|
(a) What is meant by molar heat of combustion?
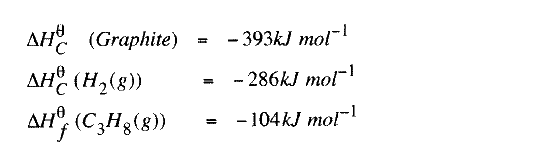
(b) State the Hess's Law. c) Use the following standard enthalpies of combustion of graphite, hydrogen and enthalpy of formation of propane.
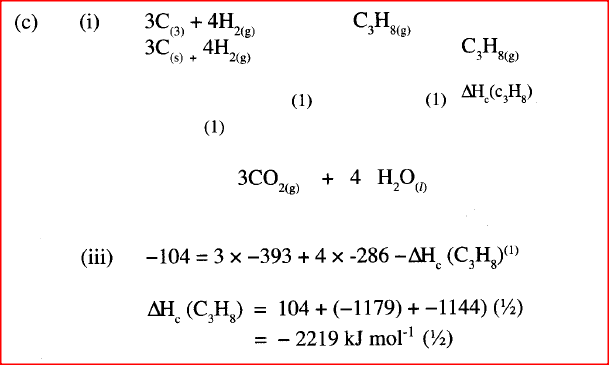
(i) Write the equation for the formation of propane.
(ii) Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the heat of formation of propane with its heat of combustion and the heats of combustion of graphite and hydrogen. (iii) Calculate the standard heat of combustion of propane. Other than the enthalpy of combustion, state one factor which should be considered when choosing a fuel. (e) The molar enthalpies of neutralization for dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric (V) acid are -57.2kJ/mol while that of ethanoic acid is -55.2kJ/mol. Explain this. observation.
ANSWERS
(a) The amount of heat liberated when one mole of a substance is burnt in excess Oxygen.
(b) The heat evolved are absorbed in a chemical change is the same whether the change occurs in one step or through many steps.
(d) cost
effect on environment availability storage (e) Ethanoic acid is a weak acid therefore heat is used to ionize it before neutralization occurs . It value is therefore lower than that of hydrochloric acid which is fully ionized
0 Comments
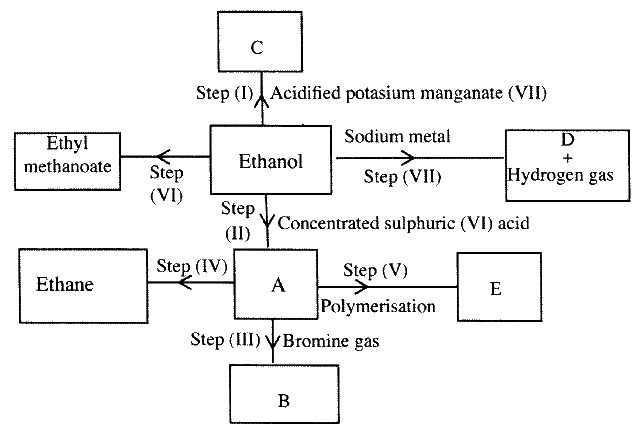
(a) Study the flowchart below and answer the questions that follows;
(i) I What observation will be made in Step I
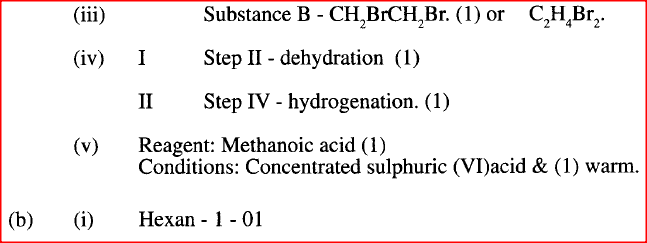
II Describe a chemical test that can be carried out to show the identity of compound C (ii) Give the names of the following I E II substance D (iii)Give the formula of substance B . (iv) Name the type of reaction that occurs in: I Step (II) II Step (IV) (v) Give the reagent and conditions necessary for Step (VI). Reagent: Conditions (b) (i) Name the following structure.
(ii) Draw the structure of an isomer of pentene.
ANSWERS
(a) (i) I The potassium permanganate is decolorized or changes from purple to colourless.
II C is a ethanoic acid (carboxylic acid) Add sodium carbonate, you will see effervescence, test gas evolved with lime water, it will form a white precipitate. (ii) I Polyethene II Substance D - sodium ethoxide
(a) Other than their location in the atom, name two other differences between an electron and a proton.
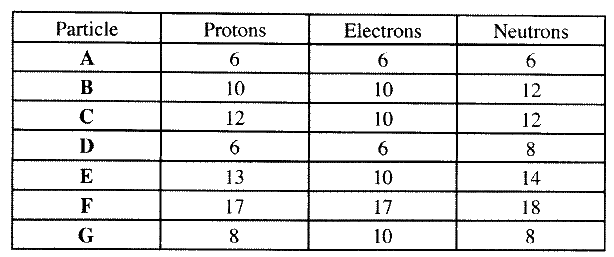
(b) the table below gives the number of electrons ,protons and neutrons in particles A,B, C , D, E, F and G
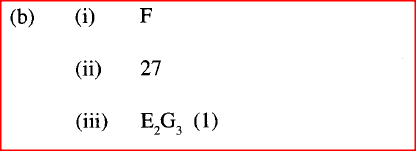
(i) Which particle is likely to be a halogen?
(ii) what is the mass number of E (iii) write the formula of the compound formed when E combines with G iv) Name the type of bond formed in (iii) above. (v) How does the radii of C and E compare ? Give reason. (vi) Draw a dot (.) and cross(x) diagram for the compound formed between (vii) Why would particle B not react with particle D?
ANSWERS
(a)- electron has I mass while proton has mass of one mass unit. 1840
- proton is positively charged while electron is negatively charged.
(iv)Ionic bond or electrostatic
(v)E has a smaller atomic radius than C E has more protons than C : nuclear attraction stronger.
(vii)Particle B is inert with a stable electronic configuration will not react.
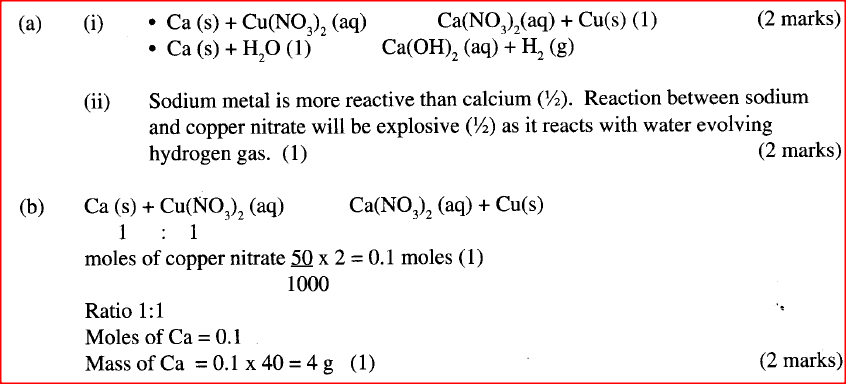
(a) When excess calcium metal was added to 50 cm3 of 2 M aqueous copper (II) nitrate in a beaker, a brown solid and bubbles of gas were observed.
(i) "Write two equations for the reactions which occurred in the beaker. (ii) Explain why it is not advisable to use sodium metal for this reaction.
(b) Calculate the mass of calcium metal which reacted with copper (II) nitrate solution. (Relative atomic mass of Ca = 40)
(c) The resulting mixture in (a) above was filtered and sodium hydroxide added to the filtrate dropwise until in excess. What observations were made? (d) (i) Starting with calcium oxide, describe how a solid sample of calcium carbonate can be prepared. (ii) Name one use of calcium carbonate
ANSWERS
(c)A white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess.
(d) (I) Add dilute nitric (V) acid to calcium oxide to form the soluble salt calcium nitrate. Add sodium carbonate (another soluble salt) to form insoluble. Calcium Carbonate and sodium nitrate . Filter out the calcium carbonate, wash it with distilled water to remove traces of sodium nitrate and dry between filter papers (ii) Manufacture of cement Manufacture of sodium carbonate.
(a) Ethanol can be manufactured from ethene and steam as shown in the equation below:
Temperature and pressure will affect the position of equilibrium of the above reaction. Name the other factor that will affect the position of equilibrium of the above reaction.
(b) The data in the table below was recorded when one mole of ethene was reacted with excess steam. The amount of ethanol in the equilibrium mixture was recorded under different conditions of temperature and pressure. Use the data to answer the questions that follow.
(i)State whether the reaction between ethene and steam is exothermic or endothermic.
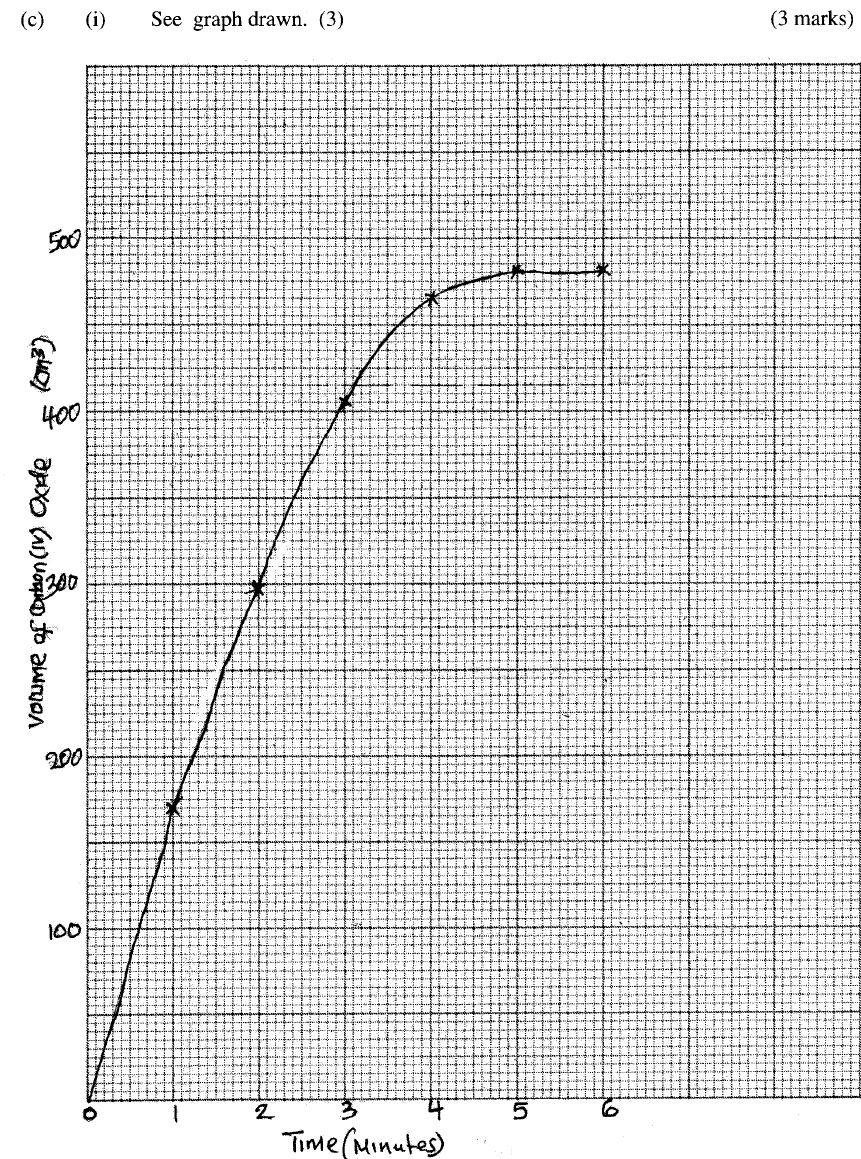
Explain your answer. (ii) State and explain one advantage and one disadvantage of using extremely high pressure in this reaction. I Advantage II disadvantage (c) In an experiment to determine the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid, 2g of calcium carbonate were reacted with excess 2 M hydrochloric acid, The volume of carbon (IV) oxide evolved was recorded at regular intervals of one minute for six minutes. The results are shown in the table below.
(i) plot a graph of time in minutes on the horizontal axis against volume of carbon (IV) oxide on the vertical axis.
(ii) determine the rate of reaction at 4 minutes
ANSWERS
(a) Increase or change in amount of reagent either reactants or products.
(Concentration). (b) (i) Exothermic increase in temperature from 250 - 350 at constant pressure the amount of ethanol formed at equilibrium decreases. (ii) I Advantage - it would increase the yield of ethanol ; since increase in pressure will favour side with less moles i.e. the products. II Disadvantage - it would mean investment in equipment to withstand the high pressure and would be expensive.
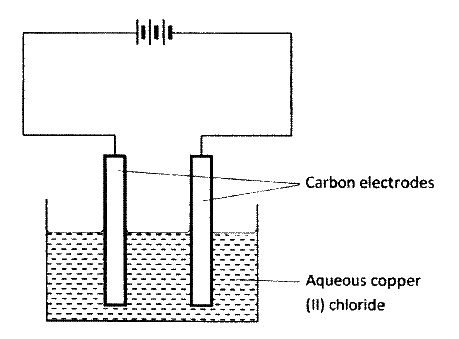
The set-up below was used by a student to investigate the products formed when aqueous copper (II) chloride was electrolyzed using carbon electrodes.
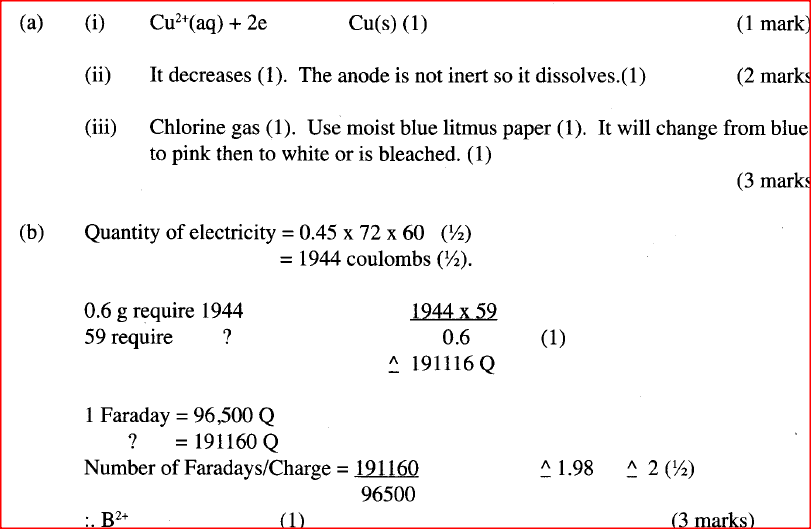
(a) (i) Write the equation for the reaction that takes place at the cathode.
(ii) Name and describe a chemical test for the product initially formed at the anode when a highly concentrated solution of copper (II) chloride is electrolysed. (iii) How would the mass of the anode change if the carbon anode was replaced With copper metal? Explain. (b) 0.6 g of metal B were deposited when a current of 0.45A was passed through an electrolyte for 72 minutes. Determine the charge on the ion of metal B. (Relative atomic mass of B = 59, 1 Faraday = 96 500 coulombs) (c) The electrode potentials for cadmium and zinc are given below:
Explain why it is not advisable to store a solution of cadmium nitrate in a container made of zinc
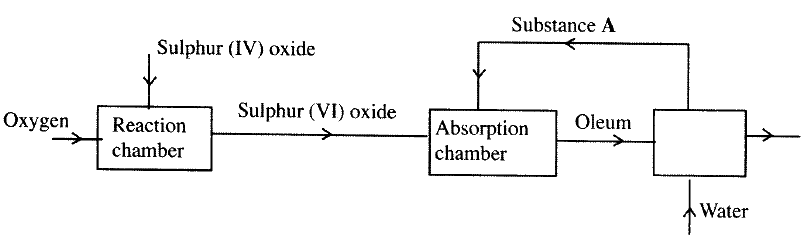
The flow chart below shows some of the processes involved in large scale production of sulphuric (VI) acid. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
a) Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale
(b) (i) Name substance A. (ii)Write an equation for the process that takes place in the absorption chamber. (c) Vanadium (V) oxide is a commonly used catalyst in the contact process. (i) Name another catalyst which can be used for this process. (ii) Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is the commonly used catalyst. (d) State and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals of copper (II) sulphate in a bearer. (e) The reaction of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with sodium chloride produces hydrogen chloride gas. State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid , illustrated in this reaction. (f) Name four uses of sulphuric (VI) acid
What name is given to elements which appear in group (II) of the periodic table?
ANSWER
A sample of river water is suspected to contain zinc and sulphate ions.
Describe how the presence of zinc ions and sulphate ions can be established.
ANSWERS
Explain why the following substances conduct an electric current.
(a) Magnesium metal. (b) Molten magnesium chloride.
The diagram below shows the bonding between aluminium chloride and ammonia.
(a) Name the types of bonds that exist in the molecule.
(b) How many electrons are used for bonding in the molecule?
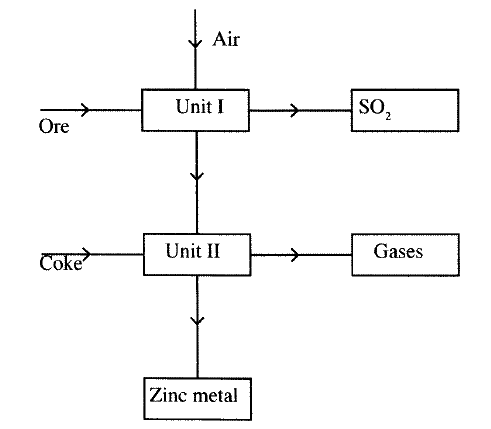
The flow chart below shows some processes involved in the extraction of zinc metal:
a) Name oneore from which zinc is extracted.
b) Write the equation of the reaction taking place in unit II c) Name two uses of zinc metal.
The data given below was recorded when Metal M was completely burnt in air. M is not the actual symbol of the metal. (RA.M; M = 56, O ==16)
Mass of empty crucible and lid = I0.240g Mass of crucible, ;lid and metal M = 10.352g Mass crucible, lid and metal oxide = 10.400g (a) Determine the mass of: (i) Metal M (ii) oxygen. (b) Determine the empirical formula of the metal oxide.
(a) State the Gay Lussac's Law.
(b) 10cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, C2HX required 30cm3 of oxygen for complete combustion. If steam and 20cm3 of carbon (IV) oxide were produced, what is the value of X?
The table below gives the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in substances X, Y and Z. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Which letter represents an ion?
(b) Which of the substances are isotopes? Give a reason.
ANSWERS
(a) Y
(b) Y and Z They have the same number of protons (8) but different atomic masses.
The thermal chemical reaction between carbon and sulphur is as shown by the equation below:
The table below gives some properties three elements in group (VII) of the periodic table .Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Which element is in liquid form at room temperature? Give a reason.
(b) Explain why the boiling point of iodine is much higher than that of chlorine.
ANSWERS
(a) Bromine M
At room temperature (25°C), Bromine is liquid since its MP and BP is between -7 and 59 (b) Atomic mass of iodine is higher than that of chlorine. Van der waal’s forces are stronger in iodine than chlorine hence iodine’s BP is higher than that of chlorine.
Graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon.
(a) Name one other element which exhibits allotropy. (b) Explain why graphite is used in the making of pencil leads.
ANSWERS
(a) Sulphur or phosphorus.
(b) Carbon atoms in graphite are arranged in layers of hexagons which are held by weak van der waal forces. The layers slide over each other when some force is applied on them; hence suitable in making pencil leads.
Describe how the PH of anti-acid (Actal) powder can be determined in the laboratory
ANSWERS
50kg of ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4and 30kg of urea CO(NH2)2 fertilizers were applied in two equal sizes of plots A and B to enrich their nitrogen content.Show by working, which plot was more enriched with nitrogen. (N =14;S = 32; O = 16; C = 12; H = 1)
Under certain conditions, chlorine gas reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium hypochlorite.
(a) Name the conditions under which sodium hydroxide reacts with chlorine to form sodium hypochlorite. (b) State two uses of sodium hypochlorite.
ANSWERS
(a) Cold and dilute sodium hydroxide.
(b) Used in sterilizing of water. Used as a bleaching agent.
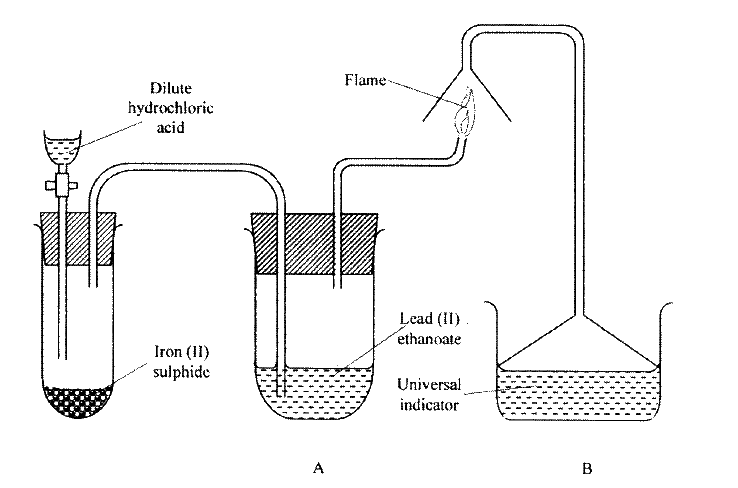
The set up below was used to prepare a gas and study some of its properties. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) State and explain the observations made in the:
(i) tube labelled A; (ii) beaker labelled B. (b) State one precaution that should be taken when carrying out this experiment.
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Black solid is deposited.
(ii) The indicator turns red. (b) The experiment should be done in fume chamber or in open air.
Ethanoic acid and ethanol react as shown in the equation below:
Other than warming, how would the state of equilibrium be established within a short time?
Soap dissolves in water according to the equation below;
NaSt(aq) —> Na+(aq) + St- where St- is the stearate ion. (a) Write the formula of the scum formed when soap is used in hard water. (b) Write the ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when sodium carbonate is used to remove hardness in water.
Two organic compounds P and Q decolourise acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution but only P reacts with sodium metal to give a colourless gas. Which homologous series does compound P belong? Give a reason.
ANSWERS
P is in alkanol R - OH. The alkanol reacts with sodium metal to produce the colourless gas.
|
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |
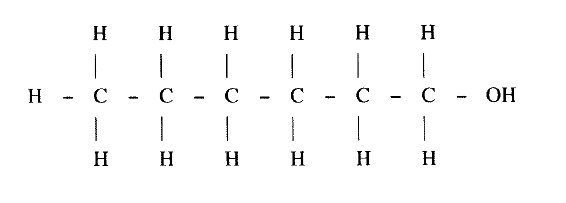
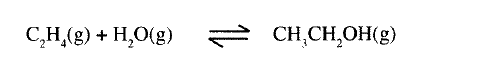


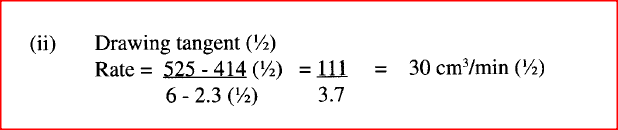
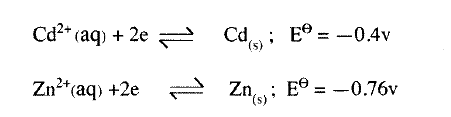











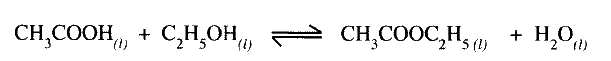



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

