LATEST BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AND PLANNINGEconomic Growth
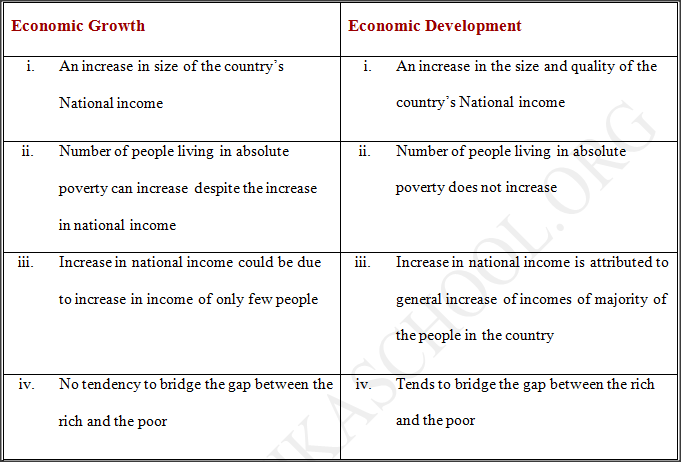
This is the increase in the productivity of a country which can be seen in the continued increase in the national income over a period of years.
It can be measured by taking the average percentage of increase in national income over a period of time (number of years) and be assumed to be the average rate of economic growth in the country. Economic Development
This is the quantitative change or increase in a country’s national income over the years, accompanied by favorable changes in the structures within the country that leads to general improvement of the individual well being, as well as the entire nation.
A country may experience economic growth without experiencing economic development. This is because the increase in the national income may be as a result of people working for long hours without any time for rest, recreation and other development to occur in their body. This will make them not to have better living, despite the fact that the national income shall have increased. The expected structural changes to be realized in a case of economic development include;
Outline the differences that exist between economic growth and economic development
Underdevelopment
This refers to a situation whereby the economic growth is in the negative direction (decreasing) accompanied by uneven distribution of wealth and decrease in quality and quantity of the factors of production available
Characteristics of Underdevelopment
Goals of Economic Development
The following are the changes that economic development seeks to put in place, which in Kenya they have been joined together in what is referred to as the millennium development goals. They includes
Factor which may hinder development in a country
The rate of a country’s economic development may be influenced negatively by the following factors
Development Planning
This is the process through which the country establishes their objectives to be achieved, identify the resources that will be required and put in place the strategies or methods of acquiring the resources and achieving their pre-determined objectives.
In most cases their objectives or goals are the goals of economic development The plan will prioritize the objectives to be achieved and even break it down in to targets that if achieved with the planned strategy and resources, the objective shall have been achieved. Need for economic planning
It enhances the following
Problems encountered in development planning
Problems at the planning stage
Problems at the implementation stage
Not downloading? Check Pricing
0 Comments
Trends in International Trade
Most of them employ foreigners in their management team, denying the locals a chance to get employed
Not downloading? Check Pricing
International Financial Institutions
Some of the institutions that play a role in international monetary system include;
International Monetary Fund (I.M.F)
This bank operates like the central bank of the central banks of the member countries. Its objective includes the following;
African Development Bank (A.D.B)
This bank was formed to promote the economic and social progress of its regional member countries in Africa. It main source of finance is the members’ contributions and the interest charged on the money they lend members.
Its functions include;
African Development Fund (A.D.F)
This was formed to provide long term financial assistance to the low income countries that cannot obtain loan from other financial institutions at the prevailing terms and condition. Their loans may recover a longer repayment periods with no interest except the commitment fees and service charge which is minimal.
They fund activities, which includes;
International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (World Bank)
The World Bank was formed to carry out the following functions;
Not downloading? Check Pricing
Economic Integration
This occurs where two or more countries enter into a mutual agreement to cooperate with each other for their own economic benefit. They may do this by allowing free trade or relaxing their existing trade barriers for the member countries.
Economic integration may occur in the following forms; Free Trade Area
This is a case where the member countries agree to abolish or minimize tariffs and other trade restrictions but the individual countries are free to impose restrictions on non-member countries. They includes; Preferential Trade Area (P.T.A), European Free Trade Area (E.F.T.A), Latin America Free Trade Area (L.A.F.T.A), etc.
Custom union
This is where the members of the free trade area may agree not only to abolish or minimize their tariffs, but also establish a common tariff for the exchange of goods and services with the non member countries. They include; Economic Community of West Africa States (E.C.O.W.A.S), East Africa Custom Union (E.A.C.U), Central Africa Custom and Economic Union (C.A.C.E.U)
Common Market
This is where the member countries allow for free movement of factors of production across the boarders. People are free to move and establish their business in any member country. They include; East Africa Common Market (E.A.C.M), European Economic Community (E.E.C), Central American Common Market (C.A.C.M), Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
Economic Union
This is where the members of the common market agree for put in place a common currency and a common central bank for the member countries. They even develop common infrastructures which includes railways, communication networks, common tariffs, etc
Importance of economic integration
Economic integration will ensure the following benefits for the member countries;
Free Trade Area
This is a situation where there is unrestricted exchange of goods and services between the countries. It has benefits/advantages similar to those of economic integration.
Disadvantages of free trade area
Some of the problems it is likely to bring include;
Trade Restrictions
These are deliberate measures by the government to limit the imports and exports of a country.
They are also known as protectionism and include the following;
Reasons for trade restrictions
Advantages of trade restrictions
Disadvantages of trade restriction
Not downloading? Check Pricing
TERMS OF TRADE
This refers to the rate at which the country’s export exchanges with those from other country. That is:
It determine the value of export in relations to import so that a country can know whether its trade with the other country is favourable or unfavourable
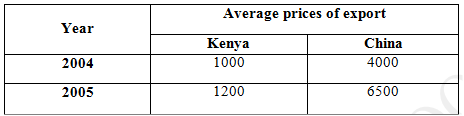
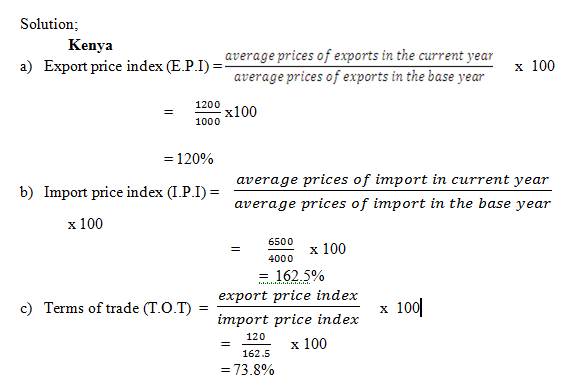
Favourable terms of trade will make the country spent little on import and gain a lot of foreign exchange from other countries For example; Then table below shows trade between Kenya and China in the year 2004 and 2005, with the Kenyan government exporting and importing to and from china, and China also importing and Exporting from and to Kenya.
Calculate the Terms of trade for;
BALANCE/IMBALANCE OF TRADEFactors that may lead to either favourable or unfavourable terms of trade
The country is experiencing a favourable terms of trade if:
The country will experience unfavourable terms of trade if;
Reasons for differences in terms of trade between countries
The terms of trade may differ due to:
Balance of trade
This is the difference between value of country’s visible exports and visible imports over a period of time. If the value of visible/tangible export is higher than the value of visible/tangible imports, then the country experiences favourable terms. If less than the invisible value, then the country is experiencing unfavourable. The country is at equilibrium if the value of visible export and import is the same,
BALANCE OF PAYMENT
This is the difference in the sum of visible and invisible export and the visible and invisible imports. If positive then it means the country is having favourable terms, while if negative, then it means unfavourable It goes beyond the balance of trade in that it considers the following
Balance of Payment account
This is the summary showing all the transactions that have taken place between a particular country and the rest of the world over a period of time. The transaction may arise from
Components of balance of payments account
The balance of payment account is made up of the following
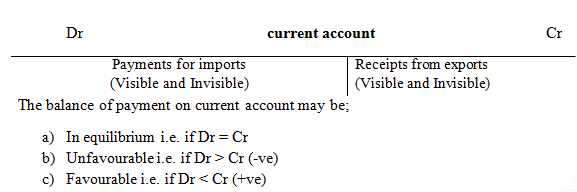
Balance of payment on current account
This is the account that is used to determine the difference between the value of the country’s visible and invisible imports and exports. That is
In the account, the payments for the visible and invisible imports are debited while the receipts from visible and invisible exports are credited that is
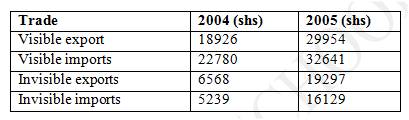
For example;
A given country had the following values of visible and invisible export and import during the year 2004 and 2005
Required;
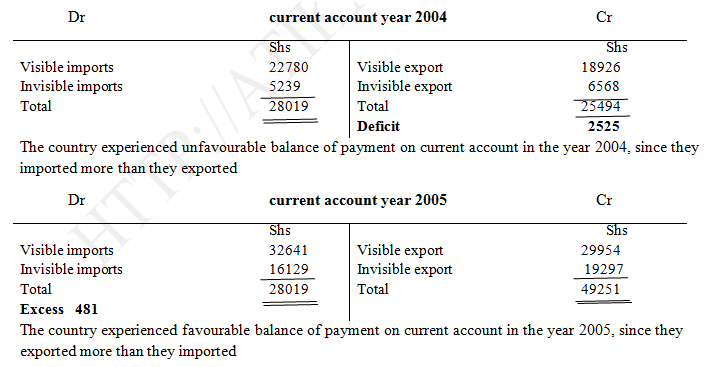
Prepare the country’s balance of payments on current account for the years 2004 and 2005 and comment on each of them. Balance of payments on capital account
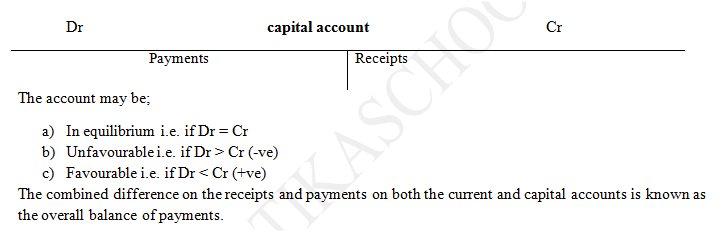
This account shows the summary of the difference between the receipt and payments on the investment (capital). Receipts are income from investments in foreign countries while payments are income on local investments by foreigners paid out of the country. The capital inflow includes investments, loans and grants from foreign donors, while capital outflow includes dividends paid to the foreign investors, loan repayments, donations and grants to other countries. In the account the payments are debited, while the receipts are credited. That is;
The official settlement account
This account records the financial dealings with other countries through the IMF. It is also called the foreign exchange transaction account, and is always expected to balance which a times may not be the case. That is;
Balance of payment disequilibrium
This occurs when there is either deficit or surplus in the balance of payments accounts. If there is surplus, then the country would like to maintain it because it is favourable, while if deficit, the country would like to correct it.
Causes of balance of payment disequilibrium
It may be caused by the following;
Correcting the balance of payment disequilibrium
The measures that may be taken to correct this may include;
Terms of sales in international trade
Here the cost trading which includes the cost of the product, cost of transporting, loading, shipping, insurance, warehousing and unloading may be expensive. This makes some of the cost to be borne by the exporter, as some being borne by the importer. The price of the goods quoted therefore at the exporters premises should clearly explain the part of the cost that he/she is going to bear and the ones that the importer will bear before receiving his/her goods. This is what is referred to as the terms of sale
Terms of sales therefore refers to the price quotation that state the expenses that are paid for by the exporter and those paid for by the importer. Some of the common terms include;
Not downloading? Check Pricing
INTRODUCTION & MEANING OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE
A trade involving the exchange of goods and services between two or more countries is referred to as international trade.
If the exchange is between two countries only, then it is referred to as bilateral trade, but if it is between more than two countries then it is referred to as multilateral trade. ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Not downloading? Check Pricing
TYPES, CAUSES, CONTROL AND CONSUMER PRICE INDEX IN INFLATIONIntroduction
Inflation refers to an economic situation where the demand for goods and services in the economy is continuously increasing without corresponding increase in supply which pushes the general prices up. The opposite of inflation is called deflation.
Inflation is measured by considering the Consumer Price Index (C.P.I) which involves comparison of prices of certain goods and services for two different periods. In constructing the C.P.I;
Types and causes of inflation
Inflation is classified in relation to its causes.
Demand pull inflation
This is a type of inflation caused by excessive demand for goods and services without a corresponding increase in production resulting into rise in prices.
Causes of demand pull inflation
Cost push inflation
This is a type of inflation caused by increase in cost of factors of production which translates to increased prices of goods and services.
Causes of cost push inflation.
Imported inflation
This is a type of inflation which is caused by importation of high priced inputs of production such as; technology/machines, skilled human resources and crude oil.
This in turn increases the prices of locally produced goods which may lead to inflation. Causes of imported inflation
LEVELS OF INFLATION
Effects of inflation in an economy
Desirable effects of inflation
Negative effects
Control of Inflation
The govt. may adopt the following policies depending on their situation to reduce inflation to manageable levels. They include;
a) Monetary policy
This is a deliberate move by the govt. through the central bank to regulate and control the money supply in the economy which may lead to demand pull inflation. The policies include;
These are the measures taken by the govt. to influence the level of demand in the economy especially through taxation process controlling government expenditure. They include;
These are laws made by the govt. to help in controlling the inflation. They include;
Introduction to InflationWhat is inflation?
The rate at which the price of goods and services rise over a given period of time is referred to as inflation.
Inflation has a major effect on the economy of a country or can even impact the life of individuals on a daily basis. Causes of Inflation
Measures Governments put in place to combat/control inflation
a) Monetary policy
This is a deliberate move by the government through the central bank to regulate and control the money supply in the economy which may lead to demand price inflation. The policies include:
b) Fiscal policy
These are the measures taken by the government to influence the level of demand in the economy through taxation process. They include
c) Statutory Measures
These are laws made by the government to help in controlling the inflation. They include:
Sampled KNEC KCSE Questions & Answers
Download a copy of these notes inclusive of answers Here. |
Business Studies Notes Form 1 - 4
Categories
All
Archives
April 2024
AuthorAtika School Team |
||||||
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|
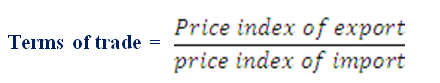

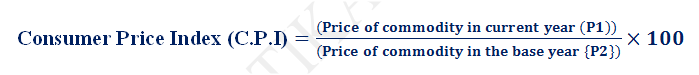
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed