LATEST BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
|
OBJECTIVES
PUBLIC FINANCE SPECIFIC OBJECTIVESBy the end of the topic, the learner should be able to:
COURSE OUTLINE
CONTENT
PUBLIC FINANCEPublic finance refers to the activities carried out by the government associated with raising of finances and the spending of the finances raised (it is the study of how government collects revenue and how it spends it) The components of public finance are;
Purpose of public finance
Sources of public financeThere are two major sources of public finance i.e.
This is the income that the government gets from its citizens. The main sources of public revenue are:
This refers to borrowing by government from firms and individuals within the country. This may be done through: Open market operation; the government sells its securities such as treasury bonds and treasury bills. This however has a disadvantage of causing ‘crowding out effect’ where the government leaves the private investors with little to borrow from. External borrowing
Classes of public (National debt)These are two classes of national debt:
This is borrowed money used to finance project(s) that can generate revenue. Such projects, once started may become self-sustaining and may contribute towards servicing/repaying the debt. E.g. money used to finance irrigation schemes, electricity production etc. Dead-weight debt This is borrowed money that is used to finance activities that do not generate any revenue. Examples are money used to finance recurrent expenditure e.g. payment of salaries or for famine relief etc. Dead-weight debt is a burden to members of the public since they are the ones who are expected to contribute towards its repayment. Factors to consider before the government decides whether to borrow internally or externally This refers to how the government spends the finances it has raised on behalf of its citizens. Categories of government expenditure
This refers to government spending that takes place regularly e.g. payments of salaries to civil servants, fuelling of government vehicles e.g. Every financial year, the government must allocate funds to meet such expenditure. Recurrent expenditure is also known as consumption expenditure. Development expenditure This is also referred to as capital expenditure .It is government spending on projects that facilitate economic development. Such projects includes construction of railway lines, roads, airports, rural electrification etc. Once completed expenditure on such projects ceases and may only require maintenance. Transfer payments This is expenditure on things/people who do not directly contribute to a country’s national income. Such expenditure include money spent on famine relief, pension, bursaries etc. Principles of Public/Government ExpenditureThese are the considerations that are necessary before any expenditure can be incurred by the government. They include:
TaxationTax: is a compulsory payment by either individuals or organizations to the government without any direct benefit to the payer. Taxation-refers to the process through which the government raises revenue by collecting taxes. Purposes/reasons for taxation
Principles of taxationDownload full PDF copy to continue reading ... learn about membership plans question & answer sessionDiscuss five principles of taxation
Outline five sources of non-tax public revenue
Explain five principles of public expenditure
Highlight five reasons for imposition of tax by the government
Discuss five characteristics of a good tax system
Outline five reasons why the Kenya government must impose tax
KCSE PAST PAPERS
KCPE PAST PAPERS
0 Comments
<
>
MONEY AND BANKINGSPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
By the end of the topic, the learner should be able to:
Money and Banking
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| form_4-topic_27-money___banking_questions_part_1.pdf | |
| File Size: | 154 kb |
| File Type: | |
| form_4-topic_27-money___banking_questions_part_2.pdf | |
| File Size: | 8282 kb |
| File Type: | |
View | Download 307k
FORM 3-Topic19-NATIONAL INCOME.pdf
View | Download 431k
FORM 3-Topic21-THE LEDGER AND THE CASHBOOK.pdf
View | Download 439k
FORM 4-Topic 26-FINANCIAL STATEMENTS.pdf
View | Download 1147k
FORM 4-Topic 27-MONEY & BANKING.pdf
View | Download
-
CONTENTS
-
NOTES
-
Q & A
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - KCSE BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES, AUDIOVISUALS, QUESTION AND ANSWER
CONTENTS
- Financial Statements
- Trading account
- Profit and loss account
- Trading, profit and loss account
- Balance sheet
- Importance of the financial statements
- Concept of trading period
- Preparation of simple financial statements
- Types of capital
- Working capital
- Borrowed capital
- Capital owned
- Capital employed
- Calculating basic financial ratios e.g
- Margins and mark-ups
- Current ratio/ working capital ratio
- Rate of stock turn-over
- Return on capital
- Importance of financial ratios
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
- identify the various financial statements
- explain the importance of each of the financial statements
- explain the concept of trading period
- prepare simple Financial Statements
- explain the various types of capital
- calculate basic ratios from financial statements
- explain the importance of each of the basic financial ratios.
Financial Statements
The trading period is the duration through which the trading activities are carried out in the business before it decides to determines it performances in terms of profit or loss. It may be one week, month, six months or even a year depending on what the owner wants. Most of the business use one year as their trading period. It is also referred to as the accounting period.
At the end of the accounting period, the following takes place;
- All the accounts are balanced off
- A trial balance is extracted
- Profit or loss is determined
- The balance sheet is prepared
Determining the profit or loss of a business
It is referred to as the gross profit /loss because it has not been used to cater for the expenses that may have been incurred in selling that stock, such as the salary of the salesman, rent for the premises, water bills, etc. it therefore implies that the businessman cannot take the whole gross profit for its personal use but must first deduct the total cost of all other expenses that may have been incurred.
The profit realized after the cost of all the expenses incurred has been deducted is what becomes the real profit for the owner of the business, and is referred to as Net profit. The net profit can be determined through calculation or preparation of profit and loss account.
In calculating the gross profit, the following adjustments are put in place
- Return inwards/Sales return: - these are goods that had been sold to the customers, but they have returned them to the business for one reason or the other. It therefore reduces the value of sales, and is therefore subtracted from sales to obtain the net sales
Therefore Net sales = Sales – Return inwards - Return outwards/purchases return: - these are goods that had been bought from the suppliers to the business and have been returned to them for one reason or another. It reduces the purchases and is therefore subtracted from the purchases to obtain the net purchases.
- Drawings: - this refers to goods that the owner of the business has taken from the business for his own use. It reduces the value of purchases, and is therefore subtracted from purchases when determining the net purchases. It is different from the other drawing in that it is purely goods and not money
- Carriage inwards/Carriage on purchases: - this is the cost incurred by the suppliers in transporting the goods from his premises to the customers’ business. It is treated as part of the purchases, and therefore increases the value of purchases. It is added to purchases to determine the actual value of purchases/Net purchases.
Therefore Net Purchases = Purchases + Carriage inwards – Return Outwards - Drawings - Carriage outwards/Carriage on sales: - this is the cost that the business has incurred in transporting goods from its premises to the customer’s premises. The cost reduces the business profit that would have been realized as a result of the sale, and is therefore treated as an expense and is subtracted from the gross profit, before determining the net profit.
- Opening stock is the stock of goods at the beginning of the trading period, while the closing stock is the stock of the goods at the end of the trading period
Gross profit is therefore calculated as follows;
Gross Profit = Sales – Return inwards – (Opening stock + Purchases + carriage inwards – Return outwards – Closing stock)
Or
Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS = Opening Stock + Net Purchases – Closing stock
Net Profit = Gross profit – Total expenses
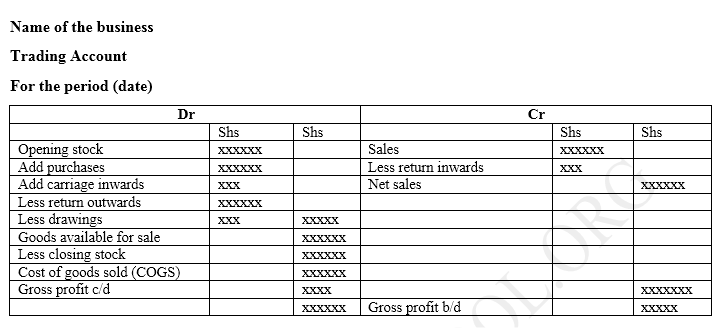
Trading Account
It takes the following format
For example
The following balances were obtained from the books of Ramera Traders for the year ending may 31st 2010
- Sales 670 000
- Purchases 380 000
- Return inwards 40 000
- Carriage outwards 18 000
- Return outwards 20 000
- Carriage inwards 10 000
- During the year the owner took goods worth shs 5 000 for his family use
- The stock as at 1st June 2009 was shs 60 000, while the stock as at 31st May 2011 was shs 70 000
financial statements questions & answers
| financial_statements_q_and_a.pdf | |
| File Size: | 6987 kb |
| File Type: | |
Business Studies Notes Form 1 - 4
| business_notes_form_1-4.pdf | |
| File Size: | 3043 kb |
| File Type: | |
Categories
All
BUSINESS STUDIES FORM 3 NOTES
BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
CHAIN OF DISTRIBUTION
Communication
Company
Demand And Supply
DOCUMENTS USED IN HOME TRADE
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AND PLANNING
Entrepreneurship
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FORM 1 LEVEL
FORM 3 BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
FORM 4
Forms Of Business Units
Free On Board (FOB)
Free On Rail (FOR)
HOME TRADE
In Bond
INFLATION
INSURANCE
INTERNATIONAL TRADE
Intro To BS
Intro-to-BS
KCSE NOTES
Means Of Payments
MONEY & BANKING
NATIONAL INCOME
On Nearest Offer (ONO)
PDF NOTES
Pipeline
PRODUCTION
PRODUCT MARKETS
PRODUCT PROMOTION
PUBLIC FINANCE
RETAIL TRADE
SATISFACTION OF HUMAN WANTS
Terms Of Payments
THE LEDGER AND THE CASHBOOK
THE OFFICE
THEORY OF THE FIRM
Transport
Verbal Communication
WAREHOUSING
WHOLESALE TRADE
Archives
April 2024
October 2023
November 2022
March 2021
November 2020
October 2020
July 2020
February 2019
May 2018
April 2018
March 2018
December 2017
November 2017
Author
Atika School Team
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed