LATEST BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
Key Principles Governing Insurance Operations and Fairness
The principles of insurance are a set of fundamental concepts that govern the operation and functioning of insurance contracts. These principles ensure fairness, transparency, and the proper functioning of the insurance industry. Here are the explanations of the principles you mentioned:
These principles provide a framework for the fair and efficient operation of insurance contracts, protecting the interests of both the insured and the insurer and promoting trust and stability in the insurance industry.
0 Comments
Give the difference between: (4 mks)(a) Double and co-insurance
It is where an insured takes the same insurance policy / insures the same subject matter against the same risk with more than one insurance company. Whereas co-insurance is whereby one insurance company invites other insurers to insure with them the same property against the same risk.
(b) Premiums and surrender value
Premium is the specified amount of money paid at regular intervals by the insured to the insurer in exchange for cover against losses arising from an insured risk. Whereas surrender payment of the premium before the policy matures, is an amount less than the amount of premium already paid.
INSURANCE - KCSE BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES, SCHEMES OF WORK, QUESTIONS, ANSWERS AND OBJECTIVES4/12/2017
<
>
INSURANCE (12 LESSONS)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Whole life |
Endownment |
Compensation is paid after the death of the assured |
Compensation is paid after the expiry of an agreed period |
Premiums are paid throughout the life of the assured |
Premiums are paid only during an agreed period |
Benefits go to the dependents rather than the assured |
The assured benefits unless death proceeds the expiry of the agreed period |
Aims at financial security of dependants |
Aims at financial security of the assured and dependants |
- Term insurance- The insured here covers his life against death for a given time period e.g. 1yr, 5yrs etc. If the policyholder dies within this period, his/her dependants are compensated. If the insured does not die within this specified period, there is no compensation. However, a renewal can be taken.
- Education plan/policies - This policy is normally taken by parents for their children’s future educational needs.
The policy gives details of when the payments are due. - Statutory schemes - The Government offers some types of insurance schemes which are aimed at improving/providing welfare to the members of the scheme such as medical services and retirement benefits.
A member and the employer contribute, at regular intervals, certain amounts of money towards the scheme.
- N.S.S.F
- N.H.I.F
- Widows and children pension scheme (W.C.P.S)
Characteristics of life Assurance
- It is a cover for life until death or for a specified period of time
- It may be a saving plan
- It is normally a long term contract and does not require an annual renewal
- It has a surrender value
- It has a maturity date when the assured is paid the sum assured bonuses and interests.
- A life assurance policy can be assigned to beneficiaries
- The policy can be any amount depending on the assureds’ financial ability to pay premiums
- The policy can be used as security for a loan
1. General insurance (property insurance)
General insurance is usually divided into;
- Fire insurance/department
- Accident insurance/department
- Marine insurance/department
Accident insurance
Motor policies
- These provide compensation for partial or total loss to a vehicle if the loss results from an accident.
- The policy could either be third party or comprehensive.
- Third party policies cover all damages caused by the vehicle to people and property other than the owner and his/her vehicle. This includes pedestrians, fare-paying passengers, cows, fences and other vehicles
Comprehensive policy covers damages caused not only to the third party but also to the vehicle itself and injuries suffered by the owner. Comprehensive policies include full third party, fire, theft and malicious damage to the vehicle.
Personal accident policy
- Injury to the person
- Partial or total physical disability as a result of the injury
- Loss of income as a result of death
In case of a partial or total disability as a result of accident, the insured can be paid on regular periods, e.g. monthly as stipulated in the policy.
Compensation for injuries where one loses a part of his/her body can be done on a lump sum basis.
The insured is also paid the value of hospital expenses incurred if hospitalized as a result of an accident.
Cash and / or Goods in Transit policies
E.g. Goods and cash moved from business to the markets, from suppliers to business etc.
Burglary and Theft policies
Burglary policies are enforceable only if the insured has met the specified safety and precautionary measures for protection of the insured items.
E.g.
- How much money should be maintained in different kinds of safety boxes?
- Positioning of each of the cash boxes is also an important precautionary measure.
Fidelity Guarantee policies
- The losses may be as a result of embezzlement, fraud, arithmetical errors e.t.c
- The policies may cover specified employees or all the employees
Workmen’s compensation (Employer’s Accident liability)
The employer insures his employee against industrial injuries i.e the employer is only liable for the compensation of workers who suffer injuries at work.
Public liability
This insurance covers injury, damages or losses which the business or its employees cause to the public through accidents.
The insurer pays all claims from the public up to an agreed maximum
Bad debts
This policy covers firms against losses that might result from debtor’s failure to pay their debts.
Marine Insurance
This type of insurance covers ships and cargo against the risk of damage or destruction at the sea. The main risks sea vessels are exposed to include; fire, theft, collision with others, stormy weather, sinking etc.
Types of Marine Insurance policies
Marine Hull
This policy covers the body of the ship against loss or damage that might be caused by sea perils.
Included here are any equipment, furniture or machinery on the ship.
A special type of marine hull is the part policy, which is for a specified period when the ship is loading, unloading or at service.
Marine Cargo
This type of policy covers the cargo or goods carried by the ship
The policy is taken by the owners of the sea vessels to cover the cargo being transported. It has the following sub-divisions.
- Voyage policy - Here cargo and ship are insured for a specific voyage/journey. The policy terminates automatically once the ship reaches the destination.
- Time policy - Here insurance is taken to cover losses that may occur within a specified period of time, irrespective of the voyage taken
- Fleet policy - This covers a fleet of ships, i.e. several ships belonging to one person, under one policy.
- Floating policy - This policy covers losses that may occur on a particular route, covering all the ships insured along that route for a specified period
- Mixed policy - This policy provides insurance for the ship and cargo on specified voyages and for a particular period of time. No compensation can be made if the ship was on a voyage different from the ones specified even if time has not expired
- Composite policy - This is where several insurance companies have insured one policy of a particular ship especially when the sum insured is too large to be adequately covered by one insurer.
- Construction policy/builders policy - This covers risks that a ship is exposed to while it is either being constructed, tested or being delivered.
- Freight policy - This is an insurance cover taken by the owner of the ship for compensation against failure to pay hiring charges by a hirer of the ship.
- Third parties liability - This is an insurance policy taken by the owner of the ship to cover claims that might arise from damage caused to other people’s property.
Description of marine losses
Total loss,
This occurs where there is complete loss or damage to the ship and cargo insured. Total loss can be constructive or actual.
In Actual total loss, the claims are as a result of the ships and/or cargos complete destruction. It could also occur;
When a ship and its cargo are so damaged that what is salvaged is of no market value to both the insurer and the insured.
When a ship is missing for a considerable period of time enough to assume that it has sunk.
Constructive total loss occurs when the ship and/or cargo are totally damaged but retrieved. It may also occur;
Where a ship and its cargo are damaged but of market value. This could be as a result of decision to abandon the ship and cargo as the probability of total loss appears imminent.
If the cost of preventing total loss may be higher than that of the ship and its cargo when retrieved e.g. many lives may be lost in the process of trying to prevent total loss.
- General average - This is a loss that occurs as a result of some of the cargo being thrown into the sea deliberately to save the ship and the rest of the cargo from sinking. The losses made are shared by the ship owners and the cargo owners proportionately as the effort was in the interest of both.
- Particular average - This occurs where there is a partial but accidental loss to either the ship or the cargo. When this happens each of the affected party is solidly responsible for the loss that has occurred to his property. A claim can, however be made if the loss incurred amounts to more than 3% of the value insured.
Fire insurance
In order to claim for compensation as a result of loss by fire, the following conditions must be fulfilled;
- Fire must be accidental
- Fire must be immediate cause of loss
- There must be actual fire.
Consequential loss policy; (profit interruption policy)
It is offered to protect future earnings of an enterprise after fire damage.
- Sprinkler leakage policy - This provides cover against loss or damage caused to goods or premises by accidental leakages from firefighting sprinklers
- Fire and Related perils policy - This covers buildings which include factories, warehouses, shops, offices and their contents. The policy does not cover loss of profit arising from fire damage.
Characteristics of General Insurance
- It’s a contract of indemnity
- It cannot be assigned even to ones relatives
- The insured must have an insurable interest in the property to be insured
- Premiums charged depends on the degree of risk, the higher the premium charged.
- Compensation for loss can only be up to a maximum of the value of the insured property or the sum insured in case of under insurance.
- It has no surrender value
- It’s normally a short term contract which can be renewed periodically, usually after one year.
Factors to be considered when Determining Premiums to be charged
- Health of the person
- Frequency of occurrence of previous losses
- Extent of the previous losses
- Value of the property insured
- Occupation of the insured
- Age of the person or of the property in question
- Location of the insured(address and geographical location)
- Period to be covered by the policy
- Residence of the insured.
Procedure for taking a policy
- Filling a proposal form
- Calculation of the premium to be paid
- Issuing of cover note (Binder)
- Issuing of the policy
Procedure of claiming compensation
- Notification to the insurer - The insurer has to be notified about the occurrence of any incident immediately.
- Filling a claim form - The insurer provides the insured with a claim form which he fills to give details of the risk that has occurred
- Investigation of the claim - The insurer arranges to investigate the cause of the incident and to assess the extent of the loss incurred. The insurer is then able to establish whether the insured is to be compensated and if so, for how much.
- Payment of claim - On receipt of the report of the assessor, the insurer pays the due compensation to the insured. (Payment of the compensation shows that both the insurer and the insured have agreed on the extent of the loss and the payment is the settlement of the claim)
Insurance and Gambling
Insurance
|
Gambling
|
insurance questions on topic
Describe the procedures that should be followed when taking an insurance policy. (10 marks)
2. 1996 P2
Explain four ways in which the insurance industry promotes the growth of business enterprises. (5 marks)
3. 1997 P2
Explain four ways in which the insurance industry contributes to the development of Kenya’s economy. (10 marks)
4. 1998 P2
Discuss various insurance policies under which an insurance company would not compensate the insured in the event of the loss. (10 marks)
5. 1999 P2
Discuss various insurance policies that the owner of a supermarket may find it useful for the business. (12 marks)
6. 2000 P2
Explain four benefits of the ‘pooling of risks’ to an insurance company. (8 marks)
7. 2001 P2
Explain the factors that may make it necessary for an insurance company re-ensure.
8. 2002 P2
Explain the meaning of the following terms as used in insurance (10 marks)
i) Uberrimae fidei
ii) Indemnity
iii) Third party motor vehicle insurance
iv) Contribution.
v) Subrogation
9. 2003 P2
Discuss four circumstances under which an insurance contract may be terminated. (8 marks)
10. 2004 P2
Explain five benefits that could be enjoyed by a person who decided to take out an endowment policy. (10 marks)
11. 2006 Q2 P1
Outline four risks against which a shopkeeper may insure. (4 marks)
12. 2007 Q3 P1
Outline three features of a Re – insurance company
13. 2008 Q22 P1
Elephant Enterprises acquired a building valued at sh 1 000 000 on 1 January 2007. The building was insured with two insurance Companies. Zebra and Simba for sh. 600 000 and Sh.400 000 respectively. In May 2007, fire damaged the building, causing Elephant Enterprises to suffer a loss of 20% of the building value. Determine contribution made by Simba and Zebra to cover the loss. (4 marks)
14. 2009 Q25 P1
KAMAT owned a motor vehicle, valued at sh 1,000,000. He comprehensively insured the car at Sh 800,000. The motor vehicle was involved in an accident and declared a write off. Calculate the amount KAMAT should get from the insurer. (4 marks)
15. 2010 Q11 P1
Outline four differences between insurance and assurance. (4 marks)
16. 2012 Q4a P2
(a) Explain five characteristics of property insurance. (10 marks)
Business Studies Notes Form 1 - 4
| business_notes_form_1-4.pdf | |
| File Size: | 3043 kb |
| File Type: | |
Categories
All
BUSINESS STUDIES FORM 3 NOTES
BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
CHAIN OF DISTRIBUTION
Communication
Company
Demand And Supply
DOCUMENTS USED IN HOME TRADE
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AND PLANNING
Entrepreneurship
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FORM 1 LEVEL
FORM 3 BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
FORM 4
Forms Of Business Units
Free On Board (FOB)
Free On Rail (FOR)
HOME TRADE
In Bond
INFLATION
INSURANCE
INTERNATIONAL TRADE
Intro To BS
Intro-to-BS
KCSE NOTES
Means Of Payments
MONEY & BANKING
NATIONAL INCOME
On Nearest Offer (ONO)
PDF NOTES
Pipeline
PRODUCTION
PRODUCT MARKETS
PRODUCT PROMOTION
PUBLIC FINANCE
RETAIL TRADE
SATISFACTION OF HUMAN WANTS
Terms Of Payments
THE LEDGER AND THE CASHBOOK
THE OFFICE
THEORY OF THE FIRM
Transport
Verbal Communication
WAREHOUSING
WHOLESALE TRADE
Archives
April 2024
October 2023
November 2022
March 2021
November 2020
October 2020
July 2020
February 2019
May 2018
April 2018
March 2018
December 2017
November 2017
Author
Atika School Team
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|


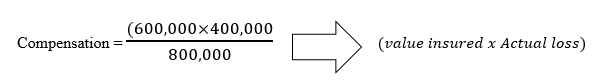

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed