|
a) The diagram below is part of set up used to prepare and collect dry chlorine gas.
i) Complete the diagram to show how a dry sample of chlorine gas can be collected.
ii) Name another substance and condition that can be used instead of manganese (VI) oxide. iii) Write an equation for each of the following; I. chlorine gas reacting with iron II. chlorine gas reacting with hot concentrated sodium hydroxide solution. b) An oxide of chlorine of mass 1.83g was found to contain 1.12g of oxygen. Determine the empirical formula of the oxide (O = 16.0; Cl = 35.5). c) Other than the manufacture of weed killers, name two other uses of chlorine.
0 Comments
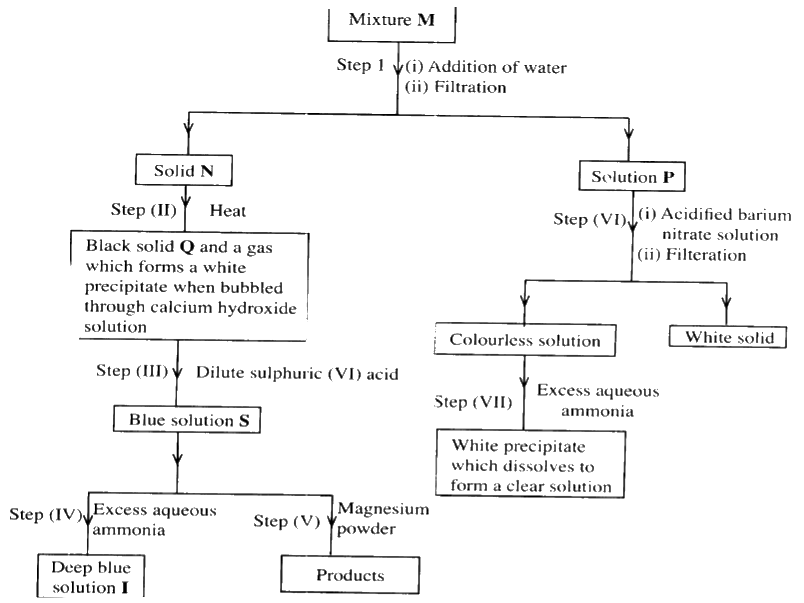
The flow chart below shows a sequence of reactions involving a mixture of two salts, mixture M. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) Write the formula of the following;
i) anion in solid Q ii) the two salts present in mixture M. b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in step (VI) c) State and explain the observations made in step (V). d) i) Starting with Lead (II) oxide, describe how a pure solid sample of lead sulphate can be prepared in the laboratory. ii) How can one determine whether the lead sulphate prepared is pure?
ANSWERS
(c)The solution changes from blue to colourless and a brown solid is formed.
The magnesium which is above copper in the reactivity series displaces the copper ions from the solution. Apparatus become warm. The reaction is exothermic. (d)(i) Add nitric (V) acid to lead oxide, filter add a soluble sulphate/ sulphuric acid to the filtrate . Filter and wash residue with distilled water to remove traces of the filtrate, then dry residue between i. filter papers /oven. (ii) Determine the melting point, if it is pure the melting point will be constant.
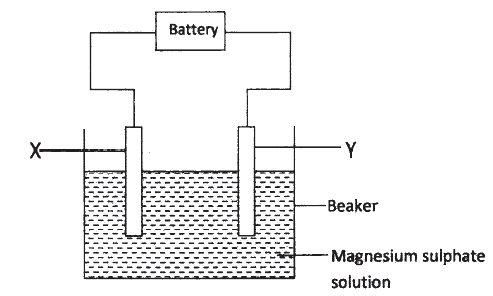
a) The set up below was used to investigate the products formed at electrodes during electrolysis of aqueous magnesium sulphate using inert electrodes. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
i) During the electrolysis, hydrogen gas was formed at electrode Y. identify the anode. Give a reason for your answer.
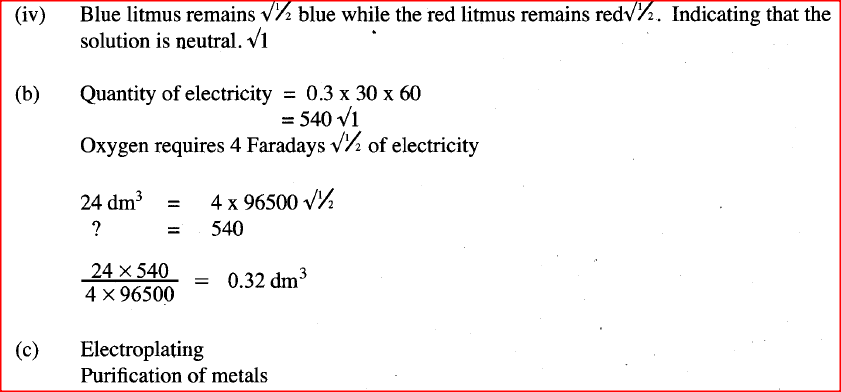
ii) Write the equation for the reaction with takes place at electrode X. iii) Why is the concentration of magnesium sulphate expected to increase during electrolysis? iv) What will be observed if red and blue litmus papers were dipped into the solution after electrolysis? b) During electrolysis of magnesium sulphate, a current of 0.3A was passed for 30 minutes. Calculate the volume of gas produced at the anode.(Molar gas volume = 24dm3; 1 Faraday = 96,500C.). c) State two applications of electrolysis.
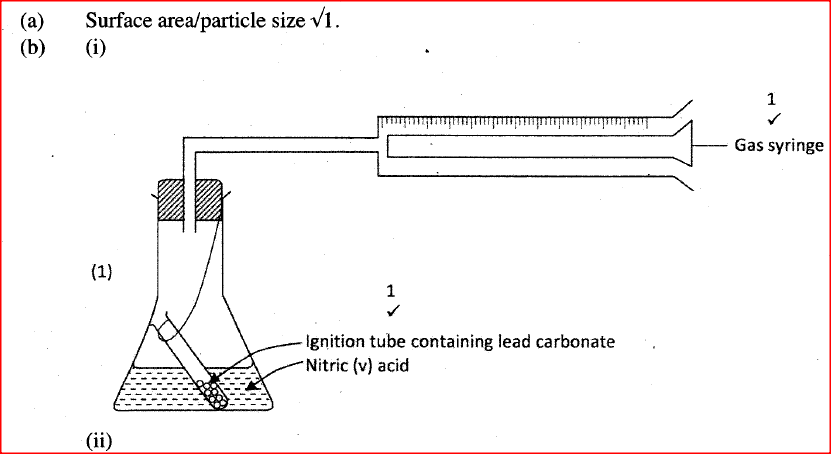
The factors which affect the rate of reaction between lead carbonate and dilute nitric (V) acid were investigated by carrying out three experiments;
a) Other than concentration , name the factor that was investigated in the experiments.
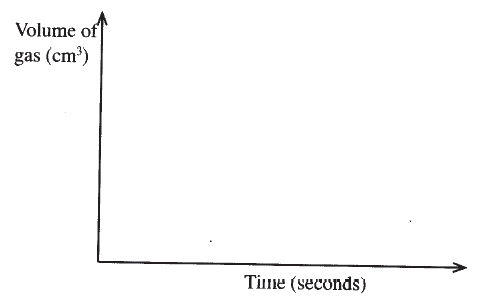
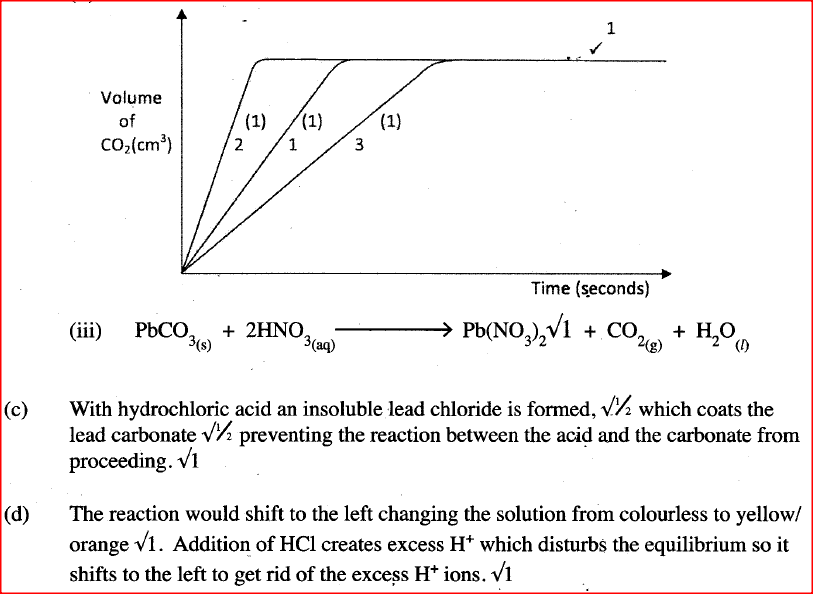
b) For each experiment, the same volume of acid (excess) and mass of lead carbonate were used and the volume of gas liberated measured with time. i) Draw a set up that can be used to investigate the rate of reaction for one of the experiments. ii) On the grid provided, sketch the curves obtained when the volume of gas produced was plotted against time for each of the three experiments and label each as 1, 2 or 3.
iii) Write an equation for the reaction that took place.
c) If the experiments were carried out using dilute hydrochloric acid in place of dilute nitric (V) acid, the reaction would start, slow down and eventually stop. Explain these observations. d) A solution of bromine gas in water is an example of a chemical reaction in a state of balance. The reaction involved is represented by the equation below.
State and explain the observation made when hydrochloric acid is added to the mixture at equilibrium.
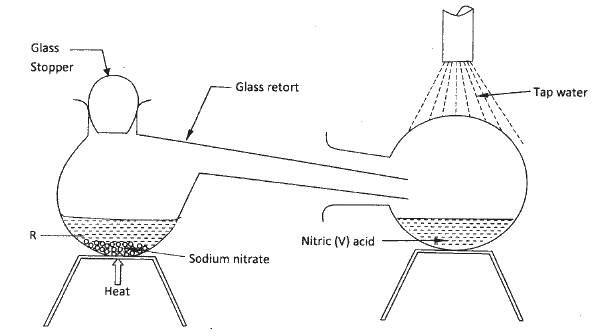
In the laboratory, small quantities of nitric (V) acid can be generated using the following set up. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) i) Give the name of substance R.
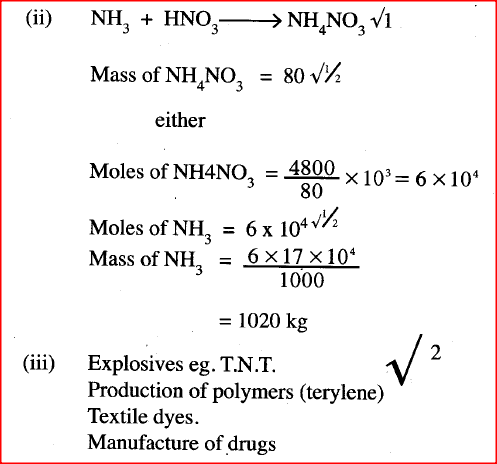
ii) Name one other substance that can be used in place of sodium nitrate. iii) What is the purpose of using tap water in the set up above? b) Explain the following; i) It is not advisable to use a stopper made of rubber in the set-up ii) the reaction between copper metal with 50% nitric (V) acid in an open test-tube produces brown fumes. c) i) Nitrogen is one of the reactants used in the production of ammonia, name two sources of the other reactant. ii) A factory uses nitric (V) acid and ammonia gas in the preparation of a fertilizer. If the daily production of the fertilizer is 4800kg; calculate the mass of ammonia gas used in kg. (N = 14.0; O = 16.0; H = 1.0) iii) State two other uses of nitric (V) acid other than the production of fertilizers.
ANSWERS
(a) (I) Concentrated /sulphuric (VI) acid.
(ii) Potassium nitrate (iii) To condense the fumes or vapour of nitric (V) acid into liquid (b) (i) Nitric acid (V) will corrode the rubber (ii) The reaction produces nitrogen monoxide (colourless) which is oxidised by oxygen from the air to form nitrogen(IV) oxide. (c)(i) Water Alkanes Biogas Water gas
The grid below is part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow. (The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements)
a) Which is the most reactive non-metallic element shown in the table? Explain.
b) i) Write the formula of the compound formed when element A reacts with element B. ii) Name the bond type in the compound formed in b (i) above. c) i) What is the name given to the group of elements where C, G and H belong? ii) Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when C in gaseous form is passed through a solution containing ions of element H. d) The melting points of elements F and G are 1410°C and -101°C respectively. In terms of structure and bonding, explain why there is a large difference in the melting points of F and G. e) D forms two oxides. Write the formula of each of the two oxides. f) J is an element that belongs to the 3rd period of the periodic table and a member of the alkaline earth elements. Show the position of J in the grid.
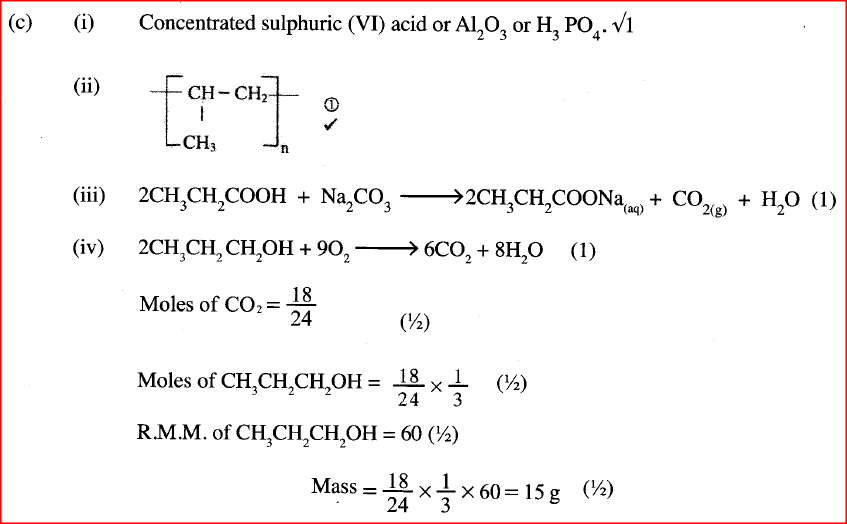
a) Draw the structural formula for all the isomers of C2H3CL3
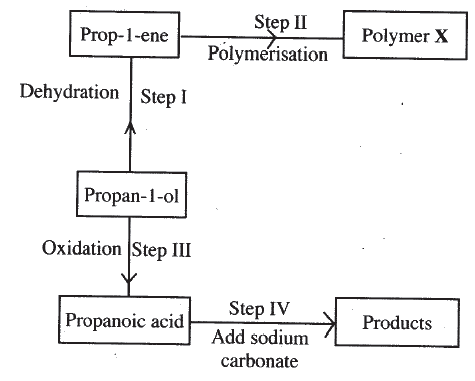
b) Describe two chemical tests that can be used to distinguish between ethane and ethane. c) The following scheme represents various reactions starting with propan-1-ol. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
i) Name one substance that can be used in step I.
ii) Give the general formula of X. iii) Write the equation for the reaction in step IV. iv) Calculate the mass of propan-I-ol which when burnt completely in air at room temperature and pressure would produce 18dm3 of gas. (C = 12.0; O = 16.0; H = 1.0; Molar gas volume = 24dm3)
ANSWERS
a) State and explain what would happen if a dry blue litmus paper was dropped in a gas.
b) By using only dilute hydrochloric acid, describe how a student can distinguish between barium sulphite from barium sulphate.
The apparatus shown in the diagram below were used to investigate the products formed when concentrated sodium chloride was electrolysed using inert electrodes.
(a) Write the equation for the reaction that takes place at electrode A.
(b) If the concentrated sodium chloride was replaced with dilute sodium chloride, what product would be formed at electrode A? Explain.
(a) The electronic arrangement of the ion of element Q is 2.8.8. If the formula of the ion is Q3-,state the group and period to which Q belongs.
Group: Period: (b) Helium, neon and argon belong to group 8 of the periodic table. Give: (i) the general name of these elements; (ii) one use of these elements.
Describe two chemical tests that can be used to distinguish ethanol from ethanoic acid.
Describe how a solid sample of potassium sulphate can be prepared starting with 200cm3 of 2M potassium hydroxide.
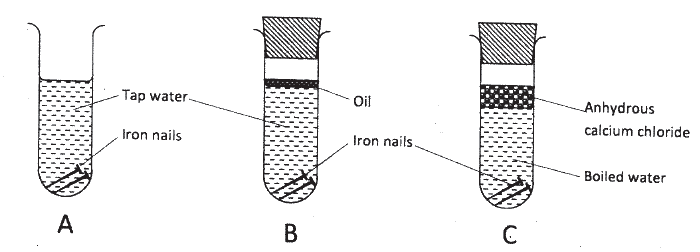
The following set up of three test-tubes was used to investigate rusting of iron.
Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Give a reason why rusting did not occur in test-tube C.
(b) Aluminium is used to protect iron sheets from rusting. Explain two ways in which aluminium protects iron from rusting.
ANSWERS
(a) No air due to boiling.
(b) Aluminium being very reactive forms a layer of Al2O3 on the metal making it impervious to moisture. Aluminium being more reactive than iron protects the iron through sacrificial protection cathodic protection.
Describe how the percentage by mass of copper in copper carbonate can be determined.
Aluminium is both malleable and ductile,
(a) What is meant by? (i) malleable; (ii) ductible. (b) State one use of aluminium based on: (i) malleability (ii) ductility
ANSWERS
(a) (i) Malleable - Can be hammed into sheets
(ii) Ductile - Can be drawn into wires (b) (i) Saucepans (ii) Electrical transmission lines
Give two uses of the polymer polystyrene.
ANSWERS
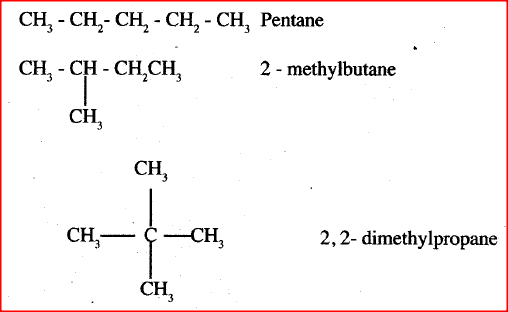
Draw and name the isomers of pentane.
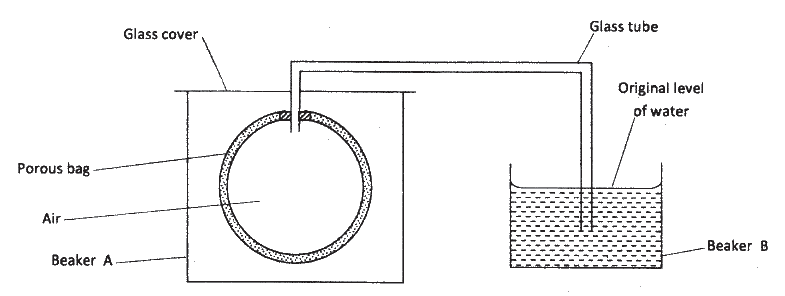
The set up shown below was used to investigate a property of hydrogen gas.
State and explain the observation that would be made in the glass tube if beaker A was filled with hydrogen gas.
ANSWERS
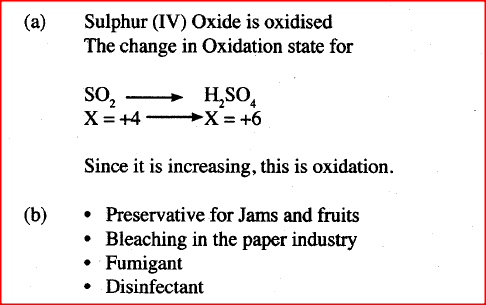
Acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution is decolourised when sulplur (IV) oxide is bubbled through it. The equation for the reaction is given below.
2H2O(1) + 5S02(g) + 2KMnO4(aq) —►K2SO4(aq) + 2MnSO4(aq)+ 2H2SO4(aq) (a) Which reactant is oxidised? Explain. (b) Other than the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid, state one other use of sulphur (IV) oxide.
Study the energy level diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Give the name of ΔHA
(b) How can ΔHB be reduced? Give a reason.
ANSWERS
(a) Heat of reaction
(b) Using a catalyst Catalyst reduce activation energy.
Use the following information on substances S, T, V and hydrogen to answer the questions that follow:
(i) T displaces V from a solution containing V ions. (ii) Hydrogen reacts with the heated oxide of S but has no effect on heated oxide of V. (a) Arrange substances S, T, V and hydrogen in the order of increasing reactivity. (b) If T and V are divalent metals, write an ionic equation for the reaction in (i) above.
Below is a representation of an electrochemical cell.
Calculate the E.M.F of the electrochemical cell.
Distinguish between ionisation energy and electron affinity of an element.
ANSWERS
A dynamic equilibrium is established when hydrogen and carbon (IV) oxide react as shown below:
What is the effect of adding powdered iron catalyst on the position of the equilibrium?
Give a reason.
ANSWERS
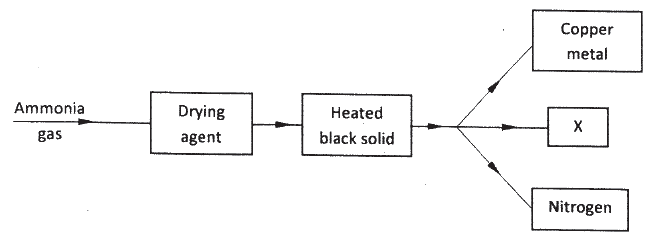
Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name a suitable drying agent for ammonia.
(b) Describe one chemical test for ammonia. (c) Name X.
ANSWERS
(a) Calcium Oxide
(b) Expose ammonia to hydrogen chloride gas, dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are observed. (c)Steam/water . |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |






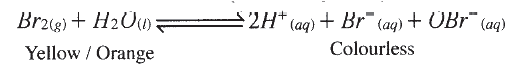









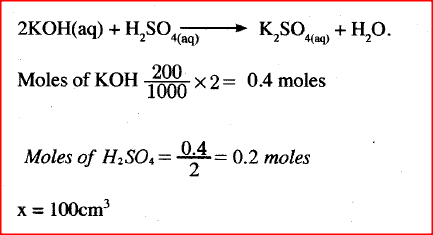






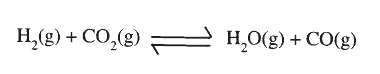

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

