a) i) Are the members in this group likely to be conductor or non – conductors? (1mk)
ii) Which element would have the lowest atomic number? Explain. (1mk)
b) The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. (The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements)i) Select the element in period three which has the shortest atomic radius. Give a reason for your answer. (2mks)
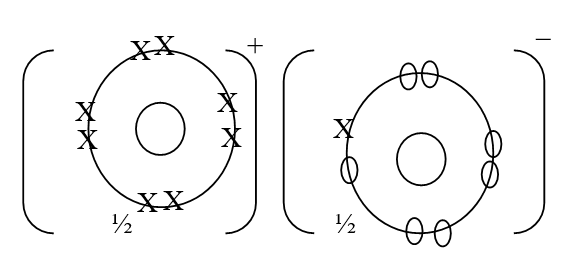
ii) Using dots (•) and crosses (x) to represent outermost electrons, draw a diagram to show the bonding in the compound formed when chlorine reacts with element X (1mk)
iii) When three liters of chlorine gas were completely reacted with element Y, 11.85g of the product were formed. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element Y. (3mks)(R.A.M of chlorine = 35.5, molar gas volume = 24 liters)
0 Comments
Differentiate between empirical and molecular formula (2mks)
Empirical formula show the simplest whole number ration in which atoms combine to for a compound while molecular formula shows actual number of each kind of atoms present in a molecule of a compound.
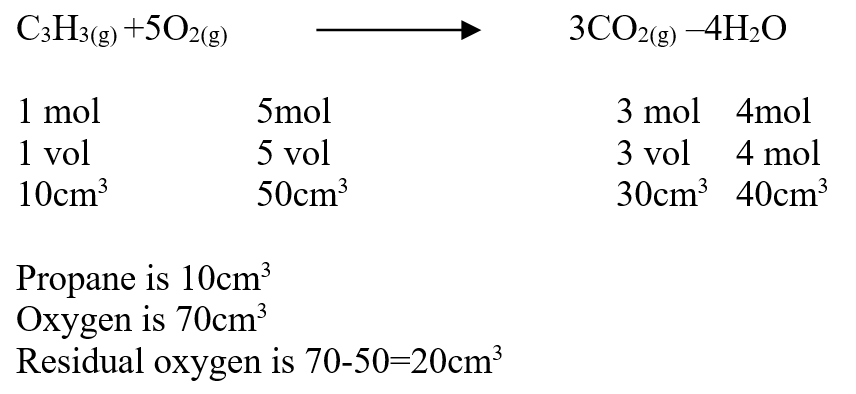
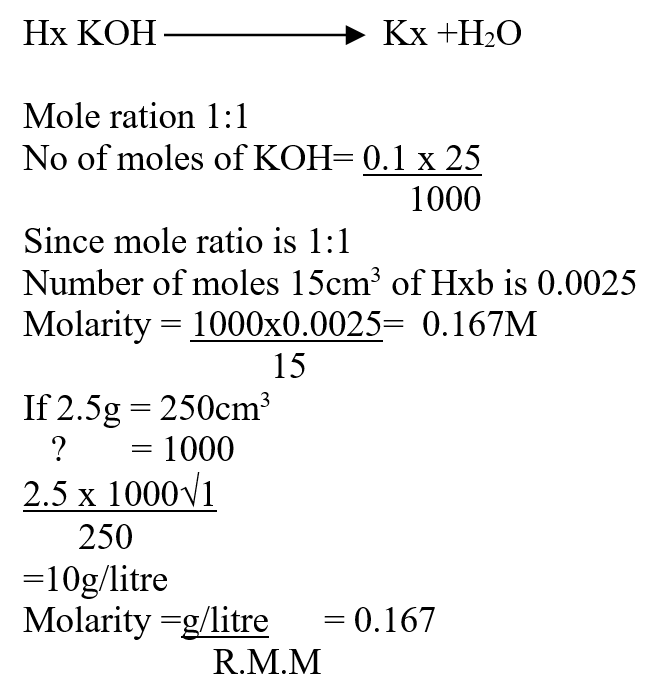
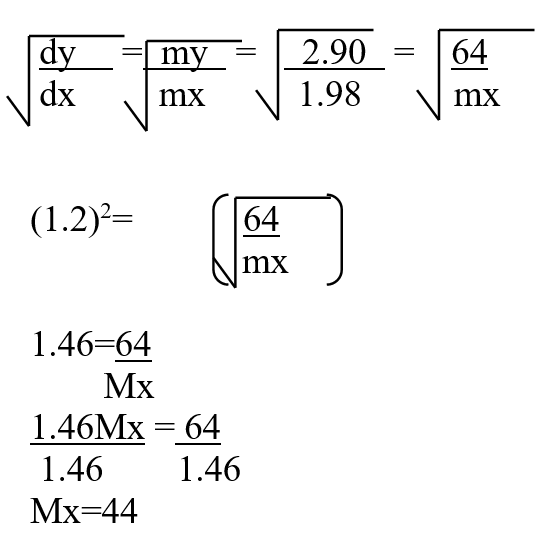
A volume of 80cm3 of a mixture of propane (C3H8) and oxygen were ignited in an experiment. The products were cooled and passed through an aqueous sodium hydroxide. The final volume was reduced by 30cm3a) Write the equation for the combustion of propane (1mk)b) Determine the volume of;i) The component of the original mixture (2mks)ii) Residual oxygen (1mk)A mass of 2.5g of acid HX was dissolved in water and the resulting solution was diluted to a total of 250cm3, 15cm3 of the final solution was required to neutralize 25.0cm3 of 0.1M aqueous potassium hydroxide. Calculate the relative molecular mass of the acid (3mks)a) How do their rate of diffusion compare? (2mks)b) Determine the relative molecular mass of X given that the relative molecular mass of Y is 64 (1mk)
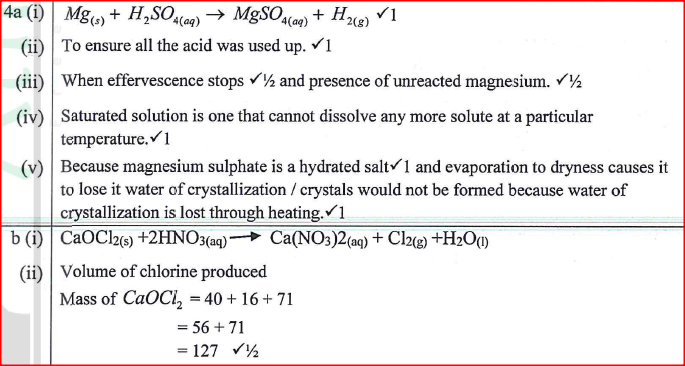
An experiment was carried out to prepare crystals of magnesium sulphate. Excess magnesium powder was added to 100 cm3 of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid in a beaker and warmed until no further reaction took place. The mixture was filtered and the filtrate evaporated to saturation, then left to cool for crystals to form.
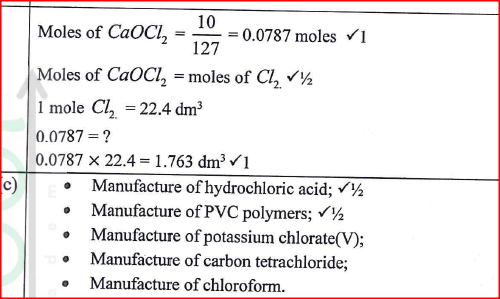
(a) (i) Write an equation for the reaction. (ii) Explain why excess magnesium powder was used. (iii) State how completion of the reaction was determined. (iv) What is meant by a saturated solution? (v) Explain why the filtrate was not evaporated to dryness. (b) When bleaching powder, CaOCl2, is treated with dilute nitric(V) acid, chlorine gas is released. This reaction can be used to determine the chlorine content of various samples of bleaching powders and liquids. (i) Write an equation for the reaction of nitric(V) acid with bleaching powder. (ii) Calculate the volume of chlorine produced when 10g of CaOCl2 is treated with excess nitric (v) acid. (Ca = 40.0; 0 = 16.0; Cl = 35.5; 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4dm3 at s.t.p) (c) Apart from use of chlorine gas in bleaches and water treatment, state two other uses of chlorine gas.
Distinguish between empirical and molecular formula of a compound.
ANSWERS
(NH4)2HPO4 is a fertilizer used by farmers to boost their crop production.
(a) Calculate the mass of phosphorus in a 20 kg packet 14.0; H = 1.0; P = 31.0; 0 16.0) (b) State one advantage of this fertilizer, (NH4)2HPO4 over urea CO(NH2)2
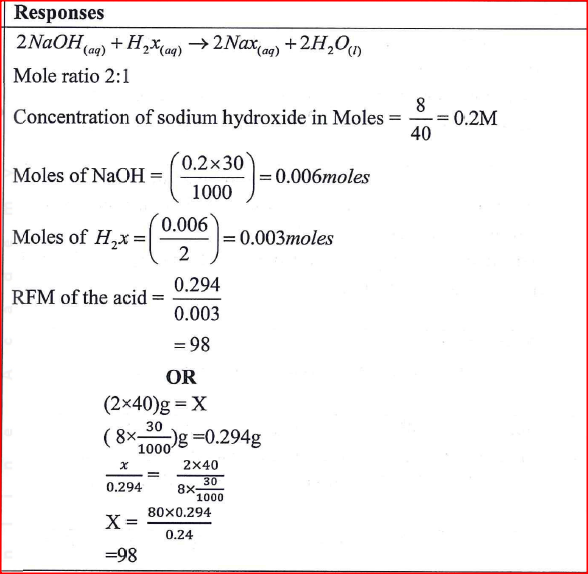
30.0 cm3 of aqueous sodium hydroxide containing 8.0 g per litre of sodium hydroxide were completely neutralized by 0.294 g of a dibasic acid. Determine the relative formula mass of the dibasic acid. (Na = 23.0 ; 0 = 16.0; H 1.0)
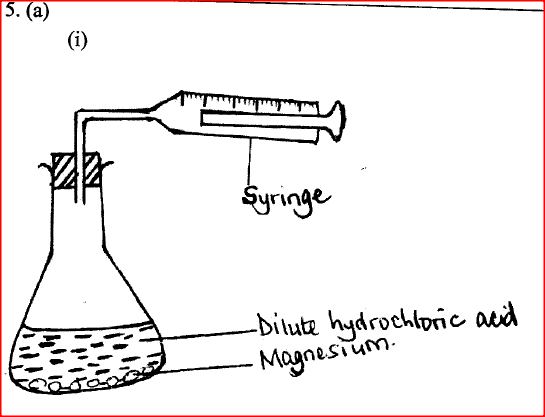
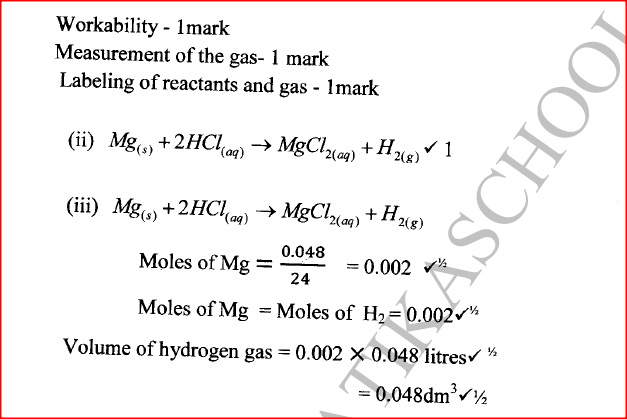
(a) When 0.048 g of magnesium was reacted with excess dilute hydrochloric acid at room temperature and pressure, 50 cm3 of hydrogen gas was collected. (Mg = 24.0; Molar gas volume = 24.0 dm3)
(i) Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to carry out the experiment described above.
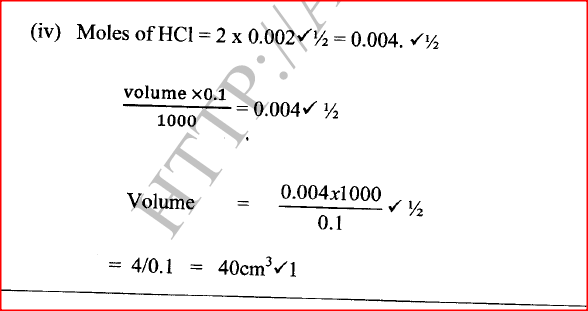
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction. (iii) Calculate the volume of hydrogen gas produced. (iv) Calculate the volume of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid required to react with 0.048 g of magnesium.
W is a colourless aqueous solution with the following properties:
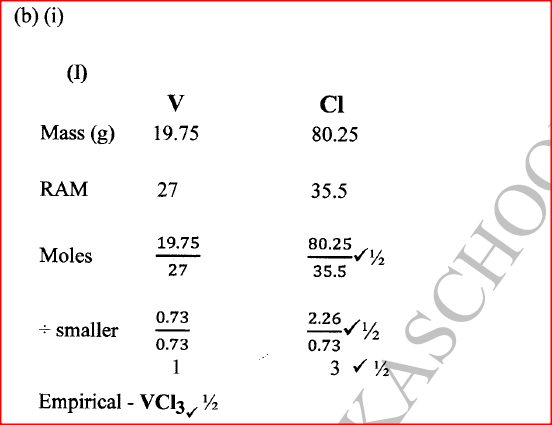
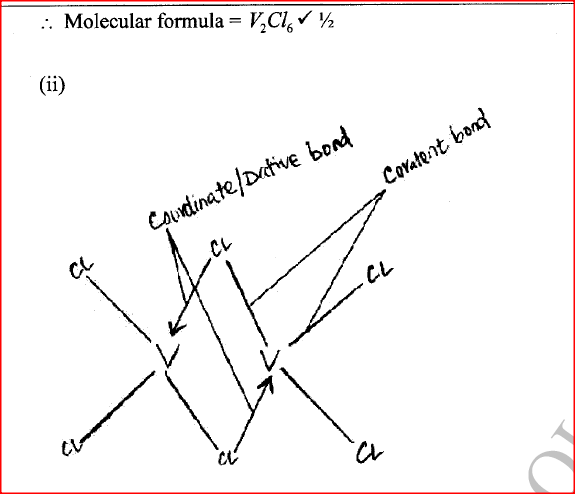
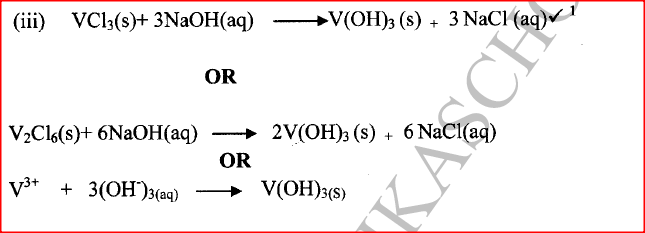
(ii) Give the identity of W. (iii) Name the colourless solution formed in (II) and (III). (iv) Write an ionic equation for the reaction indicated in (V). (b) Element V conducts electricity and melts at 933K. When chlorine gas is passed over heated V, it forms a vapour that solidifies on cooling. The solid chloride dissolves in water to form an acidic solution. The chloride vapour has a relative molecular mass of 267 and contains 19.75% of V. At a higher temperature, it dissociates to a compound of relative molecular mass 133.5. When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to the aqueous solution of the chloride, a white precipitate is formed which dissolves in excess alkali. (V = 27.0 ; CI = 35.5) (i) Determine the:
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction that form a white precipitate with sodium hydroxide.
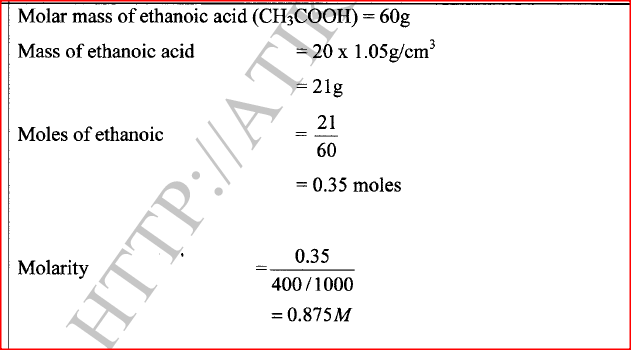
20 cm3 of ethanoic acid was diluted to 400 cm3 of solution. Calculate the concentration of the solution in moles per litre. (C = 12.0 ; H = 1.0 ; 0 =16.0) (Density of ethanoic acid = 1.05 g/cm3)
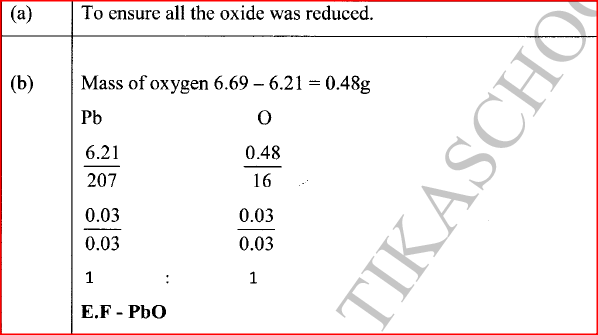
The empirical formula of lead(II) oxide was determined by passing excess dry hydrogen gas over 6.69g of heated lead(II) oxide.
(a) What was the purpose of using excess dry hydrogen gas? (b) The mass of lead was found to he 6.21g. Determine the empirical formula of the oxide. (Pb = 207.0 0 = 16.0)
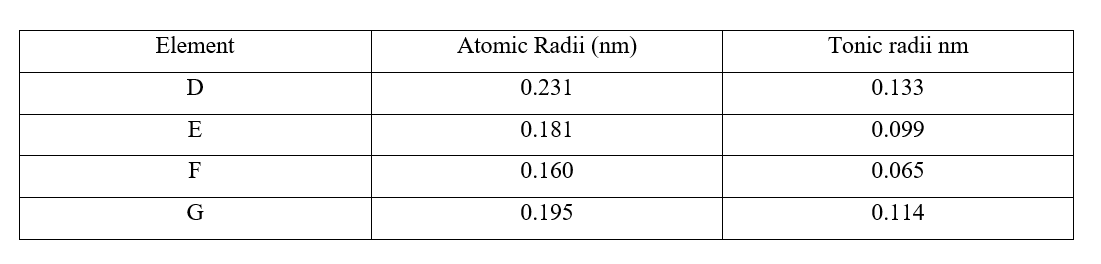
Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
(a) Give reasons why the melting point of:
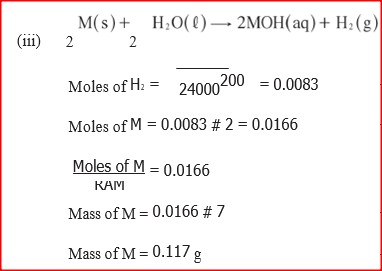
(i) S is higher than that of R; (ii) V is lower than that of U. (b) How does the reactivity of W with Chlorine compare with that of R with chlorine? Explain. (c) Write an equation for the reaction between T and excess oxygen. (d) When 1.15g of R were reacted with water, 600cm3 of gas was produced. Determine the relative atomic mass of R. (Molar gas volume = 24 000 cm3). (e) Give one use of element V.
(a) Explain the following observations:
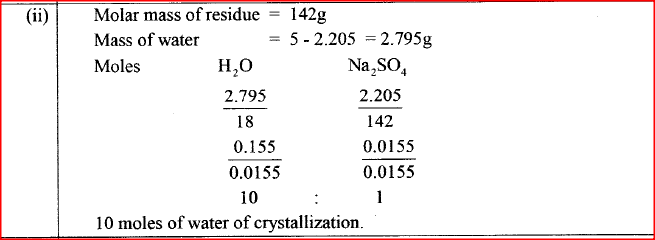
(b) A sample of water is suspected to contain aluminium ions (AI3+) . Describe a laboratory experiment that can be carried out to show that AI3+ ions are present in the water sample. (3 marks) (c) In an experiment to determine the number of moles of water of crystallisation of a hydrated compound, Na2S04. X H2O, 5g of the compound were heated strongly to a constant mass.
When 8.53g of sodium nitrate were heated in an open test-tube, the mass of oxygen gas produced was 0.83 g . Given the equation of the reaction as;
2NaNO 3 (s) -> 2NaNO 2 (s) + O 2 (g) Calculate the percentage of sodium nitrate that was converted to sodium nitrite. (Na = 23.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0)
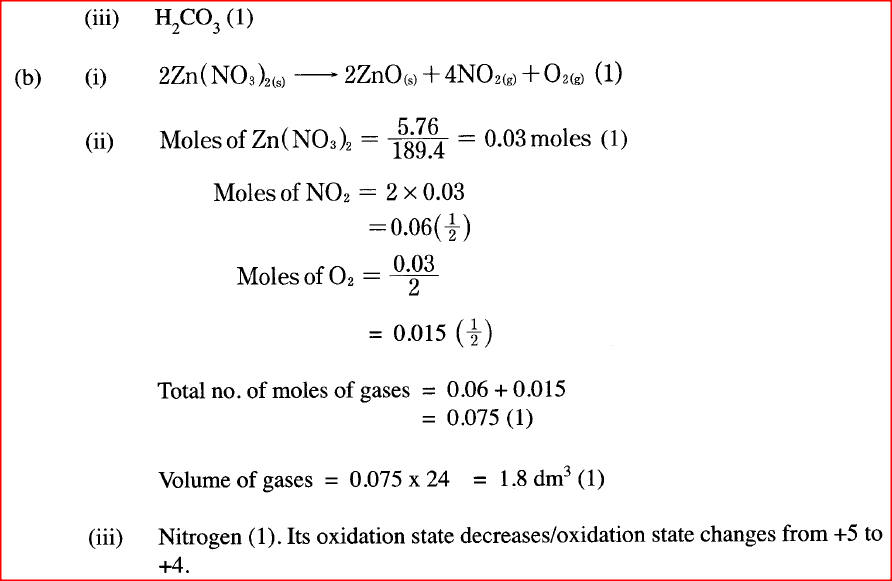
(a) (i) Carbon (IV) oxide is present in soft drinks. State two roles of carbon
(IV) oxide in soft drinks. (ii) Explain the observation made when a bottle containing a soft drink is opened. (iii) Carbon (IV) oxide dissolves slightly in water to give an acidic solution. Give the formula of the acid. (b) Zinc oxide can be obtained by heating zinc nitrate. A student heated 5.76 g of zinc nitrate. (i) Write an equation for the reaction that occurred. (ii) Calculate the total volume of gases produced. (Molar gas volume is 24 dm3; Zn = 65.4; O = 16.0; N = 14.0). (iii) Identify the element that is reduced when zinc nitrate is heated. Give a reason.
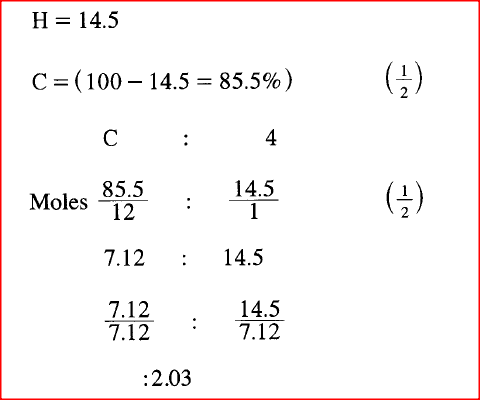
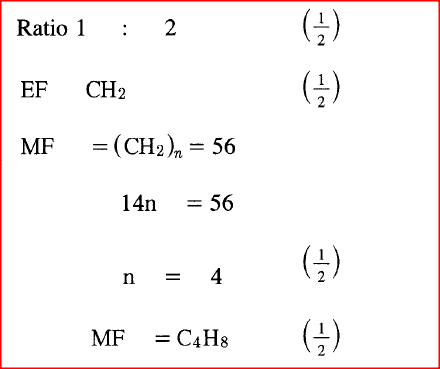
A hydrocarbon contains 14.5% of hydrogen. If the molar mass of the hydrocarbon is 56, determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon.
(C = 12.0; H = 1.0)
5g of calcium carbonate was strongly heated to a constant mass. Calculate the mass of the solid residue formed (Ca=40 0; C= 12.0; 0= 16.0). (2 marks)
Calculate the mass of Zinc oxide that will just neutralize dilute nitric (V) acid containing 12.6 g of nitric (V) acid in water. (Zn = 65.0; O =16.0, H = 1.0, N = 14.0).
A solution contains 40.3 g of substance XOH per litre. 25M cm3 of this solution required 30.0cm3 of 0.3 M sulphuric(Vl) acid for complete neutralisation. (a) Calculate the number of moles of XOH that reacted. (½ mark) (b) Determine the relative atomic mass of X. (1½ marks)
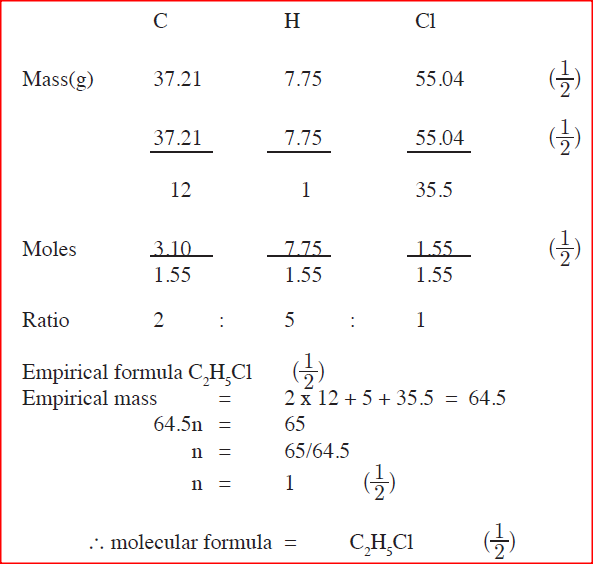
An organic compound had the following composition 37.21% carbon, 7.75% hydrogen and the rest chlorine. Determine the molecular formula of the compound, given that
the molecular mass of the compound is 65. (C=12.0; H=1.0; CL=35.5)
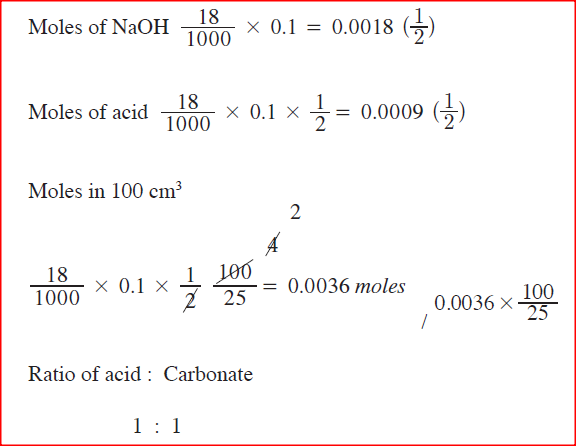
100cm3 of 0.005 M sulphuric (VI) acid were placed in a flask and a small quantity of anhydrous sodium carbonate added. The mixture was boiled to expel all the carbon (IV) oxide. 25cm3 of the resulting solution required 18cm3 of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution to neutralize it.
Calculate the mass of sodium carbonate added. (Na = 23.0; O=16.0; C=12.0)
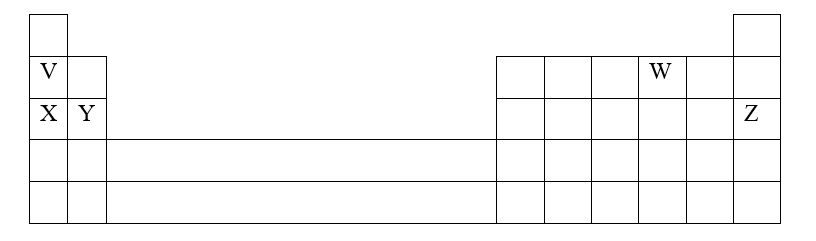
The grid given below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the element
(i) Select a letter which represents an element that looses electrons most readily. Give a reason for your answer.
(ii) Explain why the atomic radius of P is found to be smaller than that of N (iii) Element M reacts with water at room temperature to produce 0.2 dm3 of gas. Determine the mass of M which was reacted with water. (molar gas volume at room temperature is 24 dm3 , relative atomic mass of M=7 (b) Use the information in the table below to answer the question that follows. (The letters are not the symbols of the elements)
Identify a letter which represents an element in the table that could be calcium, carbon or sculpture. Give reasons in each case.
(i) Calcium: Reason (ii) Carbon Reason (iii)Sulphur: Reason
ANSWERS
(a)(i)R - it has the largest atomic radius with the weakest nuclear attraction for outermost electron
(ii)Across the period the atomic radius decreases due to the increase in nuclear attraction Number of electrons in P is greater than in H
(b)(i) W - forms a basic oxide which forms an ionic bond
(ii)Y - the oxide is gaseous that forms a neutral solution (iii)U - the oxide is solid at room temperature, which is acidic with covalent bond
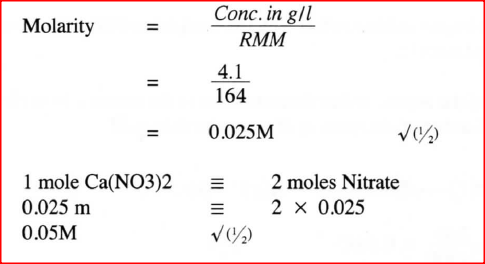
A solution was made by dissolving 8.2g of calcium nitrate to give 2 litres of solution. (Ca= 40.0; N=14.0; O= 16.0)
Determine the concentration of nitrate ions in moles per litre. |
Chemistry Topics
All
Archives
December 2024
|
Can't find what you are looking for? Don't worry, Use the Search Box Below.
|
Primary Resources
College Resources
|
Secondary Resources
|
Contact Us
Manyam Franchise
P.O Box 1189 - 40200 Kisii Tel: 0728 450 424 Tel: 0738 619 279 E-mail - sales@manyamfranchise.com |


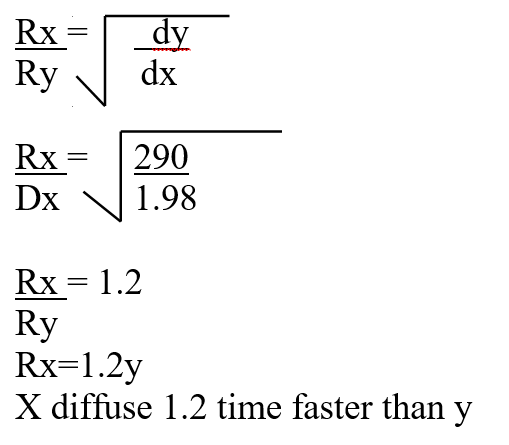


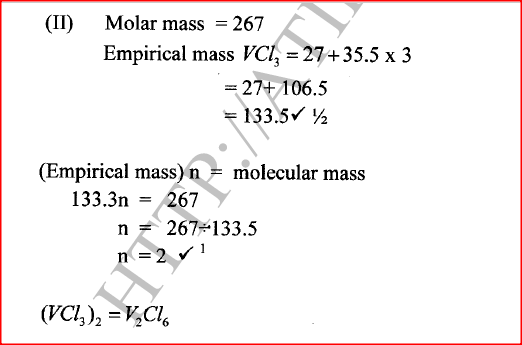















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

