LATEST BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES
THEORY OF THE FIRM - KCSE BUSINESS STUDIES NOTES, SCHEMES OF WORK, OBJECTIVES, QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS31/3/2018
<
>
THE THEORY OF THE FIRMAt the end of this topic, the learner should be able to:
THE THEORY OF THE FIRM COURSE OUTLINE
THEORY OF THE FIRM Definition:(i)A firm;
This refers to all those firms producing the same product for a specific market/a group of related firms that compete with one another i.e.
DECISION ON WHAT GOODS AND SERVICES TO PRODUCEA firm makes a number of important production decisions. Some of the decision may involve;
Factors that influence decisions on what goods and services to produceCertain factors have to be considered before committing a firm into production of either a new product, adopting or redesigning the existing product.
These factors include; Whether the firm is product-oriented or market-oriented Product oriented firms: This is when the nature of the product itself (its functions and unique qualities) are enough to make sure that the product sells e.g. when cars were first developed, its uniqueness sold it Market oriented firms; these are firms that produce products that are meant to meet the consumer needs e.g. over time cars are being developed to suit consumer needs. Level of competition In order to survive in a competitive market, firms must come up with products that consumers prefer. Firms may therefore develop products which are not currently available or copy rivals ideas and improve on them Level of available technology The level of technology has a strong influence on the product that a firm produces New inventions and innovations often result in new products or improved products Improved technology may also reduce the costs of production. This means the same output maybe produced using less factors of production or more output may be produced using the same factors of production. Management role Senior management have the sole responsibility of deciding on what product to produce. A wrong decision may ruin rather than bailed the enterprise. The manager’s ability to design a viable product is therefore a vital factor in product development Financial viability In order to determine whether a product will be viable or not, the cost of production and the expected returns should be considered. Funds may only be approved for the product that promises long term benefits to the firm. So if the benefits of the product outweigh the costs, then such product will be developed and if not so, it will be dropped. Amount and type of capital in the firm Capital refers to machines, equipment, factories, plants and other human made aids to production. Both financial and physical capital facilitates the production process. The amount of capital in a business will therefore influence what goods it can produce and in what qualities i.e. a firm with physical capital that is very specific may not be able to produce other type of products e.g. a clothing factory may not be able to produce any other goods such as cement. Other factors may include;
COST OF PRODUCTIONCost:
This is a payment made to the factors of production for their services. Production costs thus refers to the expenses incurred in acquiring factors of production (inputs) The sum total of all payments to the factors of production engaged in its production. Types of production costs: Opportunity costs; These are values of any alternatives forgone. The cost forgone when the choice of one thing requires the next best alternative to be abandoned Example: A student with only sh.50 may have to decide on whether to buy a textbook or a pair of shoes. If she decides to buy a textbook, the pair of shoes will have to be forgone because it’s not possible to buy both with only sh.500. The opportunity cost of buying a text book in this case is the cost of the pair of shoes which was abandoned. Fixed and variable costs Costs may be classified according to their behavior in relation to various levels of output as follows:
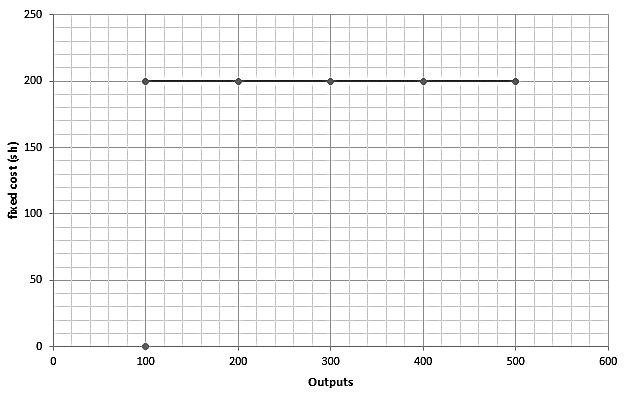
These are expenses which do not change with changes in levels of output/quantity of output. These costs therefore remain the same whether the firm is producing anything or not i.e. whether production is maximum or zero. Examples:
This may be represented graphically as:
the theory of the firm questions on topic
Continue reading (below) ... but first learn on Membership plans see here latest kcse past papers
latest kcpe past papers
form 1,2,3,4 revision papers and other RESOURCES
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Business Studies Notes Form 1 - 4
Categories
All
Archives
April 2024
AuthorAtika School Team |
||||||||||||||||||
We Would Love to Have You Visit Soon! |
Hours24 HR Service
|
Telephone0728 450425
|
|
8-4-4 materialsLevels
Subjects
|
cbc materialsE.C.D.E
Lower Primary
Upper Primary
Lower Secondary
Upper Secondary
|
teacher support
Other Blogs
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed