KCSE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS PER TOPIC
Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts: A Comprehensive GuideReview:
Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts: A Comprehensive Guide Acids, bases, and salts play crucial roles in various chemical reactions and are fundamental concepts in chemistry. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of these substances, shedding light on their definitions, properties, and reactions. The guide begins by introducing the different definitions of acids and bases. According to the Arrhenius definition, an acid is a substance that dissolves in water to form H+ or H3O+ ions, while a base dissolves in water to form OH- ions. The Bronsted-Lowry definition expands upon this, defining an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. To illustrate these definitions, the guide presents examples of acid-base reactions, highlighting the exchange of protons between the reactants. Through these examples, readers gain a deeper understanding of how acids and bases interact with each other. The guide also emphasizes the importance of water as a solvent for acids and bases. It explains that acids and bases exhibit their acidic or alkaline properties only in water, making it a crucial medium for their reactions. In other solvents, acids and bases may not display their characteristic properties. Furthermore, the guide explores the various properties and characteristics of acids and bases. It explains how acids can turn litmus paper red and have low pH values, while bases can turn litmus paper blue and have higher pH values. Additionally, acids and bases are good electrolytes and can undergo electrolysis. The guide also touches upon the reactions of acids and bases with metals and metal carbonates. It explains how acids can react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and salts, while reacting with metal carbonates can produce carbon dioxide gas, water, and salts. It also highlights how acids can neutralize metal oxides and hydroxides to form salts and water. In summary, "Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts: A Comprehensive Guide" provides a detailed exploration of these essential chemical substances. It offers a clear understanding of their definitions, properties, and reactions, making it an invaluable resource for students and enthusiasts of chemistry.
0 Comments
Chemistry Practical Guide: Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis TechniquesReview
The Chemistry Practical Guide is a comprehensive resource that provides students with specific objectives and techniques for conducting chemistry experiments. The guide aims to test students' abilities to select and handle apparatus, make accurate observations, and draw conclusions based on those observations. It focuses on three main areas: qualitative analysis, quantitative analysis, and graphical work. Qualitative analysis involves performing chemical tests to identify substances. To obtain accurate results, students need to accurately identify the test reagents, understand what these reagents test, and predict the expected results. One of the key aspects of qualitative analysis is testing for cations, which involves adding certain reagents to a solution and noting the resulting observations and inferences. The guide provides a detailed list of cations and their corresponding observations and inferences. Another important aspect of qualitative analysis is testing for anions. This involves adding specific reagents and observing the resulting precipitates or color changes. The guide outlines the steps and observations for testing six common anions. Quantitative analysis focuses on making accurate measurements. It involves techniques such as titration and gravimetric analysis to determine the concentration or amount of a substance in a given sample. The guide provides an overview of these techniques and their applications. Graphical work involves the interpretation and analysis of data using graphs and charts. It includes techniques such as plotting graphs, determining gradients, and analyzing trends. Overall, the Chemistry Practical Guide serves as a valuable resource for students to enhance their understanding and skills in experimental chemistry. It provides clear instructions, observations, and inferences for qualitative and quantitative analysis techniques. By following the guide, students can develop the necessary proficiency in handling apparatus, making accurate observations, and drawing conclusions. With a strong foundation in practical chemistry, students will be well-prepared for their examinations and future scientific endeavors. Comprehensive Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes for Effective LearningReview:
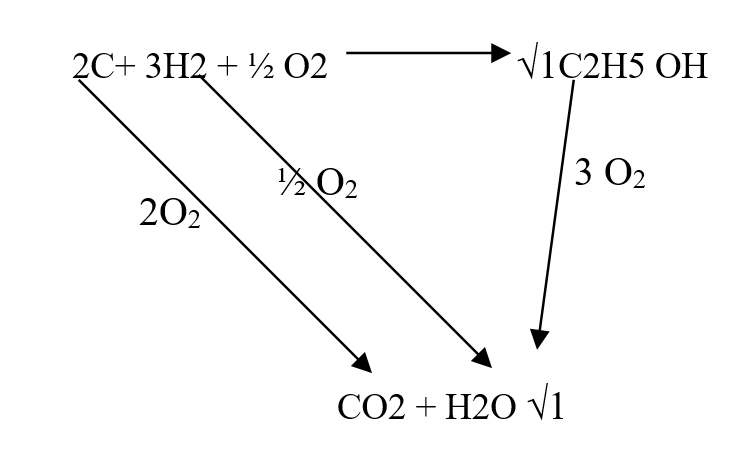
Our Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes are an invaluable resource for students seeking a thorough understanding of the subject. The notes cover a wide range of topics, from the states of matter to the role of chemistry in society. Each concept is explained in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to grasp even the most complex ideas. One of the strengths of these notes is the inclusion of practical examples, which help students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. For example, the section on separation of mixtures provides simple methods that can be used to separate different substances, allowing students to see the practical applications of their learning. Furthermore, the notes emphasize the importance of safety in the chemistry laboratory. Clear guidelines are provided to ensure that students understand how to handle chemicals safely and minimize the risk of accidents. This focus on safety is crucial in fostering responsible and conscientious scientific practices. The layout and organization of the notes are also commendable. Each topic is presented in a logical sequence, building upon previous knowledge and paving the way for a smooth progression of learning. The use of headings, subheadings, and bullet points makes it easy for students to navigate through the content and locate specific information. Overall, our Chemistry Form 1-4 Notes provide a comprehensive and well-structured resource for students studying chemistry. With its clear explanations, practical examples, and emphasis on safety, this resource is sure to enhance students' understanding and appreciation of the subject. Comprehensive Chemistry Summary Notes for Form 1 to Form 4Review: The "FORM 1 TO FORM 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES.pdf" is an invaluable resource for students studying chemistry at the Form 1 to Form 4 level. The notes provide a comprehensive overview of the entire chemistry syllabus, covering all the key topics and concepts. The document is well-organized, with each topic clearly outlined and explained in a concise manner. The content is presented in a way that is easy to understand, making it suitable for students of all levels of ability. The notes include detailed explanations, diagrams, and examples to help students grasp the fundamental principles of chemistry. One of the standout features of these notes is the inclusion of practical applications and real-life examples. This helps students to see the relevance of chemistry in everyday life and enhances their understanding of the subject. The document also includes a section on exam tips and strategies, which is particularly helpful for students preparing for their chemistry exams. It provides guidance on how to approach different types of questions, how to structure answers, and how to effectively revise for exams. Overall, the "FORM 1 TO FORM 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES.pdf" is a comprehensive and well-structured resource that covers all the essential topics in chemistry. Whether you are a student looking for additional study material or a teacher seeking a reference guide, these notes are a valuable asset. Use the information below to answer the questions that follow Ethanol is formed as shown below11/10/2021 Use the information below to answer the questions that follow Ethanol is formed as shown belowDraw the energy cycle diagram and for the formation and combustion of ethanol and calculate the heat of formation of ethanol (3mks)a) State three differences between chemical and nuclear reactions. (3mks)
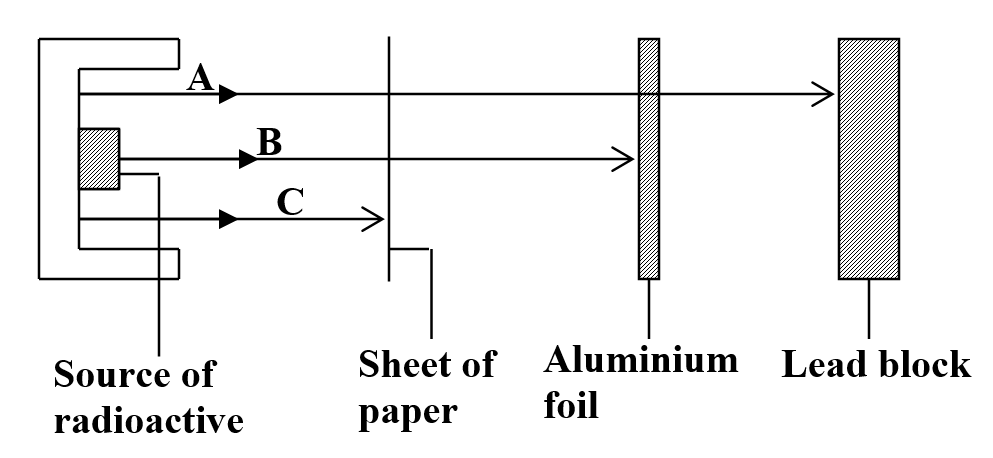
(any three 3mks) b) Study the figure below and answer the questions that followIdentify the radiations A, B and C (3mks)
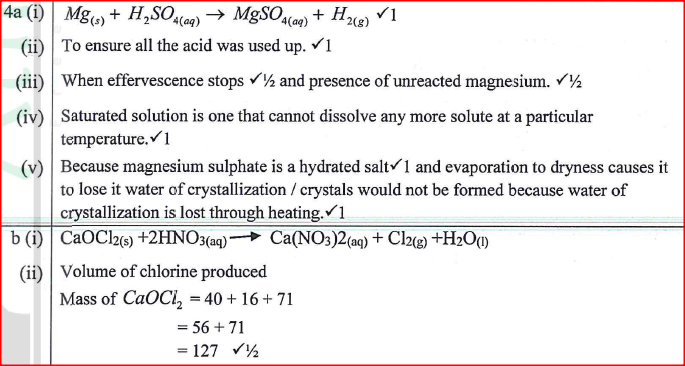
An experiment was carried out to prepare crystals of magnesium sulphate. Excess magnesium powder was added to 100 cm3 of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid in a beaker and warmed until no further reaction took place. The mixture was filtered and the filtrate evaporated to saturation, then left to cool for crystals to form.
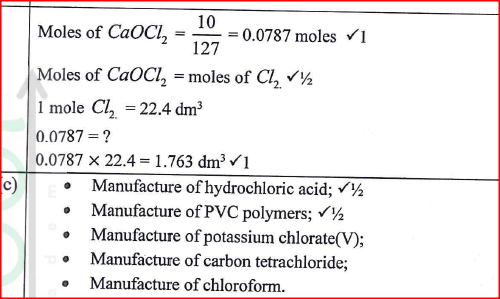
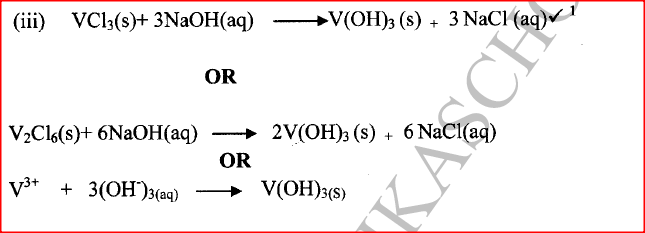
(a) (i) Write an equation for the reaction. (ii) Explain why excess magnesium powder was used. (iii) State how completion of the reaction was determined. (iv) What is meant by a saturated solution? (v) Explain why the filtrate was not evaporated to dryness. (b) When bleaching powder, CaOCl2, is treated with dilute nitric(V) acid, chlorine gas is released. This reaction can be used to determine the chlorine content of various samples of bleaching powders and liquids. (i) Write an equation for the reaction of nitric(V) acid with bleaching powder. (ii) Calculate the volume of chlorine produced when 10g of CaOCl2 is treated with excess nitric (v) acid. (Ca = 40.0; 0 = 16.0; Cl = 35.5; 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4dm3 at s.t.p) (c) Apart from use of chlorine gas in bleaches and water treatment, state two other uses of chlorine gas.
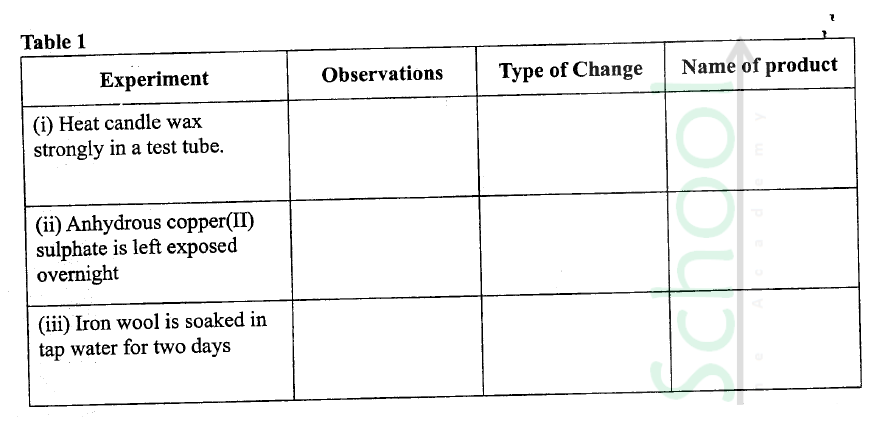
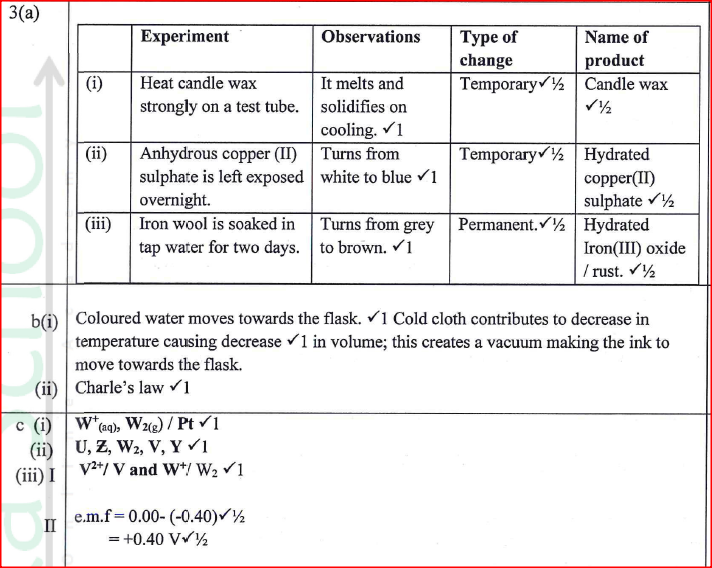
(a) Complete Table I by indicating the observations, type of permanent or temporary change and name of new compound formed.
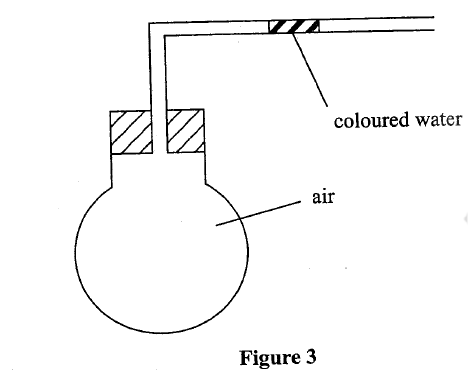
(b) Use the set-up in Figure 3 to answer the questions that follow. The flask was covered with a cloth that had been soaked in ice-cold water.
(i)State the observation made on the coloured water. Explain.
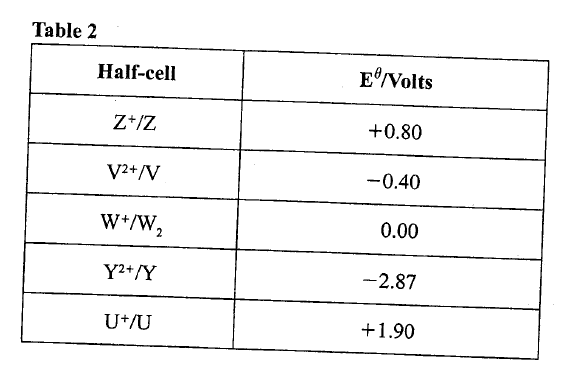
(ii) Name the gas law illustrated in Figure 3. (c)Use the standard electrode potentials in Table 2 to answer the questions that follow.
(i)Write the half-cell representation for the element whose electrode potential is for hydrogen.
(ii) Arrange the elements in order of reducing power, starting with the weakest reducing agent. (iii) I Select two half cells which combine to give a cell with the least e.m.f. II Calculate the e.m.f of the half cells identified in (iii) I.
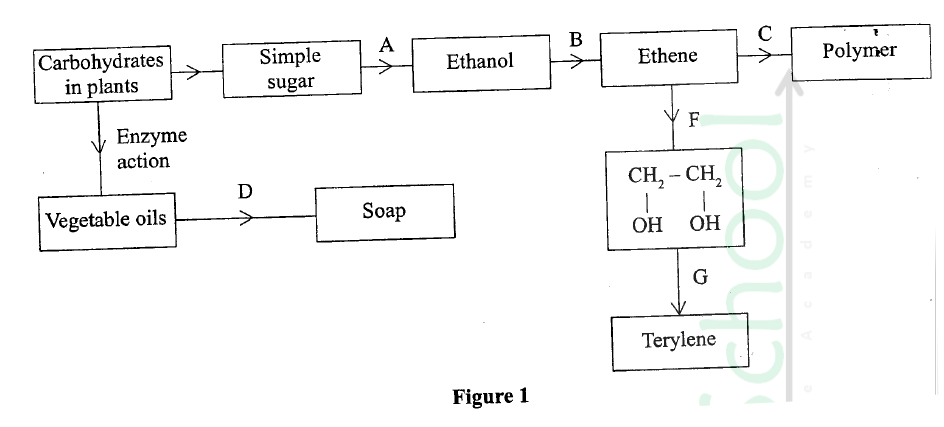
The diagram in figure I shows some natural and industrial processes. Study it and answer the questions that follows
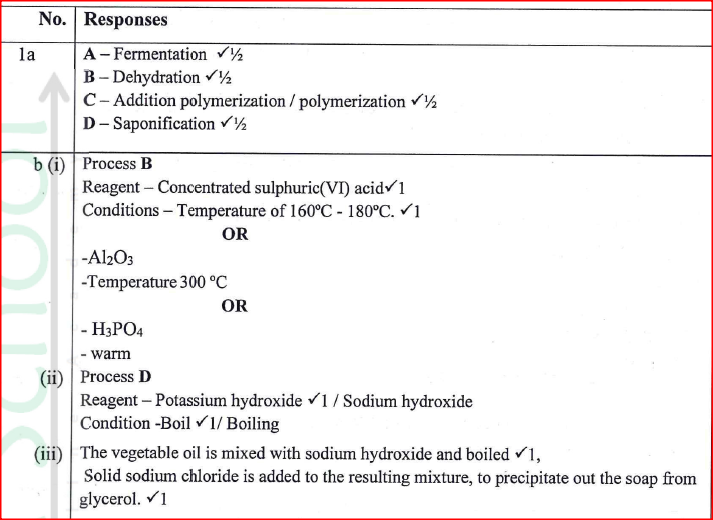
(a) Identify the processes labelled:
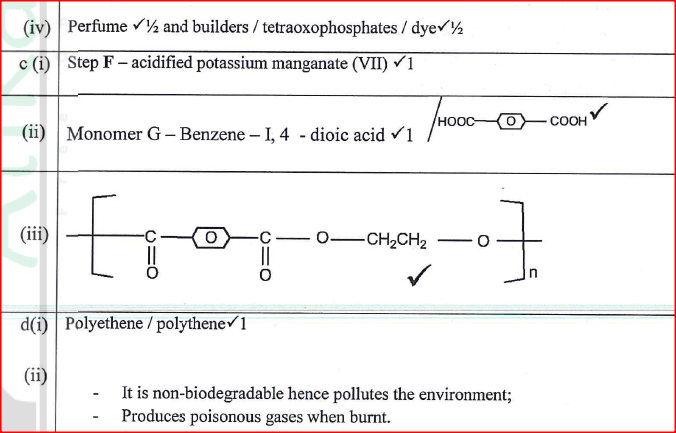
A................... B................... C................... D................... (b) State the reagents and conditions required for processes B and D. (i) Process B: Reagent................ Conditions ............ (ii) Process D: Reagent................ Conditions ............ (iii) Describe how process D is carried out. (iv) State two additives used to improve the quality of soap. (c) State the reagents required in steps F and G. (iii) Draw the structure of terylene. (d) (i) Name the polymer formed in step C. (ii) State one disadvantage of the polymer formed in (d) (i).
(a) Name two ores of iron.
(b) Describe how the amount of iron in a sample of iron(III) oxide can be determined.
ANSWERS
(a) Haematite;
Magnetite; Siderite. (b) Weigh the iron (III) oxide together with a crucible; Heat the Iron(III) oxide and coke to a constant mass; Cool and re-weigh residue and crucible The difference in mass is weight of the iron.
(a) Give the symbols of the o charged particles emitted by a radioactive isotope.
mass number
atomic number:
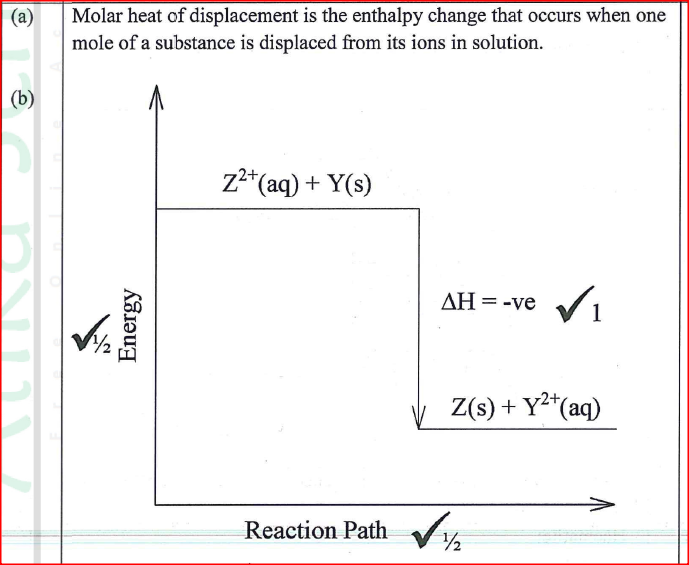
(a) Define molar heat of displacement.
(b)The following ionic equation represents the reaction between metal Y and an aqueous solution of Z2+.
Draw an energy level diagram to represent the reaction
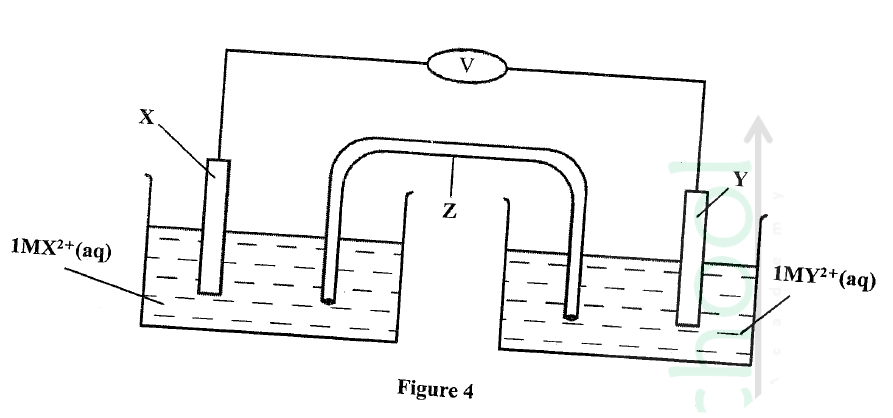
Metal X and Y have standard electrode Potentials of —0.13 V and —0.76V respectively .The metals were Connected to form a cell as shown in Figure 4.
(a) Name the part labelled z.
(b) State one functi0 of the part labelled Z. (c) Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell.
In the Haber process, nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the following equation.
(a)What would be the effect of adding a catalyst on the position of the equilibrium?
(b) Explain why it is not advisable to use temperatures higher than 773 K in the Haber process.
ANSWERS
(a)No effect/does not affect the position of the equilibrium.
(b)Forward reaction is exothermic, excessive temperatures would favour the backward reaction therefore lowering the yield of ammonia.
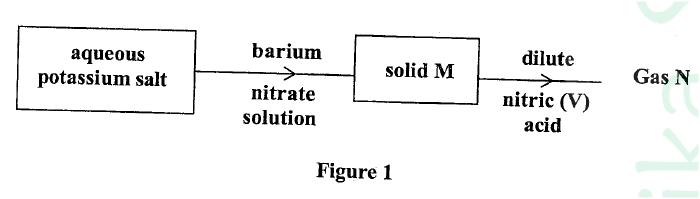
Study the flow chart in Figure 1 and answer the questions that follow.
Gas N forms a while suspension with aqueous calcium hydroxide.
(a) Name the anion present in the potassium salt. (b) Write an ionic equation for the formation of solid M. (c) Give one use of gas N.
The following are formulae of organic compounds. Use the formulae to answer the questions that follow:
(a) Select:
(i) two compounds which when reacted together produce a sweet smelling compound. (ii) an unsaturated hydrocarbon. (b) Name the compound selected in (a) (ii).
(a) Define a soluble base.
(b) Aqueous solutions of 2M ethanoic acid and 2M nitric(V) acid were tested for electrical conductivity. Which solution is a better conductor of electricity? Explain.
ANSWERS
(a)A soluble base is a substance that dissociates in water to produce hydroxide ions as the only negative ions.
(b)Nitric(V) acid. This is because nitric(V) acid is a strong acid and dissociates completely in solution producing many H+ ions.
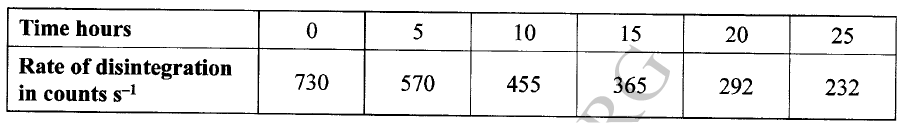
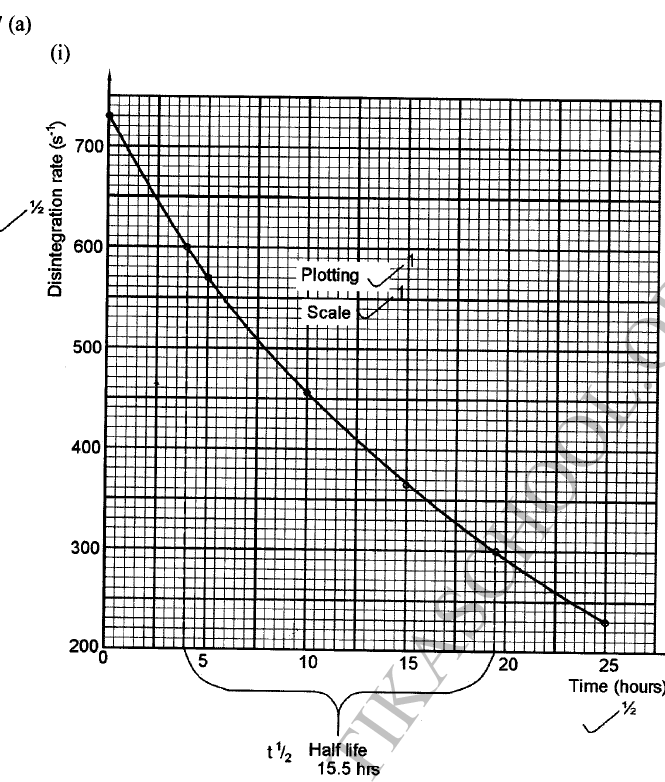
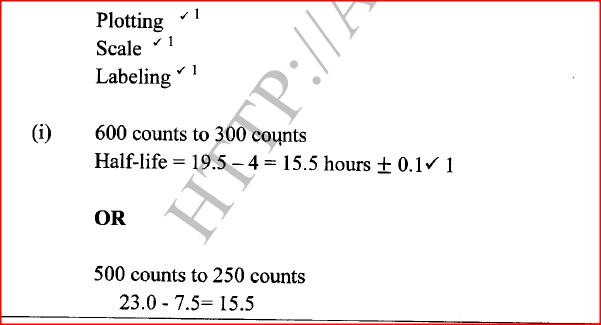
The decay rates of a sample of a radioisotope of bismuth at different time intervals is indicated in the following table.
(a)(i) Draw a graph of disintegration rate against time.
(ii) Determine the half-life of bismuth. (iii) What would be the effect on the curve if half the amount of sample of bismuth were used. (b) Radioactivity has several applications. State one application of radioactivity in: (i) Medicine (ii) Agriculture (iii) Tracers (iv) Nuclear power station (c) State two dangers associated with radioactivity.
ANSWERS
(ii) It would have no effect on the curve as the quantity of bismuth does not affect half-life.
(b)(i)Applications in medicine Sterilizing surgical instruments. Destroying cancerous tissues during radiotherapy. Provide power to the heart pace setters. (ii) Applications in agriculture Monitor photosynthesis and other related processes. Preservation of foodstuffs, by exposing Micro-organisms to gamma rays. Rate of absorption of a fertilizer by the plant. (iii)Applications in Tracers Detecting leakages in underground water or oil pipes. (iv)Applications in Nuclear power stations. To generate electricity. (d) Dangers of radioactivity Long term exposure causes genetic mutation; Radioisotopes can be used as weapon of mass Destruction; Causes skin cancer; When tested causes environmental pollution.
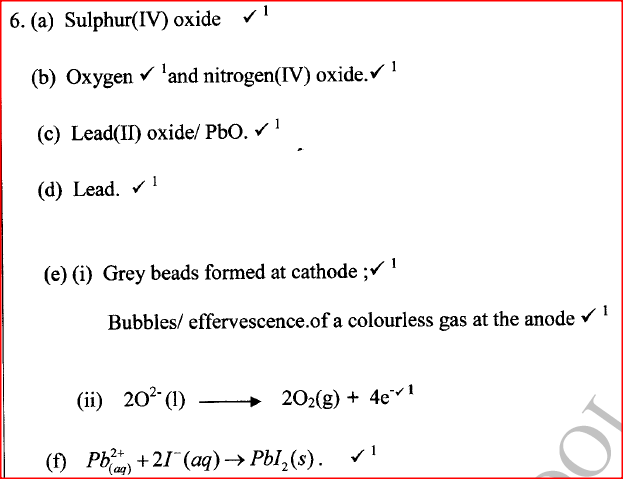
The following steps were used to analyse a metal ore.
(i) An ore of a metal was roasted in a stream of oxygen. A gas with a pungent smell was formed which turned acidified potassium dichromate(VI) green. (ii) The residue left after roasting was dissolved in hot dilute nitric(V) acid. Crystals were obtained from the solution. (iii) Some crystals were dried and heated. A brown acidic gas and a colourless gas were evolved and a yellow solid remained. (iv) The solid was yellow when cold. (v) The yellow solid was heated with powered charcoal. Shiny beads were formed. Name the: (a) gas formed when the ore was roasted in air. (b) gases evolved when crystals in step (iii) were heated. (c) yellow solid formed in step (iii). (d) shiny beads in step (iv). (e) The yellow solid from procedure (iii) was separated, dried, melted and the melt electrolysed using graphite electrodes. I. Describe the observations made at each electrode. II. Write the equation for the reaction that took place at the anode. (f) Some crystals formed in step (ii) were dissolved in water, and a portion of it reacted with potassium iodide solution. A yellow precipitate was formed. Write an ionic equation for this reaction. (g) To another portion of the solution from (f), sodium hydroxide solution was added drop by drop until there was no further change. Describe the observation made. (h) To a further portion of the solution from (f), a piece of zinc foil was added. I. Name the type of reaction taking place. II. Write an ionic equation for the above reaction.
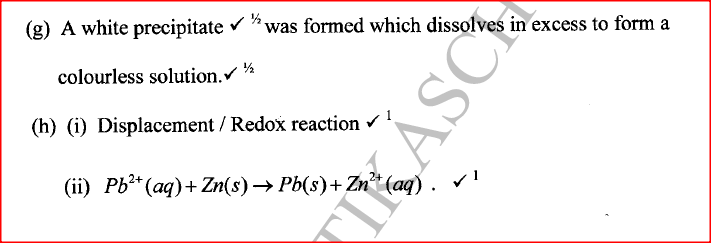
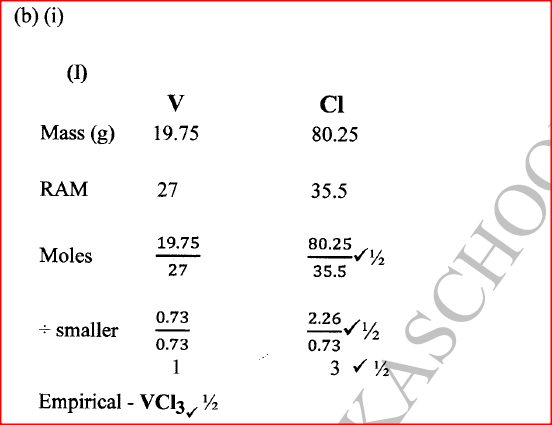
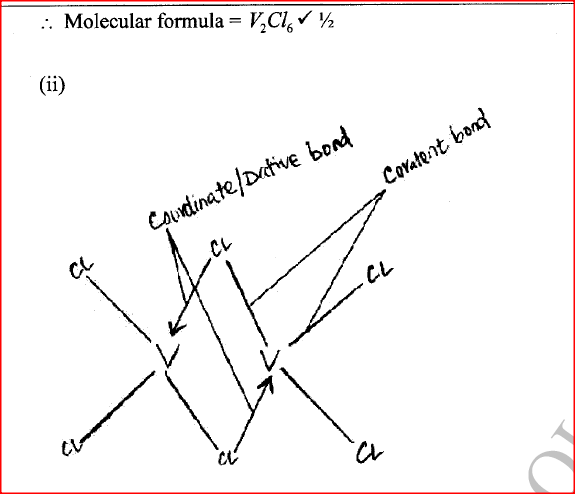
W is a colourless aqueous solution with the following properties:
(ii) Give the identity of W. (iii) Name the colourless solution formed in (II) and (III). (iv) Write an ionic equation for the reaction indicated in (V). (b) Element V conducts electricity and melts at 933K. When chlorine gas is passed over heated V, it forms a vapour that solidifies on cooling. The solid chloride dissolves in water to form an acidic solution. The chloride vapour has a relative molecular mass of 267 and contains 19.75% of V. At a higher temperature, it dissociates to a compound of relative molecular mass 133.5. When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to the aqueous solution of the chloride, a white precipitate is formed which dissolves in excess alkali. (V = 27.0 ; CI = 35.5) (i) Determine the:
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction that form a white precipitate with sodium hydroxide.
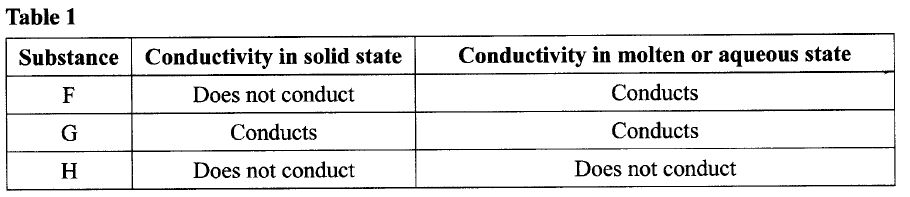
The conductivity of some substances was investigated. The observations made were recorded in
Table 1. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) (i) Identify a substance that is a metal. Give a reason.
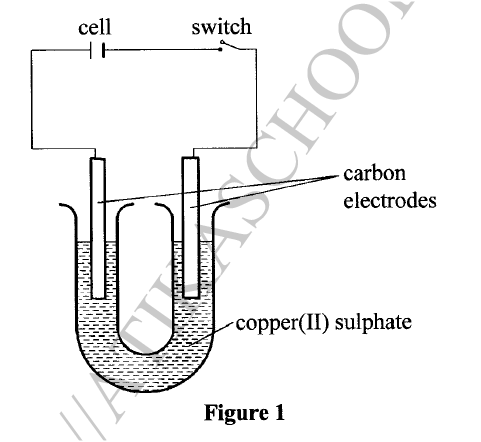
(ii) Substance F does not conduct electricity in solid state but conducts in molten or aqueous state. Explain. (b) Copper(II) sulphate solution was electrolysed using the set up in Figure 1.
(i) State the observations made during electrolysis.
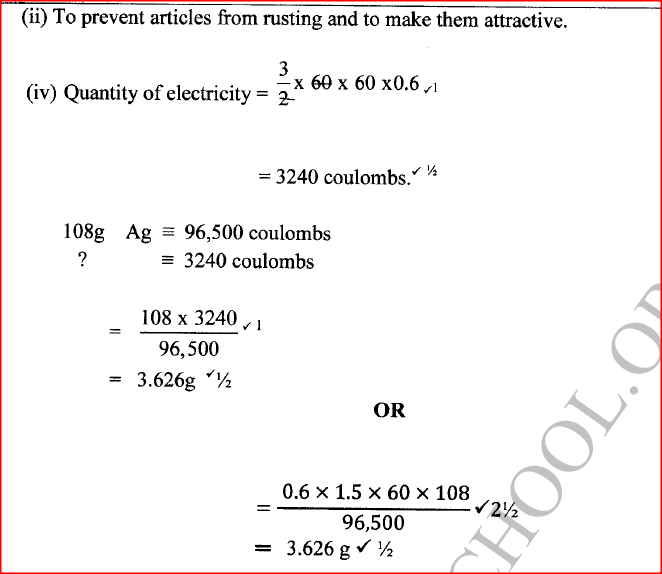
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode. (iii) State the expected change in pH of the electrolyte after electrolysis. (c) The experiment was repeated using copper electrodes instead of carbon electrodes. Describe the observations made at each electrode. (d) Electroplating is an important industrial process. What is meant by electroplating. (iii) During electroplating of an iron spoon, a current of 0.6 amperes was passed through aqueous silver nitrate solution for 1 1/2 hours. Calculate the mass of silver that was deposited on the spoon. (Ag = 108.0 ; I F = 96,500 C /mol)
ANSWERS
(a)(i) G — Contains delocalized electrons present in solid and molten state.
(ii) In solid state, the ions are rigidly held in position and cannot move, hence will not conduct. In molten/aqueous state, the ions are mobile and will be able to conduct electric current. (b)(i)The blue electrolyte fades and finally changes from blue to colourless, Effervescence / bubbles of a colourless gas. A brown deposit forms on the cathode.
(c) With copper electrodes:
Anode will go into solution as copper ions hence it decreases in mass/size. Brown deposit forms at the cathode hence the cathode increases in mass. (d) (i) This is the coating of an article / object with another metal by electrolytic method /electrolysis.
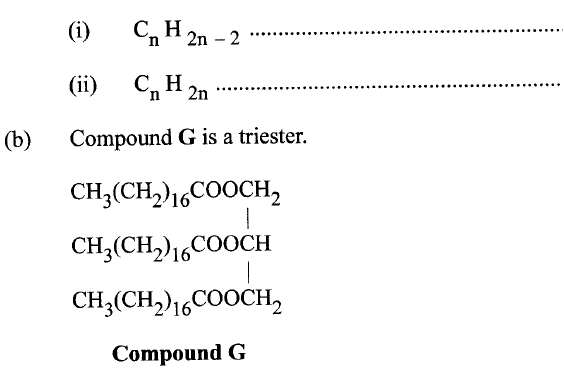
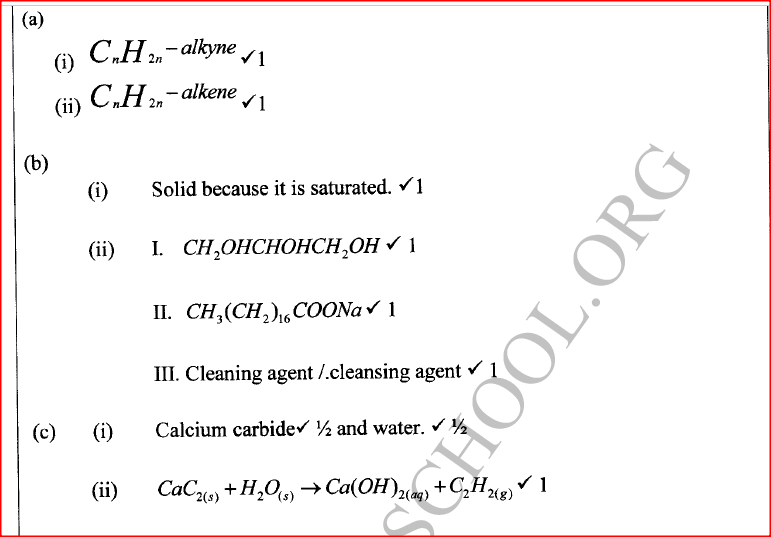
(a) Name the homologous series represented by each of the following general formulae.
(i) Give the physical state of compound G at room temperature.
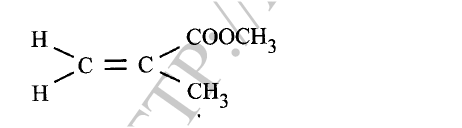
(ii) G is completely hydrolysed by heating with aqueous sodium hydroxide. I Give the structural formula of the alcohol formed. II Write a formula for the sodium salt formed. III State the use of the sodium salt. (c) Ethyne is the first member of the alkyne family. (i) Name two reagents that can be used in the laboratory to prepare the gas. (ii) Write an equation for the reaction. (d) Perspex is an addition synthetic polymer formed from the monomer,
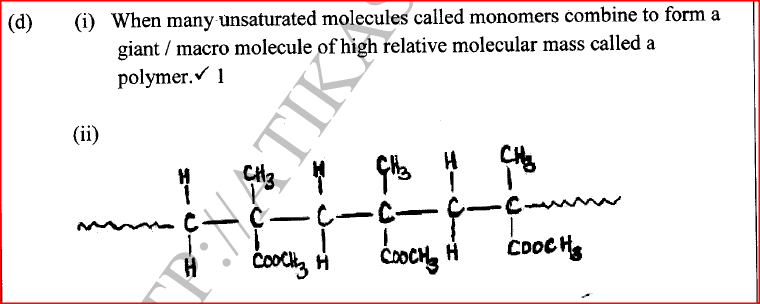
(i) What is meant by addition polymerisation?
(ii) Draw three repeat units of perspex. Give one use of perspex (iv) State two environmental hazards associated with synthetic polymers.
ANSWERS
(a) Name two ores in which sodium occurs.
(b) During extraction of sodium using the down's process, calcium chloride is added to the ore. Give a reason for the addition of calcium chloride. (c) State two uses of sodium.
(a) What is an inert electrode?
(b) State the products formed when brine is electrolysed using inert electrodes. Anode: Cathode:
ANSWERS
(a)Inert electrode is one which does not participate in the reaction / does not affect the products of electrolysis / does not react;
(b)Anode - chlorine; Cathode - Hydrogen;
The following procedure was used to investigate the temperature changes that occur when sodium hydroxide solution is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(i) Place the acid in a glass beaker and record its temperature. (ii) Add a known volume of sodium hydroxide solution. (iii) Stir the mixture and record the highest temperature reached. (iv) Repeat steps (ii) and (iii) with different volumes of sodium hydroxide solution. (a) State two factors that must be kept constant in this experiment (b) Explain how the use of a polystyrene cup will affect the results.
ANSWERS
|
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|



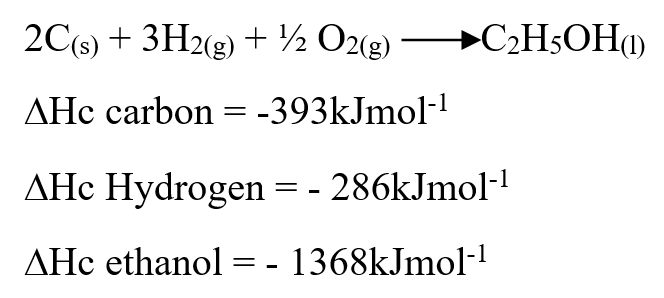
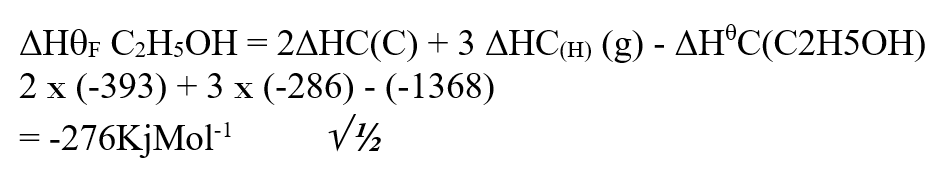

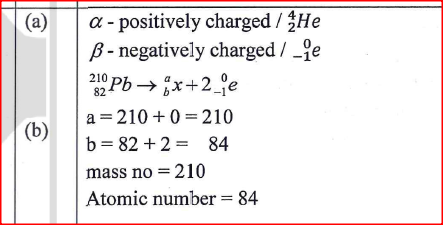
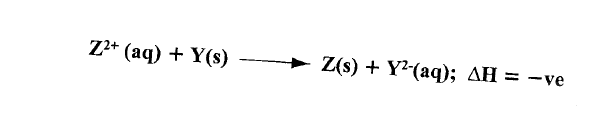

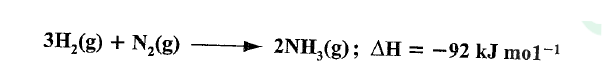

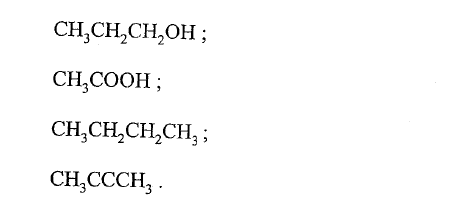


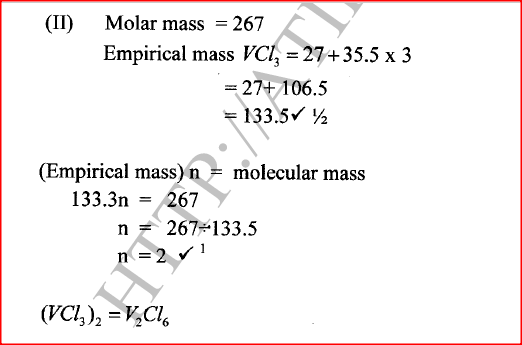
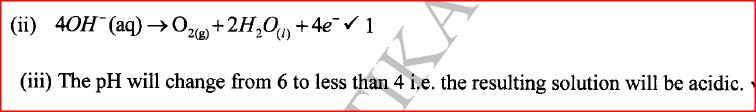


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed