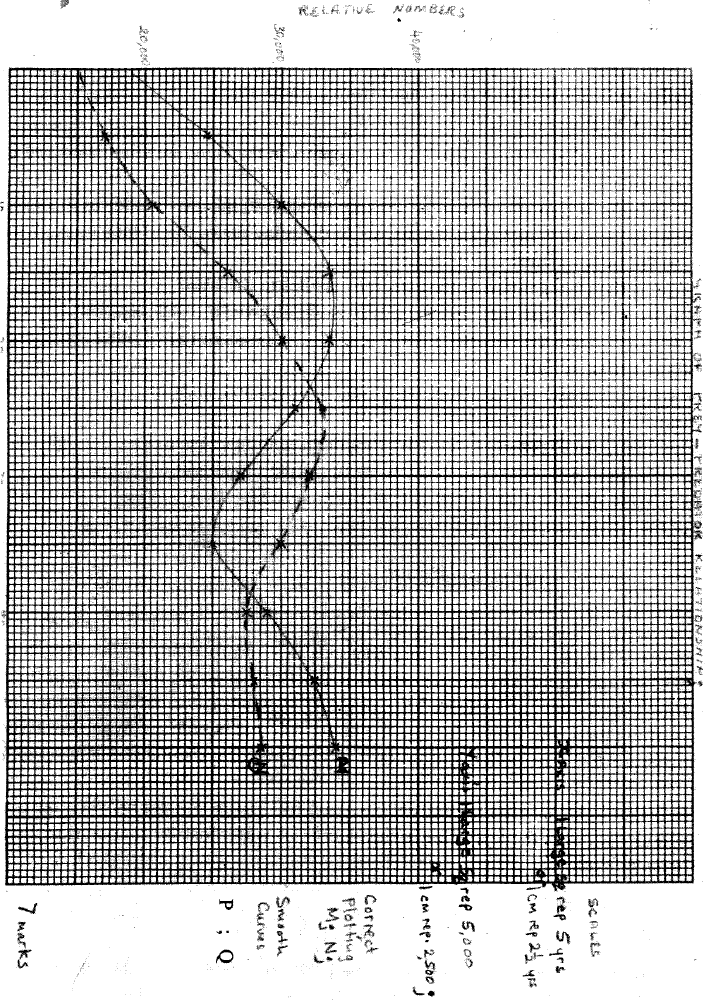
The data provided below represent populations of a predator and its prey over a fifty years’period.
(a) (i) Using the same axes, draw graphs of the relative populations of P and Q against time.
(ii) With a reason, identify the curve that represents the prey. (iii) Account for the two populations between 25 arid 32 years. (iv) Which years were the two populations equal? (v) A part from predation, state three biotic factors that may have led to the decline of the prey population. (b) Describe the hazards of air pollution by Sulphur (IV) Oxide.
answers
(a) (i) title - Graph of Prey-predator relationship; (OWTE)
Scales X axis; Graph should cover more than half of the grid provided. Y axis; Graph should cover more than half of the grid provided. correct plotting P; Q; smooth curves P; Q; labelling axes;
(ii) P represents the prey;
Prey population is initially higher prey population usually starts falling earlier; (iii) Both populations decrease; because prey is not enough to sustain predator/population environmental stress limit population of prey; (iv) at 23±0.5 years; and at 39±0.5; (v) less food for the prey/intra specific competition; emigration of the prey; diseases causing death of the prey; parasitism; human activities b)sulphur dioxide in the air - causes respiratory diseases; poisons plants; forms acid rain which increase soil pi-J; corrodes metals in buildings; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP2QN03
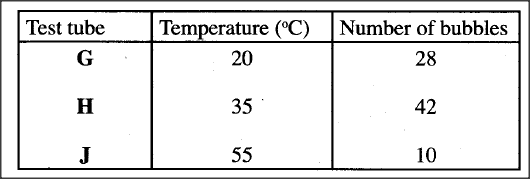
(a) In an investigation, equal amounts of water was placed in. three test-tubes labelled G, H and J. Pondweeds of equal length were dropped in each test tube. The test-tubes were then placed in identical conditions of light and carbon (IV) oxide at different temperatures for five minutes. After the five minutes, the bubbles produced in each test-tube were counted for one minute. The results were as shown in the table below.
(i) Name one requirement for this process that is not mentioned in the investigation.
(ii) Name the gas produced in this investigation. (iii) Account for the results in test-tubes H and J. (b) State two ways in which the human intestinal villus is adapted to its function.
answers
(a) (i) chlorophyll;
(ii) oxygen; (1 mark) (iii) Test tube H is at optimum temperature for enzyme activity; hence high rate of photosynthesis/more bubbles. In test tube J most enzymes have been denaturedby the high temperature; hence low rate of photosynthesis/fewer bubbles. (b) — The villus epithelium is thin; for faster diffusion of dissolved food substances; — The epithelium has goblet cells; which produce mucus to lubricate food passage; — They have microvilli; which further increase their surface area for absorption; Have lacteal; for absorption of fatty acid & glycerol/transportation of lipids; Highly vascularised; for absorption of digested food. K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN30
Name the organelle that is involved in each of the following:
(a) manufacture of lipids (b) formation of lysosomes
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN29
Name two nutrients that are absorbed without being digested by enzymes in humans.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN28
State two differences between open and closed circulatory systems.
answers
Open Closed
Blood flows in haemocoel Blood confined in vessels; sinuses/body cavity directly in contact with cells Blood flows at low pressure Blood flows at high pressure; Blood lack pigments Blood has pigments for oxygen and Carbon (IV) Oxide transportation
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN27
What is the function of contractile vacuoles in amoeba?
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN26
(a) State the theories of evolution proposed by the following scientists.
(i) cell organelles (ii) fossils
answers
(a) Theory of natural selection;
Theory of environmental influence on inherited characteristics; (b) (i) Similar organelles performing similar functions in different organisms suggest a common ancestry/cell biology; (ii) Fossil records/palaeontology/by comparing fossils to show phyllogenetic relationship between organisms/common ancestry; K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN25
State the role of the following hormones in the life cycle of insects:
ecdysone hormone; . juvenile hormone.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN24
State four characteristics of apical meristem cells.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN23
Name the strengthening materials found in the following support tissues:
(a) collenchyrna; (b)Xylem
answers
(a) Cellulose;
(b) Lignin;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN22
State the importance of divergent evolution to organisms.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN21
Name the process through which free atmospheric nitrogen is converted into nitrates.
answer
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN20
State three aspects that can be used to estimate growth in seedlings
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2012PP1QN19
List four symptoms of diabetes mellitus.
answers
Describe how accommodation in the human eye is brought about when focusing on a near object.25/6/2020
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN08
Describe how accommodation in the human eye is brought about when focusing on a near object.
answers
Light rays from a near object are more diverged and need to bend more; in order to be focused properly on the retina; ciliary muscles contract; suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary muscles relax; the lens becomes thicker; increasing its curvature/becomes more convex; light from the object is refracted more; in order to be focused/more sharply on the retina to form an image.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN08
Describe the exoskeleton and its functions in insects.
answers
The exoskeleton is made of chitin; chitin is not evenly distributed; hence it allows for movement; exoskeleton is secreted by the epidermal cells; when still soft it allows for growth of the insect; when in contact with the air it hardens limiting growth; It is shed regularly; thus regulating the growth of insects. It also supports the internal structures; Because it is hard; it protects; internal organs from mechanical damage. It is water proof; preventing water loss/dessication; of the insect. It also provides a surface for attachment of muscles;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN07
Explain how the human skin brings about cooling of the body on a hot day.
answers
Erector pilli muscle relax; and hair lie flat; trapping less air; thus reducing insulation;
Blood capillaries under the skin vasodilate; and more blood is brought under the skin; increasing heat loss; sweat glands release more sweat to the skin surface; the sweat take away heat from the body when it evaporates;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN07
Explain how structural features in terrestrial plants affect their rate of transpiration.
answers
Plants in arid, semi-arid and desert habitats have leaves covered with thick/waxy cuticles; that are waterproof/impermeable to water; allowing for reduced rate of transpiration; Sunken stomata; in some desert/semi arid areas plants have water vapour accumulating in the pits; reducing rate of transpiration (as the moisture in the pit is carried away by wind.) Most plants have few or no stomata on the upper surface of leaf; the fewer the stomata the less the water lost from the plant. Some plants have small stomata/stomatal size decrease when guard cells are flaccid; thus reducing transpiration rate. Plants with small/folding leaves; expose less surface area; hence reduce the rate of transpiration. Leaves with shinny surfaces; reflect light resulting
reduced leaf temperatures; thus reducing the rate of transpiration. Some plants have leaves covered with hairs/scales; which trap a layer of moisture; the leaf surface reducing rate of transpiration. Mesophyte have a thin layer of cuticle; to facilitate high transpiration rate; brad lenses exposing large area to transpiration; Many stomata on both leaf surfaces provide many apartunes to enhance transpiration.
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN06
Explain how the osmotic pressure in the human blood is maintained at normal level.
answers
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP2QN06
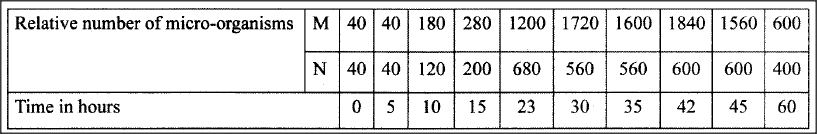
An experiment was carried out to investigate the population of a certain micro-organism. Two petri-dishes were used. Into the petri-dish label led M, 60cm3 of a culture medium was placed while 30cm3 of the same culture medium was placed in petri-dish labelled N. Equal numbers of the micro-organisms were introduced in both petri-dishes. The set-ups were then incubated at 35°C. The number of micro-organisms in each petri-dish was determined at irregular intervals for a period of 60 hours. The results were as shown in the table below.
(i)On the same axes, draw the graphs of relative number of micro-organisms against time on the grid provided.
(ii) After how many hours was the difference between the two populations greatest? (iii) Work out the difference between the two populations at 50 hours. (iv) With a reason state the effect on the population of micro-organisms in petri-dish M if the temperature was raised to 60°C after 20 hours. (v) Account for the shape of the curve for population in petri-dish N between 46 hours and 59 hours.
answers
(ii) 42 hours;
(iii) Graph M at 50 hrs is 1220 ± 20. Graph N at 50 hrs is 540 ± 20 (2 m 1220-540=680±4; (iv) Population growth stops; . High temperatures kill the microorganisms/denature enzymes; (v) 46 hours to 59 hours death rate of the microorganisms is higher, than their population growth rate; due to exhaustion of nutrients; and accumulation of toxic wastes;
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN29
State four reasons why water is significant in seed germination.
ANSWER
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN28
State two ways by which auxins regulate growth in seedlings.
ANSWERS
K.C.S.E Biology Q & A - MODEL 2011PP1QN28
What is a tropic response?
ANSWERS
|
Archives
December 2024
Categories
All
TOPICSFORM 1
Form 2
Form 3
Form 4
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed