KCSE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS PER TOPIC
|
These are chemistry questions and answers categorized according to topics, papers i.e. Paper 1 and 2, Levels i.e. form 1 to form 4, kcse year the examination was done and section A or B
Select topic/category to open topical questions from that particular option provided. Chemistry Topics
0 Comments
Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen: Properties, Preparations, and UsesReview
The Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen provides a comprehensive overview of the properties, laboratory preparations, and uses of various oxides of nitrogen. Nitrogen, belonging to the second period of Group V in the periodic table, forms five different oxides when combined with oxygen in different ratios. The document presents the oxides of nitrogen in a tabular form, including their names, formulas, oxidation states of nitrogen, and the ratio of nitrogen to oxygen. It explains that NO and N2O are neutral gases, while the other oxides are acidic. The guide also highlights that the oxides of NO and N2O are brownish gases, while NO and N2O are gases. The laboratory preparation methods for each oxide are described in detail. For example, nitric oxide (NO) is prepared by treating metallic copper with moderately concentrated nitric acid. The document provides the chemical equation for the reaction and explains the use of Wolfe's apparatus for collecting the gas. It also outlines the purification process using freshly prepared ferrous sulfate solution. The physical and chemical properties of each oxide are thoroughly explained. For instance, NO is not combustible but decomposes into N2 and O2 at high temperatures. The document also discusses the oxidizing and reducing properties of NO, as well as its reactions with other substances such as potassium permanganate and halogens. The Chemistry Notes Form 3 - Oxides of Nitrogen also covers nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) in detail. It provides information on their structures, laboratory preparations, physical properties, and chemical reactions. The uses of each oxide are highlighted, including the preparation of nitric acid and the use of nitrous oxide as a mild anaesthetic. Overall, this document serves as a comprehensive guide for students studying oxides of nitrogen in chemistry. It provides a clear understanding of the properties, laboratory preparations, and uses of these important compounds. With detailed explanations and examples, students can enhance their knowledge and excel in their chemistry studies.
(NH4)2HPO4 is a fertilizer used by farmers to boost their crop production.
(a) Calculate the mass of phosphorus in a 20 kg packet 14.0; H = 1.0; P = 31.0; 0 16.0) (b) State one advantage of this fertilizer, (NH4)2HPO4 over urea CO(NH2)2
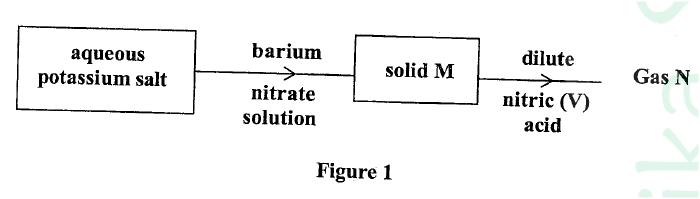
Study the flow chart in Figure 1 and answer the questions that follow.
Gas N forms a while suspension with aqueous calcium hydroxide.
(a) Name the anion present in the potassium salt. (b) Write an ionic equation for the formation of solid M. (c) Give one use of gas N.
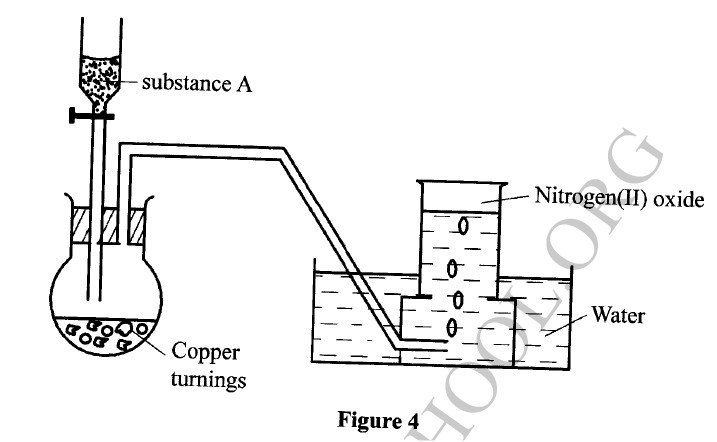
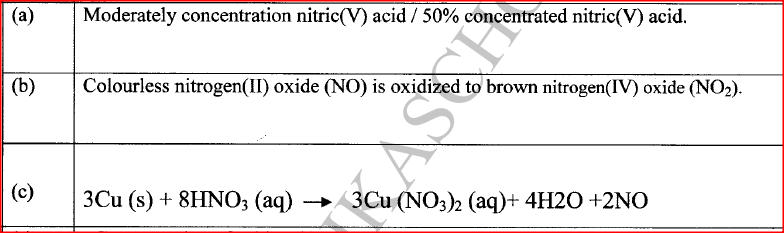
The set-up in Figure 4 can be used to prepare nitrogen (II) oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name substance A
(b) When the gas jar containing nitrogen (II) oxide is exposed to air, a brown color is observed. Explain. (c) Write an equation for the reaction which occurred in the flask.
In an experiment, concentrated nitric(V) acid was reacted with iron(II) sulphate. State and explain the observations made.
ANSWERS
The mixture changed from green to yellow / formation of a brown gas;
Iron(II) ions is oxidized by nitric(V) acid to Iron(III) ions / nitric(V) acid is reduced to nitrogen(1I) oxide which is oxidized by oxygen to nitrogen(IV ) oxide.
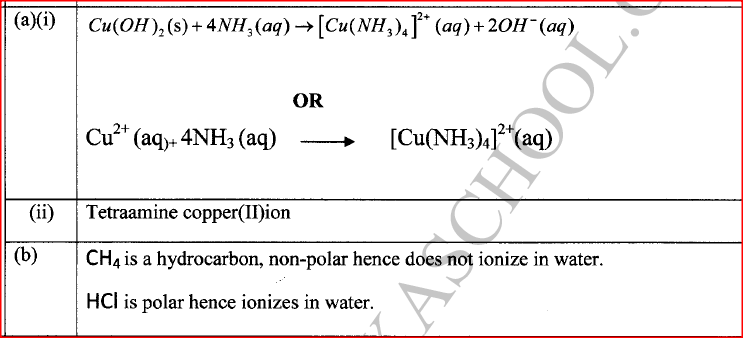
Copper(II) ions react with excess aqueous ammonia to form a complex ion.
(a) (i) Write an equation for the reaction that forms the complex ion. (ii) Name the complex ion. (b) Explain why CH4 is not acidic while HCl is acidic yet both compounds contain hydrogen.
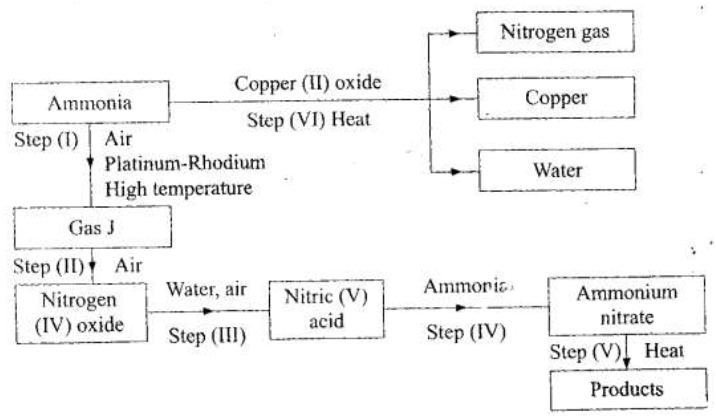
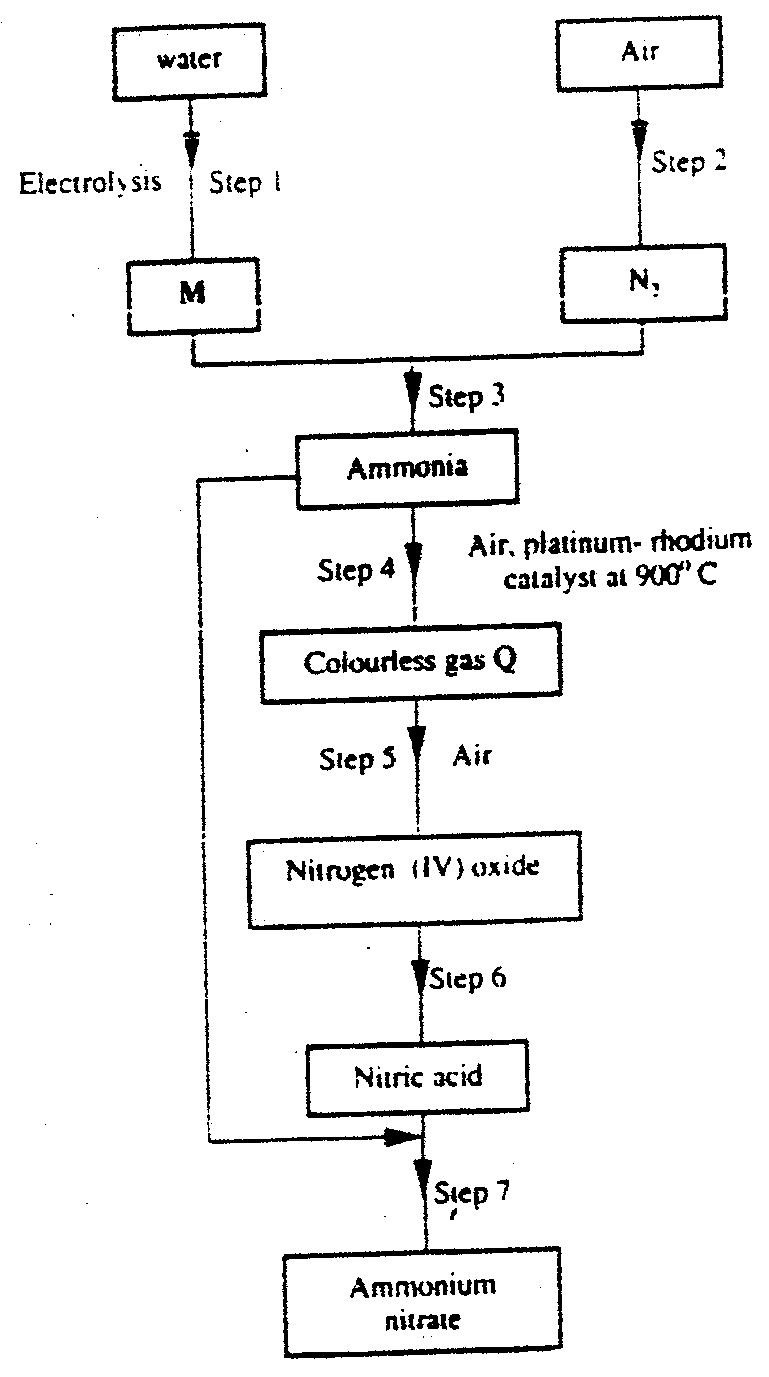
(a) Describe the process by which Nitrogen is obtained from air on a large scale.
(b) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Identify gas J.
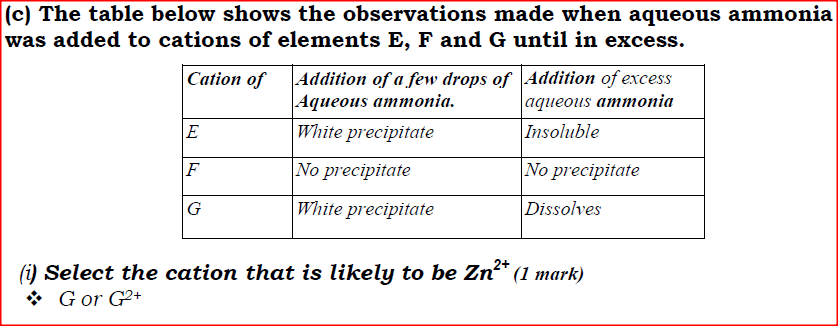
(ii) Using oxidation numbers, show that ammonia is the reducing agent in step (VI) (iii) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs in step (V). (iv) Give one use of ammonium nitrate. (c) The table below shows the observations made when aqueous ammonia was added to cations of elements E, F and G until in excess.
(i) Select the cation that is likely to be Zn2+
(ii) Given that the formula of the cation of element E is E 2+ , write the ionic equation for the reaction between E2+(aq) and aqueous ammonia.
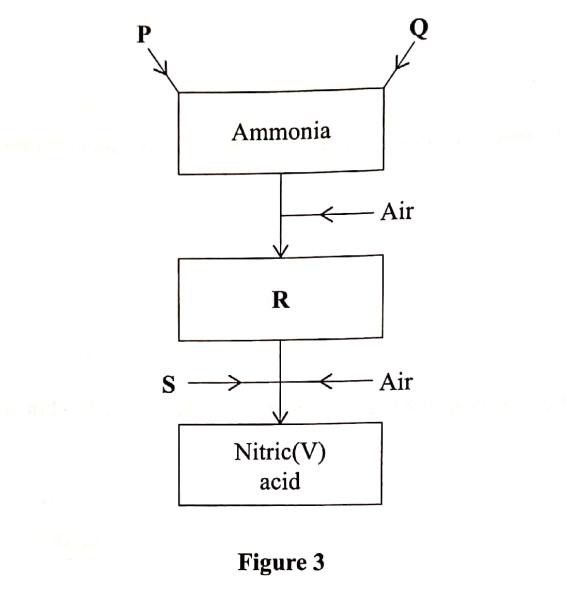
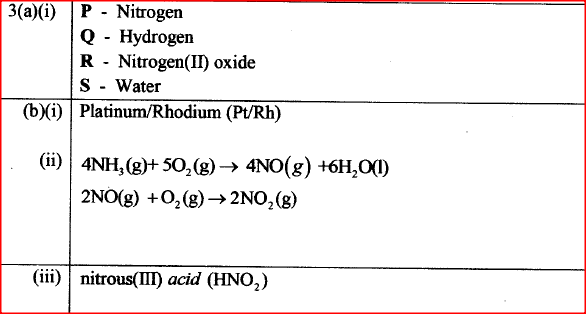
Figure 3 is a flow chart that shows the process that occurs in the manufacture of nitric (V) acid.
(a) Name substance P, Q, R and S.
To obtain substance R, ammonia is heated at 9000C in the presence of air and a catalyst.
The product is then cooled in air.
(e) When ammonia ¡s reacted with nitric(V) acid, it produces a nitrogenous fertiliser.
When fuels burn in the internal combustion engine at high temperature, one of the products formed is nitrogen (II) oxide.
(a) Write the equation for the formation of nitrogen (II) oxide. (b) Give a reason why nitrogen (II) oxide is not formed at room temperature. (c) Describe how formation of nitrogen (II) oxide in the internal combustion engine leads to gaseous pollution.
ANSWERS
(a)N2(g) + 02(g) 2NO(g)
(b)Nitrogen atoms in the molecule are joined by strong triple covalent bond that requires a lot of energy to break than provided at room temperature (c) Nitrogen (II) oxide reacts with oxygen in air to form nitrogen (IV) oxide that dissolves in water vapour causing acid rain.
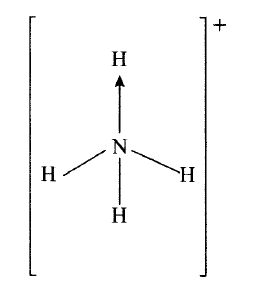
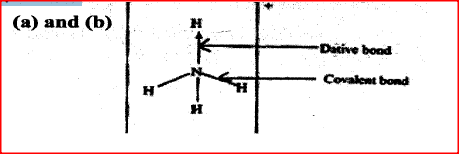
Ammonium ion has the following structure
Label on the structure:
(a) covalent bond; (b) coordinate (dative) bond.
When burning magnesium ribbon is introduced into a gas jar full of nitrogen, it continues to burn producing a greenish yellow powder.
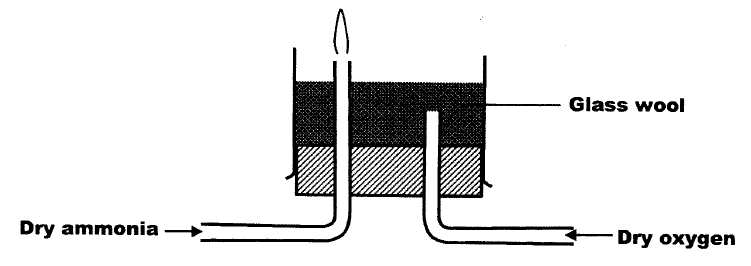
Dry ammonia and dry oxygen were reacted as shown in the diagram below
a)What is the purpose of the glass wool?
b) What products would be formed if red hot platinum was introduced into a mixture of ammonia and oxygen?
ANSWERS
(a)The purpose of the glass wool. It spreads the oxygen evenly/increase surface area or enriches the air with oxygen.
(b)Forms NO, Nitrogen (II) Oxide and steam
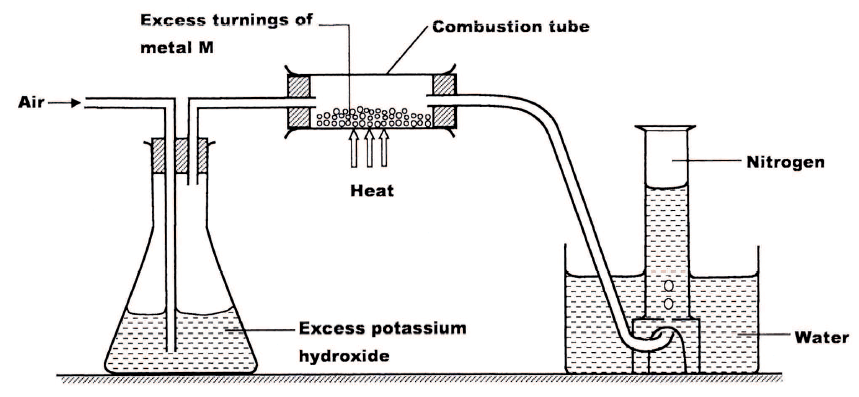
A student used the set up below to prepare a sample of nitrogen gas.
a) State the function of potassium hydroxide in the set up
b) Give a suitable metal M for use in the combustion tube c) Give a reason why the nitrogen gas obtained is not pure.
ANSWERS
(a) It absorbs carbon (IV) oxide present in the air.
(b) Copper /Cu(S) (c) It has rare noble gases which have not been removed / Argon.
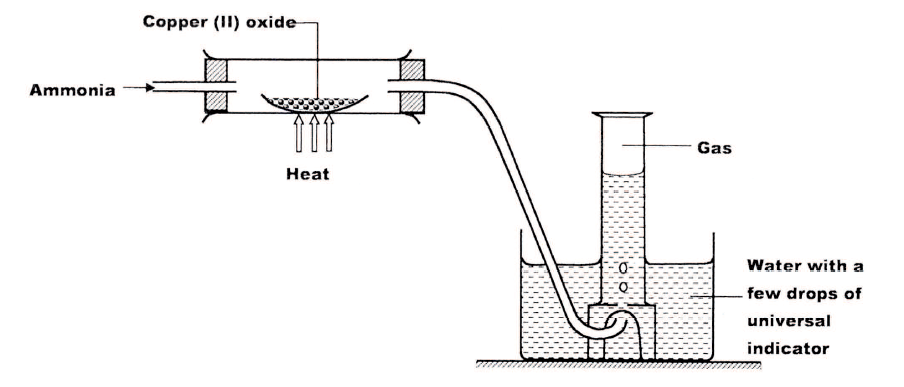
Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow
(a)Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and copper (II) oxide.
(b) During the experiment, the colour of the contents in the water trough changed. State the colour change observed and give an explanation.
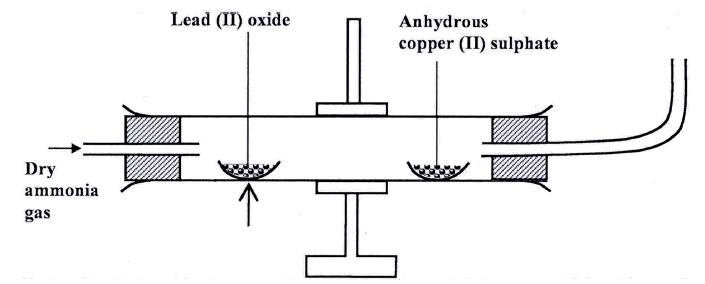
Dry ammonia gas was passed over heated lead (II) oxide and the product passed over anhydrous Copper (II) sulphate as shown in the diagram below.
State:
(a)Two observations made in the combustion tube. (b) The property of ammonia gas shown in this experiment
ANSWERS
(a)The anhydrous copper (II) Sulphate turns from white to blue.
A grey solid is formed/droplets of a colourless liquid condense at cool part (b)Reducing property.
a) Fraction distillation of liquid air usually produces nitrogen and oxygen as the major products.
(Boiling points nitrogen = - 1960C, oxygen = -1830C)
b) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
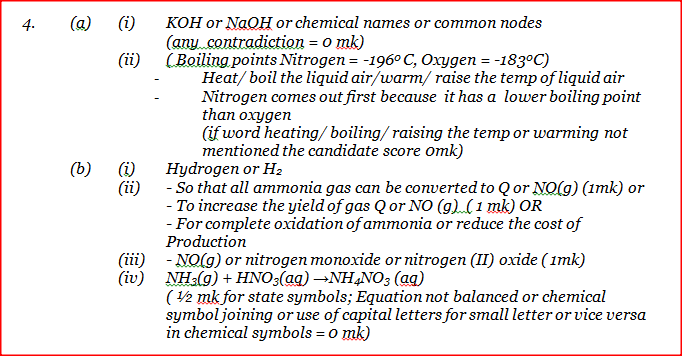
(a) describes one method that can be used to distinguish between sodium sulphate and sodium hydrogen sulphate.
b) Describe how a pure sample of lead (II) sulphate can be prepared in the laboratory starting with lead metal c) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
i) Write an equation for the reaction in:
I step II; II step IV ii) State the observation made in step III. Explain. iii) Name another substance that can be used in step V.
ANSWERS
(a)Test the acidity using a litmus pager. There will be no change on litmus when dipped into a solution of sodium sulphate . The litmus paper turns to red when dipped into a solution of sodium hydrogen sulphate .
OR Add a solid carbonate to each solution. No effervescence observed when the carbonate is added to a solution of sodium sulphate. Effervescence is observed when the carbonate is added to a solution of sodium hydrogen sulphate. (b)Add dilute nitric acid to lead to form a soluble salt, Pb(NO3)2, add a soluble salt, Na2SO4. Then dry the salt between filter papers . (c)(i) NH4 NO3 → N2O + 2H2O II 2Fe(OH)3(S) → Fe2O3(s) + 3H2O(l) (ii) The colour changes from pale green to brown . The iron (II) is oxidised to iron (III) chloride by hydrogen peroxide (iii) Carbon monoxide
On heating a pale green solid K, carbon (IV) oxide gas and a black solid M were formed. On reacting K with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon (IV) oxide gas and
green solution S were formed. When excess aqueous ammonia was added to solution S, a deep blue solution was formed. a) Identify the cation in solid K b) Identify the two onions in solution S.
When fuels burn in the internal combustion engine at high temperature, one of the products formed is nitrogen (II) oxide.
a) Write the equation for the formation of nitrogen (II) oxide. b) Give a reason why nitrogen (II) oxide is not formed at room temperature. c) Describe how formation of nitrogen (II) oxide in the internal combustion engine leads to gaseous pollution.
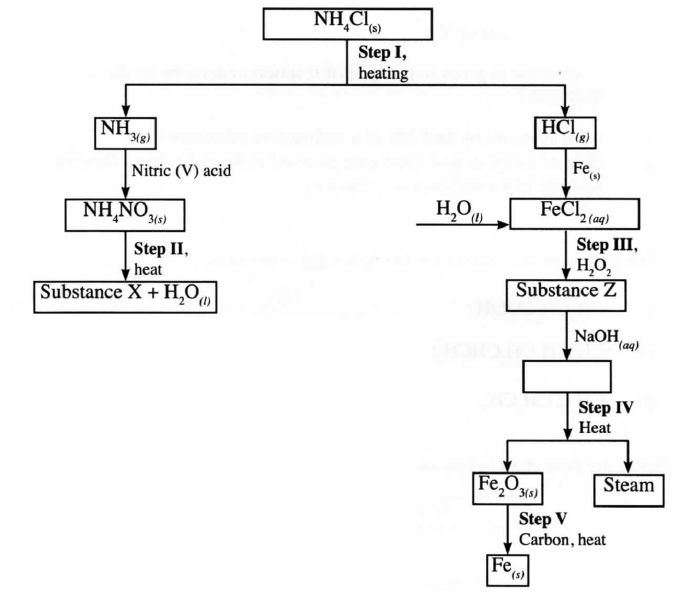
The scheme below shoes some reaction sequence starting with slid N. Study it and answer the questions that follows.
a) Write the formula of the complex ion in solution Q.
b) Write an equation for the reaction in step IV.
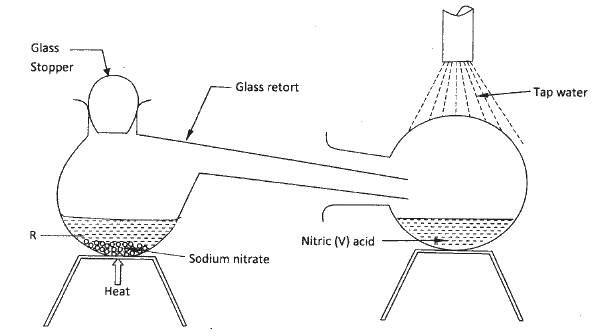
In the laboratory, small quantities of nitric (V) acid can be generated using the following set up. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) i) Give the name of substance R.
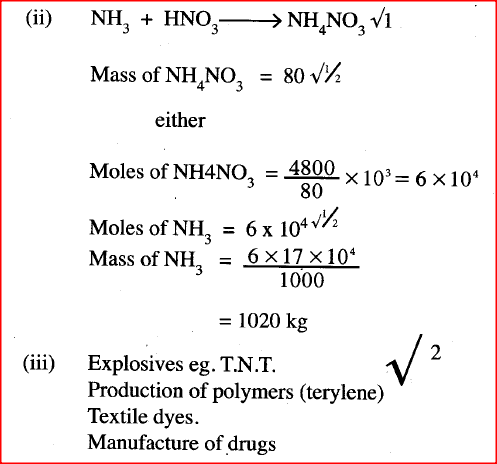
ii) Name one other substance that can be used in place of sodium nitrate. iii) What is the purpose of using tap water in the set up above? b) Explain the following; i) It is not advisable to use a stopper made of rubber in the set-up ii) the reaction between copper metal with 50% nitric (V) acid in an open test-tube produces brown fumes. c) i) Nitrogen is one of the reactants used in the production of ammonia, name two sources of the other reactant. ii) A factory uses nitric (V) acid and ammonia gas in the preparation of a fertilizer. If the daily production of the fertilizer is 4800kg; calculate the mass of ammonia gas used in kg. (N = 14.0; O = 16.0; H = 1.0) iii) State two other uses of nitric (V) acid other than the production of fertilizers.
ANSWERS
(a) (I) Concentrated /sulphuric (VI) acid.
(ii) Potassium nitrate (iii) To condense the fumes or vapour of nitric (V) acid into liquid (b) (i) Nitric acid (V) will corrode the rubber (ii) The reaction produces nitrogen monoxide (colourless) which is oxidised by oxygen from the air to form nitrogen(IV) oxide. (c)(i) Water Alkanes Biogas Water gas
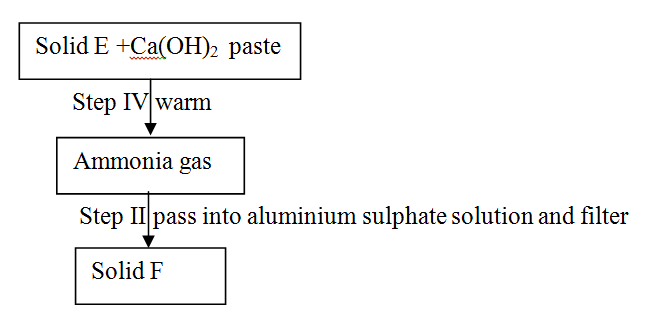
Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
a) Identify solid E.
b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in step II that produces solid F.
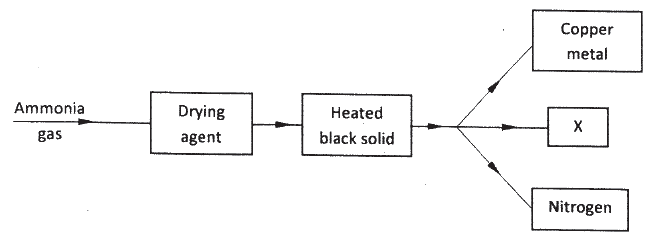
Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name a suitable drying agent for ammonia.
(b) Describe one chemical test for ammonia. (c) Name X.
ANSWERS
(a) Calcium Oxide
(b) Expose ammonia to hydrogen chloride gas, dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are observed. (c)Steam/water .
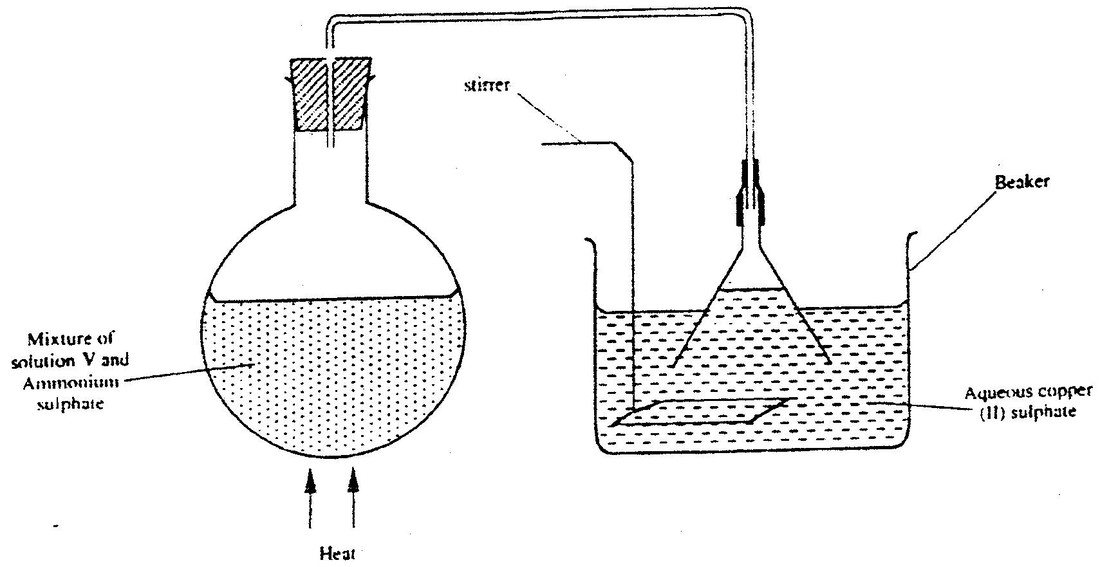
A student set up the apparatus shown below to prepare ammonia gas and react it with copper (II) sulphate solution
(a) Identify solution V
(b) State the observations which were made in the beaker
Expected Response
|
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|







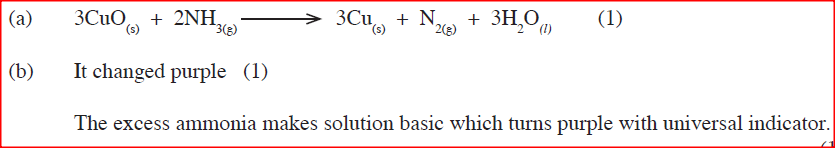



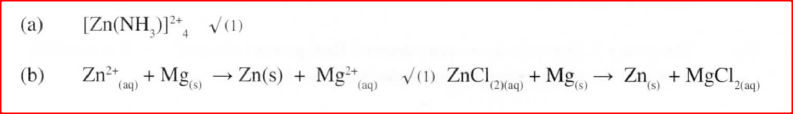

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed